How Can Uv Light Cause Skin Cancer
UV light is a known carcinogen . Every time UV light hits our skin, it can damage some of the DNA inside. The body tries to repair this damage.
When the damage becomes more than the body can repair, changes develop in our skins cells. As the mutations build up, skin cancer can develop.
The type of skin cancer a person gets depends on which cells have mutations. Melanoma develops when mutations develop inside cells called melanocytes . These cells give skin its color.
How often do you protect your skin from the sun?
Spending time outside without protecting your skin from the sun increases your risk of getting melanoma.
What Should People Do If They Have A Dysplastic Nevus
Everyone should protect their skin from the sun and stay away from sunlamps and tanning booths, but for people who have dysplastic nevi, it is even more important to protect the skin and avoid getting a suntan or sunburn.
In addition, many doctors recommend that people with dysplastic nevi check their skin once a month . People should tell their doctor if they see any of the following changes in a dysplastic nevus :
- The color changes.
- It gets smaller or bigger.
- It changes in shape, texture, or height.
- The skin on the surface becomes dry or scaly.
- It becomes hard or feels lumpy.
- It starts to itch.
- It bleeds or oozes.
Another thing that people with dysplastic nevi should do is get their skin examined by a doctor . Sometimes people or their doctors take photographs of dysplastic nevi so changes over time are easier to see . For people with many dysplastic nevi, doctors may conduct a skin exam once or twice a year because of the moderately increased chance of melanoma. For people who also have a family history of melanoma, doctors may suggest a more frequent skin exam, such as every 3 to 6 months .
Cosmetics And Skin Care Products
Many cosmetic, skin care, and other personal care products have long lists of ingredients. Some of these ingredients may be harmful in large quantities.
For the most part, though, cosmetics and personal care products dont have high enough levels of certain toxic ingredients to cause cancer.
According to the ACS , there havent been enough long-term studies in humans to make claims about cancer risk. But, the health risks of long-term exposure to certain toxins cant be ruled out completely.
If you have concerns about a product youre using, check the ingredients and consult with a dermatologist.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Both types of skin cancer occur when mutations develop in the DNA of your skin cells. These mutations cause skin cells to grow uncontrollably and form a mass of cancer cells.
Basal cell skin cancer is caused by ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds. UV rays can damage the DNA inside your skin cells, causing the unusual cell growth. Squamous cell skin cancer is also caused by UV exposure.
Squamous cell skin cancer can also develop after long-term exposure to cancer-causing chemicals. It can develop within a burn scar or ulcer, and may also be caused by some types of human papillomavirus .
The cause of melanoma is unclear. Most moles dont turn into melanomas, and researchers arent sure why some do. Like basal and squamous cell skin cancers, melanoma can be caused by UV rays. But melanomas can develop in parts of your body that arent typically exposed to sunlight.
Your recommended treatment plan will depend on different factors, like the size, location, type, and stage of your skin cancer. After considering these factors, your healthcare team may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented

Skin cancer is almost entirely preventable. Making a part of your life, avoiding sunburn, and checking your skin regularly will help prevent further damage to your skin.
Protect your skin from UV radiation and help prevent skin cancer by:
- slipping on sun-protective clothing: cover your shoulders, neck, arms, legs and body.
- slopping on sunscreen thats rated SPF 30+ or higher, broad-spectrum and water resistant.
- slapping on a hat that shades your face, neck and ears.
- seeking shade under trees, umbrellas and buildings from direct sunlight and reflective surfaces.
- sliding on sunglasses that wrap around your face to protect your eyes and surrounding skin.
- staying away from sun lamps, solariums or sunbeds, which emit dangerous levels of UV radiation.
UV radiation from the sun varies depending on time of day, season, where you live and cloud coverage. Protect your skin whenever UV Index levels are above 3. Use Cancer Council Australias free SunSmart app to check the UV Index for your area any time.
Most Australians will get enough vitamin D even with sun protection at UV level 3 or above. Babies and children should be protected from the sun, since they are particularly vulnerable to UV radiation harm.
While using fake tanning cream isnt harmful to your skin, it offers no protection from UV radiation. You still need to protect yourself from the sun.
You May Like: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers arent all identical, and they may not cause many symptoms. Still, unusual changes to your skin can be a warning sign for the different types of cancer. Being alert for changes to your skin may help you get a diagnosis earlier.
