Why Should I Choose Integrated Dermatology To Diagnose And Treat My Skin Cancer
Our board certified dermatologists and providers are experts in the field of dermatology and can properly diagnose and treat skin cancers. Our experts perform complete body exams and skin cancer examinations routinely and can accurately diagnose various types of skin cancers. Our dermatologists are also trained as dermatologic surgeons and can treat your skin cancer to the gold standard of care. Any suspicious lesion will be biopsied and sent out for analysis at a laboratory. We also work with specialized physicians called dermatopathologists that have expert training in properly diagnosing skin cancer under the microscope. Our physicians and providers have every patients best interest at heart and strive to provide the highest level of care.
Exam By A Health Care Professional
Some doctors and other health care professionals do skin exams as part of routine health check-ups.
Having regular skin exams is especially important for people who are at high risk of skin cancer, such as people with a weakened immune system or people with conditions such as basal cell nevus syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum . Talk to your doctor about how often you should have your skin examined.
Does This Mean That The Tumor Has Invaded Deeply And Is Associated With A Poor Prognosis
No, all it means is that it is a true cancer . On a biopsy, only a small sample of tissue is removed, and the pathologist usually cannot tell how deeply the tumor is invading into the wall of the esophagus.
Some early, small cancers can be treated with a special procedure called an endoscopic mucosal resection , which removes only part of the inner lining of the esophagus. In other situations, an esophagectomy is needed, and the depth of invasion is measured when the entire tumor is removed at surgery.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Undifferentiated Tumors: Solving The Mystery
Q. When a squamous cell carcinoma is designated as poorly differentiated, what other parameters/tests are performed to determine the tissue of origin?
A. Differentiation, for those of you who have just joined us, is a quality of tumors that has to do with how much the tumor cells resemble their tissue of origin. Well-differentiated tumors are composed of cells that closely resemble their tissue of origin, whereas poorly-differentiated tumors are composed of cells that have little resemblance to their tissue of origin. Anaplastic tumors are the least differentiated of all: they show no resemblance to their tissue of origin.
This concept is important for a couple reasons. First, the degree of differentiation of a tumor often has a bearing on prognosis. Well-differentiated tumors generally carry a better prognosis than poorly differentiated tumors. Second, when a tumor is totally undifferentiated , you have to resort to special tests in order to figure out its origin .
Back to our question: when you have a poorly-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, how do you know its a squamous cell carcinoma ? If the tumor is poorly-differentiated, that means there are still some morphologic features that reveal the squamous nature of the tumor. If you look carefully, you should be able to find some of these features, which would then point you towards the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
- Older age
- Blue, green, or gray eyes
- Blonde or red hair
- Spend time outside, exposed to the sun’s UV Rays
- History of sunburns, precancerous spots on your skin, or skin cancer
- Tanning beds and bulbs
- Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic in the water
- Bowens disease, HPV, HIV, or AIDS
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
You May Like: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
Effective Options For Early Stage Scc
Most squamous cell carcinomas of the skin can be cured when found and treated early. Treatment should happen as soon as possible after diagnosis, since more advanced SCCs of the skin are more difficult to treat and can become dangerous, spreading to local lymph nodes, distant tissues and organs. Find out more about treatment options for advanced or recurring SCCs here.
If youve been diagnosed with an SCC that has not spread, there are several effective treatments that can usually be performed on an outpatient basis. The choices available to you depend on the tumor type, size, location and depth, as well as your age and overall health.
