How Is Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. Basal cell cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes, but they can grow quite large and invade local structures. Squamous cell cancers have a much higher incidence of lymph node involvement in the neck and parotid gland and can spread along nerves.
Melanoma is staged, based not on size but on how deeply it invades the skin layers. Therefore, a superficial or shave biopsy will not provide accurate staging information used to guide treatment. Melanomas can have a very unpredictable course and may spread to distant organs. Melanomas with intermediate thickness often require sentinel node biopsy, a surgical procedure performed by a head and neck surgeon, to determine if microscopic spreading to lymph nodes has occurred.
Dont Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
After Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
What Are The Survival Rates For Scc
The vast majority of SCC is cured. Only about 2 percent to 5 percent of SCC cases grow back or spread. Unfortunately, because cases of SCC are not reported to the U.S. cancer registry it is hard to estimate survival rates. It is clear that metastatic SCC is very difficult to treat. . In large groups of people studied who have distant metastatic SCC, about 70 percent died from their disease.14,15
Read Also: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
For More Information About Skin Cancer
National Cancer Institute, Cancer Information Service Toll-free: 4-CANCER 422-6237TTY : 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
Media file 1: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
Media file 2: Skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma.
Media file 3: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 5: Skin cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Continued
Media file 6: Skin cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.
How Are Skin Cancer Survival Rates Measured
Cancer survival is measured in many different ways, including:1
- Five-year overall survival rate is the percentage of people who are still alive 5 years after diagnosis or treatment. If the 5-year overall survival rate after diagnosis is 85 percent, that means that 5 years after being diagnosed with melanoma, 85 of 100 people are still alive. Some of those people may still have cancer, others do not.
- Disease-free survival is how long a person survives after treatment without any sign of that cancer.
- Median overall survival is the average length of time from treatment that half the study population is still alive. For example, consider 100 people who are treated with a medication and 3.1 years later, 50 have died and 50 are alive. The median overall survival is 3.1 years.
When looking at a skin cancer survival rate, it is important to know what group was studied. Survival rates can differ greatly by cancer stage, age at diagnosis, gender, and race/ethnicity. The most accurate numbers about skin cancer survival are about melanoma because cases of melanoma are tracked in national cancer registries.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Where Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
It’s important to know that basal cell carcinoma can spread to other surrounding tissue and can grow around nerves. I had two separate basal cells that grew around nerves: one in my forehead and one in my upper lip. Both of those surgeries required moving the nerve to remove the cancer, and I was left with permanent numbness in both areas because of that.
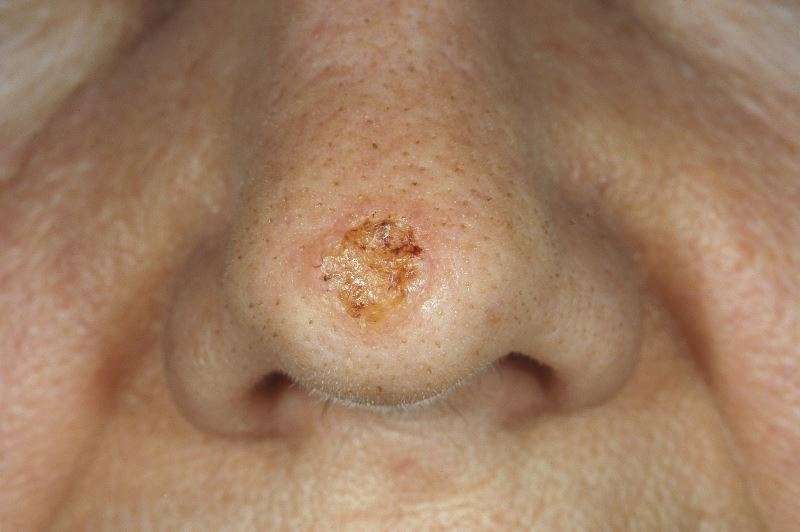
What Does Scc Look Like
SCCs can appear as scaly red patches, open sores, rough, thickened or wart-like skin, or raised growths with a central depression. At times, SCCs may crust over, itch or bleed. The lesions most commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body.
SCCs can also occur in other areas of the body, including the genitals.
SCCs look different on everyone. You can find more images, as well as signs, symptoms and early detection strategies on our SCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all SCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as general reference for what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
A persistent, scaly red patch with irregular borders that sometimes crusts or bleeds.
An open sore that bleeds or crusts and persists for weeks.
An elevated growth with a central depression that occasionally bleeds. It may rapidly increase in size.
A wart-like growth that crusts and occasionally bleeds.
Also Check: What Does Well Differentiated Mean
So Youve Had Skin Cancer Now What
Melanoma survivors may well be expected to be alert for a recurrence, but anyone whos had any type of skin cancer should remain extra vigilant.
This entails being scrupulous about scheduling follow-up visits to the dermatologist , conducting frequent skin self-exams, and limiting UV exposure.
If not removed completely, basal cell carcinoma can grow back on the same place on the skin. People who have had basal cell cancer are at higher risk of developing it again in other areas of the skin, too.
People with squamous cell carcinoma are also at increased risk for recurrence, especially in the same skin area or nearby. Growths on the nose, ears, and lips pose the highest risks.
Studies also suggest that people with basal or squamous cell cancers are at increased risk of developing another type of cancer, particularly melanoma. For women, this risk also includes breast and lung cancer.
How The Stage Is Determined
Once you have been diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, your doctor will want to determine its stage. While the risk of this type of cancer spreading is low, determining the stage will help your doctor develop the best treatment plan.
The TNM system is a uniform system for staging many types of cancer. TNM stands for:
- T is for tumor: How far has the primary tumor grown through the layers of skin or to nearby tissues?
- N is for nodes: Have cancer cells spread to the lymph nodes near the tumor?
- M is for metastasis: Has the cancer metastasized to distant sites in the body such as the lungs or liver?
Skin Cancer Doctor Discussion Guide
Also Check: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
Basal cell carcinoma, the most common type of skin cancer, develops most commonly after frequent sun exposure or tanning bed use. Basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing cancer, but early treatment is important because, if left untreated, basal cell carcinoma can spread and grow deep into the skin. My surgeon told me many years ago that, what appears to be a small area of basal cell carcinoma on the surface of the skin, can actually be as large as a silver dollar in other layers of the skin.
Answer: Risk Of Not Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a locally destructive type of skin cancer that is notorious for recurrence when not adequately treated. It can become quite disfiguring if left untreated, especially when located in cosmetically sensitive areas such as the nose. Typically this type of skin biopsy is performed for diagnosis and is not adequate treatment for a skin cancer. Biopsies sample a portion of the lesion, leaving some behind. This type of sampling biopsy is not intended to remove the entire lesion. It is not advisable to leave a known skin cancer untreated as it will likely grow and become more of a problem to remove in the future. Mohs micrographic surgery allows for 100% margin control and is tissue-sparing, which means it offers the highest cure rate while preserving as much normal tissue as possible.
Also Check: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinomas are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals. Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do not heal or go away on their own.
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Let’s Talk About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The second most common type of skin cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is also frequently caused by sun exposure or tanning bed use. Like basal cells, squamous cells can grow deep into the skin. However, unlike basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma can spread to lymph nodes and other organs.
Read Also: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
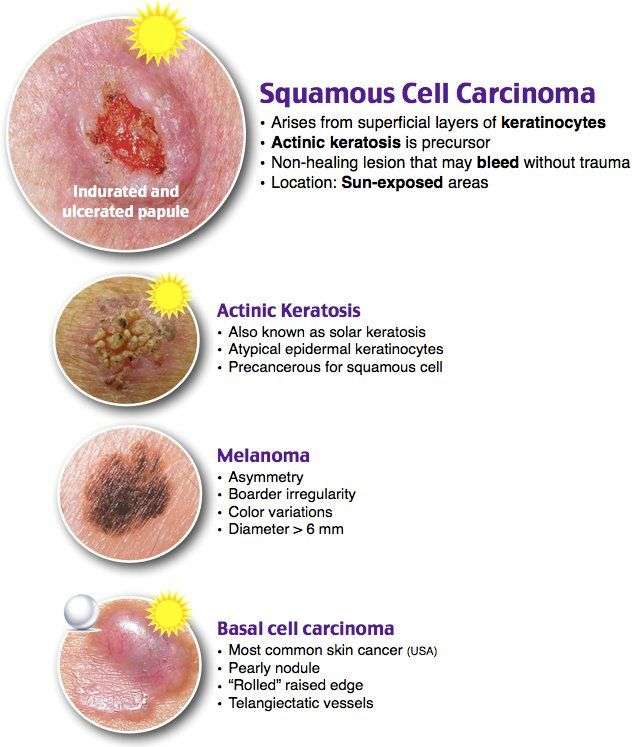
Skin Cancer Types: Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Basal cell carcinoma
What is basal cell carcinoma?The most common type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma can show up on the skin in many ways.
Is it contagious? No
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
Also Check: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers: Treatment Including Mohs Surgery Video
Chrysalyne D. Schmults, MD, MSCE, Director, Mohs and Dermatologic Surgery Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Director, High-Risk Skin Cancer Clinic at Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center discusses the prevalence of non-melanoma skin cancer and treatment options for patients, including Mohs surgery. Mohs surgery, a form of skin cancer removal in which the borders are examined by the surgeon microscopically while the patient waits, boasts a remarkable 99% cure rate for most basal and squamous cell skin cancers as well as a high cure rate for other rare forms of skin cancer. Since very little normal tissue is removed during the treatment, our surgeons are able to reconstruct most wounds with excellent cosmetic results. When surgical removal is not necessary, our Center also offers cream and other topical treatments for superficial skin cancers. Our Mohs Dermatologic Surgery Center located at Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital offers highly specialized outpatient treatment of skin cancer with excellent outcomes. Learn more at: –
Dermatology – basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, . We Have got 15 pix about Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers images, photos, pictures, backgrounds, and more. In such page, we additionally have number of images out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, images, etc.
What Do I Need To Know
- AKs are evidence of sustained sun damage. Having them raises your lifetime risk for skin cancer. Since having one AK means that its likely you have already developed more, this may translate into an especially elevated risk for developing an SCC.
- An untreated SCC can become invasive and even life-threatening.
Recommended Reading: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
Dna Mismatch Repair Proteins
DNA mismatch repair proteins are a group of proteins that physiologically stimulate G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis. Failure of MMR proteins to detect induced DNA damage results in the survival of mutating cells. MMR protein levels have been found to be higher in nonmelanoma skin cancers than in normal skin, and there is also some evidence of MMR dysregulation.
Dont Leave Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated
Now that you know what happens if you leave basal cell carcinoma untreated, its time to take action on your skin cancer diagnosis. To learn more about how IG-SRT works, contact our skin cancer specialist team at 855-222-6858. We can answer your questions and help you understand whether IG-SRT is right for you.
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer impacts the lives of 4 million Americans each year. GentleCure is committed to raising awareness of IG-SRT and is a trademark owned by SkinCure Oncology, LLC.
The information on this website is provided without any representations or warranties. You should not rely on this website as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or healthcare provider. The information on this site, as well as any information provided by the skin cancer information specialists on our educational hotline, is intended to help you make a better-informed treatment decision in conjunction with trained and licensed medical professionals.
Read Also: Merkel Cancer Prognosis
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color