Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment At Moffitt Cancer Center
As a National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center, Moffitt Cancer Center is a recognized leader in breast cancer research. Because our services are research-based, our patients have access to cutting-edge techniques and promising new medications that are available only through clinical trials. We continue to make great strides in understanding the causes of breast cancer and developing effective approaches to its prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
If youd like to discuss possible causes of invasive ductal carcinoma with the breast cancer experts at Moffitt, call or complete a new patient registration form online. No referrals are required.
Is Surgery Always Necessary For Dcis
We almost always recommend surgery. Even though DCIS is noninvasive and not life-threatening, it has the potential to turn into something more serious. When we do surgery for DCIS, 20% of the time we find an invasive cancer in the tissue that we did not know about from the needle biopsy. For this reason, the only time we dont do surgery for DCIS is when we think the risks of the surgery dont outweigh the benefits. For example, some patients might not be able to tolerate the procedure because of their age or other health problems.
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Microcalcifications Or Calcifications
Microcalcifications or calcifications are calcium deposits that can be found in both non-cancerous and cancerous breast lesions. They can be seen both on mammograms and under the microscope. Because certain calcifications are found in areas containing cancer, their presence on a mammogram may lead to a biopsy of the area. Then, when the biopsy is done, the pathologist looks at the tissue removed to be sure that it contains calcifications. If the calcifications are there, the treating physician knows that the biopsy sampled the correct area .
Also Check: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Additional Histological Characteristics Of Breast Comedo Carcinoma
There is some histological evidence to support the observation that breast comedo carcinomas in situ are usually estrogen receptor negative. As a result, there would generally be little benefit to treated comedo breast carcinoma with anti-estrogen chemotherapy . Chemical therapy for DCIS is a controversial area anyways, but is almost certainly not advised for breast comedo DCIS. Comedo breast carcinoma in situ is also frequently associated with a higher HER2/neu gene amplification or protein over expression, and a higher proliferation rate. Researchers suggest that apoptosis, which means programmed cell death is one reason for the clinically more aggressive behavior of comedo breast carcinoma in situ. It is suggested that the genetic control mechanisms which regulate proliferation and apoptosis have somehow been compromised in comedo DCIS.
Recommended Reading: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Radiation Therapy For Idc
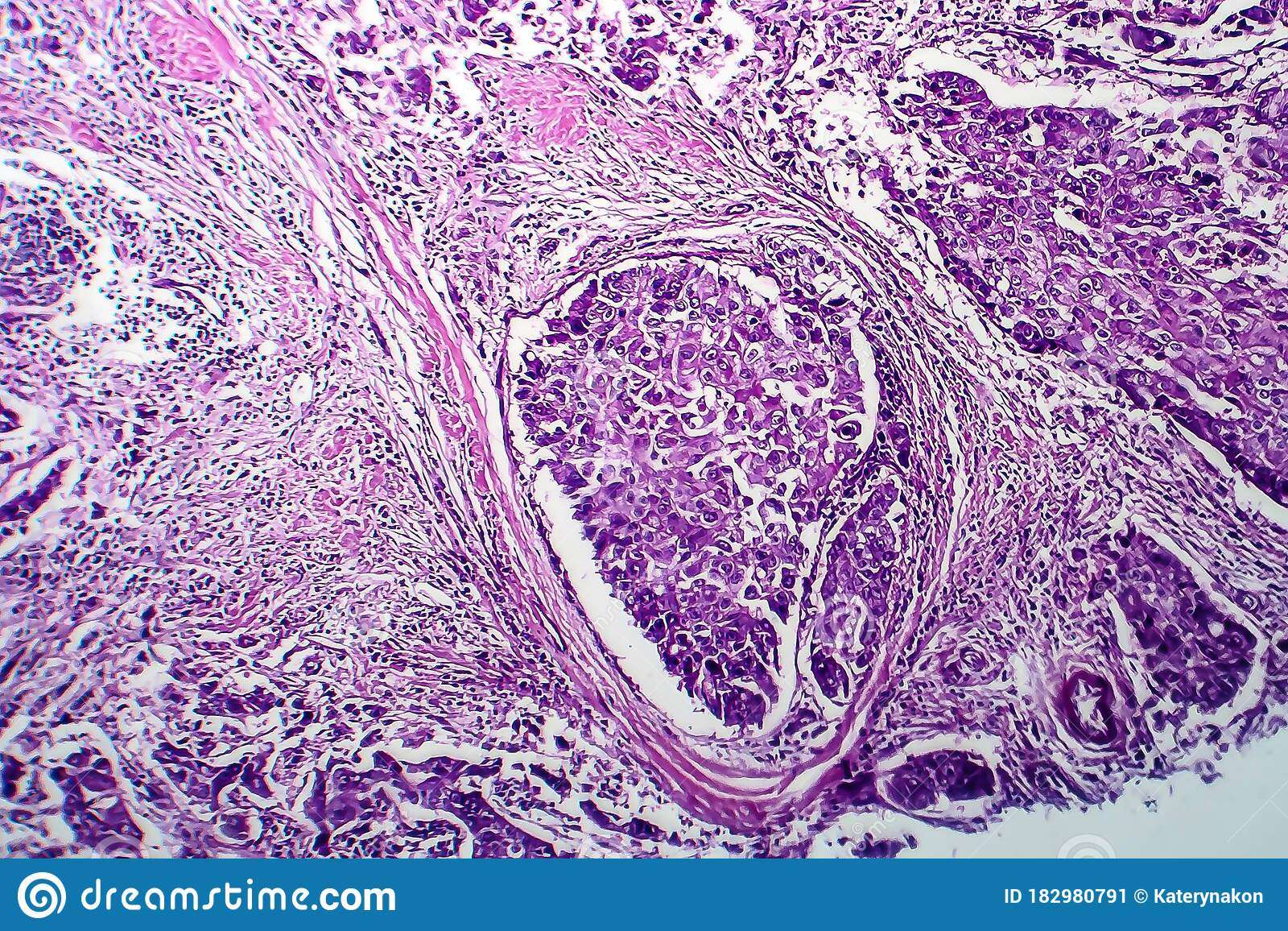
Radiation therapy directs high-energy rays at the breast, chest area, under the arm, and/or the collarbone area to destroy any cancer cells that may be left behind after surgery. This treatment also reduces the risk of recurrence .
Radiation therapy is most often recommended after surgeries that conserve healthy breast tissue, such as lumpectomy and partial mastectomy. Radiation therapy may be recommended after mastectomy as well, especially if the tumor was large and/or the lymph nodes were involved.
Like surgery, radiation is considered a local treatment because it treats just the tumor and surrounding area.
There are different ways of giving radiation therapy, including:
Researchers are studying partial-breast radiation for use after lumpectomy to see how the benefits compare to the current standard of radiation to the whole breast. Because this technique is still under investigation, it is not yet widely available.
You and your doctor can work together to determine what form of radiation therapy is best for you.
Recommended Reading: Is High Grade Cancer Curable
How Is Dcis Detected And Diagnosed
Most DCIS is detected from a mammogram that shows abnormal calcifications in the breast. The doctor may need to conduct additional imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI. These are used to determine the full extent of the disease.
DCIS is diagnosed by a needle biopsy. Pathologists examine the abnormal cells to determine the grade of the DCIS and the hormone-receptor status. DCIS is classified as low, intermediate, or high grade, depending on how abnormal the cells look under a microscope. High-grade DCIS cells are the most abnormal and grow the fastest.
Hormone-receptor status refers to whether the cancer cells have receptors for estrogen, progesterone, or both. The presence of these receptors on the DCIS suggests that these hormones fuel the growth of the cells, which affects how well the DCIS responds to certain hormone-blocking drugs.
How Long Does It Take For High Grade Dcis To Become Invasive
Research has shown that the interval between DCIS detection and the occurrence of invasive cancer averages five years in highgrade cases. For the retrospective study, researchers divided 733,905 women aged 50 to 69 years participating for the first time in a screening program into five-year age groups.
Should I take tamoxifen for DCIS? If your DCIS is ER-positive, your doctor may recommend that you take tamoxifen. The study randomized 1,804 women who had been treated with surgery followed by radiation for DCIS to tamoxifen or a placebo for five years.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Medication Treat Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Tamoxifen may be prescribed for woman of all ages who have been treated for DCIS. In those women past menopause, the doctor may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor. These medications help lower the risk of DCIS or another type of cancer developing in either breast. If either is prescribed, it is suggested that these drugs be taken for five years after surgery.
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ , also known as intraductal carcinoma, accounts for one of every five new breast cancer diagnoses. It’s an uncontrolled growth of cells within the breast ducts. Itâs noninvasive, meaning it hasnât grown into the breast tissue outside of the ducts. The phrase “in situ” means “in its original place.”
DCIS is the earliest stage at which breast cancer can be diagnosed. It’s known as stage 0 breast cancer. The vast majority of women diagnosed with it can be cured.
Even though itâs noninvasive, it can lead to invasive cancer. It’s important that women with the disease get treatment. Research shows that the risk of getting invasive cancer is low if youâve been treated for DCIS. If it isnât treated, 30% to 50% of women with DCIS will get invasive cancer. The invasive cancer usually develops in the same breast and in the same area as where the DCIS happened.
Don’t Miss: Cancer Spread All Over Body
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ is a condition that affects the cells of the milk ducts in the breast. The cells lining the milk ducts turn malignant but stay in place . DCIS is an early form of breast cancer. It is not invasive the malignant cells do not grow through the wall of the duct or spread to lymph nodes or the blood stream.
Bonnie Sun, M.D., of Johns Hopkins breast center, provides perspective:
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ What You Need to Know
- DCIS accounts for about 20% of breast cancers.
- The condition does not usually cause symptoms but can show up on a mammogram, typically as microcalcification clusters.
- DCIS can be treated with surgery, sometimes with radiation and medicine. Chemotherapy is not needed.
- With timely diagnosis and treatment, patients can expect a good outcome.
What are DCIS symptoms?
Ductal carcinoma in situ does not have specific symptoms such a lump or breast pain. Most cases are diagnosed in a mammogram before causing any symptoms, Sun says. DCIS most commonly shows up on a mammogram as new calcium deposits, but not always sometimes, a distortion of the breast tissue on the scan can be a sign of DCIS.
Once the cancerous cells start to invade the milk duct, you might notice itching or ulceration .
Sun notes that DCIS can occur in men, and since they do not get regular screening mammograms as a rule, the problem can show up as a bloody nipple discharge or lump.
What Are Some Advantages Of Receiving Treatment For Dcis At Msk
At MSK, we have a very thoughtful approach to personalizing treatment for each person with DCIS. The doctors and patients make treatment decisions as a team. Much of the research determining risk factors for DCIS-related recurrence was done at MSK, and we have a computerized prediction model that can help calculate an individuals risk of recurrence, which helps us decide what treatments are best. Weve tried to figure out who really needs additional treatments, such as radiation or hormone therapy, and who may be able to avoid certain treatments. Our goal is to find the right treatment for each patient, so that they can remain cancer free with an excellent quality of life moving forward.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
Removal Of The Whole Breast
You might have a mastectomy if:
- the area of the DCIS is large
- there are several areas of DCIS
- you have small breasts and too much of the breast is affected by DCIS to make breast conserving surgery possible
You may have surgery to your armpit called a sentinel lymph node biopsy if you have a mastectomy. This means having about 1 to 3 lymph nodes removed.
If you want to, you can choose to have a new breast made at the time of the mastectomy, or some time afterwards.
Hormone therapy is recommended for 5 years if you have breast conserving surgery for DCIS and:
- your cancer calls have oestrogen receptors
- you do not have radiotherapy
Research shows that taking hormone therapy after breast conserving surgery for DCIS reduces the risk of it coming back .
Trials show that hormone therapy can reduce the number of further invasive breast cancers or DCIS. But in these trials, the people taking a hormone therapy tablet called tamoxifen did not live any longer than those who didn’t take it.
Read Also: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Cytotoxics And Targeted Therapies
are a relatively new class of cancer drugs that can overcome many of the issues seen with the use of cytotoxics. They are divided into two groups: small molecule and antibodies. The massive toxicity seen with the use of cytotoxics is due to the lack of cell specificity of the drugs. They will kill any rapidly dividing cell, tumor or normal. Targeted therapies are designed to affect cellular proteins or processes that are utilised by the cancer cells. This allows a high dose to cancer tissues with a relatively low dose to other tissues. Although the are often less severe than that seen of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics, life-threatening effects can occur. Initially, the targeted therapeutics were supposed to be solely selective for one protein. Now it is clear that there is often a range of protein targets that the drug can bind. An example target for targeted therapy is the BCR-ABL1 protein produced from the , a genetic lesion found commonly in and in some patients with . This has enzyme activity that can be inhibited by , a drug.
There Is No Accepted Correlation Between Type And Grade Of Dcis And Probability Of Future Invasive Breast Cancer Status
In the ongoing attempt to discover and treat breast cancer at the earliest possible stage, there have been a number of studies that speculate on the features of DCIS that are most likely to evolve into an invasive breast cancer.
The two factors specialists most commonly discuss in this regard are the nuclear grade of malignant cells and the presence of necrosis. Which of these two factors is of greater importance is still a subject of debate and interpretation.
Read Also: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Read Also: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
What Is Stage 0 Lcis
Lobular carcinoma in situ at Stage 0 generally is not considered cancer. Although it has carcinoma in the name, it really describes a growth of abnormal but non-invasive cells forming in the lobules. Some experts prefer the name lobular neoplasia for this reason because it accurately refers to the abnormal cells without naming them as cancer. LCIS, however, may indicate a woman has an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
If you have been diagnosed with LCIS, your doctor may recommend regular clinical breast exams and mammograms. He or she may also prescribe Tamoxifen, a hormone therapy medication that helps prevent cancer cells from growing.
What Is Stage 0 Dcis
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. In Stage 0 breast cancer, the atypical cells have not spread outside of the ducts or lobules into the surrounding breast tissue. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if its left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Also Check: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
Understanding Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Most women diagnosed with this noninvasive breast cancer are alive 10 years later, and better treatments are emerging.
For the 62,000 women who will be diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ this year, the good news is far more important than the bad. While cancer is never a picnic, DCIS is the earliest detectable form of the disease. Some news that sounds “bad” for instance, that the incidence of DCIS is increasing faster than that of any other type of breast cancer is encouraging news. It means that more breast cancers are being detected early, while they can be nipped in the bud. Today, with standard treatment, 10-year survival rates for DCIS are approaching 100%, and the treatment is usually not too difficult to tolerate.
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Diagnosed
Same Day Results
At the Johns Hopkins Breast Center, we know how quickly patients want results from a biopsy or scan if there is a suspicion of breast cancer. We follow strict guidelines for biopsies and pathology reports. Most of our patients will receive the probability of cancer immediately following their biopsy procedure and a pathology confirmation within 24 hours.
Learn more about the steps of diagnosis, including:
- Digital mammography
- Biologic targeted therapy
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
What Does It Mean To Have Stage 1 Breast Cancer
In Stage 1 breast cancer, cancer is evident, but it is contained to only the area where the first abnormal cells began to develop. The breast cancer has been detected in the early stages and can be very effectively treated.
Stage 1 can be divided into Stage 1A and Stage 1B. The difference is determined by the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes with evidence of cancer.
Inserting A Metal Marker
If you have a biopsy, sometimes a small metal clip called a marker is placed in the breast where the biopsy samples were taken. This is so the area can be found again if another biopsy or surgery is needed. It can safely be left in the breast and does not need to be removed, even if no further procedures are needed.
You May Like: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Is Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer
Breast cancer treatments can have a direct effect on your sex life.
For example, surgery may affect how you think and feel about your body . It can take time to adjust to changes to your body. If you have a partner, it can help to talk openly with them about your feelings.
Some treatments for DCIS may cause menopausal symptoms. Doctors do not recommend hormone replacement therapy . This is because it contains oestrogen, which could encourage breast cancer cells to grow.
Your cancer doctor or breast care nurse will also advise you not to use contraception that contains hormones.
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Because DCIS is contained within a specific area of the breast and has not spread, the disease can be controlled and cured with appropriate treatment. After treatment, the outcome for the patient with DCIS is usually excellent.
However, those patients who have had DCIS, even if treated successfully, are at a greater risk than people who have never had breast cancer to have the cancer return or for another type of breast cancer to develop.
Don’t Miss: Braf And Melanoma
The Good News About Dcis
DCIS is sometimes classified as Stage 0 of breast cancer, the earliest stage of the disease. The question for women with this diagnosis is not “Will I live?” but “How much treatment will I need?” One of the biggest risks today is overtreatment. That, too, is changing, as researchers get better at distinguishing the types of tumors that can be subdued without extensive surgery or radiation. DCIS is one cancer that can truly be considered curable.
If you have DCIS, you might consider entering a clinical trial. You would get the best available care and might benefit from a new type of therapy or approach. At the very least, you would be contributing to much-needed knowledge about this condition. Check the National Cancer Institute’s registry of clinical trials at www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials for a site near you.
What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for about 80% of all cases of breast cancer. Invasive ductal carcinoma begins in the milk ducts of the breast and invades the surrounding breast tissue. It can also spread to the lymph nodes and other areas of the body.
What Are Symptoms of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma may not cause any symptoms initially.
When symptoms of invasive ductal carcinoma do occur, they may include:
- New lump or mass in the breast
- Swelling in all or part of the breast
- Skin irritation
- Redness, scaliness, or thickening of the nipple or breast skin
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk
- Lump in the underarm area
These can also be symptoms of other types of breast cancer.
Don’t Miss: Late Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma