When To See A Doctor
Its important to see a doctor right away for any moles or skin growths that look unusual or have concerning characteristics. Its especially important to get medical attention as soon as possible for nodular melanoma due to how quickly it can spread to other parts of your body.
See a doctor immediately if you have a skin bump, growth, mole, or lesion that:
- is larger than most regular moles or spots on your body
- used to be flat but is now elevated or thicker than it used to be
- is dome-shaped or has a firm lump
- is either a single color or a mix of colors
- has either a smooth or rough, crusted surface
- has changed in its appearance
- itches or stings
If youre not sure whether a bump or growth meets these criteria, its better to be safe and have it checked out. There is no downside to being cautious and careful when it comes to your health.
To determine whether you have melanoma, a doctor will begin by first asking for details about:
- your exposure to the sun
- any personal or family history of skin cancer
- when you first noticed the growth on your skin
- how or if it has changed in shape, color, size, or elevation
During your visit, your doctor will also carefully examine your skin with a high quality magnifying glass that allows them to get a much more detailed view of the growth on your skin. They will likely also check for enlarged lymph nodes.
The next step may involve a biopsy of the mole or growth. This is the most accurate way to diagnose nodular melanoma.
What Is Nodular And Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma
An evidence-based approach to basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is relatively common. Patients often first present to the primary care provider with complaints of an abnormal skin lesion. When diagnosed early, it has an excellent prognosis, but if there is a delay in diagnosis, the tumor can advance and lead to significant morbidity. Basal cell cancer is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes a dermatologist, mohs surgeon, plastic surgeon, nurse practitioner, primary care provider, and a dermatopathologist. Basal cell carcinomas typically have a slow growth rate and tend to be locally invasive. Tumors around the nose and eye can lead to vision loss. In most cases, surgical excision is curative. However, because recurrences can occur, these patients need long-term follow up.
What Do I Need To Know
- AKs are evidence of sustained sun damage. Having them raises your lifetime risk for skin cancer. Since having one AK means that its likely you have already developed more, this may translate into an especially elevated risk for developing an SCC.
- An untreated SCC can become invasive and even life-threatening.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin signs and symptoms may include:
- Infiltrating BCC of Skin is a slow-growing malignant tumor. The tumor is a typical skin lesion, with thickened skin, presenting as a poorly-demarcated plaque
- The surface of the plaque may be red, if intact. Else, it may appear as an ulcer, if the surface is eroded
- It is typically observed on sun-exposed areas of the body common sites include the head and neck region, arms and legs, etc.
- The tumor may be solitary or many in number. In children, if it is associated with basal cell nevus syndrome, then multiple lesions may be observed
- Some Infiltrating BCC of Skin may have pigmented appearance and may resemble a melanoma
- Most lesions are less than 1-2 cm, but some may grow to larger sizes of even 10 cm
- The carcinoma has a tendency to penetrate deep into the subcutaneous tissue
- The lesion may grow and there may be itching sensation, ulceration, and bleeding
Basal Cell Carcinoma Overview
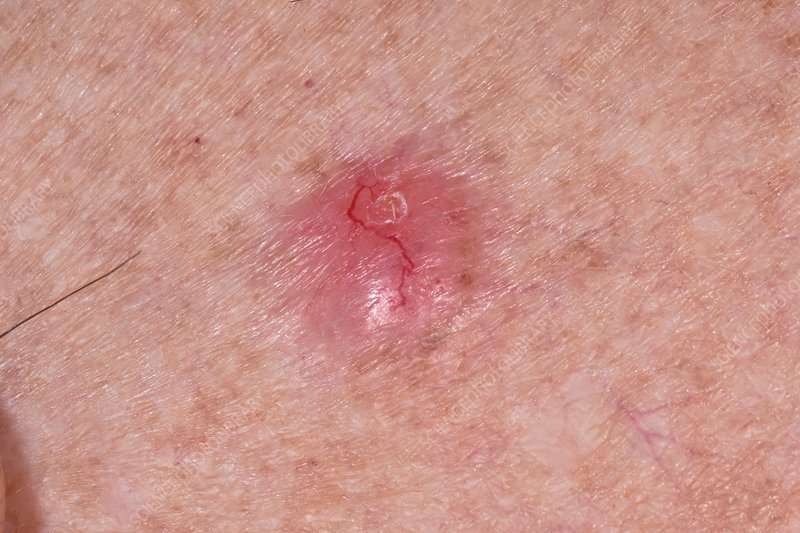
Basal cell carcinoma, also called epithelioma, is the uncontrolled growth of the skins basal cells. These are the cells that line the deepest layer of the epidermis, the skins outermost layer. This type of cancer rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
It is mainly caused by repeated long-term exposure to sunlight. Light-skinned people who spent a lot of time in the sun as children, or who spend time in tanning booths, are especially susceptible. X-ray treatments for acne and exposure to industrial pollutants such as arsenic and hydrocarbons also increase the risk of developing basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common skin cancer in the United States, with nearly 3 million cases diagnosed each year.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
What Are The Possible Complications Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
The complications of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin could include:
- If the tumor becomes big, develops into a firm mass and ulcerates, it can get secondarily infected with bacteria or fungus
- Metastasis to regional lymph nodes can occur. The tumor can also infiltrate into surrounding structures
- Nodular BCC of Skin can cause cosmetic issues, since these skin tumors can cause large ulceration
- Recurrence of the tumor after a period of time recurrence is frequently common with large tumors
- Side effects of chemotherapy and radiation
Lump With Small Depression
Some basal cell carcinoma lesions have small indentations in the center, similar to a canker sore. These depressions in the skin may weep and crust. The temptation to pick at a sore is normal, but it is important not to disrupt these growths and to see a doctor if they appear to grow or spread or do not heal promptly.
Read Also: Melanoma On Nose Prognosis
How Can You Prevent Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma can happen to anyone, but taking certain precautions may help lower your risk of this type of cancer:
- Use sunscreen. Apply a broad spectrum sunscreen with a sun-protective factor of 30 or higher whenever youre outside, even in the winter.
- Reapply sunscreen often. Reapply your sunscreen every 2 hours, especially if youre swimming or sweating.
- Protect your lips. Protect your lips with SPF lip products.
- Stay out of the sun. Avoid direct sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. every day. Seek shade and protection from the sun when possible.
- Cover your skin. Wear sun-protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, long-sleeve shirts, and long pants when outside to protect your skin from the suns harmful UV rays.
- Avoid tanning beds. Tanning beds and indoor tanning booths are also dangerous sources of UV radiation. Its best to avoid them.
than other types of melanoma. It becomes more difficult to treat once it has spread beyond the initial area where it developed.
According to research, the 5-year survival rate for nodular melanoma is 51.67 percent . However, statistics show that if any type of melanoma is found, diagnosed, and treated before it begins to spread, the 5-year survival rate is much higher, between 95 and 100 percent.
When Should I See My Doctor
If you have had one BCC, you have a 50% chance of developing another one, so it is important to check your skin regularly.
Most people find BCCs by checking their own skin and looking for changes. See a doctor if you find:
- a spot that is different from other spots on your skin
- a spot that has changed size, shape, colour or texture
- a sore that doesnt heal
- a sore that is itchy or bleeds
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Causes And Prevention
Several causes for basal cell carcinoma have been identified. BCC can, however, arise without any of these. They start with a single cell that becomes abnormal due to damage to its DNA. These cells then multiply, and as abnormal cells build-up, the skin lesion becomes visible.4
Basal cell carcinoma risk factors include: 5
- Ultraviolet lightUV light from sunshine and commercial tanning beds can both cause damage to cells mentioned, ultimately resulting in abnormal skin lesions. More sun exposure from warm climates, excess suntanning and excess use of tanning beds all make BCC more likely. Severe sunburn can also be a factor.
- Fair skinFair skin is a risk factor as there is less protection for the deeper skin layers from melanin.
- AgeAs detailed, BCC starts with damage to cells and as we get more damage over time, increasing age is a significant factor.
- Medical treatmentRadiotherapy for other medical conditions and immunosuppressants drugs can increase the risks of basal carcinoma and must be taken into account when assessing skin lesions.
For more details of risks factors, see this article.
Basal cell carcinoma prevention
Avoiding or minimising these risk factors is the mainstay of basal cell carcinoma prevention. The most important preventable factor is sun exposure.
What Are The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is treated by removing it. The choice of treatment depends on many things, including patient health and age, the location of the tumor, and the extent and type of the cancer. Treatment may occur in many ways:
- Scratching off with a curette, an instrument that may end in a ring or a spoon, and then burning with a special electric needle. This method is called electrodessication and curettage.
- Surgical removal
- Mohs surgery: This is a specialized technique. The doctor first removes the visible cancer and then begins cutting around the edges. The tissues are examined during the surgery until no more cancer cells are found in tissues around the wound. If necessary, a skin graft or flap might be applied to help the wound heal.
- Excisional surgery: The growth and a bit of surrounding skin is removed with a scalpel.
If the BCC has advanced locally or spread to another location, which is very rare for BCC, the FDA has approved two medicines: vismodegib and sonidegib . These drugs are of a class called hedgehog inhibitors.
Don’t Miss: Is An Itchy Neck A Sign Of Cancer
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
The commonest cause is exposure to ultraviolet light from the sun or from sunbeds. BCCs can occur anywhere on the body, but are most common on areas that are exposed to the sun such as your face, head, neck and ears. It is also possible for a BCC to develop in a longstanding scar. BCCs are not infectious.
BCCs mainly affect fair skinned adults, but other skin types are also at risk. Those with the highest risk of developing a basal cell carcinoma are:
- People with pale skin who burn easily and rarely tan .
- Those who have had a lot of exposure to the sun, such as people with outdoor hobbies or outdoor workers, and people who have lived in sunny climates.
- People who have used sun beds or have regularly sunbathed.
- People who have previously had a basal cell carcinoma.
Why Not To Leave Skin Cancer Untreated
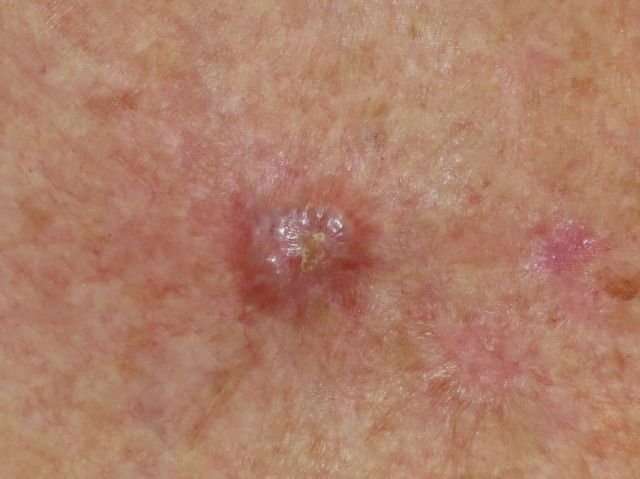
Skin cancer has two sides. On the one hand, it is fairly easy to detect and treat when done so at an early stage. On the other hand, when left untreated, skin cancer can cause disfigurement and even death. This is the dark side of skin cancer. Find out the sobering consequences of allowing skin cancer to develop into later stages.
You May Like: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Stage 3 Symptoms
What Does A Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
BCCs can vary greatly in their appearance, but people often first become aware of them as a scab that bleeds and does not heal completely or a new lump on the skin. Some BCCs are superficial and look like a scaly red flat mark on the skin. Others form a lump and have a pearl-like rim surrounding a central crater and there may be small red blood vessels present across the surface. If left untreated, BCCs can eventually cause an ulcer hence the name rodent ulcer. Most BCCs are painless, although sometimes they can be itchy or bleed if caught.
Other Risk Factors For Sporadic Bcc
The incidence of BCC is much more common in individuals who have received a solid organ transplant, in whom herpes virus like DNA sequences have been demonstrated, and in whom tumors appear to have an increased tendency for recurrence and metastasis. In concert with this more aggressive behavior, the histologic types are different in patients with immune suppression in whom infiltrative growth BCC is more common than nodular and/or superficial variants. In contrast, superficial BCC predominates in individuals with renal failure, diabetes mellitus and human immunodeficiency virus infection.
You May Like: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
Read Also: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
Pay Attention To Your Skin
Check your body often for changes. That way youâll know when something on your body changes or starts to look âoff.â
Itâs also a good idea to get your skin checked by a dermatologist once a year, especially if youâve had BCC before. Thatâs because youâre more likely to get it again. And itâs sometimes hard to tell if itâs come back. But dermatologists are trained to spot new or recurring signs of skin cancer. Theyâll know for sure.
Show Sources
What Layer Of Skin Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
4.4/5epidermis
Also, what layer of skin does skin cancer develop?
Most skin cancers develop from cells found in the epidermis layer of the skin.
Similarly, is Basal Cell Carcinoma considered benign? Basal cell carcinoma is most often a benign form of skin cancer caused by exposure to ultraviolet light. Although BCC is considered benign, frequent BCCs may predispose patients to a more-serious problem.
Accordingly, what looks like basal cell carcinoma?
At first, a basal cell carcinoma comes up like a small “pearly” bump that looks like a flesh-colored mole or a pimple that doesn’t go away. Sometimes these growths can look dark. Or you may also see shiny pink or red patches that are slightly scaly. Basal cell carcinomas are also fragile and can bleed easily.
What happens to untreated basal cell carcinoma?
