Treating Advanced Squamous Cell Cancers
Lymph node dissection:Removing regional lymph nodes might be recommended for some squamous cell cancers that are very large or have grown deeply into the skin, as well as if the lymph nodes feel enlarged and/or hard. The removed lymph nodes are looked at under a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Sometimes, radiation therapy might be recommended after surgery.
Immunotherapy: For advanced squamous cell cancers that cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, one option might be using an immunotherapy drug such as cemiplimab or pembrolizumab . However, these drugs havent been studied in people with weakened immune systems, such as people who take medicines for autoimmune diseases or who have had an organ transplant, so the balance between benefits and risks for these people isnt clear.
Systemic chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy:Chemotherapy and targeted therapy drugs might be other options for patients with squamous cell cancer that has spread to lymph nodes or distant organs. These types of treatment might be combined or used separately.
What Is The Prognosis Of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Anus
- The prognosis of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Anus depends upon many factors, such as the age of the individual, their health status, and stage of tumor at diagnosis
- Without treatment , invasive carcinomas can metastasize aggressively and this may result in a poor prognosis
- The outcomes are excellent with early diagnosis and treatment of squamous cell carcinoma in situ
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City
MEDICINE B1M3L1
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City
MEDICINE B1M3L1
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City
MEDICINE B1M3L1
Medical Pers PORT 1 RP .docx
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City
MEDICINE B1M3L1
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City MEDICINE B1M3L1
L1B2M1 Experiment 1.docx
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City MEDICINE B1M3L1
Portfolio #5.docx .docx
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City MEDICINE B1M3L1
LEADER script.docx
Cebu Doctors’ University – Mandaue City MEDICINE B1M3L1
Medical Pers PORT 1 RP .docx
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Are The Clinical Features Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCCs present as enlarging scaly or crusted lumps. They usually arise within pre-existing actinic keratosis or intraepidermal carcinoma.
- They grow over weeks to months
- They may ulcerate
- They are often tender or painful
- Located on sun-exposed sites, particularly the face, lips, ears, hands, forearms and lower legs
- Size varies from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Surgery For Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
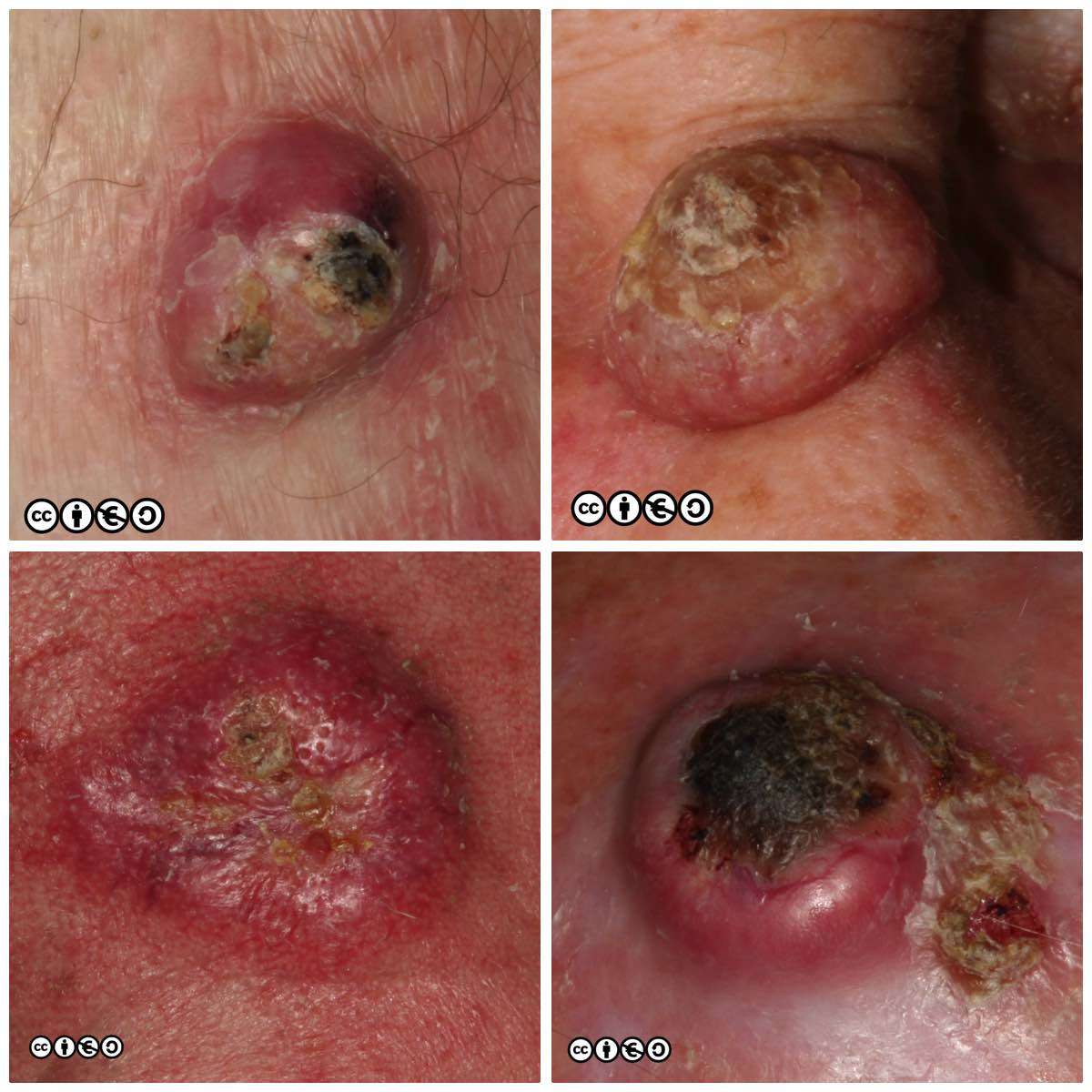
Surgery is a common treatment for basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers. Different surgical techniques can be used. The options depend on the type of skin cancer, how large the cancer is, where it is on the body, and other factors. Most often the surgery can be done in a doctors office or hospital clinic using a local anesthetic . For skin cancers with a high risk of spreading, surgery sometimes will be followed by other treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Skin Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Recurrence
Over the next two years, while I had other basal cell areas, I had no other squamous cell areas…..until November 2017.
I realized while at work one afternoon that an area on my chest felt painful, and after work, I saw that I had a new bump on it that wasnt there the day before. It wasnt bleeding or scabbing, though, and I was more bothered by the pain of it.
What Are The Different Types Of Skin Cancer
Your skin has multiple layers. The outer, protective layer of the skin is known as the epidermis. The epidermis is made up of squamous cells, basal cells, and melanocytes. These cells are constantly shedding to make way for fresh, new skin cells.
However, when certain genetic changes occur in the DNA of any of these cells, skin cancer can occur. The main types of skin cancer are squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and malignant melanoma.
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
My Appointment With A Plastic Surgeon
Unfortunately, when they started showing up, I had a really terrible health insurance policy so I was unable to get them treated. Once I got better insurance and had built up some vacation time at work so I could be off for recovery, I made an appointment with my plastic surgeon.
As I was showing him the areas, he commented wryly that I must have been saving them up for him. In all, there were 22 areas he determined needed to be removed. He had a printout of a body map and marked each area for removal on the paper, which he would bring with him the day of surgery.
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Repeated exposure to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or from tanning beds, is the main cause of SCC. Indoor tanning is linked to about 168,000 cases of SCC in the US each year.
People with light skin, light hair , and light eyes have a higher risk of skin cancer in general, as well as SCCs. However, most of the skin cancers that develop in African Americans are SCCs.
Other risk factors include:
- Having an impaired immune system, including:
- Cancers of the blood or bone marrow.
- Chronic infections like HIV.
- Taking immunosuppressive medications, including chemotherapy or some biologic medications.
You May Like: What Kind Of Cancer Is Skin Cancer
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
Recommended Reading: Are There Any Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
How Can Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
There is a great deal of evidence to show that very careful sun protection at any time of life reduces the number of SCCs. This is particularly important in ageing, sun-damaged, fair skin in patients that are immune suppressed and in those who already have actinic keratoses or previous SCC.
- Stay indoors or under the shade in the middle of the day
- Wear covering clothing
- Avoid indoor tanning
Oral nicotinamide in a dose of 500 mg twice daily may reduce the number and severity of SCCs in people at high risk.
Patients with multiple squamous cell carcinomas may be prescribed an oral retinoid . These reduce the number of tumours but have some nuisance side effects.
What Is The Outlook For Someone Who Has Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
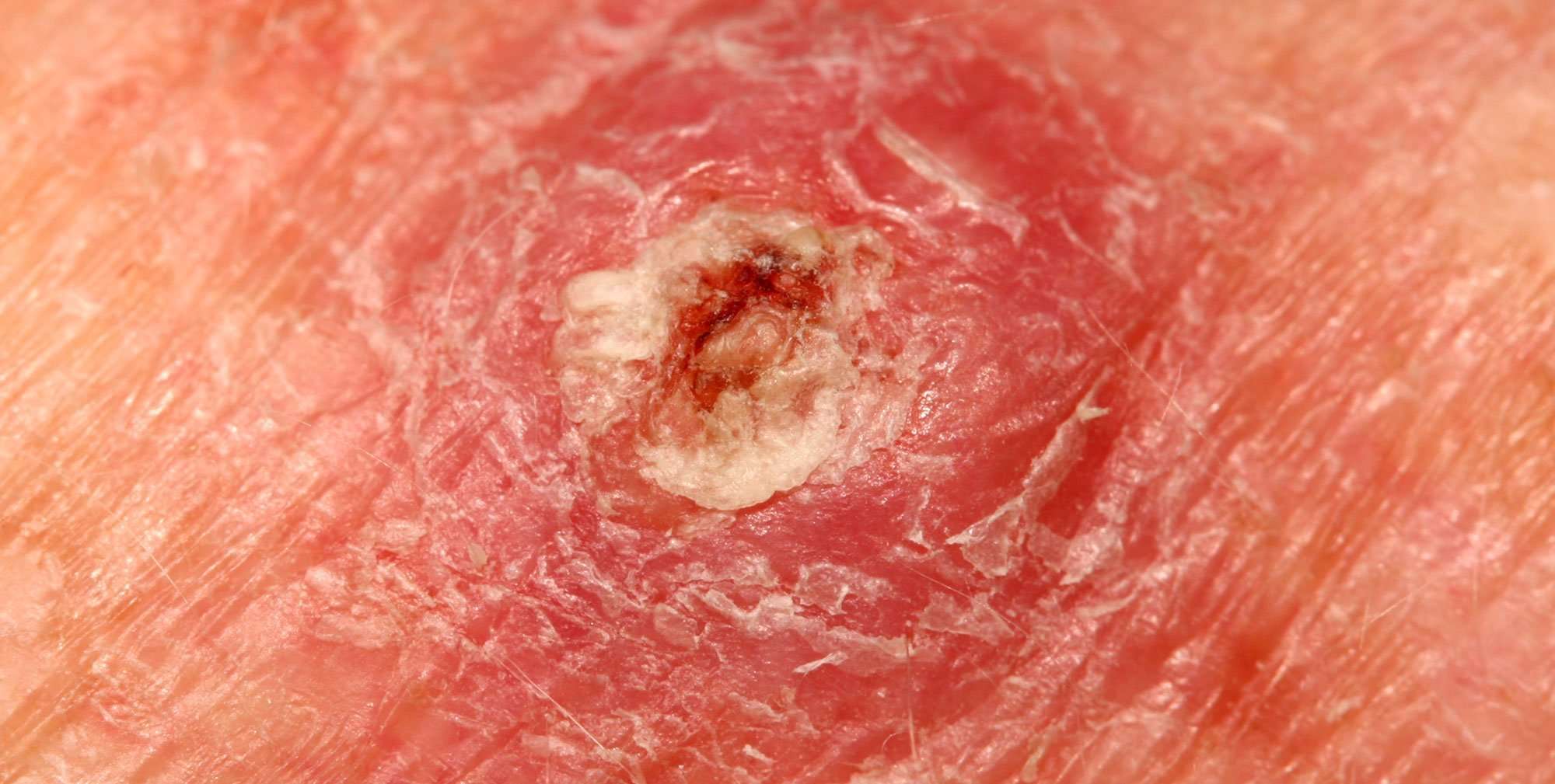
When found early, this cancer is highly treatable. Left untreated, however, SCC can spread deep into the skin and travel to other parts of the body, making treatment difficult.
While treatment can remove the cancer, its important to know that this cancer can return. You also have a greater risk of developing another skin cancer.
Thats why self-care becomes so important after treatment for SCC of the skin. Youll find the self-care that dermatologists recommend at, Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Self-care.
ImagesGetty Images
ReferencesAlam M, Armstrong A, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 78:560-78.
Anadolu-Brasie R, Patel AR, et al., Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 86-114.
Marrazzo G, Zitelli JA, et al. Clinical outcomes in high-risk squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with Mohs micrographic surgery alone. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019 80:633-8.
Que SKT, Zwald FO, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Management of advanced and high-stage tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 78:249-61.
Ribero S, Stucci LS, et al. Drug therapy of advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Is there any evidence? Curr Opin Oncol. 2017 29:129-35.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves cemiplimab-rwlc for metastatic or locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. New release issued 9/28/2018. Last accessed 1/13/2020.
Don’t Miss: How To Remove Skin Cancer On Face
What Is Cutaneoussquamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is a common type of keratinocytecancer, or non-melanomaskin cancer. It is derived from cells within the epidermis that make keratin the horny protein that makes up skin, hair and nails.
Cutaneous SCC is an invasive disease, referring to cancer cells that have grown beyond the epidermis. SCC can sometimes metastasise and may prove fatal.
Intraepidermal carcinoma and mucosal SCC are considered elsewhere.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Also Check: How Fast Does Malignant Melanoma Spread
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Tongue Treated
Early diagnosis and treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue is important to avoid complications such as metastasis to other regions. The treatment measures may include:
- In most cases, a wide surgical excision and removal of the entire tumor is the preferred treatment option . This may be followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy
- If the tumor has metastasized , then a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures may be used to treat the tumor
- Targeted therapy medications are generally used for locally infiltrated or metastatic SCCs. This therapy destroys the tumor cells by acting against the proteins that are responsible for tumor growth
- Post-operative care is important: One must maintain minimum activity levels, until the surgical wound heals
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are important and encouraged
Also Check: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
Who Gets Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for cutaneous SCC include:
- Age and sex: SCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults.
- Previous SCC or another form of skin cancer are a strong predictor for further skin cancers.
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: SCC is a particular problem with xeroderma pigmentosum, albinism, and epidermodysplasia verruciformis
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines. Organ transplant recipients have an increased risk of developing SCC.
Read Also: Can You Get Skin Cancer From Smoking
How Serious Is My Invasive Well
I have been diagnosed with invasive well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, involving biopsy border. How serious is this? It is located about one inch below ear and 1 inch diagonally below jawline. I also take an immunosuppressant for an unrelated condition, which I understand can make the cancer more serious. From what I have read, because of its location this is quite serious. Am I going to die?
What Is The Outlook For People With Squamous Cell Cancer
Early detection of SCC is key to successful treatment. If SCC isnt treated in its early stages, the cancer may spread to other areas of the body, including the lymph nodes and organs. Once this occurs, the condition can be life threatening.
Those with weakened immune systems due to certain medical conditions, such as HIV, AIDS, or leukemia, have a greater risk of developing more serious forms of SCC.
Read Also: What Is The Deadliest Skin Cancer
What Is Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Anus
- Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Anus is a malignant condition affecting the skin or mucosal membranes of the anus, which developed from in situ squamous cell carcinoma
- This malignant carcinoma, which may be present as a lesion on the anus, has the potential to metastasize , usually to the inguinal lymph nodes
- The cause of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Anus is unknown, but factors such as HPV infection, poor immunity, high-risk sexual practices, etc., are known to contribute towards its development. Middle-aged and elderly adults are at risk for the condition
- Any combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures are used to treat Anal Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma. The outcome depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor earlier the diagnosis and treatment, better is the prognosis
Sudden Bleeding And Scabbing
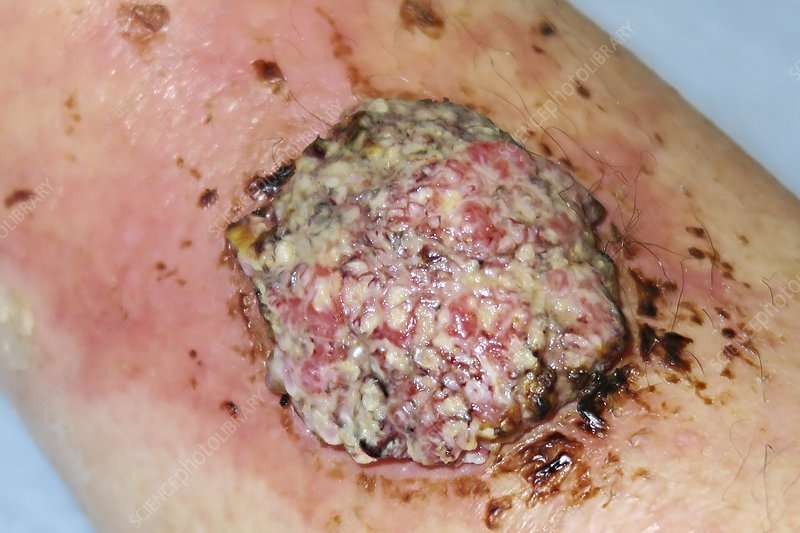
Two days before surgery, I looked in the mirror in the morning and I noticed dried blood on my face. I had a few places on my face that had been bleeding and scabbing which my doctor was going to remove, but this was on the tip of my nose. And the day before, I had nothing on the tip of my nose. While this was bothersome, I planned on mentioning it to my doctor on the day of surgery.
Also Check: What Does Skin Cancer On Scalp Feel Like
How Common Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Over 1 million people are diagnosed with SCC in the US each year. The incidence of SCC has risen about 200 percent over the past 30 years. There are more than 15,000 deaths each year in the US from SCC. Excluding head and neck SCC and CSCC in situ, about 200,000-400,000 new cases of SCC are diagnosed in the US every year, resulting in about 3,000 deaths.
Men are about two times more likely than women to develop SCCs. People over the age of 50 are most likely to get SCCs, but the incidence has been rising in younger people.
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Tongue
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue is a common malignant tumor that typically affects elderly men and women. It is more aggressive than conventional squamous cell carcinoma affecting other body regions
- The cause of the condition is unknown, but genetic mutations may be involved. Factors that may influence its development include smoking and chewing of tobacco, radiation treatment for other reasons, and exposure to coal tar and arsenic
- The squamous cell carcinoma may appear as slow-growing skin lesions. The lesions may ulcerate and cause scarring of the tongue. It may be difficult to eat, swallow food, or even to speak
- The treatment of choice is a surgical excision with clear margins followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy, as decided by the healthcare provider. In majority of the cases, the prognosis is good with appropriate treatment
- Nevertheless, the prognosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor and health status of the affected individual. There is a possibility of local or regional metastasis, which can involve the lymph nodes. This may dictate the course of the condition
Recommended Reading: How Severe Is Skin Cancer