New Concepts About Adcs
It gradually became apparent to pathologists that modifications to the revised WHO classification had to be made. An international group of pathologists, with major input from clinicians and radiologists, re-evaluated ADCs. These studies were sponsored by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer , the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society . Their consensus views were presented at the last IASLC World Congress and are now in press .
Important new features of the new classification include identifying the major ADC subtype present in mixed tumors. This will greatly aid clinicpathological correlations. In addition a micropapillary subtype is recognized as distinct from the papillary subtype, because of its association with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations . The most important clinical impact of the new proposed classification is the replacement of the term BAC with adenocarcinoma in situ .
Nine Types Of Standard Treatment Are Used:
Surgery
Four types of surgery are used to treat lung cancer:
- Wedge resection: Surgery to remove a tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. When a slightly larger amount of tissue is taken, it is called a segmental resection.
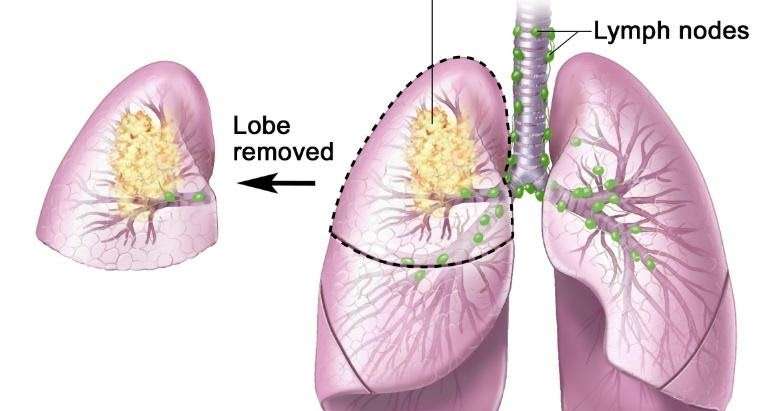
- Lobectomy: Surgery to remove a whole lobe of the lung.
- Pneumonectomy: Surgery to remove one whole lung.
- Sleeve resection: Surgery to remove part of the bronchus.
Even if the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy or radiation therapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, to increase the chances of a cure, is called adjuvant therapy.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer.
Radiosurgery is a method of delivering radiation directly to the tumor with little damage to healthy tissue. It does not involve surgery and may be used to treat certain tumors in patients who cannot have surgery.
Chemotherapy
Biologic therapy
Targeted therapy
Laser therapy
Cryosurgery
Electrocautery
Watchful waiting
What If My Report Mentions Margins
The margin is the edge or the boundary of the specimen that was removed by the surgeon. It is where the surgeon has sectioned across the lung to remove the tumor.
The margin may be free of the tumor that is, a rim of uninvolved tissues may surround the tumor, indicating that the tumor has been removed completely. This is sometimes referred to as a negative margin.
Alternatively, the tumor could extend to the edge of the specimen , implying that the tumor has not been completely removed. This is sometimes referred to as a positive margin.
The status of the margin is an important indicator of the potential for the tumor to recur and of the need for further treatment. Talk with your doctor about the best approach for you if cancer is found at the margins.
Also Check: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
Normal Structure And Function Of The Lungs
Your lungs are 2 sponge-like organs in your chest. Your right lung has 3 sections, called lobes. Your left lung has 2 lobes. The left lung is smaller because the heart takes up more room on that side of the body.
When you breathe in, air enters through your mouth or nose and goes into your lungs through the trachea . The trachea divides into tubes called bronchi, which enter the lungs and divide into smaller bronchi. These divide to form smaller branches called bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles are tiny air sacs known as alveoli.
The alveoli absorb oxygen into your blood from the inhaled air and remove carbon dioxide from the blood when you exhale. Taking in oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide are your lungs main functions.
Lung cancers typically start in the cells lining the bronchi and parts of the lung such as the bronchioles or alveoli.
A thin lining layer called the pleura surrounds the lungs. The pleura protects your lungs and helps them slide back and forth against the chest wall as they expand and contract during breathing.
Below the lungs, a thin, dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm separates the chest from the abdomen. When you breathe, the diaphragm moves up and down, forcing air in and out of the lungs.
Histology And Angiogenic Therapy
Angiogenesis is an integral part of all tumors and inhibitors of angiogenesis have elucidated much interest in NSCLC. Bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor, has been shown to benefit patients with NSCLC of non-squamous histology when combined with standard doublet therapy . Because bevacizumab therapy may be associated with serious hemorrhagic events, apparently more common among patients with predominantly SCC, drug administration is usually limited to NSCLC of non-squamous histology .
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
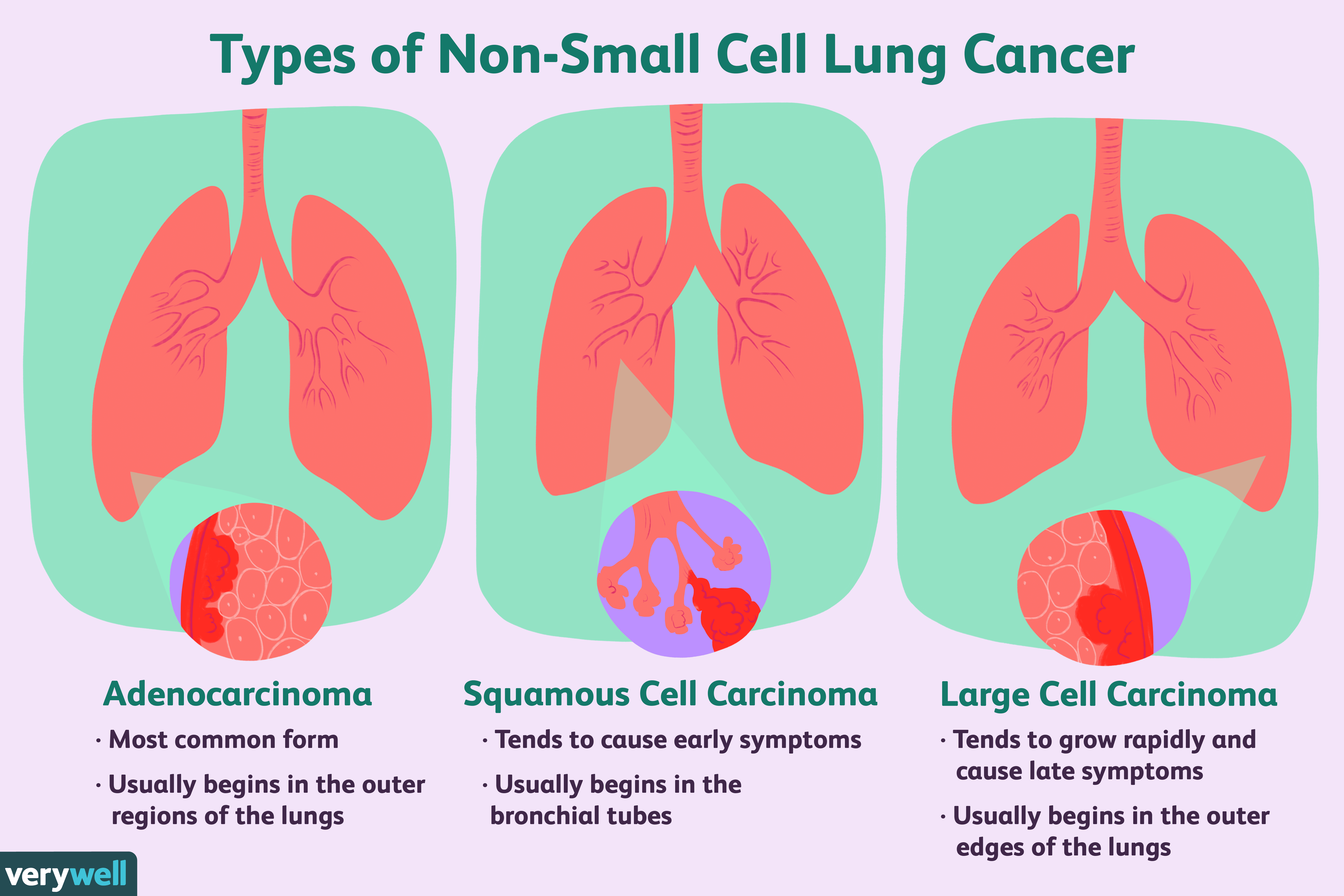
What Does It Mean If The Following Terms Are Used To Describe The Adenocarcinoma: Papillary Micropapillary Acinar Mucinous Or Solid
These terms describe different types of lung adenocarcinoma, which are based on how the cells look and are arranged under the microscope . Some tumors look basically the same throughout the tumor, and some can look different in different areas of the tumor. Some growth patterns have a better prognosis than others. Since some tumors can have a mixture of patterns, the pathologist canât always tell all the types contained in a tumor just based on a biopsy that samples only a small part of the tumor. To know what types a tumor contains, the entire tumor must be removed.
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Small Cell Lung Cancer
About 10% to 15% of all lung cancers are SCLC and it is sometimes called oat cell cancer.
This type of lung cancer tends to grow and spread faster than NSCLC. About 70% of people with SCLC will have cancer that has already spread at the time they are diagnosed. Since this cancer grows quickly, it tends to respond well to chemotherapy andradiation therapy. Unfortunately, for most people, the cancer will return at some point.
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Stage 3 Melanoma
After Lung Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Lungs Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the lungs or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. Some of the tests used to diagnosenon-small cell lung cancer are also used to stage the disease.
Other tests and procedures that may be used in the staging process include the following:
Adc And Response To Tkis
The widespread use of TKIs gefitinib and erlotinib identified certain subsets of NSCLC as being more likely to respondADC histology, never-smoker status, female gender and East Asian ethnicity. After the discovery of EGFR mutations in 2004, it was noted that mutations targeted the same subtypes, and numerous studies have demonstrated that mutations predict response . Whether ADC histology predicts response in the absence of mutations is more controversial, as is the role of increased gene copy number. However, ADC histology remains one of the main clinico-pathological factors in the decision to treat with TKIs in the absence of the mutational status, or in the decision as to whether to perform mutation testing. At some institutions the diagnosis of lung ADC initiates automatic testing for EGFR mutations . KRAS mutations have been associated with resistance to TKI therapy both clinically and in vitro .
You May Like: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Dna Repair Deficiency In Nsclc
Deficiencies in DNA repair underlie many forms of cancer. If DNA repair is deficient, the frequency of unrepaired DNA damages increases, and these tend to cause inaccurate translesion synthesis leading to mutation. Furthermore, increased damages can elevate incomplete repair, leading to epigenetic alterations.
As indicated as in the article Carcinogenesis, mutations in DNA repair genes occasionally occur in cancer, but deficiencies of DNA repair due to epigenetic alterations that reduce or silence DNA repair-gene expression occur much more frequently in cancer.
Epigenetic gene silencing of DNA repair genes occurs frequently in NSCLC. At least nine DNA repair genes that normally function in relatively accurate DNA repair pathways are often repressed by promoter hypermethylation in NSCLC. One DNA repair gene, FEN1, that functions in an inaccurate DNA repair pathway, is expressed at an increased level due to hypo-, rather than hyper-, methylation of its promoter region in NSCLC.
Epigenetic promoter methylation in DNA repair genes in NSCLC
| Gene |
|---|
Patients Can Enter Clinical Trials Before During Or After Starting Their Cancer Treatment
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCIs clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
What Is Poorly Differentiated Squamous Cell Cancer
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
What Is A 5
A 5-year survival rate is the percentage of people with a certain cancer who are still alive 5 years after their diagnosis. For example, if 90 percent of people with a certain type of cancer are alive 5 years later, the 5-year survival rate would be 90 percent.
The 5-year survival rate is commonly used to measure a cancers deadliness. Cancer is most likely to return within 5 years , which is why many sources include a 5-year survival rate in their statistics. You may also see some sources list 1-, 2-, or 3-year survival rates.
Another common statistic used to measure cancer outlook is the 5-year relative survival rate. A 5-year relative survival rate compares the survival rate of people with a certain cancer with the survival rate of the general population in the same period. It aims to show how much the cancer lowers lifespan.
For example, a 95 percent 5-year relative survival rate means that people with a disease are 95 percent as likely to be alive after 5 years than people without the disease.
Radiosensitizers and new combinations of treatment are currently being investigated in clinical trials.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Furthers Tests After Diagnosis
If tests show you have non-small cell lung cancer, your specialist will arrange further tests. Some of these help with the staging of lung cancer.
- Mediastinoscopy
A mediastinoscopy is sometimes done instead of an EBUS or EUS. It lets the doctor look at the area in the middle of your chest and nearby lymph nodes. You have it under a general anaesthetic.
- Thoracoscopy
A thoracoscopy lets the doctor look at the lining of the lungs . It is usually done under a general anaesthetic.
- MRI scan
An MRI scan uses magnetism to build up a detailed picture of areas of your body.
- Molecular testing
Your doctors may arrange more detailed tests on cancer cells taken during a biopsy or surgery. They look for certain gene changes in the cancer cell. This can show if the cancer cell is making an abnormal protein or has too much of a certain protein.
The results can tell your doctor if certain targeted or immunotherapy drugs are likely to work for you.
Sometime doctors take a blood sample and look for pieces of cancer cells and of the tumour DNA. This is called a liquid biopsy. It is rarely done and still being researched. It may tell them more about the genetics of the cancer and help with treatment decisions.
- Breathing tests
If your treatment plan involves having surgery or radiotherapy your doctor will arrange breathing tests and exercise tests. These help doctors see how well your lungs are working. You may also have tests to check how well your heart is working.
See also
Smoking Is The Major Risk Factor For Non
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for lung cancer.
Risk factors for lung cancer include the following:
- Smoking cigarettes, pipes, or cigars, now or in the past. This is the most important risk factor for lung cancer. The earlier in life a person starts smoking, the more often a person smokes, and the more years a person smokes, the greater the risk of lung cancer.
- Being exposed to secondhand smoke.
- Being exposed to asbestos, arsenic, chromium, beryllium, nickel, soot, or tar in the workplace.
- Being exposed to radiation from any of the following:
- Radiation therapy to the breast or chest.
- Radon in the home or workplace.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
When smoking is combined with other risk factors, the risk of lung cancer is increased.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Other Types Of Cancer In The Uterus
Uterine sarcomas start in the muscle layer or supporting connective tissue of the uterus. These include uterine leiomyosarcomas and endometrial stromal sarcomas. These cancers are not covered here, but are discussed in detail in Uterine Sarcoma.
Cancers that start in the cervix and then spread to the uterus are different from cancers that start in the body of the uterus. They’re described in Cervical Cancer.
What Are Symptoms Of Scc
Squamous cell carcinoma usually first appears as:
- a red, scaly, sometimes crusty plaque of skin that may get bigger and develop a sore
- a red, hard domed bump that wont go away
- a wart-like growth that may bleed or crust
The growths may also be pink and dry and may itch or burn. Squamous cell carcinoma typically shows up on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, lips, arms, legs, and tops of hands, but it can also more rarely appear on areas not exposed to the sun including the lower lip, genitals, in the lining of organs and the passages of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Read Also: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
If Lung Cancer Is Suspected A Biopsy Is Done
One of the following types of biopsies is usually used:
One or more of the following laboratory tests may be done to study the tissue samples:
- Molecular test: A laboratory test to check for certain genes, proteins, or other molecules in a sample of tissue, blood, or other body fluid. Molecular tests check for certain gene or chromosome changes that occur in non-small cell lung cancer.
- Immunohistochemistry: A laboratory test that uses antibodies to check for certain antigens in a sample of a patients tissue. The antibodies are usually linked to an enzyme or a fluorescent dye. After the antibodies bind to a specific antigen in the tissue sample, the enzyme or dye is activated, and the antigen can then be seen under a microscope. This type of test is used to help diagnose cancer and to help tell one type of cancer from another type of cancer.