Surgical Treatment Of Stage Iii Disease
Outcomes of patients with stage III melanoma relates primarily to the extent of lymph node metastasis. Standard surgical treatment for patients with stage III melanoma is removal of the primary cancer with up to 2-centimeter margins of the adjacent skin, depending on the thickness of the primary tumor, and removal of all of the regional lymph nodes. Regional lymph node dissection may be performed in the neck, armpit or groin, depending on the site of the primary tumor and presence of palpable nodes. Chronic side effects of removing lymph nodes vary, depending on the extent of disease, body habits of the patient, and inclusion of postoperative radiation to site, but may include numbness, and swelling of the associated extremity, which is called lymphedema.
One of the challenges facing oncologists is assessing the risks for individual patients on the basis of data from previously published studies. Five-year overall survival rates for patients with stage III melanoma have been reported as ranging from 70% for stage IIIA to 27% for stage IIIC disease. In this group of patients, assembled largely during the pre-sentinel lymph node era, patients with stage I and II disease were reported to have 5-year recurrence-free survival rates of 90% and 70%, respectively. The 10% to 30% recurrence rates likely reflect unidentified microscopic disease, which can be detected with present-day techniques.
Also Check: Is A Sore That Doesn T Heal Always Cancer
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are part of a system of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluids and fights infection.
The most common symptom if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes is that they feel hard or swollen. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck area can make it hard to swallow.
Cancer cells can also stop lymph fluid from draining away. This might lead to swelling in the neck or face due to fluid buildup in that area. The swelling is called lymphoedema.
Number Of Metastatic Lymph Nodes Involved
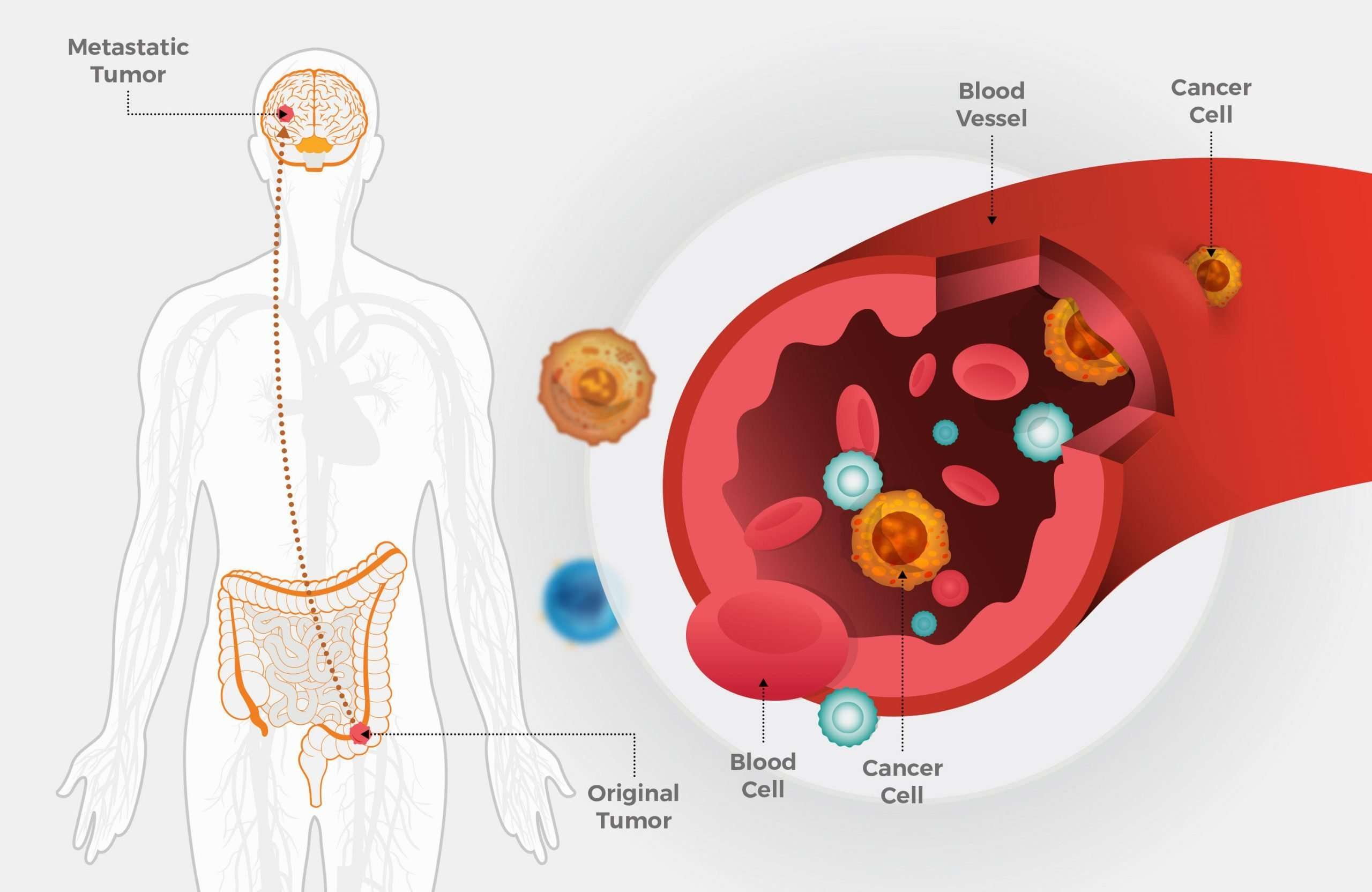
If the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the risk of spread to other parts of the body is higher. The greater the number of lymph nodes containing melanoma, the less favourable the prognosis.
A sentinel node biopsy is a technique used to determine whether melanoma cells have spread to lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the skin primary lesion. The procedure involves the injection of a radioactive tracer by a radiologist , to show where the site and lymph node where the lymph fluid from the skin at the primary melanoma will flow. Afterwards, at the same time as the extra surgery for the primary melanoma a blue dye is injected around the site of the primary lesion. Using the guide from the radiologist a surgeon looks for the first lymph node to take up the dye. The lymph node is removed and sent to be examined by a histopathologist to determine if the node tests positive for melanoma. The procedure is considered when the Breslow thickness of the melanoma is more than 0.8mm.
Patients may develop lumps in the lymph node regions such as the neck, armpit and groin. This is lymph node metastasis.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
What Are Symptoms Of Melanoma Besides Moles
Other melanoma warning signs may include: Pigment, redness or swelling that spreads outside the border of a spot to the surrounding skin. Itchiness, tenderness or pain. Changes in texture, or scales, oozing or bleeding from an existing mole. Blurry vision or partial loss of sight, or dark spots in the iris.
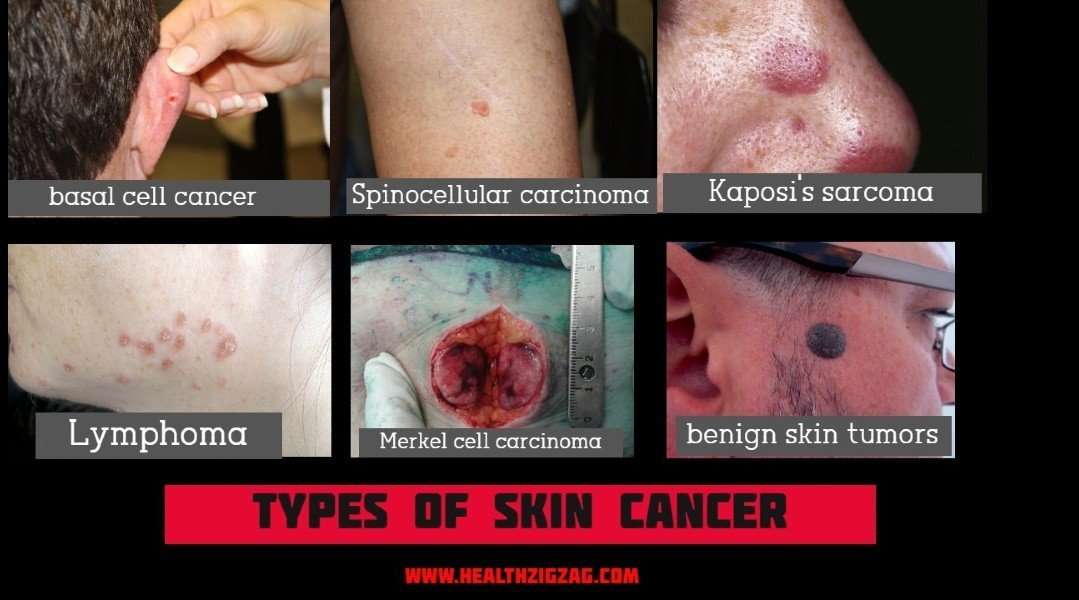
Three Common Types Of Skin Cancer:
Basal cell Carcinoma:
This type of skin cancer usually occur in the area which is exposed directly to sunlight like our neck, face, scalp, lips, chest, etc.
What are the symptoms of Basal cell Carcinoma:
Bleeding at the sores of the skin,
Waxy bump on the skin,
Flat scars on the skin.
Squamous cell Carcinoma:
Squamous cell Carcinoma also occurs at those areas which is directly exposed to sun such as at the chest, at neck, at face or scalp, etc. People with darker skin are more likely to develop squamous cell Carcinoma.
Symptoms of Squamous cell Carcinoma:
Flat lesion with a scaly may appear on skin,
Red nodules may appear on skin.
Melanoma signs and Symptoms:
symptoms of Melanoma Melanoma can be developed at any part of the body, this is why this is considered as the most severe form of skin cancer, and this is very difficult to treat because this can be develop at anywhere in the skin and this developed in the cells of the skin.
Symptoms of Melanoma signs:
Brown spots on the skin,
A mole on the skin which changes its color frequently,
Painful itching on skin,
Dark lesions on your palms, soles or at fingertips or at other part of the skin.
Recommended Reading: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Amelanotic Melanoma Risk Factors
Though these risk factors dont mean someone will develop melanoma, they are linked with increased risk of all forms of the cancer, including amelanotic melanoma.
Exposure to UV rays: Damage to DNA in your skin cells, from exposure to UV rays , is the No. 1 risk factor for all types of melanoma. Both natural sunlight and artificial tanning lamps increase the risk of developing this type of skin cancer. Getting many sunburns during childhood also has been associated with the development of melanoma on the chest, back and legs.
Moles: If you have a lot of moles or have atypical moles, youre at greater risk of developing melanoma. Additionally, patients with the inherited condition dysplastic nevus syndrome are at a high risk of developing melanoma during their lifetime.
Fair skin: People who have light-colored, freckled skin and blond or red hair with blue or green eyes are at a greater risk of developing melanoma. This is especially true if your skin tends to burn as opposed to tanning when exposed to UV rays.
Race: Melanoma is 20 times more likely for white people than it is for black people, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology .
Family and personal history: If your close relatives have a history of melanoma, youre at increased risk. If youve previously had melanoma or another type of skin cancer, the chance of developing it again is also greater.
Diagnosis Of Metastatic Melanoma
Your care team may use several tests to diagnose metastatic melanoma.
If theres evidence of a primary tumor, a biopsy may be taken. For this, a small section of suspected cancerous skin is removed with a razor, scalpel or small punch tool. The removed tissue is examined under a microscope to determine whether its melanoma.
Additional tests are needed to determine whether the cancer is metastatic melanoma, or if theres no visible primary tumor. To test for metastatic melanoma, or melanoma that has spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body, your care team may perform the following tests.
- Lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy : Your doctor may perform a physical exam of your lymph nodes and check for swelling or physical masses. If no tumors are found , an SLNB may be done. For an SLNB, a radioactive dye is injected to locate the primary tumor. Then, the doctor will remove the lymph nodes that the dye traveled to and check them for melanoma.
- Computed tomography scan, positron emission tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging scan or ultrasound exam: Each of these scans is a noninvasive way to look inside your body and check for tumors.
- Blood chemistry studies: Cancer may cause elevated or abnormal levels of certain substances in your blood. A laboratory test can identify if your blood chemistry shows signs of a cancerous tumor.
You May Like: Scalp Melanoma Stages
How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Become Metastatic
214 patients with MM were evaluated retrospectively. Distant metastases were the most frequent for patients initially metastatic. The median and 1-year survival rates of initially MM patients were 10 months and 41%, respectively. The median time to metastasis for patients with localized disease was 28 months.
How Can I Prevent Superficial Spreading Melanoma
Exposure to UV rays is strongly associated with superficial spreading melanoma. The easiest way to reduce your risk is to limit your exposure to UV rays from both the sun and tanning lights and beds.
When youre in the sun, make sure to apply sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15. Wearing a wide-brimmed hat and covering your skin can also help limit your exposure to UV rays.
Also Check: If You Have Skin Cancer How Do You Feel
Stop Tumors In Their Tracks
Every melanoma has the potential to become deadly, but the difference between an in situ melanoma and one that has begun to metastasize cannot be overstated. There is a drastic change in the survival rate for the various stages of tumors, highlighting the importance of detecting and treating melanomas before they have a chance to progress. Its impossible to predict exactly how fast a melanoma will move from stage to stage, so you should be taking action as soon as possible.
To be sure youre spotting any potential skin cancers early, The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends monthly skin checks, and scheduling an annual total-body skin-exam with a dermatologist. These skin exams can help you take note of any new or changing lesions that have the potential to be cancerous, and have them biopsied and taken care of before they can escalate.
Trust your instincts and dont take no for an answer, Leland says. Insist that a doctor biopsy anything you believe is suspicious.
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
You May Like: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Symptoms Of Metastatic Melanoma Other Than A Mole
Other symptoms of this type of cancer may not appear until a later stage, when the melanoma has metastasized to another area of the body. Metastatic melanoma most often spreads to the lymph nodes, brain, bones, liver or lungs, and the additional symptoms experienced at this late stage will depend on where the melanoma has spread. For example:
- Lungs A persistent cough or shortness of breath
- Brain Headaches or seizures
- Lymph nodes Swelling of the lymph nodes
- Liver Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
- Bone Bone pain or unusual fractures
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
Benign Tumors That Start In Melanocytes
A mole is a benign skin tumor that develops from melanocytes. Almost everyone has some moles. Nearly all moles are harmless, but having some types can raise your risk of melanoma. See Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer for more information about moles.
A Spitz nevus is a kind of mole that sometimes looks like melanoma. Its more common in children and teens, but it can also be seen in adults. These tumors are typically benign and dont spread. But sometimes doctors have trouble telling Spitz nevi from true melanomas, even when looking at them under a microscope. Therefore, they are often removed, just to be safe.
What Causes Superficial Spreading Melanoma
The exact causes of superficial spreading melanoma are unknown, but it seems to be related to environmental factors and genetic mutations.
While anyone can develop superficial spreading melanoma, some are more likely to than others. Things that make you more likely to develop it include:
- Middle age: It tends to occur most often in people in their 40s and 50s.
- Light-colored skin: As with other skin cancers, people with fair skin are most at risk for developing superficial spreading melanoma. This is likely because fair skin has less melanin, a skin pigment that can help protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
- UV exposure: It tends to occur in the back, chest, and legs, which are all likely to get intense, periodic UV exposure from the sun. Getting sunburns at an early age and UV exposure from tanning beds also increase your risk.
- Having a lot of moles: Since many cases develop within moles, the more moles you have, the greater your chance of having superficial spreading melanoma. People with 50 or more moles have a greater risk of melanoma, according to the American Skin Association.
- Family history: While it isnt inherited, some of the gene mutations responsible for superficial spreading melanoma are. The BRAF gene, which can allow cancer cells to grow freely, may play a role in melanoma.
Read Also: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Red Flag #: Abdominal Pain And Tenderness
Early on, there may be no noticeable symptoms that melanoma has spread to the liver. When symptoms do show up, they commonly include an enlarged, hard, or tender liver and pain in the upper right area of your abdomen, just below your ribs. Other signs cancer has spread to the liver are similar to symptoms of liver disease: fluid buildup in the belly and yellowing of the skin and eyes .
What Is Amelanotic Melanoma
Amelanotic melanoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer that doesn’t produce the pigment melanin, which gives most melanomas their dark appearance. As a result, they dont look like other melanomas. Instead, they may appear skin-colored, pink or even reddish, with gray or brownish edges.
Amelanotic melanomas may be easily confused with basal or squamous cell carcinomas, or misidentified as harmless scars or moles, which is dangerous, because they often spread faster than the more easy-to-recognize melanomas.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Benign Tumors That Develop From Other Types Of Skin Cells
- Seborrheic keratoses: tan, brown, or black raised spots with a waxy texture
- Hemangiomas: benign blood vessel growths, often called strawberry spots
- Lipomas: soft growths made up of fat cells
- Warts: rough-surfaced growths caused by some types of human papilloma virus
Most of these tumors rarely, if ever, turn into cancers. There are many other kinds of benign skin tumors, but most are not very common.
What Causes Melanoma Skin Cancer:
The exact cause of Melanoma is still unknown, but the most probable reason for this skin cancer is the exposition with Ultra-violet rays or UV rays may be directly due to sunlight or due to some sort of radiation.
Melanoma is one form of skin cancer, and basically it begins with an ugly looking mole on your skin cancer. But all moles dont means they are supposed to be skin cancer causing Melanoma symptoms.
Melanoma is the skin cancer which starts in the skin cells which are called melanocytes and Melanoma can even spread throughout body if not diagnosed early. Melanoma initially affects the skin only, but if its not diagnosed then it spreads to other organs and even to bones. Luckily, melanoma can be cured if diagnosed early and there is immediate treatment given.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Putting The Results Of These Clinical Trials Into Context
The clinical studies described above have shown that both immunotherapies and targeted therapies are adjuvant treatment options following surgery, which are intended to delay or prevent the recurrence of melanoma in patients with high-risk stage III disease. Although both types of therapy provide good options for individuals with late-stage melanoma, patients should be aware of the clear differences in the side effect profiles of immunotherapies and targeted therapies.39
About 1 in 4 patients who received the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and about 1 in 3 patients who received the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab in the clinical trials described above have reported experiencing severe side effects.31,36 Immune-related severe side effects that were observed in the clinical trials, such as the onset of type 1 diabetes or disorders of the thyroid and pituitary gland, have been confirmed in the treatment of real-world patients .
Because they work differently, targeted therapies do not carry the risk of triggering immune-related adverse effects. Nevertheless, about 2 of every 5 patients who received dabrafenib plus trametinib in the COMBI-AD study reported experiencing severe side effects.33 The proportion of patients treated with dabrafenib plus trametinib who withdrew from the study early because of side effects was 26%.33
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma