What Is The Treatment For Dcis
Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy another surgery to remove all of the cancer. Typically, the remaining breast will then have radiation therapy to reduce the risk of local recurrence. Lumpectomy plus radiation is a good alternative to mastectomy for treatment of DCIS.
Mastectomy. Some patients have ductal carcinoma in situ in more than one quadrant of the same breast . Sometimes, the DCIS is very large relative to the patients breast size. In these situations, a mastectomy is required to address malignant cells that are more widespread. Radiation therapy is not needed for DCIS treated with mastectomy.
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is not needed for DCIS since the disease is noninvasive.
Hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy may be appropriate for those whose ductal carcinoma in situ is hormone receptor positive.
Is Surgery The Right Decision For Women With Dcis
Women with ductal carcinoma in situ face the difficult decision of howto treat the condition. Researchers at MD Anderson are studying ways tomake this tough choice easier.
Ligia Toro de Stefani, Ph.D., had just retired from a busy academic medical research career when a mammogram revealed a suspicious mass in her right breast. Her doctors in Brownsville, Texas, referred her to MD Anderson, where she was diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ, or DCIS, often called stage 0 breast cancer the very earliest stage.
Toro and her husband, Enrico Stefani, M.D., Ph.D., researched everything they could about the condition before meeting with MD Anderson surgeon Alastair Thompson, M.D., to discuss treatment options.
Investigating came naturally to the scientific couple. Toro is an emeritus professor of anesthesiology and molecular and medical pharmacology at the University of California, Los Angeles. Her husband is a former director of UCLAs anesthesiology division of molecular medicine.
We started reading a lot of papers, not just Googling the disease, but doing a serious literature search, Toro de Stefani says.
DCIS is a cluster of cancer cells inside a milk duct. The cells are held in place by the ducts wall, but they have the ability to break through the wall. Thats when they become invasive.
That wont happen to everyone, Toro de Stefani says, but theres no predicting when cells will break through the duct and spread, and when they wont.
Whats The Most Effective Treatment For Dcis
Surgery is typically the first treatment for DCIS, and it is very effective. There are two types of surgery used for DCIS. The less-invasive option is a lumpectomy, in which a surgeon removes the area of DCIS as well as a little bit of the normal tissue around it, also referred to as a margin. The other option is a mastectomy, which involves removing the entire breast.
Most people with DCIS undergo a lumpectomy, possibly followed by additional treatments. In some cases, a mastectomy is recommended, especially if the DCIS covers a large area or appears in multiple spots throughout the breast. With either of these surgeries, the survival rate is excellent. Our job is to figure out which type of surgery is best for each patient.
Recommended Reading: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
Diagnosis And Pathology Of Dcis
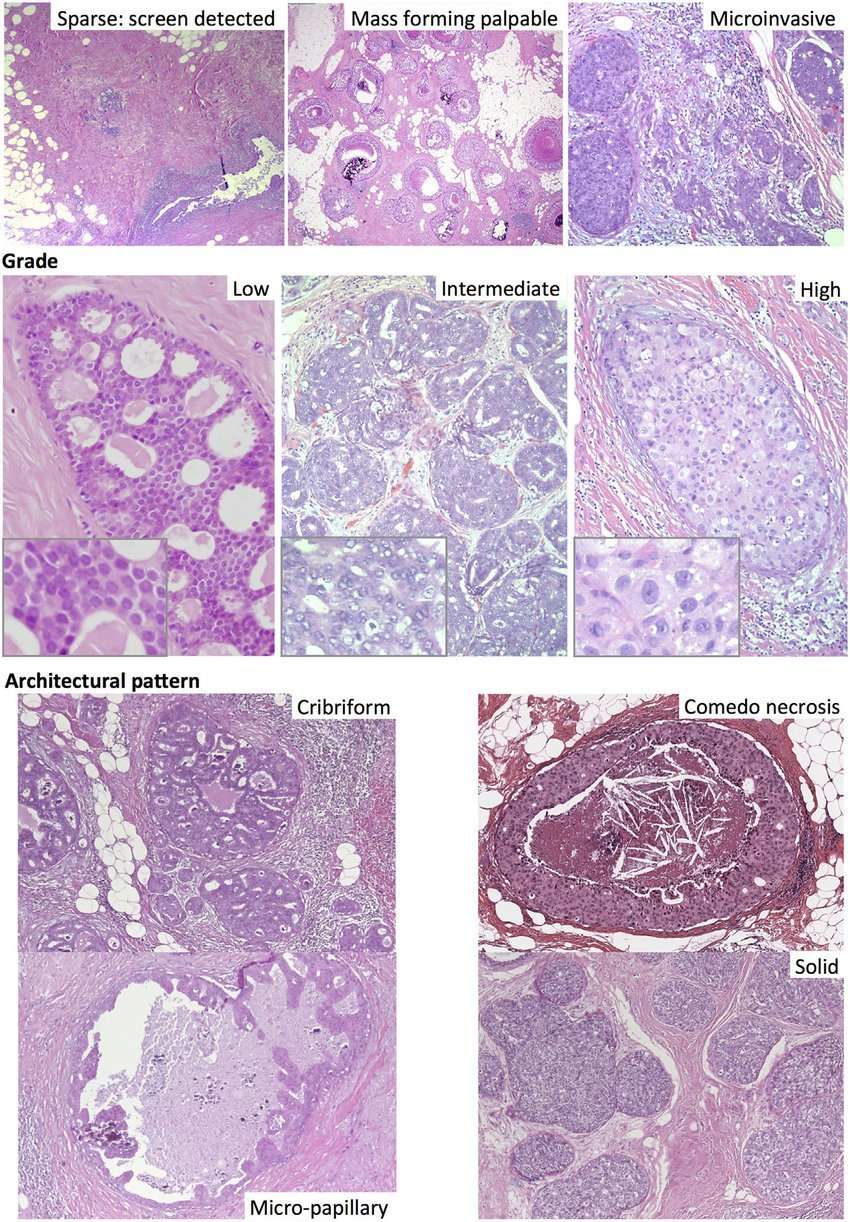
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a proliferation of atypical epithelial cells that is contained within the lumen of the breast ductal system. Nowadays, it is usually detected in the context of a mammographic screening program, but can occasionally present as a palpable lump or with other physical symptoms like nipple discharge . Approximately 8% of core needle biopsies are initially diagnosed as DCIS , and this diagnosis is confirmed in ~74% of cases after excision. A recent meta-analysis found that under-diagnosis on core biopsy was associated with large tumor size, palpable mass, a mammographic mass lesion, use of image guidance other than stereotactic, and high mammographic density .
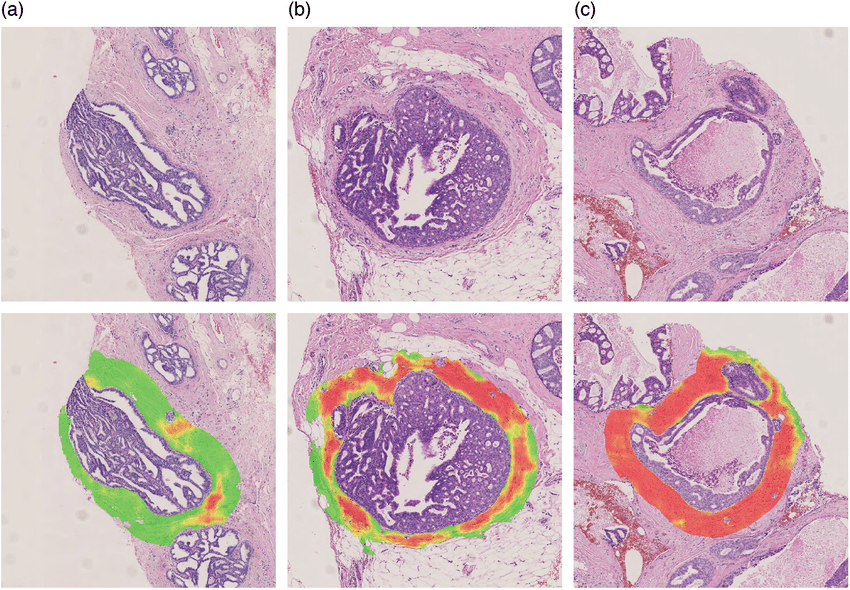
In addition to nuclear atypia, a range of different architectural patterns are observed, including cribriform, solid, comedo , micropapillary, and papillary . Multiple patterns are often observed within the same tumor , which may explain the low level of concordance of studies using these categories as prognostic markers. The prognostic value of these architectural features has been found to be limited comedo necrosis is associated with high grade and worse breast cancer-specific survival but only inconsistently with recurrence . The increase in incidence of DCIS after the introduction of mammographic screening has been more strongly associated with an increase in the non-comedo subtypes .
What Types Of Treatment Are Available For Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
If a biopsy has confirmed that there are cancer cells within the breast, treatment for DCIS includes:
Lumpectomy with radiation after surgery: This is the most common treatment for DCIS. A lumpectomy is surgery that removes all of the DCIS along with a bit of the surrounding healthy breast tissue that borders the cancer growth. This is to make sure that all of the abnormal cancer cells have been removed. With a lumpectomy, the surgeon will leave the majority of the breast intact. The amount of tissue removed depends on the size and location of the DCIS.
Radiation therapy, a common cancer treatment, is a process that typically follows a lumpectomy. It is usually combined with surgery to make sure that all abnormal cells are gone. This treatment also reduces the risk of the cancer coming back.
Mastectomy: This surgery removes the entire breast and is recommended if the DCIS is found in a large area or seen throughout the breast. No radiation therapy follows a mastectomy.
Chemotherapy, or medicine that is used to kill cancer cells throughout the body, is usually not needed to treat DCIS.
Each individual case is different. The patient and doctor will decide what treatment is best for the situation.
Don’t Miss: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
What Is The Significance Of The Reported Size Of The Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
If the entire tumor or area of DCIS is removed , the pathologist will say how big the DCIS is by measuring how long it is across , either by looking at it under the microscope or by gross examination of the tissue taken out at surgery. Another way to measure DCIS is to note the number of microscopic slides that contain DCIS. For example, the report may say that DCIS was found in 3 slides.
On needle biopsy, measurements of the area of DCIS are not often reported because this type of biopsy only samples a part of the tumor. Later, when the entire area of DCIS is removed , an accurate measurement can be done.
The larger the area of DCIS, the more likely it is to come back after surgery. Doctors use information about the size of the DCIS when recommending further treatments.
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Because DCIS is contained within a specific area of the breast and has not spread, the disease can be controlled and cured with appropriate treatment. After treatment, the outcome for the patient with DCIS is usually excellent.
However, those patients who have had DCIS, even if treated successfully, are at a greater risk than people who have never had breast cancer to have the cancer return or for another type of breast cancer to develop.
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Sex Life And Fertility
Breast cancer treatments can have a direct effect on your sex life.
For example, surgery may affect how you think and feel about your body . It can take time to adjust to changes to your body. If you have a partner, it can help to talk openly with them about your feelings.
Some treatments for DCIS may cause menopausal symptoms. Doctors do not recommend hormone replacement therapy . This is because it contains oestrogen, which could encourage breast cancer cells to grow.
Your cancer doctor or breast care nurse will also advise you not to use contraception that contains hormones.
The Good News About Dcis
DCIS is sometimes classified as Stage 0 of breast cancer, the earliest stage of the disease. The question for women with this diagnosis is not “Will I live?” but “How much treatment will I need?” One of the biggest risks today is overtreatment. That, too, is changing, as researchers get better at distinguishing the types of tumors that can be subdued without extensive surgery or radiation. DCIS is one cancer that can truly be considered curable.
If you have DCIS, you might consider entering a clinical trial. You would get the best available care and might benefit from a new type of therapy or approach. At the very least, you would be contributing to much-needed knowledge about this condition. Check the National Cancer Institute’s registry of clinical trials at www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials for a site near you.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma On Nose Prognosis
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a condition that affects the cells of the milk ducts in the breast. The cells lining the milk ducts turn malignant but stay in place . DCIS is an early form of breast cancer. It is not invasive the malignant cells do not grow through the wall of the duct or spread to lymph nodes or the blood stream.
Bonnie Sun, M.D., of Johns Hopkins breast center, provides perspective:
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ What You Need to Know
- DCIS accounts for about 20% of breast cancers.
- The condition does not usually cause symptoms but can show up on a mammogram, typically as microcalcification clusters.
- DCIS can be treated with surgery, sometimes with radiation and medicine. Chemotherapy is not needed.
- With timely diagnosis and treatment, patients can expect a good outcome.
What are DCIS symptoms?
Ductal carcinoma in situ does not have specific symptoms such a lump or breast pain. Most cases are diagnosed in a mammogram before causing any symptoms, Sun says. DCIS most commonly shows up on a mammogram as new calcium deposits, but not always sometimes, a distortion of the breast tissue on the scan can be a sign of DCIS.
Once the cancerous cells start to invade the milk duct, you might notice itching or ulceration .
Sun notes that DCIS can occur in men, and since they do not get regular screening mammograms as a rule, the problem can show up as a bloody nipple discharge or lump.
Hormone Therapy After Breast Surgery
If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive , treatment with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor, such as exemestane or anastrozole, for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast. If you have hormone receptor-positive DCIS, discuss the reasons for and against hormone therapy with your doctor.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Total Mastectomy With Breast Reconstruction
Almost all women undergoing mastectomy for DCIS have the option of having breast reconstruction. There are a number of ways that the breast can be reconstructed following mastectomy. Options include reconstruction with a breast implant or a reconstruction with a flap . If the DCIS is away from your nipple you may be able to have a mastectomy that preserves your nipple .
Breast reconstruction can be done immediately or delayed . Breast reconstruction may be performed by a breast cancer surgeon or by a plastic surgeon, or as a joint procedure by both surgeons. This will depend on your individual situation and the type of reconstruction that you choose.
Treatment And Prognosis For Dcis
Surgery is recommended to treat DCIS. Some women also take hormone therapy .
With treatment, prognosis for DCIS is usually excellent.
Learn more about treatment for DCIS.
Kornelia Polyak, M.D., Ph.D.Komen Scientific Advisory Board member
Understanding why some patients with DCIS develop invasive breast cancer, while others do not, would help our understanding of drivers of tumor progression and the design of more effective therapies.
Don’t Miss: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Biology Biomarkers And Diagnosis
- 1Cancer Genomics Program, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- 2The Sir Peter MacCallum Department of Oncology, University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia
- 3Department of Pathology, Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Ductal carcinoma in situ is an often-diagnosed breast disease and a known, non-obligate, precursor to invasive breast carcinoma. In this review, we explore the clinical and pathological features of DCIS, fundamental elements of DCIS biology including gene expression and genetic events, the relationship of DCIS with recurrence and invasive breast cancer, and the interaction of DCIS with the microenvironment. We also survey how these various elements are being used to solve the clinical conundrum of how to optimally treat a disease that has potential to progress, and yet is also likely over-treated in a significant proportion of cases.
Carcinoma In Situ Vs Precancerous Cells Vs Dysplasia
There are many terms describing the spectrum of normal cells and invasive cancer cells. One of these is dysplasia. Dysplasia can run the spectrum from mild dysplasia in which the cells are barely abnormal appearing, to carcinoma in situ, which some pathologists describe as severe dysplasia involving the full thickness of the epithelium. The term precancerous cells may also be used to describe cells on this continuum between normal and cancer cells.
These terms are also used in different ways depending on the sample analyzed. For example, cells visualized on a pap smear may show dysplasia , but since the cells are “loose,” nothing can be said about whether carcinoma in situ is present or not. With cervical dysplasia, a biopsy is required before the diagnosis of CIS is made. A biopsy sample provides a view of the cells as they occur in relation to the basement membrane and other cells, and is needed to understand if abnormal cells seen on a pap smear are concerning.
You May Like: Melanoma Braf Positive
Dcis Microenvironment And Relevance To Progression
The apparent molecular similarities between DCIS and invasive disease together with lack of detection of robust tumor-intrinsic biomarkers for invasive recurrence after DCIS suggests that the breast microenvironment could play a critical role in progression of DCIS to IBC. The microenvironment includes multiple cell types, including the myoepithelial cells that encircle the duct, the stromal fibroblasts, the vascular system, and the immune cells, as well as the duct/acini basement membrane. All components are likely to be important in restraining DCIS within the duct.
Inserting A Metal Marker
If you have a biopsy, sometimes a small metal clip called a marker is placed in the breast where the biopsy samples were taken. This is so the area can be found again if another biopsy or surgery is needed. It can safely be left in the breast and does not need to be removed, even if no further procedures are needed.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
Understanding Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Most women diagnosed with this noninvasive breast cancer are alive 10 years later, and better treatments are emerging.
For the 62,000 women who will be diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ this year, the good news is far more important than the bad. While cancer is never a picnic, DCIS is the earliest detectable form of the disease. Some news that sounds “bad” for instance, that the incidence of DCIS is increasing faster than that of any other type of breast cancer is encouraging news. It means that more breast cancers are being detected early, while they can be nipped in the bud. Today, with standard treatment, 10-year survival rates for DCIS are approaching 100%, and the treatment is usually not too difficult to tolerate.
If Someone Has Dcis What Should Be The First Step In Deciding On Treatment
A person diagnosed with DCIS usually meets with a breast surgeon first. The doctor will assess the tumors size, grade, and hormone-receptor status, as well as other risk factors that are important for treatment decisions. For example, should a patient get genetic testing for inherited mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, which are known to raise risk for future breast cancer? Do they have a strong family history of the disease?
You May Like: Cancer Lesion Pictures
What If My Report On Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Mentions Margins Or Ink
When the entire area of DCIS is removed, the outside surface of the specimen is coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the DCIS under the microscope to see how close the DCIS cells get to the ink . If DCIS is touching the ink , it can mean that some DCIS cells were left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue to help make sure that this isnt needed. If your pathology report shows DCIS with positive margins, your doctor will talk to you about what treatment is best.
How Is Dcis Diagnosed
If a doctor sees the calcifications on your mammogram, he or she will recommend more tests, which could include a breast biopsy. During the biopsy, a doctor or other health care provider takes samples of cells or tissues from your body. The cells are examined by a pathologist a doctor who checks for signs of disease in body tissues. The pathologist looks at the cells under a microscope to see if cancer is present.
A particular kind of biopsy called a stereotactic core needle biopsy can diagnose DCIS. This is a nonsurgical, outpatient procedure. After giving you medicine to numb the breast area, the doctor or technologist collects cells from the area of concern using a needle guided by mammography.
Read Also: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Paget Disease
Paget disease is when cells resembling the cells of ductal carcinoma in situ are found in the skin of the nipple and the nearby skin . Paget disease of the nipple is usually associated with DCIS or invasive carcinoma in the underlying breast tissue. If Paget disease is found on needle or punch biopsy, more tissue in that area usually needs to be removed with the goal of entirely removing the area of Paget disease. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment for you.