It usually does not spread to distant parts of the body or into the blood stream. Basal cell carcinoma does spread on the skin and can become quite large over time. If left untreated, it can spread to the muscles, nerves, bones, brain, and in rare cases, cause death. Basal cell carcinoma has a variety of appearances.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Who Gets Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is an uncommon skin cancer that generally affects elderly or older adults some cases rarely develop in children too
- It can occur in both males and females however
- Among the older age group, males are affected more than females
- In the younger age group, females are affected more than males, which may be attributed to their tendency to acquire sun-tanned bodies or visit skin tanning parlors more
Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in how they look. They usually occur on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp or ear.
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Proby for her permission and the photography.
You should see your doctor if you have:
- a spot or sore that doesn’t heal within 4 weeks
- a spot or sore that hurts, is itchy, crusty, scabs over, or bleeds for more than 4 weeks
- areas where the skin has broken down and doesn’t heal within 4 weeks, and you can’t think of a reason for this change
Your doctor can decide whether you need any tests.
-
Cancer and its management J Tobias and D HochhauserBlackwell, 2015
-
Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology VT De Vita, TS Lawrence and SA RosenbergWolters Kluwer, 2018
Also Check: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for BCC include:
- Age and sex: BCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults
- Repeated prior episodes of sunburn
- Fair skin, blue eyes and blond or red hairnote BCC can also affect darker skin types
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: BCC is a particular problem for families with basal cell naevus syndrome , Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines
Basal Cell Carcinoma: What You Need To Know
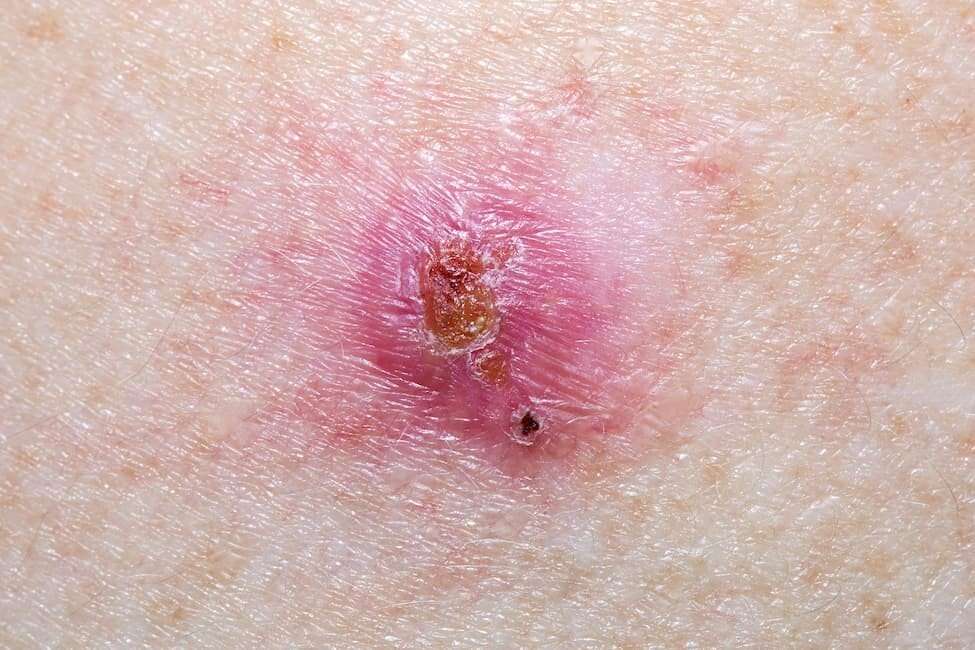
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer in the world. One out of two people will have a BCC growth before age 65. Although BCC is rarely life threatening, it should be taken seriously. If left untreated, this cancer can be disfiguring, especially on the face.
The information in these pages will help you understand more about BCC: what it is, what causes it, how it is diagnosed and treated, and how you can prevent it.
What is basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer. It begins in the basal cells, the deepest part of the skins outermost layer. Basal cell carcinomas almost never spread beyond their original site to other parts of the body, especially when treated early.
What do basal cell carcinomas look and feel like?
As shown below, basal cell carcinomas vary widely, with a number of different appearances:
-
Open sores that dont heal
-
A round ulcer that looks as though a bite has been taken out of the middle
-
Red patches that have a sandpapery feel
-
Shiny bumps that are raised, hard, pearly pink or gray
-
An area of thickened skin
-
A bump with a rolled edge
-
A lesion with blood vessels that look like the spokes of a wheel
Basal cell carcinomas can occur anywhere on the body they may appear to sit on top of the skin, or burrow into it. Most lesions are painless. Sometimes they can feel itchy. They may bleed easily if caught on clothing or nicked during shaving.
What causes basal cell carcinoma?
How is basal cell carcinoma diagnosed?
Surgery
Don’t Miss: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate