The Five Stages Of Skin Cancer
Cancer in the skin thats at high risk for spreading shares features with basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Some of these features are:
- Not less than 2 mm in thickness
- Has spread into the inner layers of the skin
- Has invaded skin nerves
Stage 0
In the earliest stage, cancer is only present in the upper layer of the skin. You may notice the appearance of blood vessels or a dent in the center of the skin growth. There are no traces of malignant cells beyond this layer.
Stage 1
At stage 1, cancer has not spread to muscles, bone, and other organs. It measures roughly 4/5 of an inch. Theres a possibility that it may have spread into the inner layer of the skin.
Stage 2
In this stage, cancer has become larger than 4/5 of an inch. Cancer still has not spread to muscles, bone, and other organs.
Stage 3
At stage 3, the cancer is still larger than 4/5 of an inch. Facial bones or a nearby lymph node may have been affected, but other organs remain safe. It may also spread to areas below the skin, such as into muscle, bone, and cartilage but not far from the original site.
Stage 4
Cancer can now be of any size and has likely spread into lymph nodes, bones, cartilage, muscle, or other organs. Distant organs such as the brain or lungs may also be affected. In rare cases, this stage might cause death when allowed to grow and become more invasive.
How Can I Help My Child Live With Skin Cancer
If your child has skin cancer, you can help him or her during treatment in these ways:
-
Your child may have trouble eating. A dietitian or nutritionist may be able to help.
-
Your child may be very tired. He or she will need to learn to balance rest and activity.
-
Get emotional support for your child. Counselors and support groups can help.
-
Keep all follow-up appointments.
-
Keep your child out of the sun.
After treatment, check your child’s skin every month or as often as advised.
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Read Also: 2nd Stage Cancer
How To Look For Melanoma On Your Scalp
Melanoma on the scalp is one of the more dangerous types of skin cancer, as it forms in an area thats not easily detectable and can grow at a much faster rate due to an abundant amount of blood vessels and tissues. A regular skin self-exam should always include inspecting the scalp, as this part of the body is constantly exposed to the sun and can burn easily, especially if you are bald or have thin hair.
Tracking Changes To Your Skin With An App
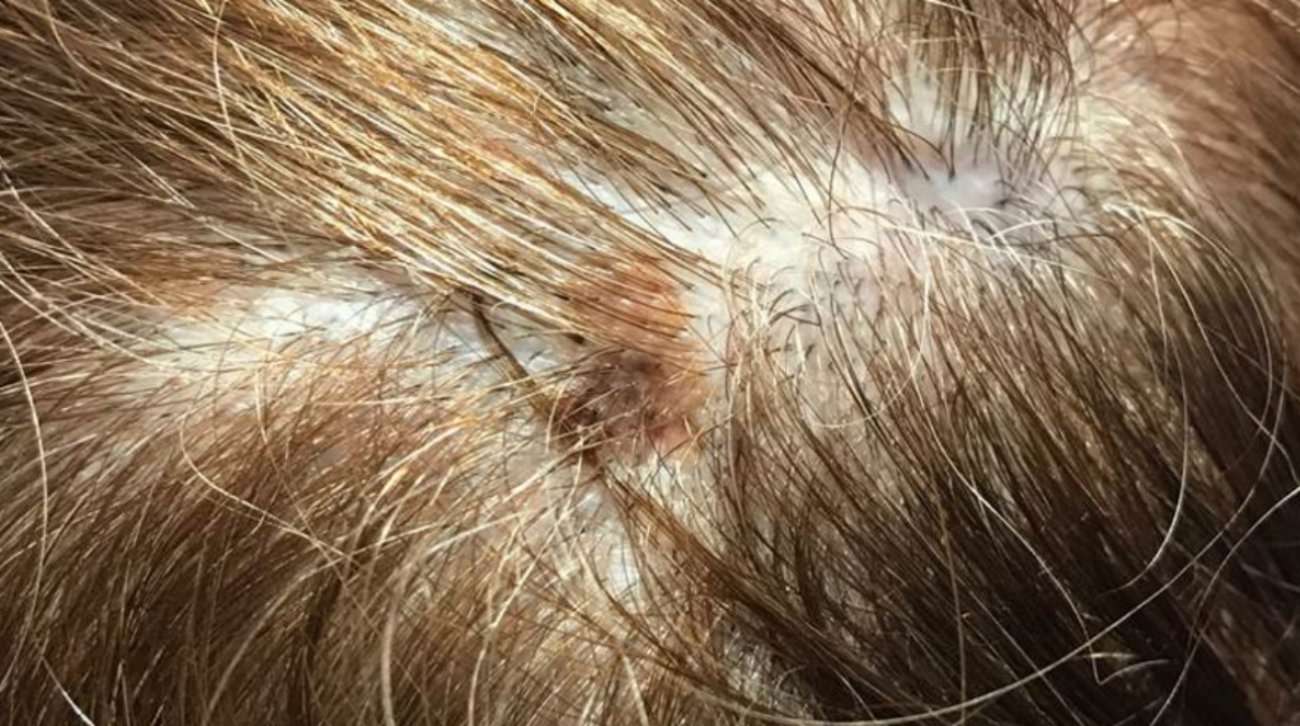
Some people find it helpful to photograph areas of their skin such as the back or individual lesions to be able to better spot any future changes.