Watch out for symptoms, including:
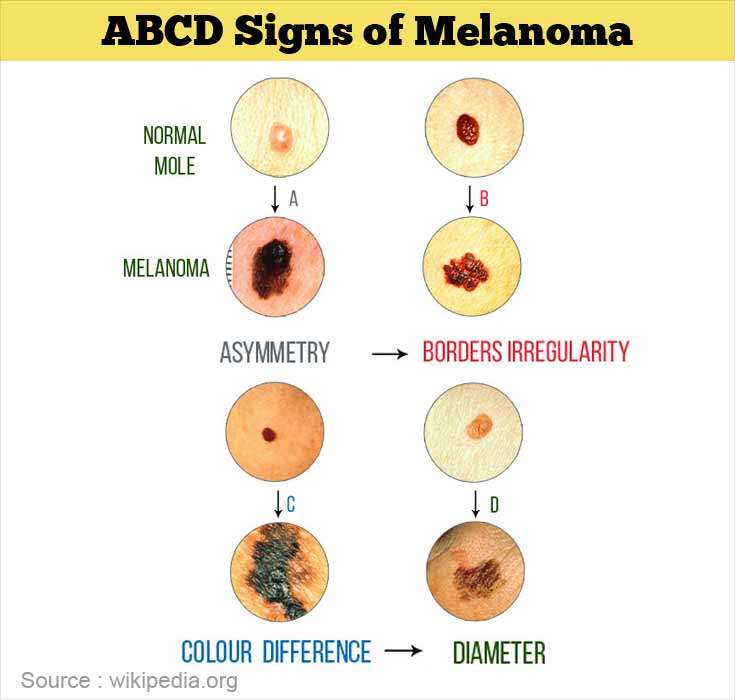
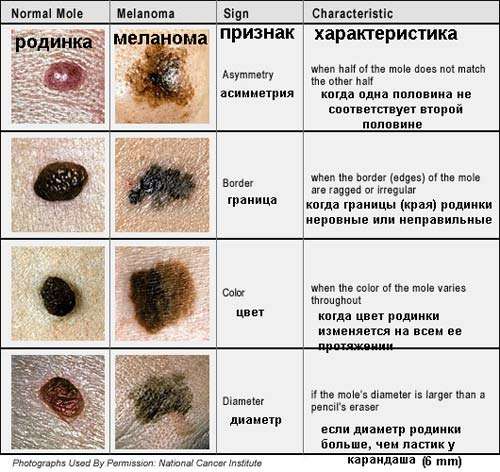
- skin lesions: A new mole, unusual growth, bump, sore, scaly patch, or dark spot develops and doesnt go away.
- asymmetry: The two halves of the lesion or mole arent even or identical.
- border: The lesions have ragged, uneven edges.
- color: The spot has an unusual color, such as white, pink, black, blue, or red.
- diameter: The spot is larger than one-quarter inch, or about the size of a pencil eraser.
- evolving: You can detect that the mole is changing size, color, or shape.
Is Cancer Causing The Itching
Itching related to cancer is sometimes identical to itching related to skin conditions or other benign causes, but there are some characteristics that may differ.
Signs of cancer-related itching may include:
- Itching in response to water, which is called aquagenic pruritus
- Lack of any rash or hives
- The presence of other symptoms such as a yellowish discoloration of the skin , and the B symptoms, which are body-wide symptoms of lymphoma including fever, weight loss, and drenching night sweats
In addition, itching associated with cancer may feel the worst on the lower legs and chest and may be associated with a burning sensation.
Also Check: Last Stage Of Cancer Symptoms
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are by far the most common skin cancers, and actually are more common than any other form of cancer. Because they rarely spread to other parts of the body, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are usually less concerning and are treated differently from melanoma. These cancers are discussed in Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer.
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Also Check: Well Differentiated
How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.
What Is A Dysplastic Nevus
A dysplastic nevus is a type of mole that looks different from a common mole. A dysplastic nevus may be bigger than a common mole, and its color, surface, and border may be different. It is usually more than 5 millimeters wide . A dysplastic nevus can have a mixture of several colors, from pink to dark brown. Usually, it is flat with a smooth, slightly scaly, or pebbly surface, and it has an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding skin. Some examples of dysplastic nevi are shown here. More examples are on the What Does a Mole Look Like? page.
Dysplastic Nevi Photos
This dysplastic nevus has a raised area at the center that doctors may call a fried egg appearance.
This dysplastic nevus is more than 5 millimeters in diameter.
This dysplastic nevus is more than 10 millimeters wide .
A dysplastic nevus may occur anywhere on the body, but it is usually seen in areas exposed to the sun, such as on the back. A dysplastic nevus may also appear in areas not exposed to the sun, such as the scalp, breasts, and areas below the waist . Some people have only a couple of dysplastic nevi, but other people have more than 10. People who have dysplastic nevi usually also have an increased number of common moles.
Recommended Reading: 3b Melanoma
Benign Tumors That Develop From Other Types Of Skin Cells
- Seborrheic keratoses: tan, brown, or black raised spots with a waxy texture
- Hemangiomas: benign blood vessel growths, often called strawberry spots
- Lipomas: soft growths made up of fat cells
- Warts: rough-surfaced growths caused by some types of human papilloma virus
Most of these tumors rarely, if ever, turn into cancers. There are many other kinds of benign skin tumors, but most are not very common.
When Should I See My Doctor
Its important to check your own skin regularly to find any new or changing spots.
See your doctor or dermatologist straight away if you notice any changes to your skin, such as:
- an ‘ugly duckling’ a spot that looks or feels different to any others
- a spot that changes size, shape, colour or texture over time
- a sore that doesnt go away after a few weeks
- a sore that itches or bleeds
See the ‘ABCDE’ of skin cancer, above.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
What Causes Melanoma
Melanoma occurs when skin is damaged and the DNA fails to repair. During the process of producing melanin cells, something goes wrong which triggers mutations in those skin cells. These mutated skin cells can multiply rapidly and form malignant tumours.
Skin cells ordinarily develop in a contained and calm matter. New healthy cells form under your skins surface and push the older cells out, where they eventually die and fall off this happens constantly to every one of us. As mentioned before, some cells develop DNA damage which triggers the production of cells that are abnormal and dangerous.
Unfortunately, it is unclear exactly what damages DNA in skin cells and how it leads to melanoma, however, it is very likely a combination of multiple factors. These factors include exposure to ultraviolet light, skin type, personal & family history and more.
This page will go into more detail about the multiple factors that cause melanoma.
Causes
What You Can Do
Be on the lookout: If you have FAMMM or other hereditary risk factors, be sure to self-check more frequently and visit your dermatologist often for thorough professional skin exams.
Start early: Children in melanoma-prone families need special attention. Some doctors recommend skin checks at puberty and during adolescence.
The good news is that the survival rate for familial melanoma is even higher than that for non-familial melanomas most likely because these families are carefully watching and melanomas are usually found while the cancer is very early and more likely to be cured.
Protect against UV rays: You can reduce the melanoma risk posed by UV radiation by taking simple, smart protective measures. Safeguard your skin against the sun every day, even when its cloudy. Avoid indoor tanning entirely. Get more details here: Skin Cancer Prevention Guidelines.
Reviewed by:
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Can A Common Mole Turn Into Melanoma
Yes, but a common mole rarely turns into melanoma, which is the most serious type of skin cancer.
Although common moles are not cancerous, people who have more than 50 common moles have an increased chance of developing melanoma .
People should tell their doctor if they notice any of the following changes in a common mole :
- The color changes.
- It bleeds or oozes.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Cancer Prognosis
A Dangerous Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
Melanoma Fact
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Read Also: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Melanoma Or Age Spots How To Tell The Difference
Staging melanoma is a complex, vitally important process that both indicates how severe the cancer is and what kinds of treatment could help most.
Doctors define severity along a continuum that begins with stage 0 and goes up to stage 4. The later the stage, the more advanced the cancer.
While myriad considerations go into staging melanoma, there are three fundamentals:
How Skinvision Can Help You
SkinVision enables you to check your skin spots for signs of skin cancer within 30 seconds. Our algorithm is currently at the level of a specialist dermatologist.In skin spots with a potential health risk, SkinVision provides feedback about the preferred next step to take.
SkinVision also enables you to store photos to keep track of changes over time, helping you to monitor your health in the long term.
The efficient and easy-to-use solution is available for iOS and Android and helps to make skin monitoring a simple routine.
Recommended Reading: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups.
Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems.
After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. A combination of sun protection measures should be used during sun protection times .
As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times.
It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.