Treatment For Liver Cancer
Your treatment will be planned by a team of specialists called a multidisciplinary team .
Your cancer doctor or specialist nurse will explain the different treatments and their side effects. If two treatments are likely to be equally helpful, your doctor may ask you to decide which one to have. They will also talk to you about certain things to think about when making treatment decisions.
The treatment you have will usually depend on:
- where the cancer is in the liver there may be several areas of cancer in different parts of the liver
- the size of the tumour or tumours
- how many tumours there are
- whether the cancer has spread outside the liver
- whether any important blood vessels in the liver are affected
- how well your liver is working
- your general health.
Selective Internal Radiation Therapy
Also known as radioembolisation, this treatment targets liver tumours directly with high doses of internal radiation in tiny beads. It is used for both primary and secondary cancers in the liver when the tumours can’t be removed with surgery. It is not available in all areas, so talk to your doctor about availability and costs involved.
What Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that starts in your liver. It’s different from “secondary” liver cancers, which have spread to the liver from other organs.
If caught early, it can sometimes be cured with surgery or transplant. In more advanced cases it canât be cured, but treatment and support can help you live longer and better.
It’s important to remember that you still have control over the decisions you make about your treatment and your life. Make sure you have people you can talk to about your plans, your fears, and your feelings. Ask your doctor about support groups, where you can meet people who know what you’re going through.
Your doctor can help you understand your treatment options. Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and target therapy may be some of your choices.
You May Like: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
Box 2 Role Of Liquid Biopsy In Hcc
Liquid biopsy refers to the analysis of tumour components, mainly fragments of DNA , extracellular vesicles or actual tumour cells . The clinical applications of liquid biopsy in oncology include cancer surveillance, early detection of minimal residual disease after curative therapies, prognosis prediction and molecular monitoring of therapeutic response.
Unlike tissue biopsies, liquid biopsy provides an easy access to the molecular information of the tumour. It also enables sequential sampling, which is crucial to implement molecular monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma and to streamline the real-time detection of mechanisms of resistance and tumour clonal composition. Indeed, the FDA has approved the use of ctDNA-based testing to detect mutations in EGFR in patients with lung cancer who are candidates for mutant EGFR therapies.
In HCC, liquid biopsy is being explored as a source to identify novel HCC surveillance tools and to predict the response to systemic therapies. Mutation analysis of ctDNA can detect tissue mutations in patients at early-stage HCC treated with resection. A combined blood-based approach of -fetoprotein and ctDNA mutation analysis had a 100% sensitivity and 95% specificity for the detection of HCC. However, the positive predictive value of this approach was very low , which could negatively impact the surveillance recall policy.
Prognosis Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
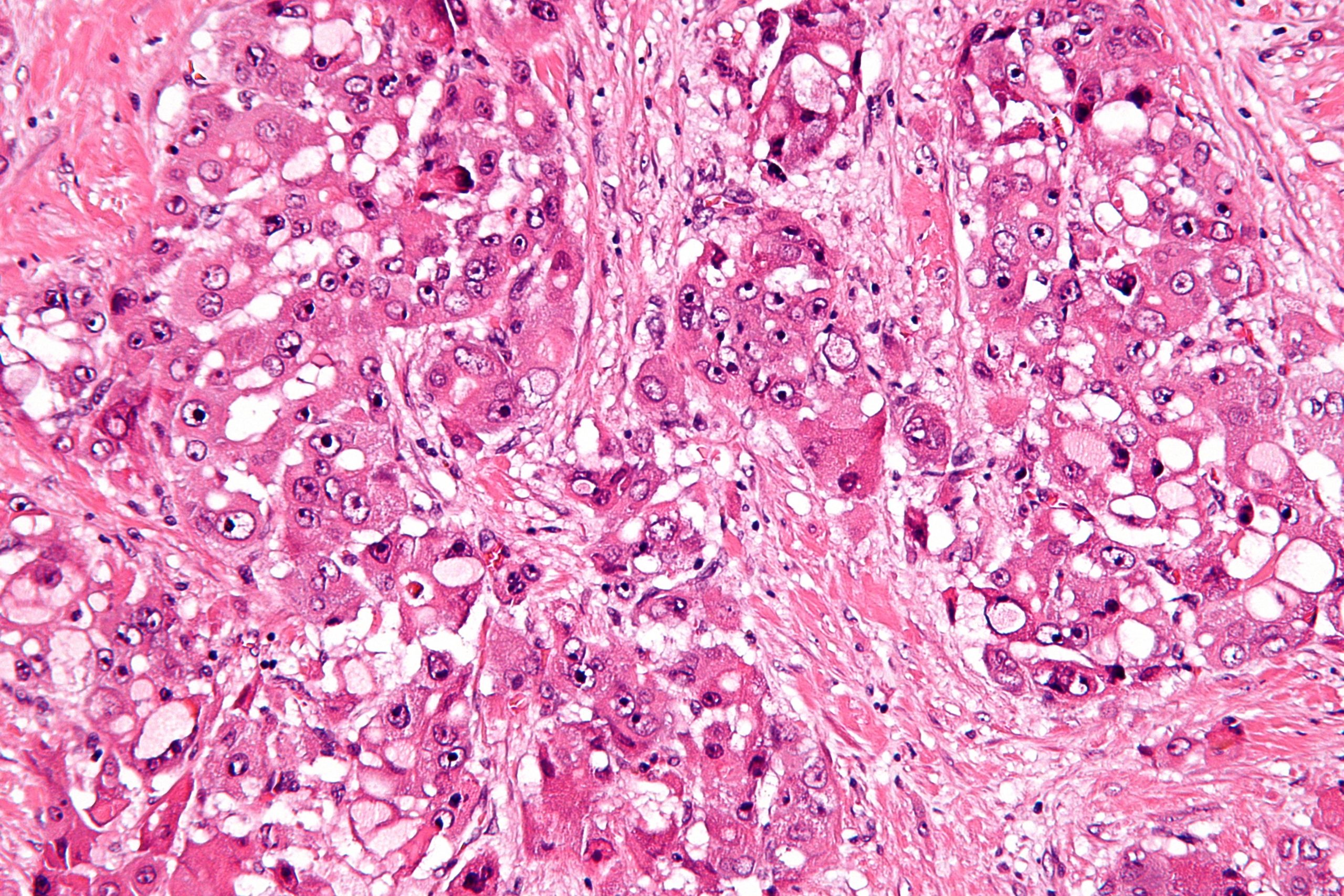
Most people with hepatocellular carcinoma do not live for more than a few years because the cancer is detected at a late stage. Screening and early detection result in a better prognosis. If the cancer is small and has not spread and liver transplantation Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation is the surgical removal of a healthy liver or sometimes a part of a liver from a living person and then its transfer into a person whose liver no longer functions. (See… read more can be done, the person can often live a number of years.
You May Like: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Prevention Of Liver Cancer: Is It Possible To Prevent Liver Cancer
Cirrhosis is the leading cause of liver cancer. Prevention of cirrhosis can help in preventing the development of liver cancer.
Regular screening for liver cancer by performing imaging tests such as ultrasound of the liver every six months in patients with a scarred liver can help detect the cancer in early stage.
Liver cancer cant always be prevented. You can reduce the risk of developing or getting liver cancer by taking these steps:
- Get the Hepatitis B Vaccine: All children should receive this vaccine. Adults who are at high risk for infection should also be vaccinated.
- Measures to Prevent Hepatitis C: Always practice safe sex by using a condom. You should not engage in unprotected sex unless you’re sure that the partner is not infected with hepatitis or any other sexually transmitted disease. Never share needles with other people as it may lead to transmission of the infection if the person is infected. Ensure safety practices about tattoos and piercings. Go to a trustworthy shop only.
- Reduce the risk of cirrhosis: Limiting the amount of alcohol you consume can help prevent liver damage. Women shouldnt drink more than one drink per day, and men shouldnt drink more than two drinks per day. Maintain a healthy weight and take healthy, balanced diet. Read more about prevention of liver cirrhosis.
Loss Of Senescence Control
Senescence is a type of irreversible growth inhibition of cells in cell culture showing distinct morphological alterations . In hepatocytes, mechanism of senescence is not clearly understood. Replicative senescence controls partial proliferative ability of liver cells by a gradual decrease in the telomeric segment . Telomere-independent mechanisms have also been suggested for hepatocyte senescence monitored in severe chronic liver diseases and these include free radical and oncogene-dependent senescence The resulting DNA damage activates ATM/Chk/p53 pathway and arrests cells at G1 phase. Alternatively, the p16/pRb pathway also performs the same function. Anomalies in DNA damage checkpoint and cell cycle regulatory pathway paved a way for the unlimited proliferation of genetically altered hepatic cells at the senescent phase and subsequently to malignant transformation. .
The proposed model of hepatocellular carcinoma development.
In human HCC, the p53 pathway has an effect on many levels i.e., about 50% aflatoxin-mediated HCC cases exhibit p53 mutations while 2030% cases of non-aflatoxin mediated HCC show p53 mutations microdeletions of p14ARF rarely occurs in HCC with p53 mutation while it is reported in 15-20% of human HCC human HCC also shows elevated Mdm2 expression over expression of gankyrin, an oncoprotein, is commonly observed in human HCC, which imposes restriction on the pRb and p53 .
Also Check: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Characterisation Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Biomarkers
With the vast input of knowledge about tumour biology, curiosity for identifying HCC related molecular markers has increased. During the new era of omics, the emergence of a number of cutting-edge technologies such as next-generation sequencing and microarray has advanced the search for biomarkers . These technologies have given an advantage in examining the tumour genome , transcriptome, proteome, epigenome, metabolome, and miRNA profile . Currently, several markers in blood and tissue have been identified . A detailed account of various HCC markers is given below.
Know The Risks Understand The Symptoms
Get screened and talk to your doctor today about treatment alternatives.
Cancer is the growth and spread of unhealthy cells in the body.
Primary liver cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the liver. Other names for primary liver cancer are hepatoma or hepatocellular carcinoma .
Secondary liver cancer is a type of cancer that starts somewhere else in the body and spreads to the liver. The medical term for a cancer that has spread is metastatic, so secondary liver cancer is also referred to as metastatic liver cancer.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of cancer among adults in the USA. Most people with hepatocellular carcinoma have many small clusters of cancer cells called nodules. Some people have only one tumor that gets larger over time. Learn more about rare forms of liver cancer.
Liver disease is a progression that follows stages of illness. Some people with liver disease progress to cirrhosis of the liver, which puts them at increased risk for liver cancer.
Liver cancer is more common among men than women.
The most current data indicates that liver cancer is among the top ten causes of death in the USA among all races, ethnicities, and genders. It claims the lives of approximately 34,000 Americans each year.
Liver cancer may have genetic or hereditary causes that are outside of our control. We may, however, be able to reduce our risk for developing liver cancer by being aware of the most common causes.
Risk Factors
Reducing Your Risk
Also Check: What Does Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mean
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
As the name suggests, AFLD is attributed to excessive alcohol consumption that causes hepatic injury by the build-up of fats, inflammation, and scarring leading to HCC, which could be fatal . Globally, the prevalence of AFLD is increasing and has become a significant contributor to the liver disease burden accounting for 30% of HCC related deaths . The safe levels of drinking as defined in the dietary guidelines in the United States is two drinks for men and one drink for women per day as one alcoholic drink accounts for about 14 g of alcohol . By contrast, excessive alcohol consumption is considered to cause AFLD . The threshold level of alcohol intake causing hepatotoxic effect varies and it depends on a variety of factors such as gender, ethnicity, and genetics .
Prevention Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Selective internal radiation therapy
However, these treatments do not destroy all the cancer cells.
Chemotherapy drugs can be injected into a blood vessel that supplies a tumor . For example, drugs can be injected into a vein or into the hepatic artery. Injecting chemotherapy drugs directly into the hepatic artery delivers a large amount of the drugs directly to the cancer cells in the liver. The chemotherapy drug sorafenib is effective against hepatocellular carcinoma. Other chemotherapy drugs and immunotherapy drugs are now being used in some people with this cancer.
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Skin Cancer Pictures
What Are Other Treatments For Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Other treatments are:
- Ablation therapy. Your healthcare provider uses a special needle to burn your tumors.
- Embolization therapy or chemoembolization therapy. Healthcare providers inject chemotherapy drugs into your livers main artery, which carries the drugs to your tumor. Then they temporarily block your artery so the drugs stay in your tumor longer.
- Targeted therapy. This treatment blocks the growth of cancer cells and limits damage to healthy cells by targeting the cancer cells genes.
Diagnostic Tests And Procedures For Liver Cancer
- Liver function tests to determine the overall health of your liver. These tests measure the levels of proteins, liver enzymes, and bilirubin in your blood.
- Presence of alpha-fetoprotein in the blood can be a sign of liver cancer.
- Imaging: CT scan or MRI scans can provide detailed images of the liver and other organs to identify and visualize problems in the liver and nearby tissues.
- Liver biopsy: A liver biopsy includes taking a small piece of your liver tissue and testing it in a lab. Biopsy is done under anesthesia so you do not feel any pain during the procedure. It is a painless procedure.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
Cryoblation And Radiofrequency Ablation
Cryoblation is performed by your physician using a thin, metal probe that is frozen. Once placed directly inside the tumor, a cold gas is blasted onto the tumor in hopes of freezing it.
With radiofrequency ablation the same method is used however instead of cold gas, a hot electric current is applied to the tumor in hopes of killing it.
What Causes Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. Increasingly, healthcare providers are seeing hepatocellular carcinoma cases in people who have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease . There are other medical conditions and activities that increase your risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Kidney function .
Recommended Reading: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Genetic And Congenital Abnormalities
Inbred strains of mice have shown genetic susceptibility to cirrhosis and liver cancer. However, in man, it has not been documented. Chinese and Alaskan inhabitants display familial clustering of HCC . The occurrence of HCC is rarely reported in congenital hepatic fibrosis, ataxia telangiectasia, familial polyposis coli, familial cholestatic cirrhosis, fetal alcohol syndrome, situs inversus and neurofibromatosis . Hereditary tyrosinemia, an inborn error of metabolism, is associated with the maximum risk of liver carcinoma . Within a short span of time, these patients exhibited faster development of macro-nodular cirrhosis from micronodular cirrhosis, followed by dysplasia and finally HCC. Adenomas may be associated with type I glycogen storage disease but the occurrence of carcinoma is rare. Carcinogenic properties have been attributed to iron through free radical production . An autosomal recessive disorder, Wilsons disease, has a tendency to affect male population usually and causes cirrhosis via copper build up in the hepatic cells. Deficiency of alpha-1-antitrypsin, a protease inhibitor, is related to jaundice and cirrhosis during infancy, as well as with pulmonary emphysema and cirrhosis in adults .
What Are The Causes Of Liver Cancer
The exact cause of liver cancer is not known in most cases. In some cases, the cause may be known. Liver cancer occurs when DNA mutations happen in the liver cells. This causes the cells to grow in an uncontrolled manner and form a tumor.
Chronic infection and hepatitis viruses can cause liver cancer. Most cases of liver cancer are due to a condition called cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis can occur due to several reasons. Read here about the causes of liver cirrhosis.
Read Also: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Person With Nash
life expectancyageSupplements That May Improve Fatty Liver
- Milk thistle, or silymarin, is an herb known for its liver-protecting effects .
- Some studies have found that milk thistle, alone or in combination with vitamin E, may help reduce insulin resistance, inflammation and liver damage in people with NAFLD .
If signs and symptoms of liver disease do occur, the may include:
- Skin and eyes that appear yellowish
- Abdominal pain and swelling.
- Swelling in the legs and ankles.
- Itchy skin.
Treatment For Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment is guided by several factors including the size of the tumor, number of tumors, location of tumor, overall liver function and other health factors. Every person is different and so too is each diagnosis of liver cancer. Working with their treatment team to make a personalized plan based on the cancer stage is important for every patient.
Choosing a doctor and healthcare team is an important and very personal decision. The chosen treatment plan may mean that the doctor that diagnosed the liver cancer is not the one doing the majority of the treatment. Consider working with a multidisciplinary team if possible. A multidisciplinary team is a group of health care professionals from different specialties working together to suggest a treatment and care plan based on your diagnosis, personal health, and preferences.
Physicians involved in liver cancer care may include
-
Hepatologist
-
Financial coordinator
-
Psychologist
Each treatment is different and most treatments have some side effects that affect people differently. It is important to remember that while people may have some side effects from treatment, most people do not experience all of the potential side effects. Talk often and openly about what to expect for treatment and plan to manage side effects before and when they happen.
Don’t Miss: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
Selective Internal Radiation Therapy Also Known As Radioembolisation
Selective internal radiation therapy is a way of giving radiotherapy treatment for cancer in the liver that cant be removed with surgery. Its a type of internal radiotherapy, and is sometimes called radioembolisation. It involves using tiny spheres or beads, made from either glass or resin , which contain a radioactive substance called yttrrium-90. The tiny beads are put down a thin tube into the main blood vessel that supplies blood to your liver . Each bead is smaller than the width of a human hair. They enable the drugs to be delivered directly to the liver tumours. These spheres cluster around the small blood vessels surrounding the tumour, where they then release radiation and destroy the cancer cells.
In England and Wales NICE has recommended selective internal radiation therapy as an option for some people with advanced liver cancer.
Is Liver Cancer Curable
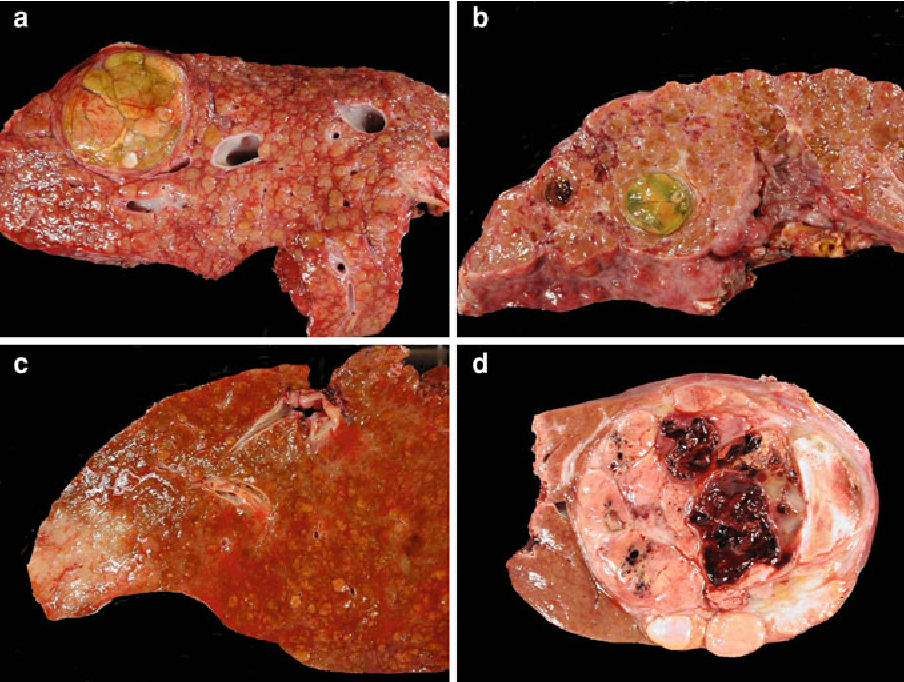
Whether the liver cancer in a particular person can be cured or not depends on various factors such as:
- the number of tumors in liver
- size of tumors in the liver
- location of tumors in the liver
- how well your liver is functioning
- whether you have cirrhosis or not
- whether the tumor has spread to other organs
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Is Hepatocellular Disease Always Cancer
4.2/5liver cancerhepatocellular carcinomaLiver cancercancerliverliver cancer is hepatocellular carcinomaliverthoroughly answered
Hepatocellular carcinoma: A cancer arising from the liver cells . Cirrhosis may be caused by viral hepatitis, primarily hepatitis B and C, alcohol abuse, hemochromatosis, certain autoimmune diseases of the liver, and other diseases that result in chronic inflammation of the liver.
Also, is hepatocellular carcinoma benign or malignant? A hemangioma is a non-cancerous tumor that consists of an overgrowth of blood vessels. Another benign tumor that can occur in the liver is focal nodular hyperplasia. A liver hemangioma and focal nodular hyperplasia are the two most common tumors of the liver.
Also Know, is hepatocellular disease the same as hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs most often in people with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
Is diffuse hepatocellular disease cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy that is frequently associated with hepatitis and cirrhosis. Treatment options for patients with diffuse, infiltrating HCC are more limited and remain poorly defined.