What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
What Skin Cancer Looks Like
by rsiadmin | Jul 13, 2020 | Dermatologist
Do You Know What Skin Cancer Looks Like?
Properly identifying marks or growths on your skin is one of the best ways to detect cancer early. Most skin cancer are treatable and often can be cured. If you can catch them in their beginning stages, your dermatologist can formally evaluate. Knowing what to look for is the key to addressing the cancer quickly. Skin cancer affects millions of people in the United States, particularly those 65 and older who are fair-skinned.
What does skin cancer look like when it starts?
It takes on a variety of forms. It can be rough and scaly. It can be a raised growth with dark bumps. It can be a flat crusty patch of skin. If you notice a new growth or one that is changing, get it checked by a dermatologist.
Here are some tips for early skin cancer detection:
Atypical black mole photo with uneven border- possibly cancerous
Close up photo of mole to be tested for skin cancer
Where Within The Skin Layers Does Skin Cancer Develop
Where skin cancer develops specifically, in which skin cells is tied to the types and names of skin cancers.
Most skin cancers begin in the epidermis, your skins top layer. The epidermis contains three main cell types:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. They constantly shed as new cells form. The skin cancer that can form in these cells is called squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cells: These cells lie beneath the squamous cells. They divide, multiply and eventually get flatter and move up in the epidermis to become new squamous cells, replacing the dead squamous cells that have sloughed off. Skin cancer that begins in basal cells is called basal cell carcinoma.
- Melanocytes: These cells make melanin, the brown pigment that gives skin its color and protects your skin against some of the suns damaging UV rays. Skin cancer that begins in melanocytes is called melanoma.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
Can Vulval Cancer Be Prevented
Its not thought to be possible to prevent vulval cancer completely, but you may be able to reduce your risk by:
- practising safer sex using a condom during sex can offer some protection against HPV
- attending cervical screening appointments cervical screening can detect HPV and precancerous conditions such as vulval intraepithelial neoplasia
- stopping smoking
The HPV vaccination may also reduce your chances of developing vulval cancer.
This is now offered to all girls and boys who are 12 to 13 years old as part of the routine childhood immunisation programme.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2021 Next review due: 30 April 2024
Also Check: How Serious Is Melanoma Cancer
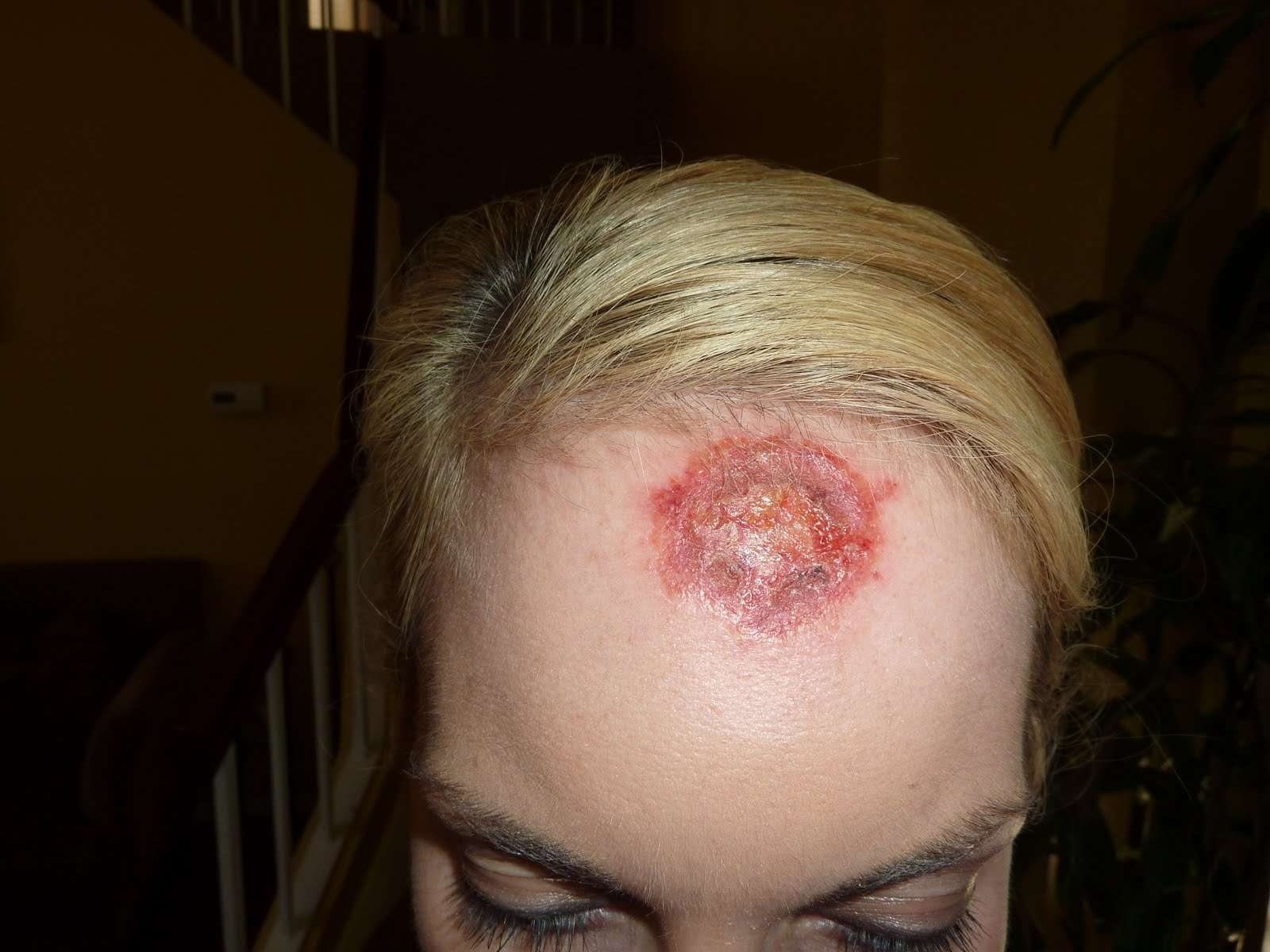
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Causes And Risk Factors
The exact cause of vaginal cancer is unknown, but certain risk factors contribute to its development such as:
Exposure to diethylstilbestrol. Women exposed to DES in utero or who have taken DES, have a high risk for developing vaginal cancer, especially adenocarcinoma of the vagina. The drug is not given at present because of the discovery that is increased the risk for certain diseases including cancer.
Human Papilloma Virus Infection. HPV causes genital warts in men and women. The presence of HPV increases the tendency to develop reproductive system cancers such as cervical and vaginal cancer. HPV infection is sexually transmitted, which means that having multiple sexual partners increases the risk for HPV infection.
Being sbove 50 years of age. Age has been a contributing factor for vaginal cancer because increasing age increases the long-term exposure to certain types of carcinogens, which changes the characteristics of cells.
History of other reproductive system malignancies. Previous malignancies in the reproductive system, specifically cervical cancer, increase the risk for secondary vaginal cancer.
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
How Reduce Your Risk For Cancer
Factors like genetics can influence your risk of getting skin cancer, but the number-one culprit is still the sun. Naturally, the biggest thing you can do is use sun protection all the time. “You really have to wear sunscreen every single day,” Karen says. When you’re actually at the beach or spending a lot of time outside in the sun’s rays, make sure to reapply every two hours, she says.
As much as we love our SPF, Karen stresses sunscreen alone isn’t enough. “It should be one component of a smart sun strategy that includes hats, long sleeves, sun-protective clothing, and sitting in the shade,” she explains.
“If you don’t go in the sun, it doesn’t guarantee that you’ll never get skin cancer, but it does greatly decrease your risk of the big three,” Day adds.
Be sure to keep up with yearly skin checks. If you have a history of skin cancer, either personally or in your family, your dermatologist might recommend upping them to every six months. And in the meantime, don’t be afraid to see your derm about something that looks weird.
McNeill recommends making an appointment to see your dermatologist if a spot a weird bump, sore, mole, or pimple that just won’t go away is not healing after a month. “You should not have a pimple or a scab or new bump for a month,” she says.
For more on how to prevent skin cancer:
Less Common Skin Cancers
Uncommon types of skin cancer include Kaposi’s sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas on the head, neck, arms, and legs but often spreads to other parts of the body.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
What Does Melanoma Skin Cancer Look Like
Instead of a perfect circle, it is a weirdly shaped oval, squiggles, or even a blotch. coloration is also difficult. Many relate to a typical mole as darker than your general tone and red, black, or brown. pink or orangish masses also appear. Sometimes, the hue is indistinguishable from the rest of your skin.
What You Need To Know About Early Detection
Finding melanoma at an early stage is crucial early detection can vastly increase your chances for cure.
Look for anything new,changing or unusual on both sun-exposed and sun-protected areas of the body. Melanomas commonly appear on the legs of women, and the number one place they develop on men is the trunk. Keep in mind, though, that melanomas can arise anywhere on the skin, even in areas where the sun doesnt shine.
Most moles, brown spots and growths on the skin are harmless but not always. The ABCDEs and the Ugly Duckling sign can help you detect melanoma.
Early detection makes a difference
99%5-year survival rate for patients in the U.S. whose melanoma is detected early. The survival rate drops to 66% if the disease reaches the lymph nodes and27% if it spreads to distant organs.
Don’t Miss: What Does Cancer Tissue Look Like
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed In A Child
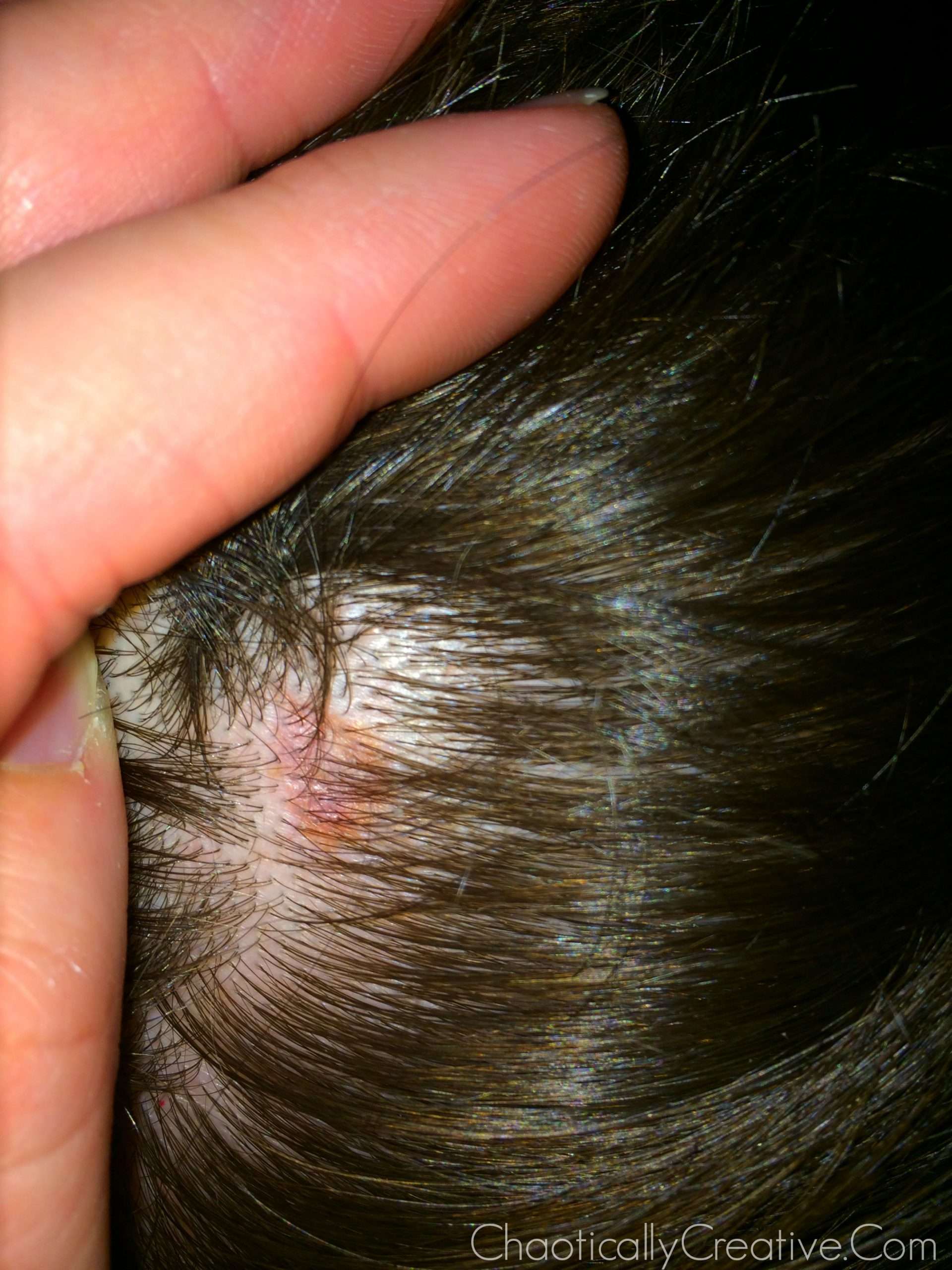
The healthcare provider will examine your child’s skin. Tell the healthcare provider:
-
When you first noticed the skin problem
-
If it oozes fluid or bleeds, or gets crusty
-
If its changed in size, color, or shape
-
If your child has pain or itching
Tell the healthcare provider if your child has had skin cancer in the past, and if other your family members have had skin cancer.
Your child’s healthcare provider will likely take a small piece of tissue from a mole or other skin mark that may look like cancer. The tissue is sent to a lab. A doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope. He or she may do other tests to see if cancer cells are in the sample. The biopsy results will likely be ready in a few days or a week. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you the results. He or she will talk with you about other tests that may be needed if cancer is found.
Also Check: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Basal Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
Basal cells are found within the skin and are responsible for producing new skin cells as old ones degenerate. Basal cell carcinoma starts with the appearance of slightly transparent bumps, but they may also show through other symptoms.
In the beginning, a basal cell carcinoma resembles a small bump, similar to a flesh-colored mole or a pimple. The abnormal growths can also look dark, shiny pink, or scaly red in some cases.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
An Unexplained Change In Your Skin
According to the CDC, a change in your skin is the first and most common sign of skin cancer. A sore that doesn’t heal, a new growth, or a mole that changes are all possible symptoms of skin cancer and should be examined by a health professional. “It’s important to go to your dermatologist and have an annual exam,” says Evelyn Jones, MD, a dermatologist and owner of WellSprings Dermatology and WellSprings SkinCare in Paducah, Kentucky. “But I also like to tell peoplethe first of every month, get in the habit of looking at their skin and becoming familiar with it.”
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Look Out For An Ugly Duckling
The Ugly Duckling is another warning sign of melanoma. This recognition strategy is based on the concept that most normal moles on your body resemble one another, while melanomas stand out like ugly ducklings in comparison. This highlights the importance of not just checking for irregularities, but also comparing any suspicious spot to surrounding moles to determine whether it looks different from its neighbors. These ugly duckling lesions or outlier lesions can be larger, smaller, lighter or darker, compared to surrounding moles. Also, isolated lesions without any surrounding moles for comparison are considered ugly ducklings.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Questions to ask your dermatologist may include:
- What type of skin cancer do I have?
- What stage is my skin cancer?
- What tests will I need?
- Whats the best treatment for my skin cancer?
- What are the side effects of that treatment?
- What are the potential complications of this cancer and the treatment for it?
- What outcome can I expect?
- Do I have an increased risk of additional skin cancers?
- How often should I be seen for follow-up checkups?
Read Also: Well Differentiated
How To Check Your Skin
- Make sure you check your entire body, as skin cancers can sometimes occur on parts of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet, between fingers and toes and under nails.
- Undress completely and make sure you have good light.
- Use a mirror to check hard to see spots, like your back and scalp, or get a family member, partner or friend to check for you.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
It is always vital to seek medical advice early for a skin change, no matter how small it may appear. Make an appointment with your healthcare provider for a skin exam if you notice:
- Any new changes, lesions, or persistent marks on your skin
- A mole that is asymmetrical, has an irregular border, is multicolored, is large in diameter, is evolving, or has begun to crust or bleed
- An “ugly duckling” mole on the skin
- Any changes to your skin that you are concerned about
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Isnt Skin Cancer
The only way to be 100% sure that a lesion is not cancerous is to have it removed or biopsied and to have a pathologist look at the histology of the tissue.
However, the following are unlikely to be malignant and can usually just be monitored:
-
Typical skin tagsthese are usually found in areas of the body that rub against each other, such as under the arms or breasts.
-
Freckles that have been present since childhoodthese are small, flat, pigmented lesions that have been present since a young age and that usually fade without sun exposure. Use the ABCDE method to monitor them.
-
Age spotsalso called liver spots or solar lentigines. These are common in people over the age of 50 but may also be present in younger people who have spent a lot of time in the sun. They are typically present on areas of skin that have been exposed to the sun or that are sun-damaged. They can co-exist with skin cancers. Use the ABCDE approach to monitor age spots for malignant change.
Features of solar lentigines :
-
Flat, oval areas of increased pigmentation
-
Usually tan to dark brown
-
Occur on skin that has had the most sun exposure over the years, such as the backs of hands, tops of feet, face, shoulders, and upper back
-
Range from freckle size to about 1/2 inch across
-
Can group together, making them more noticeable
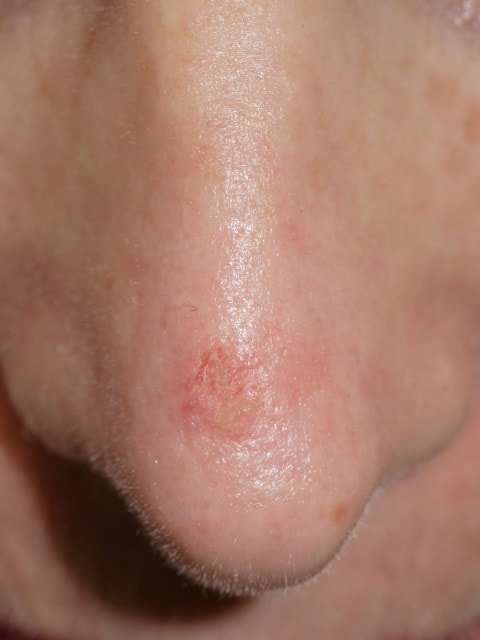
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Face
Are you wondering what skin cancer looks like on your face? Is there a spot that is new or changing? For starters, let us just say kudos on paying attention! It is so vital to watch yourself for these things because early detection truly saves lives. Secondly, skin cancer has a variety of appearances so we will need to start by explaining exactly what skin cancer is and the types it can occur as.
What is Skin Cancer?Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells. It most often develops on areas of the skin exposed to the suns rays. Skin cancer affects people of all colors and races, although those with light skin who sunburn easily have a higher risk. Research has estimated that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. According to the American Cancer Society, about 3.3 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed in America each year with an estimated 87,000+ new cases of melanoma predicted for 2020.
While rare types of skin cancer do exist, there are four main types of skin cancer:
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. SCC often appears as a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens. SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent this and stop SCC from spreading to other areas of the body.
Also Check: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like