Over the past years, smartphone apps that can help consumers track moles and skin lesions for changes over time have become very popular and can be a very helpful tool for at-home skin checks.
This page does not replace a medical opinion and is for informational purposes only.
Please note, that some skin cancers may look different from these examples. See your doctor if you have any concerns about your skin.
It might also be a good idea to visit your doctor and have an open talk about your risk of skin cancer and seek for an advice on the early identification of skin changes.
* Prof. Bunker donates his fee for this review to the British Skin Foundation , a charity dedicated to fund research to help people with skin disease and skin cancer.
Make a difference. Share this article.
Don’t Miss: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
What Is The Treatment For Skin Cancer
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is straightforward. Usually, surgical removal of the lesion is adequate. Malignant melanoma, however, may require several treatment methods, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy or immunotherapy or both. Because of the complexity of treatment decisions, people with malignant melanoma may benefit from the combined expertise of the dermatologist, a cancer surgeon, and a medical oncologist.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Also Check: What Is The Worst Skin Cancer To Have
What Does Scalp Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of cancer, and because its appearance can closely mimic natural moles, freckles, and age spots, it can be easy to overlook. Its important to know what to look for and perform regular skin cancer screenings to ensure you receive treatment for this condition in the earliest stages. According to Dr. Gregory Walker of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Waco, Texas, Melanoma can be easily overlooked in obvious places on the body, but many people dont know that the scalp, fingernails and toenails, and other harder to see areas often hide this condition until it has progressed to more advanced stages. Patients who know what to look for and regularly screen their skin for cancers, are much more likely to receive a diagnosis in early, more treatable stages. Keep reading to hear more from Dr. Walker about what scalp melanoma looks like and how to check for this condition and prevent serious health concerns.
Also Check: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
How Are Moles Evaluated
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE’s of melanoma — or one that’s tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn’t heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole — see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
What Do The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer Look Like
People can have stages of skin cancer and yet not feel ill, which makes early treatment and diagnosis a little challenging. But by being aware of the early stages of this disease, you can protect yourself and seek effective treatment right away. Do you have scaly patches, raised growths, or sores that do not heal? Dr. Jurzyk from Advanced Dermatology Center in Wolcott, CT can help you identify and treat all types of cancer of the skin, keeping you from fatal complications.
Don’t Miss: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers do not know why certain cells become cancerous. However, they have identified some risk factors for skin cancer.
The most important risk factor for melanoma is exposure to UV rays. These damage the skin cellsâ DNA, which controls how the cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Most UV rays come from sunlight, but they also come from tanning beds.
Some other risk factors for skin cancer include:
- A lot of moles: A person with more than 100 moles is more likely to develop melanoma.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles: The risk of developing melanoma is higher among people with fair skin. Those who burn easily have an increased risk.
- Family history:
The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to limit oneâs exposure to UV rays. A person can do this by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and covering up when outdoors.
People should also avoid tanning beds and sunlamps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
It can be easy to mistake benign growths for skin cancer.
The following skin conditions have similar symptoms to skin cancer:
Speak To Your Healthcare Provider
If you notice any changes to your skin that you are concerned about, make an appointment with your healthcare provider for a skin exam.
During your skin examination, your healthcare provider will closely examine the problem area of your skin. They might use a dermatoscope, which works like a magnifying glass over the skin. If your healthcare provider thinks you may have skin cancer, they might refer you to a dermatologist .
You may need a biopsy. During this procedure, a small sample of skin is removed from the affected area for examination with a microscope.
- Incisional biopsy: Part of the growth is removed with a scalpel. The full thickness of the skin is removed, and the area is closed with stitches.
- Excisional biopsy: The whole growth, and sometimes a border around it, is removed with a scalpel. The area is closed with stitches.
- Punch biopsy: A trephine is used to remove a small circle of the full thickness of the skin. The area removed is very small, so it may heal on its own, or a few stitches may be required.
- Shave biopsy: A sterile instrument like a razor blade is used to “shave-off” the abnormal-looking growth from the top layer of the skin.
You should receive your results within a few weeks.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
How Skin Cancer Appears On Legs
Skin cancer can appear anywhere on the body, making skin cancer on the legs a real possibility. What does skin cancer on the leg look like? Depending on the exact diagnosis, signs of skin cancer on the leg may differ, which is why its always important to be aware of significant changes to your skins appearance. In this overview well look at early stage leg skin cancer and treatment options.
Surgery For Ear Cancer
The type of surgery and the amount of surgery which the patient needs depends on the location of the cancer in the patientâs ear. Surgical procedure also depends on the how much and where the cancer has spread to the surrounding tissues or to the adjacent structures. During surgery the surgeon will remove the entire tumor along with the surrounding tissue, so that the patient is completely free from cancer cells. This is known getting clear margins of the tissue and it needs to be a minimum 5 mm surrounding the tumor/cancer. Getting clear margins will decrease the risk of cancer recurrence.
Surgery for ear cancer involves having to remove a part or all of the following:
- The ear canal.
- A part or the entire temporal bone.
- The inner ear.
Mastoidectomy: The temporal bone is a bone that is present near the ear, at the side of the skull. Temporal bone resection or mastoidectomy is the surgical procedure where the temporal bone is removed.
Removal of facial nerve and lymph nodes: In rare cases, the facial nerve may need to be removed by the surgeon. The facial nerve travels down the side of the face and passes through the salivary gland. The surgeon may also need to remove the adjacent lymph nodes, which are present near the patientâs neck and the salivary gland that is present on the side of the patientâs head.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iiia Melanoma Prognosis
Skin Cancer On Outer Ear Pictures : Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Eyelid
Cancer of the ear is rare. In the united states, its estimated that doctors diagnose over 100,000 new skin cancer cases each year. Most of these cancers start in the skin of the outer ear. The strongest risk factor for developing skin cancer is ultraviolet ray exposure, typically from the sun. Read about the symptoms, types, stages and tests for outer ear cancer.
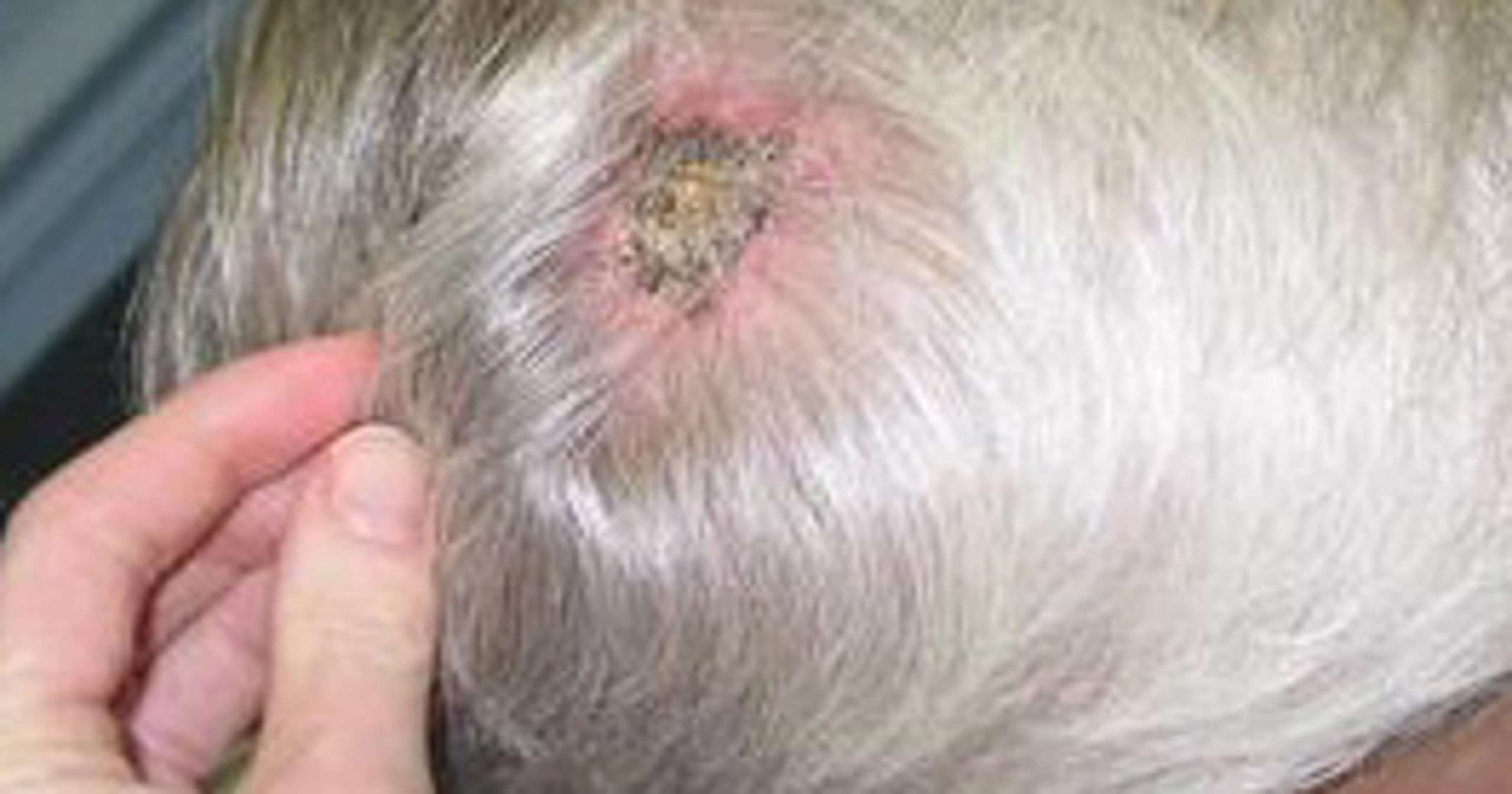
What Are The Signs Of Skin Cancer On The Scalp
There are many possible signs of skin cancer on the scalp.
These include, but are not limited to:
- Pearl-colored or waxy bumps
- Brown spots with dark speckles
- Moles that change in feel, size, and color, or that are bleeding
- Lesions that feel itchy, burning, or otherwise painful
Most signs of skin cancer on scalp areas include some discoloration, but this is not a universal sign. In particular, lesions can be flesh-colored, though this is relatively rare. Some occupations, ancestries, and foods can increase your risk of cancer.
The risks of developing specific types of skin cancer change with age. Among younger people, melanoma on scalp areas is the most common, especially between the ages of 25 and 29. In older people, squamous and basal cell skin cancers on the head are more common.
Skin cancer is not the only possible cause of changes on the scalp.
Here are some other common conditions that people often mistake for skin cancer:
- Psoriasis
- Freckles
- Skin tags
- Hemangioma
- Dermatofibroma
To the untrained eye, it can be hard to distinguish some of these from genuine scalp cancer symptoms and scalp cancer treatment. At the risk of repeating ourselves, only a trained doctor can determine whether or not someone has skin cancer on the head.
You May Like: Large Cell Cancer Of The Lung
How Can I Tell If I Have Skin Cancer
¿Cómo se ve el cáncer de la piel? ¿Cómo puedo prevenir el cáncer de piel?¿Estoy en riesgo de desarrollar melanoma?Cáncer de piel en personas de colorCómo examinar sus manchasNoe Rozas comparte su
Skin cancer is actually one of the easiest cancers to find. Thats because skin cancer usually begins where you can see it.
You can get skin cancer anywhere on your skin from your scalp to the bottoms of your feet. Even if the area gets little sun, its possible for skin cancer to develop there.
You can also get skin cancer in places that may surprise you. Skin cancer can begin under a toenail or fingernail, on your genitals, inside your mouth, or on a lip.
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
Where Within The Skin Layers Does Skin Cancer Develop
Where skin cancer develops specifically, in which skin cells is tied to the types and names of skin cancers.
Most skin cancers begin in the epidermis, your skins top layer. The epidermis contains three main cell types:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. They constantly shed as new cells form. The skin cancer that can form in these cells is called squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cells: These cells lie beneath the squamous cells. They divide, multiply and eventually get flatter and move up in the epidermis to become new squamous cells, replacing the dead squamous cells that have sloughed off. Skin cancer that begins in basal cells is called basal cell carcinoma.
- Melanocytes: These cells make melanin, the brown pigment that gives skin its color and protects your skin against some of the suns damaging UV rays. Skin cancer that begins in melanocytes is called melanoma.
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma