Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cause Complications
The most common complication of basal cell carcinoma is recurrence. BCCs commonly recur, even after successful treatment. In some cases, BCC may reappear in the same place. It can also be disfiguring, especially if not treated promptly.
A diagnosis of BCC increases the chance of developing other types of skin cancer. This includes melanoma, which can metastasize and is the most life-threatening form of skin cancer.
Rare, aggressive forms of BCC can invade the body beyond the skin. It can destroy bone, nerves, and muscles. In rare cases it can metastasize to other parts of the body, including key organs, and become life-threatening.
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Almost all BCCs develop on parts of the body frequently exposed to the sun. Tumors can develop on the face, ears, shoulders, neck, scalp, and arms. In very rare cases, tumors develop on areas not often exposed to sunlight.
BCCs are typically painless. The only symptom is the growth or change in the appearance of the skin. There are different types of BCC. Each has a different appearance:
Skin cancers, including BCC, are primarily caused by long-term sun or ultraviolet light exposure. These cancers can also be caused by intense occasional exposure often resulting in sunburn.
In rarer cases, other factors can cause BCC. These include:
- exposure to radiation
How Do You Prevent Basal Cell Skin Cancer
The best way to prevent basal cell carcinoma and other skin cancers is to protect the skin from the sun.
- Wear sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Apply sunscreen at least 30 minutes prior to sun exposure, and reapply every 2 hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Wear protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat.
- Avoid the midday sun, between the hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when the sunâs rays are the strongest.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Examine your skin regularly for new moles, spots, bumps, or growths, and inform your doctor of any skin changes.
In patients who are at higher risk for recurrence of basal cell carcinoma, certain medications may be used, however, studies on the effectiveness of these medications have had mixed results.
- Celecoxib , a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug , may offer modest risk reduction, but studies on its effectiveness for preventing tumors are mixed.
- Oral nicotinamide is a vitamin supplement available over the counter. Additional studies are needed to determine its effectiveness in preventing skin cancers. Consult your doctor before taking any supplements because of possible side effects or drug interactions.
- Topical fluorouracil has been shown to help prevent other skin conditions and precursors to basal cell carcinoma, however, the data are mixed on whether it may help prevent BCC.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma 3c
