How Common Is It
Overall, skin cancers are the most common cancers in the United States. But melanoma is less common than the other two major types, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
Each year about 91,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with melanoma of the skin, according to the American Cancer Society. By comparison, about 3.3 million are diagnosed with one or more basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas.
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Red Flag #: Swollen Lymph Nodes
If melanoma spreads, it often goes to the lymph nodes first, says Melinda L. Yushak, M.D., assistant professor of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta. The cancer cells will first travel to the nodes closest to the original tumor, she says. Lymph nodes are located throughout your entire body, but large clusters are found in the neck, underarms, chest, abdomen, and groin. If the cancer has made its way to the lymph nodes, it usually wont be painful, but theyll feel swollen or even hard to the touch, Dr. Zaba says.
You May Like: How Many People Die From Skin Cancer Every Year
Read Also: Osteomyoma
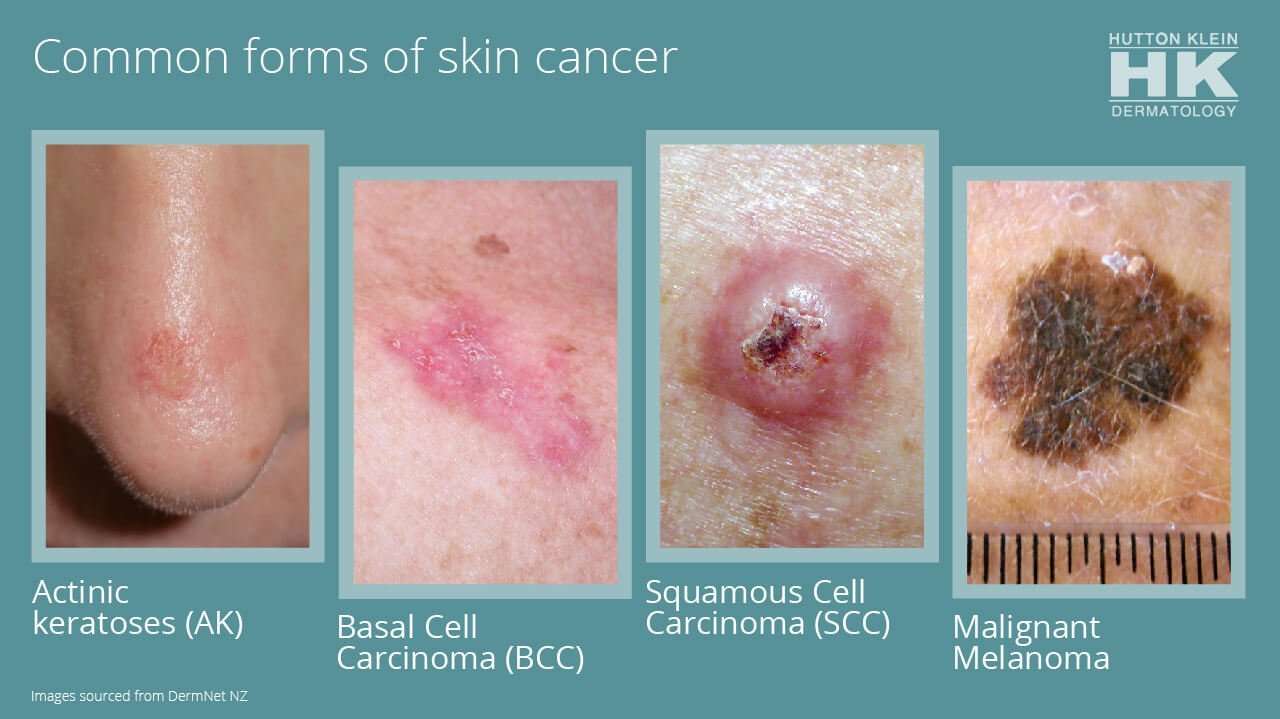
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
Don’t Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
The Braf Gene Mutation And Melanoma
Roughly half of all documented melanoma cases present with mutations in the BRAF gene. The melanoma cells that have these changes create a BRAF protein, which aids them in their growth. If a person with the BRAF gene mutation has melanoma, knowing about the mutation is of great benefit for treatment because healthcare providers can use targeted therapy to inhibit the BRAF gene mutation from aiding in the growth of the cancer.
If a diagnosis of melanoma is already established, the healthcare provider will look at two factors to determine how advanced a stage 4 melanoma has become: the location of the distant tumors and an elevated level of serum lactate dehydrogenase , which is an enzyme responsible for turning sugar into energy. The higher the LDH level in body fluids, the more damage the cancer has done.
When To See A Doctor About Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or have had extensive sun exposure, should periodically check their entire body for suggestive moles and lesions.
Have your primary healthcare professional or a skin specialist check any moles or spots that concern you.
See your healthcare professional to check your skin if you notice any changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas .
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist or cancer specialist will talk to you about symptoms of metastatic disease that might require care in a hospital.
Read Also: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system. There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Age Spots And Skin Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
A change in your skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This could be a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, or a change in a mole.external icon Not all skin cancers look the same.
For melanoma specifically, a simple way to remember the warning signs is to remember the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma
- A stands for asymmetrical. Does the mole or spot have an irregular shape with two parts that look very different?
- B stands for border. Is the border irregular or jagged?
- C is for color. Is the color uneven?
- D is for diameter. Is the mole or spot larger than the size of a pea?
- E is for evolving. Has the mole or spot changed during the past few weeks or months?
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer, arising from cells within the skin called melanocytes.
These melanocytes are normally responsible for producing melanin, a dark coloured pigment which is responsible for giving our skin its colour and the formation of moles on the skin.
As with other forms of skin cancer, melanomas are linked to exposure to UV light. It is thought that your genetics may also have a role in whether you develop melanoma and there does appear to be a higher risk of skin cancers if other family members have also had skin cancer.
Some studies also suggest that those with many moles or pale skin that burns easily in the sun are also at an increased risk of melanoma.
In its initial stages, a melanoma begins by a concentrated overgrowth of melanocytes which start to accumulate. After this process has started, the melanocytes begin to spread to other layers of skin, and if undetected or ignored, can spread to other parts of the body . After being diagnosed, the melanoma will be staged depending on the extent of its growth.
Minimising your exposure to UV light is one simple way to reduce your risk of skin cancer. This can be by reducing your amount of time out in the sun as well as using a high SPF sunscreen.
Also Check: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Although the number of skin cancers in the United States continues to rise, more and more skin cancers are being caught earlier, when they are easier to treat. Thus, illness and death rates have decreased.
When treated properly, the cure rate for both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma approaches 95%. The remaining cancers recur at some point after treatment.
- Recurrences of these cancers are almost always local , but they often cause significant tissue destruction.
- Less than 1% of squamous cell carcinomas will eventually spread elsewhere in the body and turn into dangerous cancer.
In most cases, the outcome of malignant melanoma depends on the thickness of the tumor at the time of treatment.
- Thin lesions are almost always cured by simple surgery alone.
- Thicker tumors, which usually have been present for some time but have gone undetected, may spread to other organs. Surgery removes the tumor and any local spread, but it cannot remove distant metastasis. Other therapies, new targeted agents or older approaches such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, are used to treat the metastatic tumors.
- Malignant melanoma causes more than 75% of deaths from skin cancer.
- Of the approximately 70,000 malignant melanomas diagnosed in the United States in 2007, the vast majority were cured. Still, thousands of people die of melanoma each year.
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
You May Like: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
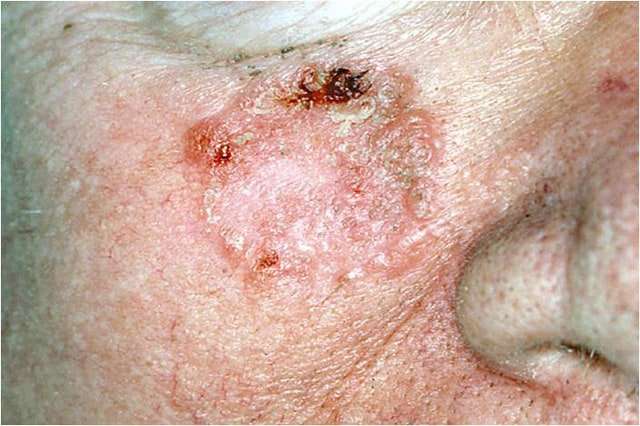
Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC generally starts out in the upper layer of your skin. Thatâs called your epidermis. Hereâs what it may look like:
- A bloody or oozing sore that doesnât go away
- A rough patch of skin, usually in a sun-exposed area
- A reddish area that may hurt or itch
- A shiny bump thatâs clear, reddish, or white
- A flat white, yellow, or âwaxyâ area that looks like a scar
- A colored mole-like bump
BCC tends to grow slower than other kind of cancer, but thatâs not always the case. And if itâs advanced BCC, it can spread much deeper into your tissue. Call your doctor if you see any of these changes in your skin. Ask them about genetic conditions and other risk factors that can raise your chances of advanced BCC.
What Is Metastaticmelanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells of the skin, mucosa, eye, and rarely other sites. Metastatic melanoma is melanoma that has spread to other sites of the body. The spread occurs through the lymphatic system and/or the blood vessels. Melanoma can spread to the subcutaneous tissue which lies underneath the skin, the lymph nodes, and to other organs such as the lungs, liver, bone or brain.
Metastatic melanoma can be classified into local recurrence, in transit metastasis, nodal metastasis, and haematogenous spread.
Also Check: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers do not know why certain cells become cancerous. However, they have identified some risk factors for skin cancer.
The most important risk factor for melanoma is exposure to UV rays. These damage the skin cellsâ DNA, which controls how the cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Most UV rays come from sunlight, but they also come from tanning beds.
Some other risk factors for skin cancer include:
- A lot of moles: A person with more than 100 moles is more likely to develop melanoma.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles: The risk of developing melanoma is higher among people with fair skin. Those who burn easily have an increased risk.
- Family history:Around 10% of people with the condition have a family history of it.
- Personal history: Melanoma is likelier to form in a person who has already had it. People who have had basal cell or squamous cell cancers also have an increased risk of developing melanoma.
The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to limit oneâs exposure to UV rays. A person can do this by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and covering up when outdoors.
People should also avoid tanning beds and sunlamps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
It can be easy to mistake benign growths for skin cancer.
The following skin conditions have similar symptoms to skin cancer:
When To Visit A Podiatrist
Podiatrists are uniquely trained as lower extremity specialists to recognize and treat abnormal conditions on the skin of the lower legs and feet. Skin cancers affecting the feet may have a very different appearance from those arising on the rest of the body. For this reason, a podiatrist’s knowledge and clinical training is of extreme importance for patients for the early detection of both benign and malignant skin tumors.
Learn the ABCDs of melanoma. If you notice a mole, bump, or patch on the skin that meets any of the following criteria, see a podiatrist immediately:
- Asymmetry – If the lesion is divided in half, the sides don’t match.
- Borders – Borders look scalloped, uneven, or ragged.
- Color – There may be more than one color. These colors may have an uneven distribution.
- Diameter The lesion is wider than a pencil eraser .
To detect other types of skin cancer, look for spontaneous ulcers and non-healing sores, bumps that crack or bleed, nodules with rolled or donut-shaped edges, or scaly areas.
Recommended Reading: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
The 4 Stages Of Melanoma
Two main things determine the stage of melanoma: The thickness or depth of the tumor and how far it has spread when its diagnosed, explains David Polsky, M.D., dermatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City. In stages 0, 1, and 2, the melanoma is limited to the skin. In stage 3, its spread to the lymph nodes, small structures throughout your body that help filter fluids and fight infection. In the most advanced stage, stage 4, melanoma cells have broken away from the original tumor, traveled through the body and formed a new tumor somewhere else.
Dont Miss: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of therapy for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.
People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, a topical cream has recently been approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers.
In advanced cases, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Is Scalp Melanoma
Melanoma is a serious and potentially deadly form of skin cancer. It is more likely to spread locally as well as metastasize , and it accounts for more skin cancer-related deaths than basal and squamous cell carcinomas combined. Melanoma takes its name from melanocytes, the skins pigment-producing cells, where this condition originates. All types of melanoma are more likely to spread to lymph nodes and other tissues, but on the scalp, there are numerous blood vessels and other tissues that can quickly be impacted by melanoma cells.
According to Dr. Walker, The good news is that scalp melanoma is one of the rarest forms of this cancer, accounting for less than 5% of melanoma cases. The bad news is that scalp melanoma tends to be a more severe prognosis than other forms of melanoma. However, research indicates that this is largely because of how late in development its typically diagnosed. Simply put, people are more likely to overlook this condition until its very advanced, making it more difficult to treat.