Options include:
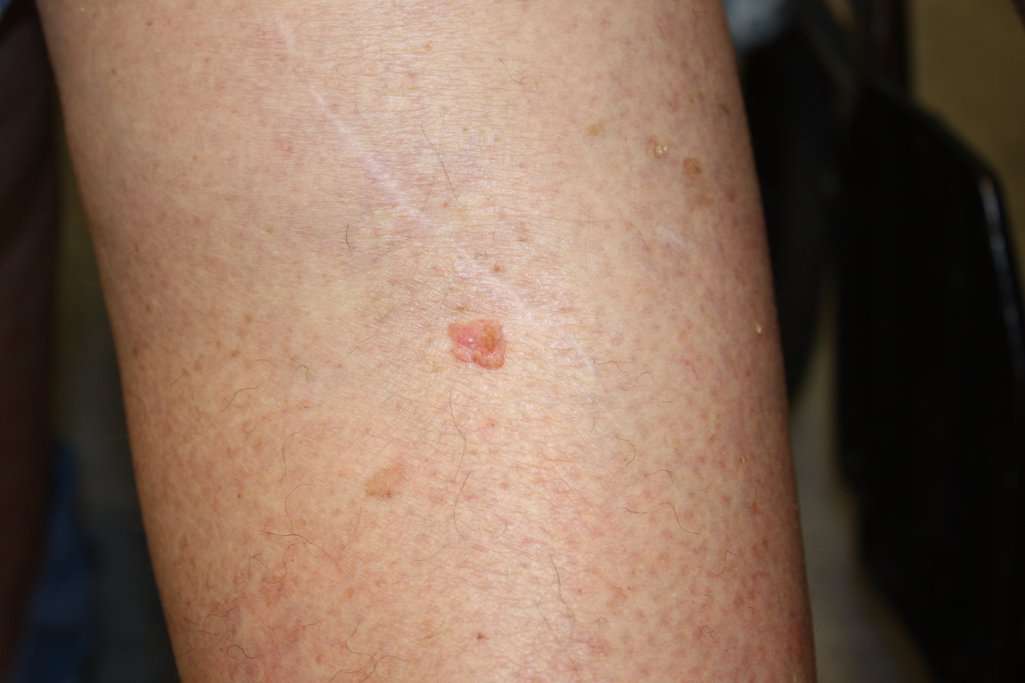
What Does A Squamous Cell Carcinoma Look Like
Squamous cell carcinomasasascells
. Furthermore, how serious is a squamous cell skin cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
can a squamous cell carcinoma kill you? If SCC isn’t treated in its early stages, the cancer may spread to other areas of the body, including the lymph nodes and organs. Once this occurs, the condition can be life-threatening.
Considering this, what does early squamous cell carcinoma look like?
SCC often looks like a rough, scaly red or brown patch. It may be thick or crusty. SCC may develop as a raised growth or lump some look like they have collapsed in the center. SCC may also appear to be an open sore that bleeds easily and does not heal.
Is a squamous cell carcinoma painful?
Signs and Symptoms of Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers. Skin cancers often don’t cause bothersome symptoms until they have grown quite large. Then they may itch, bleed, or even hurt. But typically they can be seen or felt long before they reach this point.
Don’t Miss: Cancer Spread All Over Body
What Does It Mean If The Following Terms Are Used To Describe The Adenocarcinoma: Papillary Micropapillary Acinar Mucinous Or Solid
These terms describe different types of lung adenocarcinoma, which are based on how the cells look and are arranged under the microscope . Some tumors look basically the same throughout the tumor, and some can look different in different areas of the tumor. Some growth patterns have a better prognosis than others. Since some tumors can have a mixture of patterns, the pathologist canât always tell all the types contained in a tumor just based on a biopsy that samples only a small part of the tumor. To know what types a tumor contains, the entire tumor must be removed.
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell carcinoma tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell carcinoma occurs four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell carcinoma can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell carcinoma of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
You May Like: Web Md Skin Cancers
Changes In Existing Spots
Warts and moles are rarely cause to worry. Though they may cause some irritation, most warts and moles are completely harmless. Because squamous cell carcinoma sometimes develops in existing skin lesions, its important to monitor moles, warts, or skin lesions for changes. Any observable change should raise a red flag and warrant a trip to the doctor for further examination.
The prognosis for SCC depends on a few factors, including:
- how advanced the cancer was when it was detected
- the location of the cancer on the body
- whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body
The sooner SCC is diagnosed, the better. Once found, treatment can begin quickly, which makes a cure more likely. Its important to treat precancerous lesions, like Bowens disease or actinic keratosis, early before they develop into cancer. See your doctor right away if you notice any new or unusual skin lesions.
Make regular appointments with your doctor for a skin check. Perform a self-examination once every month. Ask a partner or use a mirror to check places you cant see, like your back or the top of your head.
This is especially important for higher risk individuals, such as those with light skin, blond hair, and light-colored eyes. Anyone who spends prolonged time in the sun unprotected is also at risk.
How Your Doctor Decides On Treatment
The treatment you have depends on:
- where in the ear the cancer is
- the type of cancer you have
- the size of the tumour
- whether its spread beyond the area it started in
- your general health
This page is about treatment for cancer that starts in the skin flap of your outer ear. Although the ear canal is part of the outer ear, its treatment is different.
You can read about treatment for cancer that starts in the ear canal on the pages about cancer of the ear canal, middle ear and inner ear.
Also Check: 3b Melanoma
What Does It Mean If There Is Vascular Lymphatic Or Lymphovascular Invasion
These terms mean that cancer is present in the blood vessels and/or lymph vessels of the esophagus. If the cancer has grown into these vessels, there is an increased chance that it could have spread out of the esophagus. However, this doesnt mean that your cancer has spread. Discuss this finding with your doctor.
What Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Cancer Look Like
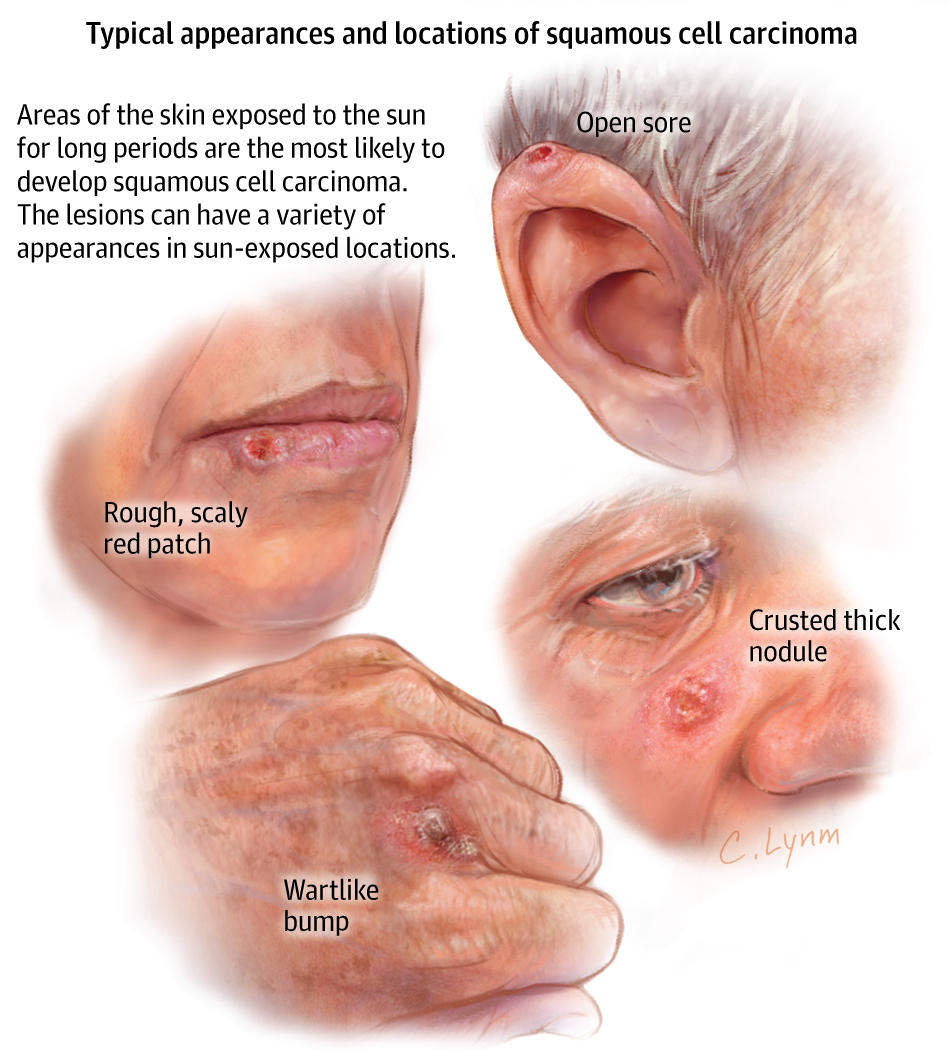
Squamous cell carcinomasasskinasskin cells
. Similarly, you may ask, what does early squamous skin cancer look like?
Squamous Cell CarcinomaThis nonmelanoma skin cancer may appear as a firm red nodule, a scaly growth that bleeds or develops a crust, or a sore that doesn’t heal. It most often occurs on the nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the body.
One may also ask, what color is squamous cell carcinoma? Rough-feeling, reddish patchThis is an early sign of squamous cell carcinoma.
Subsequently, question is, how bad is squamous cell skin cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
Can you pick off skin cancer?
“Picking at skin cancers is very bad, because you can scratch the top of it off and normal skin will grow in from the sides. So you think, “Oh, well I got rid of that.” But you can‘t pick a skin cancer completely off. The tumor is under that layer of skin and keeps growing.”
Also Check: Can Malignant Neoplasm Be Cured
Stage Iii Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The tumor cells may be of any size at the original site. A stage III SCC has begun to invade the nearby lymph nodes on the side of the body of the original cancerous growth. This new growth is still under 3 cm in size. It may also have grown into the facial bones like the bones surrounding the eye or your jaw bone.9 It has not affected any other organs.10
Where Squamous Cell Carcinoma Occurs
SCC can be found anywhere on the body, but is most commonly seen in sun-exposed areas. Common SCC sites include the face, ears, lips, scalp, shoulders, neck, hands, and forearms. Its also possible to be diagnosed with SCC in areas without sun exposure, such as inside the mouth, under fingernails or toenails, on the genitals, or in the anus.
Also Check: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
What If My Report Says Squamous Carcinoma
The inner lining of the esophagus is known as the mucosa. In most of the esophagus the top layer of the mucosa is made up of squamous cells. This is called squamous mucosa. Squamous cells are flat cells that look similar to fish scales when viewed under the microscope. Squamous carcinoma of the esophagus is a type of cancer that arises from the squamous cells that line the esophagus.
Ultraviolet Light And Other Potential Causes
Much of the damage to DNA in skin cells results from ultraviolet radiation found in sunlight and in the lights used in tanning beds. But sun exposure doesnt explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens your immune system.
Also Check: Show Me What Skin Cancer Looks Like
What Does It Mean If My Report Says Typical Carcinoid Or Atypical Carcinoid Tumor
Carcinoid tumors are a special type of tumor. They start from cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system. This system is made up of cells that are like nerve cells in certain ways and like hormone-making endocrine cells in other ways. These cells do not form an actual organ like the adrenal or thyroid glands. Instead, they are scattered throughout the body in organs like the lungs, stomach, and intestines.
Like most cells in your body, the lung neuroendocrine cells sometimes go through certain changes that cause them to grow too much and form tumors. These are known as neuroendocrine tumors or neuroendocrine cancers. There are 4 types of neuroendocrine lung tumors:
- Typical carcinoid tumor
- Small cell carcinoma
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
Typical carcinoid tumors of the lungs are not linked to smoking. They tend to be slow growing, and only rarely spread outside the lungs.
Atypical carcinoid tumors grow a little faster and are somewhat more likely to spread to other organs. Seen under a microscope, they have more cells in the process of dividing and look more like a fast-growing tumor. They are much less common than typical carcinoids. Some of the features of an atypical carcinoid that may be mentioned in your report include: mitotic figures or mitoses and necrosis .
Some carcinoid tumors can release hormone-like substances into the bloodstream, which might cause symptoms. Lung carcinoids do this far less often than carcinoid tumors that start in the intestines.
Cancer Stage Determines Risk Of Spreading And Line Of Treatment
A cancer of the upper layers of the skin in the epidermis, SCC is the second most common form of skin cancer after basal cell carcinoma and affects an estimated 1 million new people every year in the United States alone. Cancer staging is done for SCC with the intention of categorizing the size of cancer and to judge how much it has grown. And theres a clear line of treatment and way forward for each stage.1
With skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma, the likelihood of cancer spreading to other parts of the body is very low and early diagnosis and treatment usually tackles the problem before it spreads. SCC, however, is a little trickier. While the risk of spreading is still quite small, there is a relatively higher chance of it progressing depending on what stage the cancer is at. For those with weakened immune systems, say, people whove had organ transplants or anyone infected with HIV, the risk is a little higher. Also, when the cancer is in the head and neck region, it may have a slightly higher risk of recurring or spreading.2
The actual stage of this form of cancer is determined based on the TNM protocol devised by the American Joint Commission on Cancer.3
- T : The size/extent of the tumor
- N : Whether it has spread to lymph nodes
- M : Whether it has spread to other parts of the body
Read Also: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
Although squamous cell carcinomas usually grow slowly, it is important to see a dermatologist quickly. “The sooner you see your doctor and the cancer is diagnosed and treated, the less complicated the surgery to remove it will be, and the faster you will make a complete recovery, Dr. Leffell explains. The treatment for squamous cell cancer varies according to the size and location of the lesion. The surgical options are the same as those for basal cell cancer:
- Surgical excision: Removing a squamous cell lesion is a simple procedure that typically takes place in the dermatologist’s office. After numbing the cancer and the area around it with a local anesthetic, the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding skin to make sure all cancer is eliminated. Estimating how much to take requires skill and expertise, Dr. Leffell notes. The risk of taking too little tissue is that some cancer remains taking too much leaves a larger scar than is necessary. Shaped like a football, the wound is stitched together, using plastic surgery techniques. If dissolvable stitches are used, they will disappear on their own as the area heals. Though the procedure leaves some redness and a small scar, it tends to become less noticeable over time. “The cure rate for this type of excision is typically about 90 to 93 percent,” says Dr. Leffell. But, of course, this is dependent on the skill and experience of the doctor.”