What Is Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous layer of the skin. Melanoma begins in the melanocytes, which are the cells that make melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
The skin is the bodys largest organ. Skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types of skin cancer. They begin in the basal and squamous layers of the skin, respectively. Both can usually be cured, but they can be disfiguring and expensive to treat.
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
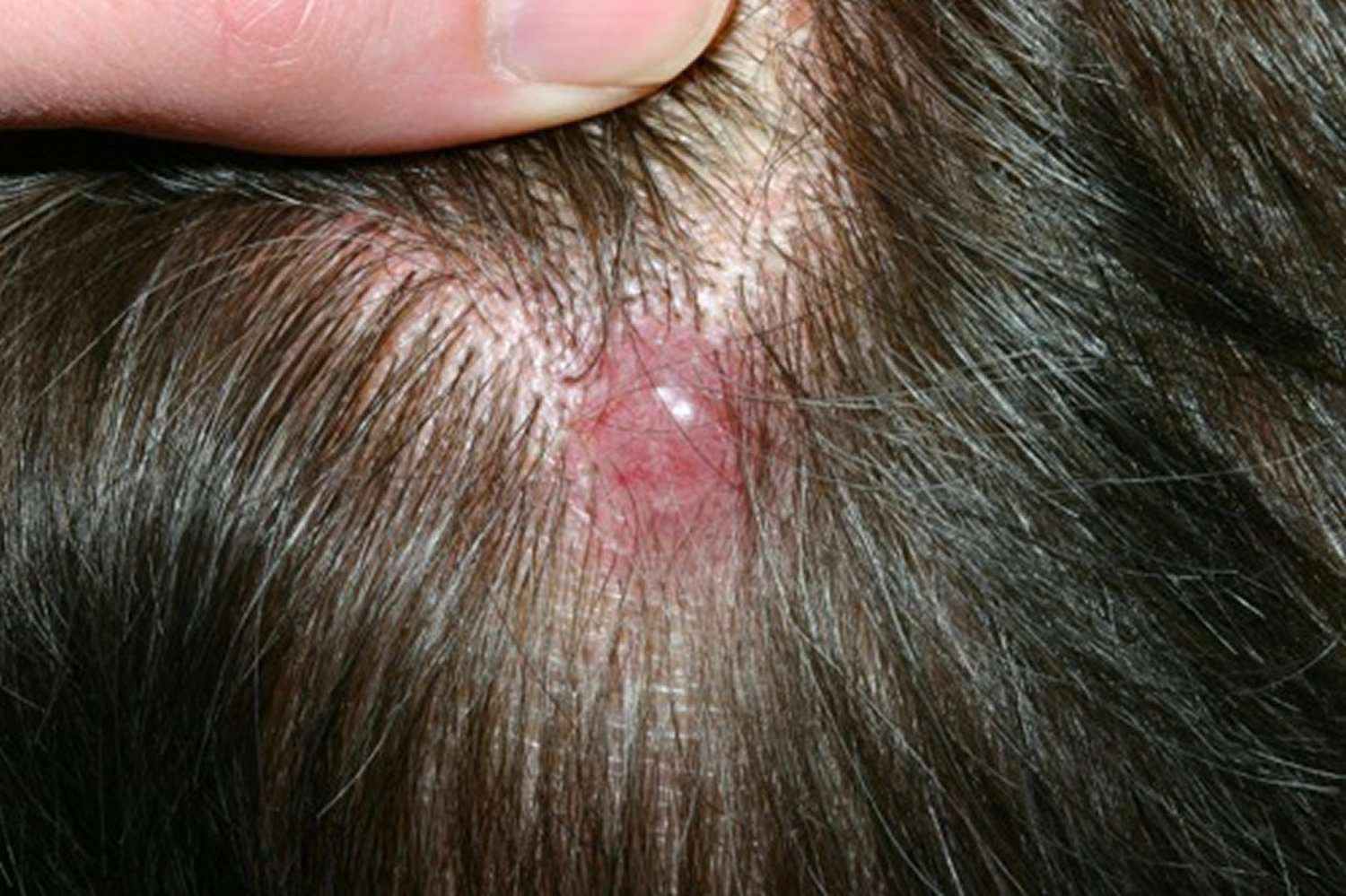
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Also Check: Whats Cancer Look Like
Lawrenceville Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Basal cell carcinoma is a skin cancer that can develop on skin overexposed to the suns harmful ultraviolet rays or tanning beds. A diagnosis can be frightening but with proper treatment, you can have a high success rate at removing the cancer. The cancer can grow slowly and may not show serious symptoms for years. For individuals residing in Gwinnett County, basal cell carcinoma treatment at Medical Dermatology Specialists in Lawrenceville can help you improve your overall health.
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
The cause of basal cell carcinoma, the most common type of skin cancer, is well known. Most people develop it because their skin has been badly damaged by ultraviolet light from:
-
The sun
-
Indoor tanning equipment
-
Both
If you use a tanning bed, you have a higher risk of developing skin cancer
Use a tanning bed just once, and you increase your risk of developing basal cell carcinoma by 29%.
Also Check: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
Who Gets Basal Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for BCC include:
- Age and sex: BCCs are particularly prevalent in elderly males. However, they also affect females and younger adults
- Repeated prior episodes of sunburn
- Fair skin, blue eyes and blond or red hairnote BCC can also affect darker skin types
- Previous cutaneous injury, thermal burn, disease
- Inherited syndromes: BCC is a particular problem for families with basal cell naevus syndrome , Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Oley syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum
- Other risk factors include ionising radiation, exposure to arsenic, and immune suppression due to disease or medicines
Don’t Miss: Merkel Cancer Prognosis
When To Seek Medical Care
If you have developed a new bump on sun-exposed skin, or if you have a spot that bleeds easily or does not seem to be healing, then you should make an appointment with your primary care physician or with a dermatologist.Try to remember to tell your doctor when you first noticed the lesion and what symptoms, if any, it may have . Also, be sure to ask your parents, siblings, and adult children whether or not they have ever been diagnosed with a skin cancer, and relay this information to your physician.
What Causes Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
While many risk factors for basal and squamous cell skin cancers have been found, its not always clear exactly how these factors might cause cancer.
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet rays from sunlight, as well as from man-made sources such as tanning beds.
UV rays can damage the DNA inside skin cells. DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes help control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth in check by slowing down cell division or causing cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control.
Researchers dont yet know all of the DNA changes that result in basal or squamous cell skin cancer, but they have found that in many skin cancers the cells have changes in tumor suppressor genes.
These are not the only gene changes that play a role in the development of skin cancer. There are many others as well.
You May Like: Metastatic Skin Cancer Pictures
What Is The Treatment For Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma
The treatment for a BCC depends on its type, size and location, the number to be treated, patient factors, and the preference or expertise of the doctor. Most BCCs are treated surgically. Long-term follow-up is recommended to check for new lesions and recurrence the latter may be unnecessary if histology has reported wide clear margins.
Syndromes Associated With A Predisposition To Basal Cell Carcinoma
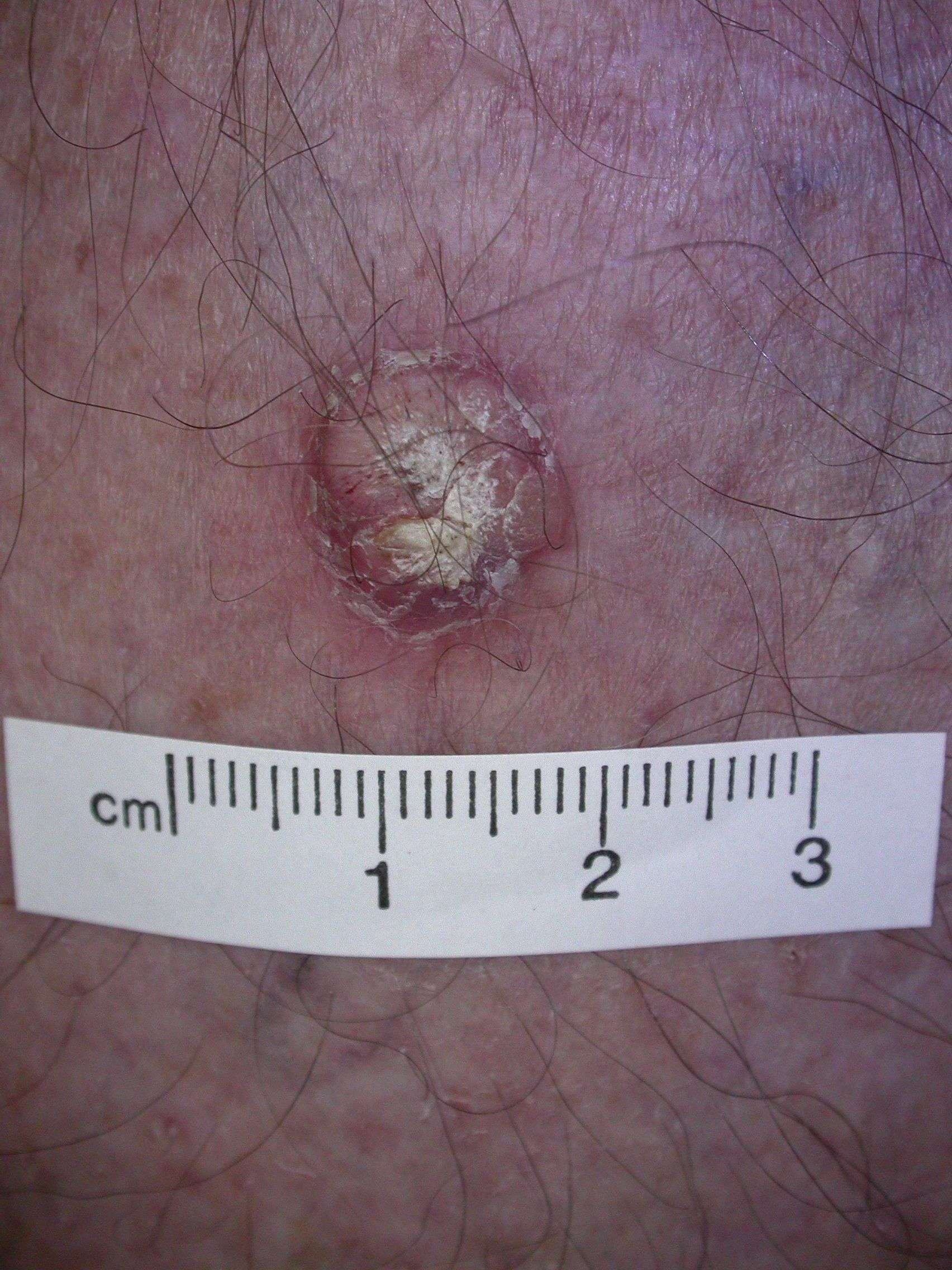
Basal cell nevus syndrome
BCNS, also known as Gorlin Syndrome, Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, and nevoid BCC syndrome, is an autosomal dominant disorder with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 57,000 individuals. The syndrome is notable for complete penetrance and high levels of variable expressivity, as evidenced by evaluation of individuals with identical genotypes but widely varying phenotypes. The clinical features of BCNS differ more among families than within families. BCNS is primarily associated with germline pathogenic variants in PTCH1, but families with this phenotype have also been associated with alterations in PTCH2 and SUFU.
Other associated benign neoplasms include gastric hamartomatous polyps, congenital pulmonary cysts, cardiac fibromas, meningiomas, craniopharyngiomas, fetal rhabdomyomas, leiomyomas, mesenchymomas, basaloid follicular hamartomas, and nasal dermoid tumors. Development of meningiomas and ependymomas occurring postradiation therapy has been documented in the general pediatric population radiation therapy for syndrome-associated intracranial processes may be partially responsible for a subset of these benign tumors in individuals with BCNS. In addition, radiation therapy of malignant medulloblastomas in the BCNS population may result in many cutaneous BCCs in the radiation ports. Similarly, treatment of BCC of the skin with radiation therapy may result in induction of large numbers of additional BCCs.
DNA repair genes
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Don’t Miss: Web Md Skin Cancers
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Untreated basal cell carcinomas can become large, disfigurement will result, and in rare cases they can spread to other parts of the body and result in death. Skin covers the entire body so that no organisms or pollution can harm it. The epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous tissue all make up a skin layer called skin tissue.
Can Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Go Away On Its Own
They may go away on their own and come back. You should call your doctor if you notice a change in the color, texture, or appearance of your skin or if you have a sore that does not heal or bleeds. Your doctor can diagnose squamous cell carcinoma by examining the growth and performing a biopsy of the suspected area.
Dont Miss: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
You May Like: Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Structure Of The Skin
The genetics of skin cancer is an extremely broad topic. There are more than 100 types of tumors that are clinically apparent on the skin many of these are known to have familial components, either in isolation or as part of a syndrome with other features. This is, in part, because the skin itself is a complex organ made up of multiple cell types. Furthermore, many of these cell types can undergo malignant transformation at various points in their differentiation, leading to tumors with distinct histology and dramatically different biological behaviors, such as squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell cancer . These have been called nonmelanoma skin cancers or keratinocyte cancers.
Figure 1 is a simple diagram of normal skin structure. It also indicates the major cell types that are normally found in each compartment. Broadly speaking, there are two large compartmentsthe avascular epidermis and the vascular dermiswith many cell types distributed in a connective tissue matrix, largely created by fibroblasts.
The true cytologic origin of BCC remains in question. BCC and basal cell keratinocytes share many histologic similarities, as is reflected in the name. Alternatively, the outer root sheath cells of the hair follicle have also been proposed as the cell of origin for BCC. This is suggested by the fact that BCCs occur predominantly on hair-bearing skin. BCCs rarely metastasize but can invade tissue locally or regionally, sometimes following along nerves.
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
Don’t Miss: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic BCC requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Radiotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy refers to the hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitors, vismodegib and sonidegib. These drugs have some important risks and side effects.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. Also known as BCC, this skin cancer tends to grow slowly and can be mistaken for a harmless pimple, scar, or sore.
Common signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma
This skin cancer often develops on the head or neck and looks like a shiny, raised, and round growth.
To help you spot BCC before it grows deep into your skin, dermatologists share these 7 warning signs that could be easily missed.
If you find any of the following signs on your skin, see a board-certified dermatologist.
You May Like: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Offices And Clinics Of Other Health Practitioners
Establishments of licensed practitioners having a degree and engaged in the practice medicine. Establishments operating as clinics included in their industry.Illustrated ExamplesChiropractors, offices and clinics, Clinics of chiropractors ,Optometrists, Podiatrists, Acupuncturists, except m.d.: offices of audiologists, offices of christian science practitioners, offices of dental hygienists, offices of dieticians, offices of hypnotists, offices of inhalation therapists, registered midwives, offices of naturopaths, offices of nurses, registered and practical: offices of, except home health nutritionists, offices of occupational therapists, offices of paramedics, offices of physical therapists, offices of physiciansassistants, offices of psychiatric social workers, offices of psychologists, clinical offices of psychotherapists, except m.d.: offices of speech clinicians, offices of speech pathologists. offices and clinics,
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
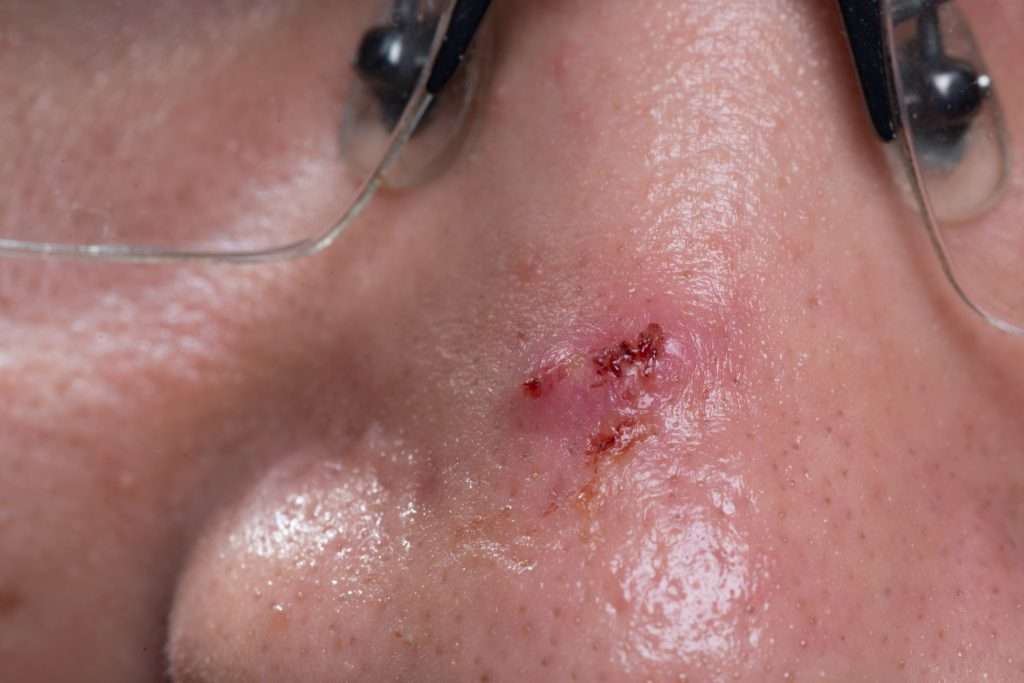
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Donât Miss: Is Melanoma The Worst Cancer
You May Like: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
Answer: Risk Of Not Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a locally destructive type of skin cancer that is notorious for recurrence when not adequately treated. It can become quite disfiguring if left untreated, especially when located in cosmetically sensitive areas such as the nose. Typically this type of skin biopsy is performed for diagnosis and is not adequate treatment for a skin cancer. Biopsies sample a portion of the lesion, leaving some behind. This type of sampling biopsy is not intended to remove the entire lesion. It is not advisable to leave a known skin cancer untreated as it will likely grow and become more of a problem to remove in the future. Mohs micrographic surgery allows for 100% margin control and is tissue-sparing, which means it offers the highest cure rate while preserving as much normal tissue as possible.