Human Antimicrobial Protein Hcap18/ll
Human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein, hCAP18, and its C-terminal peptide LL-37 is a multifunctional protein. In addition to being important in antimicrobial defense, it induces chemotaxis, stimulates an giogenesis and promotes tissue repair. We previously showed that human breast cancer cells express high amounts of hCAP18, and hypothesised that hCAP18/LL-37 may be involved in tumor progression.
Breast Cancer Risk Factors You Can Control
- Physical activity. The less you move, the higher your chances.
- Weight and diet. Being overweight after menopause raises your odds.
- Alcohol. Regular drinking — especially more than one drink a day — increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Reproductive history.
- You donât have a full-term pregnancy.
Still, most women who are at high risk for breast cancer donât get it. On the other hand, 75% of women who develop breast cancer have no known risk factors. Learn more about the risk factors for breast cancer.
What Is The Significance Of The Stage Of The Tumor
The stage of a cancer is a measurement of the extent of the tumor and its spread. The standard staging system for breast cancer uses a system known as TNM, where:
- T stands for the main tumor
- N stands for spread to nearby lymph nodes
- M stands for metastasis
If the stage is based on removal of the cancer with surgery and review by the pathologist, the letter p may appear before the T and N letters.
The T category is based on the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to the skin over the breast or to the chest wall under the breast. Higher T numbers mean a larger tumor and/or wider spread to tissues near the breast. Since the entire tumor must be removed to learn the T category, this information is not given for needle biopsies.
The N category indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and, if so, how many lymph nodes are affected. Higher numbers after the N indicate more lymph node involvement by cancer. If no nearby lymph nodes were removed to be checked for cancer spread, the report may list the N category as NX, where the letter X is used to mean that the information is not available .
The M category is usually based on the results of lab and imaging tests, and is not part of the pathology report from breast cancer surgery. In a pathology report, the M category is often left off or listed as MX .
Also Check: Whats Cancer Look Like
Papillary Breast Cancer Treatment
Local therapy is aimed at preventing the cancer from coming back in the breast. Local therapy includes surgery , and may include radiation.
Systemic therapy is used to prevent the disease from coming back or spreading to another part of the body. This may include endocrine therapy, chemotherapy, and therapy that targets the HER2 protein. Often different types of treatment are used together to achieve the best result.
Your treatment plan will be based on the features of the tumor and the stage of the disease . Your oncology team will recommend a treatment plan based on what is known about papillary breast cancer in general and tailored to your specific disease.
We know that it can be stressful to receive a diagnosis of breast cancer, and learning that you have a rare form of the disease can add to your anxiety. We hope it will be reassuring to know that our team at the Center for Rare Breast Tumors is dedicated to latest research and treatment of papillary breast cancer, and is here to support patients and their families through diagnosis, treatment, and survivorship.
Request an Appointment
What Is The Staging For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
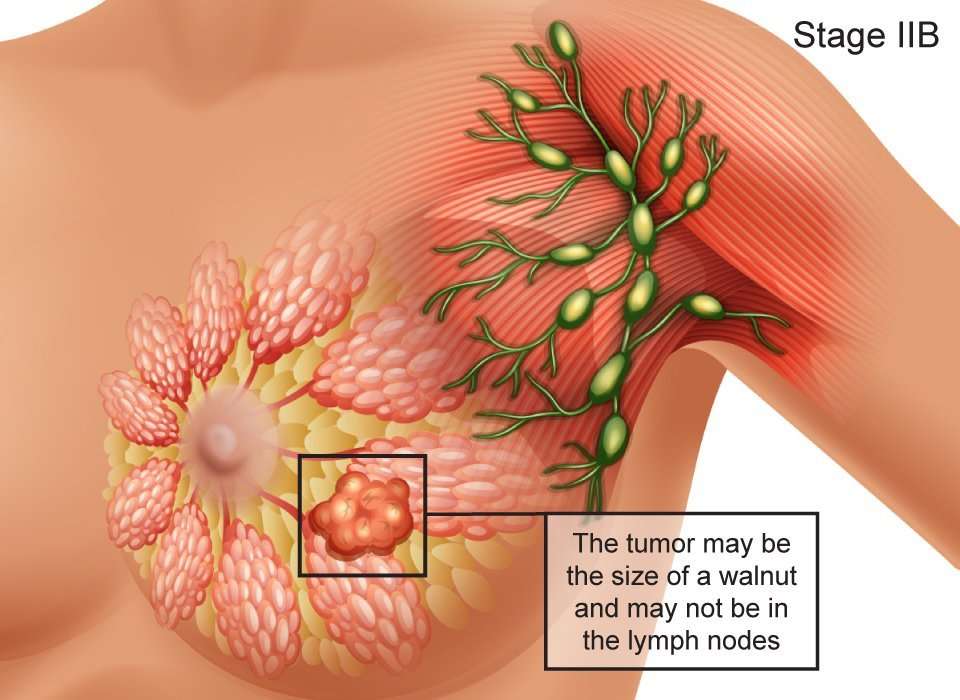
Staging refers to the extent of a cancer. A cancer is always referred to by the stage it was determined to be at diagnosis, even if it spreads.
Stages of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Stage I: Breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast
- Stage II: Breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area
- Stage III: Cancer is more extensive but it is confined to the breast, surrounding tissues, and lymph nodes
- Stage IV: Breast cancer has spread to lymph nodes beyond the underarm area or to distant sites, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or brain
In many people the cancer is found during breast screening.
Its important that you see your GP if you have any symptoms. They may refer you to a specialist breast clinic. At the breast clinic the doctor or specialist nurse takes your medical history and examines your breasts. They also feel for any swollen lymph nodes under your arms and at the base of your neck.
You may have some or all of the following tests:
- a mammogram
- an ultrasound
- a biopsy a small sample of cells or tissue is taken from your breast and looked at under a microscope
Changes seen on the mammogram or ultrasound could be due to cancer, so you may have a biopsy of the breast. You might also have an ultrasound of the lymph nodes under your arm. You may also have lymph node biopsies if they look abnormal.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Risk Factors For Breast Cancer
There are several risk factors that increase your chances of getting breast cancer. However, having any of these doesnt mean you will definitely develop the disease.
Some risk factors cant be avoided, such as family history. You can change other risk factors, such as quitting smoking, if you smoke. Risk factors for breast cancer include:
- Age. Your risk for developing breast cancer increases as you age. Most invasive breast cancers are found in women over age 55 years.
- Drinking alcohol. Alcohol use disorder raises your risk.
- Having dense breast tissue. Dense breast tissue makes mammograms hard to read. It also increases your risk for breast cancer.
- Gender. White women are
While there are risk factors you cant control, following a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and taking any preventive measures your doctor recommends can help reduce your risk for developing breast cancer.
Expert Review And References
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer. 2015: .
- Foxson SB, Lattimer JG & Felder B. Breast cancer. Yarbro, CH, Wujcki D, & Holmes Gobel B. . Cancer Nursing: Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett 2011: 48: pp. 1091-1145.
- Martini FH, Timmons MJ, Tallitsch RB. Human Anatomy. 7th ed. San Francisco: Pearson Benjamin Cummings 2012.
- Morrow M, Burstein HJ, and Harris JR. Malignant tumors of the breast. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, & Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 79: 1117-1156.
Also Check: Is High Grade Cancer Curable
Cell Necrosis Is Commonly Seen
The spindle cells may appear benign, low-grade or they may have a high-grade sarcoma-like appearance.
Malignant spindle cells will likely show atypical nuclei and evidence of high mitotic activity. Evidence of necrosis is evident in almost all spindle cell breast carcinoma tumors . Furthermore, there may be cysts that frequently contain elements of hemorrhage , necrosis and exudates. Cysts within spindle cell breast carcinoma tumors are often partially surrounded by tumor cells and granulation tissues.
Ethics Approval And Informed Consent
We obtained permission to access the SEER research data files using the reference number 15223-Nov2019. The data released by the SEER database do not require informed patient consent, and our study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Shenzhen Second Peoples Hospital. The methods were performed in accordance with the principles stated in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
Life Style And Dietary Cause
Sedentary life style, high dietary intake of fat obesity particularly in postmenopausal women may cause breast cancer. The use of alcohol is also another one cause of breast cancer. The risk increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. Women who consume two to five alcoholic beverages per day have a risk about one and a half times that of nondrinkers for the development of breast cancer.
What Is Estrogen Receptorpositive Breast Cancer And Progesterone Receptorpositive Breast Cancer
Cells from your breast cancer can be tested for receptors on two hormones that can fuel cancer growth: estrogen and progesterone. Receptors are special proteins on cells that attach to certain substances, such as estrogen and progesterone, much like a key entering a lock. Breast cancer can contain receptors for one of these hormones, both, or neither.
- Breast cancer with receptors for estrogen is called estrogen receptor positive, or ER positive.
- Breast cancer with no receptors for estrogen is called estrogen receptor negative, or ER negative.
- Breast cancer with receptors for progesterone is called progesterone receptor positive, or PR positive.
- Breast cancer with no receptors for progesterone is called progesterone receptor negative, or PR negative.
If your cancer is ER positive, PR positive, or positive for both estrogen and progesterone receptors, your treatment may include a hormone therapy a drug or drugs that keep these hormones from plugging into their receptors. The idea is to cut off the cancers access to the fuel that would otherwise power its growth, much like putting a child safety cap on an electrical outlet.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
What Are The Stages Of Breast Cancer
There are two different staging systems for breast cancer. One is called anatomic staging while the other is prognostic staging. The anatomic staging is defined by the areas of the body where the breast cancer is found and helps to define appropriate treatment. The prognostic staging helps medical professionals communicate how likely a patient is to be cured of the cancer assuming that all appropriate treatment is given.
The anatomic staging system is as follows:
Stage 0 breast disease is when the disease is localized to the milk ducts .
Stage I breast cancer is smaller than 2 cm across and hasn’t spread anywhere including no involvement in the lymph nodes.
Stage II breast cancer is one of the following:
- The tumor is less than 2 cm across but has spread to the underarm lymph nodes .
- The tumor is between 2 and 5 cm .
- The tumor is larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm .
Stage III breast cancer is also called “locally advanced breast cancer.” The tumor is any size with cancerous lymph nodes that adhere to one another or to surrounding tissue . Stage IIIB breast cancer is a tumor of any size that has spread to the skin, chest wall, or internal mammary lymph nodes .
Stage IV breast cancer is defined as a tumor, regardless of size, that has spread to areas away from the breast, such as bones, lungs, liver or brain.
What Is An Ulcerating Cancer
Ulcerating cancers are sometimes called fungating cancers or wounds. Fungating describes what the cancer might look like. They can grow in the shape of a fungus or cauliflower.
These wounds start when a tumour growing under the skin breaks through the skins surface. They can also develop from skin cancers such as melanoma.
You May Like: Stages Of Cancer Symptoms
Additional Histological Characteristics Of Breast Comedo Carcinoma
There is some histological evidence to support the observation that breast comedo carcinomas in situ are usually estrogen receptor negative. As a result, there would generally be little benefit to treated comedo breast carcinoma with anti-estrogen chemotherapy . Chemical therapy for DCIS is a controversial area anyways, but is almost certainly not advised for breast comedo DCIS. Comedo breast carcinoma in situ is also frequently associated with a higher HER2/neu gene amplification or protein over expression, and a higher proliferation rate. Researchers suggest that apoptosis, which means programmed cell death is one reason for the clinically more aggressive behavior of comedo breast carcinoma in situ. It is suggested that the genetic control mechanisms which regulate proliferation and apoptosis have somehow been compromised in comedo DCIS.
Dont Miss: What Does Stage 4 Breast Cancer Mean
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Microcalcifications Or Calcifications
Microcalcifications or calcifications are calcium deposits that can be found in both non-cancerous and cancerous breast lesions. They can be seen both on mammograms and under the microscope. Because certain calcifications are found in areas containing cancer, their presence on a mammogram may lead to a biopsy of the area. Then, when the biopsy is done, the pathologist looks at the tissue removed to be sure that it contains calcifications. If the calcifications are there, the treating physician knows that the biopsy sampled the correct area .
Don’t Miss: Can Malignant Neoplasm Be Cured
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
Cytotoxics And Targeted Therapies
are a relatively new class of cancer drugs that can overcome many of the issues seen with the use of cytotoxics. They are divided into two groups: small molecule and antibodies. The massive toxicity seen with the use of cytotoxics is due to the lack of cell specificity of the drugs. They will kill any rapidly dividing cell, tumor or normal. Targeted therapies are designed to affect cellular proteins or processes that are utilised by the cancer cells. This allows a high dose to cancer tissues with a relatively low dose to other tissues. Although the are often less severe than that seen of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics, life-threatening effects can occur. Initially, the targeted therapeutics were supposed to be solely selective for one protein. Now it is clear that there is often a range of protein targets that the drug can bind. An example target for targeted therapy is the BCR-ABL1 protein produced from the , a genetic lesion found commonly in and in some patients with . This has enzyme activity that can be inhibited by , a drug.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 3
Breast Examination By A Health Care Practitioner
A breast examination may be part of a routine physical examination. However, as with breast self-examination, a doctor’s examination may miss a cancer. If women need or want screening, a more sensitive test, such as mammography, should be done, even if a doctor’s examination did not detect any abnormalities. Many doctors and medical organizations no longer require an annual breast examination by a doctor.
During the examination, a doctor inspects the breasts for irregularities, dimpling, tightened skin, lumps, and a discharge. The doctor feels each breast with a flat hand and checks for enlarged lymph nodes in the armpitthe area most breast cancers invade firstand above the collarbone. Normal lymph nodes cannot be felt through the skin, so those that can be felt are considered enlarged. However, noncancerous conditions can also cause lymph nodes to enlarge. Lymph nodes that can be felt are checked to see if they are abnormal.
Types Of Breast Cancer And Related Conditions
Read about the different types of breast cancer and conditions related to breast cancer.
Paget’s disease is a rare skin condition of the nipple that is associated with some breast cancers. Find out what it is and how it is diagnosed and treated.
Questions about cancer? Call freephone 9 to 5 Monday to Friday or email us
Don’t Miss: Cancer Rash Symptoms
Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast :
- Japan is an exception of a developed nation with lowered incidences of breast cancer, unlike European nations and America.
- Current studies have shown that aromatase inhibitors, medications that block estrogen hormonal effects in the body, reduce the risk of recurrence of breast cancer. Recent studies have shown that treatment using aromatase inhibitors can be given up to 10 years without affecting the quality of life of women
- Tumors that are negative for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2/neu have worse prognosis. Such tumors are called âtriple-negativeâ tumors
The following DoveMed website links are useful resources for additional information:
Prior Breast Health History
A history of breast cancer is associated with a 3- to 4-fold increased risk of a second primary cancer in the contralateral breast. The presence of any premalignant ductal carcinoma in situ or LCIS confers an 8- to 10-fold increase in the risk of developing breast cancer in women who harbor untreated preinvasive lesions.
A history of breast biopsy that is positive for hyperplasia, fibroadenoma with complex features, sclerosing adenosis, and solitary papilloma have been associated with a modest increase in breast cancer risk. In contrast, any diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia that is ductal or lobular in nature, especially in a woman under the age of 45 years, carries a 4- to 5-fold increased risk of breast cancer, with the increase rising to 8- to 10-fold among women with multiple foci of atypia or calcifications in the breast.
Benign breast lesions, including fibrocystic disease such as fibrocystic change without proliferative breast disease or fibroadenoma, have not been associated with increased risk.
Read Also: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Features Of Spindle Cell Breast Cancer
Spindle cell tumors of the breast tend to be:-
- grossly nodular
- well-circumscribed
frequently with one or more cysts.
There is also some data to suggest that spindle cell tumors tend to be a little bit larger than other breast cancer tumors. Spindle cell cancer is actually more common in the oral cavity and the larynx than in the breast.
The incidence rate for spindle cell breast cancer is actually very low. Indeed, research estimates the rate to be between 0.2% and 0.5% of all breast cancers.
Spindle cell breast cancer tends to affect post-menopausal women, but not exclusively. The average age for developing spindle cell cancer of the breast is around 68 years of age. However, there is quite a wide age range.
The average tumor size tends to be between 4 cm and 5 cm at the time of diagnosis.
The prognosis for spindle cell cancer varies, depending mostly on the grade of the tumor, but even low-grade spindle cell tumors have shown some potential to metastasize. However, the tendency for the tumor to metastasize is probably related to the amount of conventional invasive ductal carcinoma component present.