What Is A Level
Melanoma levels is the depth of melanoma cell invasion in the skin. This is determined by histopathology study of the biopsy sample under the microscope by specialist pathologists. Obviously, the deeper through the skin a melanoma has invaded, the greater potential it has, of spreading. There are 5 levels of melanoma, reflecting how deep the melanoma has progressed through the anatomical layers of skin. This is always reported with Breslow thickness, which measures the physical depth of melanoma invasion in millimeters. The reason both the Level and Breslow Thickness are taken into account when considering the seriousness of the melanoma, is because in certain part of the body, the skin layers are thicker, e.g. the back. Thus even though the report may say that the melanoma is only Level II, but the thickness is 1.2mm. Some studies have shown that it is the Breslow Thickness that seem to have a better correspondence to the likelihood of spread, than the Level itself.
How Do You Treat Stage 4 Melanoma
The good news is that even stage 4 melanoma can be treated. The sooner the cancer is found, the sooner it can be removed and the higher your chances are for recovery. Stage 4 melanoma also has the most treatment options, but these options depend on:
- where the cancer is
- how advanced the cancer has become
- your age and overall health
How you respond to treatment also affects your treatment options. The five standard treatments for melanoma are:
- surgery: to remove the primary tumor and affected lymph nodes
- chemotherapy: a drug treatment to stop growth of cancer cells
- radiation therapy: the application of high-energy X-rays to inhibit growth and cancer cells
- immunotherapy: treatment to boost your immune system
- targeted therapy: the use of drugs or other substances to attack cancer drugs
Other treatments may also depend on where the cancer has spread to. Your doctor will discuss your options with you to help map out a treatment plan.
Drugs Can Target Your Type Of Tumor
If your melanoma tumor has one of the gene mutations we mentioned, your oncologist may start with a drug that targets specific proteins in the mutation. Depending on which mutation your melanoma tested positive for, your oral drug options include: BRAF inhibitors including Zelboraf , Tafinlar , and Braftovi MEK inhibitors such as Mekinist , Cotellic , and Mektovi and C-KIT inhibitors, which include Gleevac and Tasigna . Because BRAF and MEK mutations are closely associated, research has shown that combining the two types of drugs may yield better results.
You May Like: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
What Are Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small structures that filter substances and help fight infection. They are part of a network that runs throughout the body. Cancer that reaches the lymph nodes is concerning because cancer cells can easily spread to other parts of the body through this interconnected system.
Whether or not a melanoma spreads to one or more lymph nodes, it also may affect nearby skin. Such melanoma tumors are called satellite tumors. They’re defined as being within 2 centimeters of the original tumor and can be seen without a microscope.
Melanoma tumors also may spread to lymphatic channels, thin tubes that resemble blood capillaries, through which lymph fluid flows.
Your May Experience Side Effects
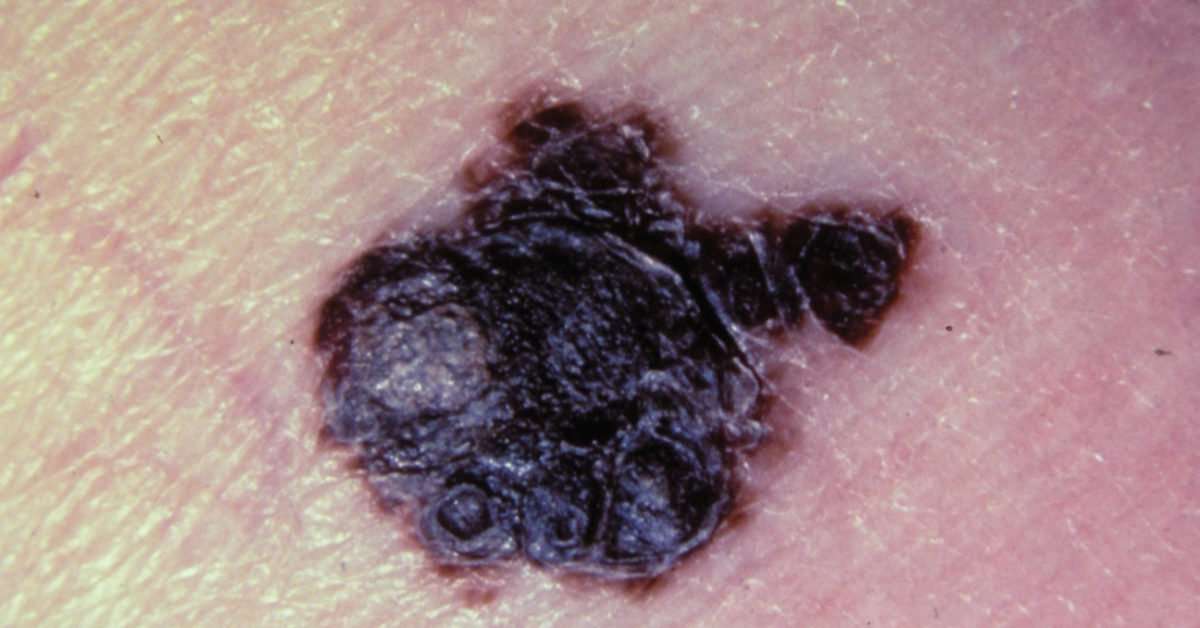
The vast majority of patients who receive immunotherapy will have little to no side effects, says Dr. Betof Warner. Its a huge change from the days when patients were on chemotherapy and were profoundly nauseous, vomiting, and had suppressed immune systems. Still, side effects can occur, including flu-like fever, aches, fatigue, and nausea. The risk of side effects with targeted therapy is a bit higher, but Dr. Betof Warner says they tend to disappear faster. These can include rashes, headaches, joint pain. And more seriously, kidney failure, bleeding, and heart and liver problems.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Putting It All Together
Some pieces of the report are used to determine the stage of the cancer and other pieces play a role in deciding what treatment is needed. By understanding the basics of the report, you will be better able to discuss your treatment options with your healthcare team. Your provider will be able to explain any questions you have about your report.
Another Symptom Might Have Tipped Your Doctor Off
Sometimes we find a stage 4 melanoma diagnosis because the patient has a symptom or abnormality somewhere else in the body, says Dr. Friedlander. That could mean shortness of breath or a lingering cough due to a lung metastasis, or severe headaches due to your melanoma spreading to the brain. In these cases, doctors have to work backward to find melanoma is the root cause.
You May Like: Stage 2 Carcinoma
What Is The Stage
Melanoma staging is whether the melanoma has advanced beyond the skin. This is often determined by either physical examination of nearby lymph node groups or imaging studies such as CT scans, Ultrasounds, PET/CT or MRI. Stage I and II Melanoma are confined to the skin, with different depth. Stage III Melanoma means it has progressed beyond the original tumour as satellite lesions in the surrounding skin or travelled to a lymph node basin nearby. Stage IV Melanoma means the Melanoma has travelled to a distant site, usually an organ such as the lung, bones, liver or brain.
How Does Tumor Grade Affect A Patients Treatment Options
Doctors use tumor grade and other factors, such as cancer stage and a patients age and general health, to develop a treatment plan and to determine a patients prognosis . Generally, a lower grade indicates a better prognosis. A higher-grade cancer may grow and spread more quickly and may require immediate or more aggressive treatment.
The importance of tumor grade in planning treatment and determining a patients prognosis is greater for certain types of cancer, such as soft tissue sarcoma, primary brain tumors, and breast and prostate cancer.
Patients should talk with their doctor for more information about tumor grade and how it relates to their treatment and prognosis.
Selected Reference
American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer 2010.
Related Resources
You May Like: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Is A Pathology Report
A pathologist is a doctor who diagnoses diseases by looking at tissue from the body. Samples of your melanoma tissue, removed during surgery or biopsy, will be sent to them for review. The pathology report is a result of their findings. This report contains important information about the tumor which is used to make treatment decisions. You should ask for a copy of this report and keep it in your personal medical files.
What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
You May Like: Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Dont Google Survival Rates
Not only because its not helpful, but because theyre not even accurate, says Dr. Betof Warner. The survival statistics for stage 4 melanoma are still evolving because most of the drugs we use were approved about five years ago, so the numbers are literally just coming out. And theyre more promising. Recent research in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that 52% of patients on a combination of two checkpoint inhibitors were alive after five years. In 2018, the survival rate for stage 4 melanoma was listed as just 22.5%. Stay focused on your own treatment rather than searching stats.
-
High-Risk Melanomas and Recurrence:JAMA Dermatology. . Risk of Melanoma Recurrence After Diagnosis of a High-Risk Primary Tumor. jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/2731995
-
Melanoma Mutations:The ASCO Post. . Melanoma Mutations: What You Need To Know. ascopost.com/issues/november-25-2017/melanoma-mutations-what-you-need-to-know/
-
Treating Stage IV Melanoma: The American Cancer Society. . Treatment of Melanoma Skin Cancer, by Stage. cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/treating/by-stage.html
-
Stage IV Melanoma Survival Rates: Melanoma Research Alliance. . Melanoma Survival Rates. curemelanoma.org/about-melanoma/melanoma-staging/melanoma-survival-rates/
What To Ask Your Doctor About Stage Iv Melanoma
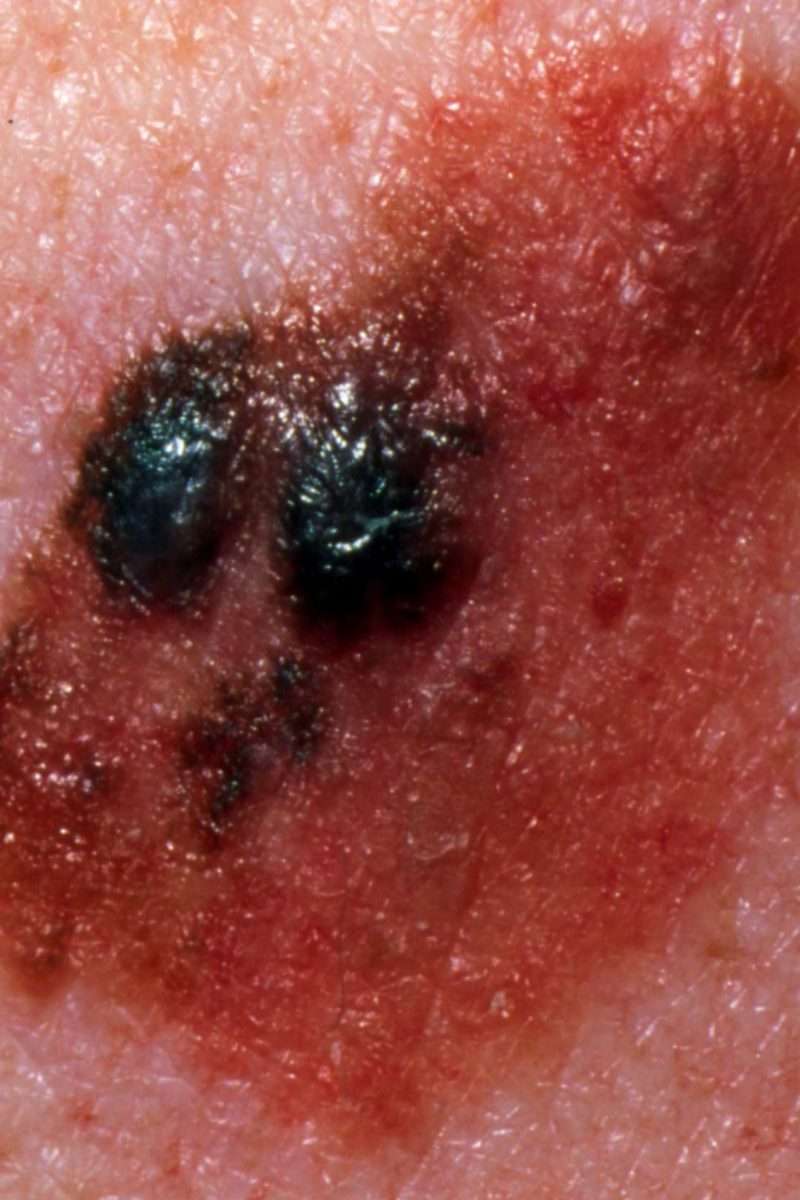
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage IV melanoma, it can be frightening and overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with all of your doctors to learn as much about your cancer as you can. Your doctors will provide you important information about your diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
It is often helpful to bring a friend or family member with you to your doctor appointments. This person can lend moral support, ask questions, and take notes.
The following questions are those you may want to ask your doctors. Some of the questions are for your medical oncologist, some are for your surgical oncologist, and some for your dermatologist. Remember, it is ALWAYS okay to ask your doctor to repeat or clarify something s/he has said so that you can better understand it. You may find it helpful to print out these questions and bring them with you to your next appointment.
Read Also: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
Stage I And Stage Ii Melanoma
Stage I and stage II melanoma describe invasive cancer that has grown below the epidermis to the next layer of skin, the dermis. It has not reached the lymph nodes.
Two major factors help determine the seriousness of stage I melanoma and stage II melanoma: Breslow depth and ulceration.
Breslow depth is a measurement that doctors use to describe the depth of an invasive melanoma in millimeters. It measures how far melanoma cells have reached below the surface of the skin. The thinner the melanoma, the better the chances for a cure.
Ulceration means that there is broken skin covering the melanoma. This breakage can be so small that it can only be seen under a microscope. Ulceration is an important factor in staging. A melanoma with ulceration may require more aggressive treatment than a melanoma of the same size without ulceration.
Melanoma is considered stage 1A when:
- the tumor is less than or equal to 1 millimeter thick in Breslow depth
Melanoma is considered stage IB when:
- the tumor is 1.1 to 2 millimeters thick in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIA when:
- the tumor is 1.1 to 2 millimeters thick in Breslow depth with ulceration
- the tumor is 2.1 to 4 millimeters thick in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIB when:
- the tumor is 2.1 to 4 millimeters thick in Breslow depth with ulceration
- the tumor is more than 4 millimeters in Breslow depth without ulceration
Melanoma is considered stage IIC when:
Stage : Melanoma In Situ
The earliest stage of melanoma is stage 0, also known as melanoma in situ or carcinoma in situ. In situ is a Latin phrase that means in position, and this diagnosis means that the cancer cells are present only in the epidermisthe bodys most superficial layer of skinand nowhere else.
This diagnosis has a very good prognosis, Noelani González, MD, an instructor of dermatology at the Mount Sinai Icahn School of Medicine in New York City, tells Health. People with localized melanomas who are treated quickly have a 5-year survival rate of 97%meaning they are, on average, about 97% as likely to still be alive in five years as people who dont have these cancers.
Treatment for this stage cancer involves a wide excision surgery, where the affected skin is cut away and the wound is stitched and bandaged. The skin will be removed with margins, explains Dr. González. That means that some normal skin will also be removed around the edges to make sure there arent any cancer cells left over.
The removed skin is then looked at under a microscope to ensure that all of the cancer was removed with clean margins, says Dr. González. Because stage 0 cancer has not spread to any other tissues or organs, no further treatment is required.
RELATED: This Woman Had to Wait 4 Months to Get a Mole Checked Outand It Turned Out She Had Skin Cancer
You May Like: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Stages Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the skin have cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for melanoma skin cancer is the TNM system. For melanoma skin cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage, doctors often use the words early stage, locoregional or metastatic.
Early stage means that the cancer is only in where it started and has not spread to other parts of the body. It includes stage 0, stage 1A, stage 1B, stage 2A, stage 2B and stage 2C melanoma skin cancers.
Locoregional means the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, or it has spread to nearby areas of skin or lymph vessels. It includes stage 3 melanoma skin cancer.
Metastatic means that the cancer is in a part of the body farther from where it started. It includes stage 4 melanoma skin cancer.
Find out more about .
What Is Melanoma
Melanoma is a kind of cancer that begins in the skin cells that create the pigment melanin. Melanoma usually starts as a dark mole on the skin. However, it can also form in other tissue, such as the eye or mouth.
Its important to keep an eye on moles and changes in your skin, as melanoma can be deadly if it spreads. There were more than 10,000
TNM system.
The stage of the disease indicates how much the cancer has progressed by taking into account the size of the tumor, whether its spread to lymph nodes, and whether its spread to other parts of the body.
A doctor can identify a possible melanoma during a physical exam and confirm the diagnosis with a biopsy, where the tissue is removed to determine if its cancerous.
But more sophisticated technology, such as PET scans and sentinel lymph node biopsies, are necessary to determine the cancers stage or how far its progressed.
There are five stages of melanoma. The first stage is called stage 0, or melanoma in situ. The last stage is called stage 4. Survival rates decrease with later stages of melanoma.
Its important to note that survival rates for each stage are just estimates. Each person with melanoma is different, and your outlook can vary based on a number of different factors.
Recommended Reading: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
What Is A Five
Five-year survival rate refers to the average number of people with a particular disease or condition who are alive five years after being diagnosed.
Cancer experts based five-year survival rates for melanoma on information from a database called SEER, which stands for the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
Survival statistics from the SEER database are not based on AJCC melanoma staging. Instead, they’re based on if and how far the melanoma has spread:
| Type |
|---|
The five-year survival rate for all three SEER stages combined is 93%.
The five-year survival rate for all three SEER stages combined is 93%.
It May Not Be Your First Run
Many people with stage 4 melanoma have a history of primary melanoma, says Philip Friedlander, M.D., a medical oncologist specializing in melanoma at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. Earlier-stage melanoma that was considered high risk may return at some point as stage 4, he says. In fact, 13.4% of those with a high-risk melanoma had a recurrence, research in JAMA Dermatology showed. Seventy percent of those recurred in a local area, while 29% had a recurrence somewhere else on their body.
Read Also: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
Clinical Staging And Pathologic Staging
To add to the complexity of staging, the cancer also may have a clinical stage and a pathologic stage.
Clinical staging takes place before surgery, based on blood tests, physical exams or imaging tests such as X-rays, a computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography scans.
What doctors discover during surgery may provide more detailed information about the cancers size and spread. Often, some tissue from the surgery will be examined afterward to provide more clues. This process is known as pathologic staging, or surgical staging.
If surgery isnt possible, doctors will use the clinical stage when determining a treatment plan.