Why Does Leukemia Cause A Rash
The cause of leukemia rashes isn’t always clear, but it can be one manifestation of the disease, says Dr. Samaniego. The most likely explanation for a leukemia rash ties back to the underlying problem in this type of blood cancer, which is an overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
Often this abundance of white cells impedes the bone marrow’s ability to make enough red blood cells and platelets , says the American Society of Hematology.
If your platelet count is low, you may bleed and bruise more easily, and broken capillaries under your skin can cause petechiae, says Moffitt Cancer Center. The tiny red or brown spots from petechiae aren’t technically a rash, but they can look like one.
Someone might also get a leukemia rash if the cancer has spread to their skin , explains the American Cancer Society. In that case, a grouping of cancer cells might form visible lumps under the skin. It can also cause patches of the skin to become discolored.
In other instances, someone can develop a leukemia rash if they have already been diagnosed with leukemia and are being treated with a granulocyte-colony stimulating factor drug. Per NORD, that medication can lead to a reaction called Sweet syndrome, which can cause a rash of tender red and bluish-red bumps or lesions to develop suddenly on the body.
Are All Moles Cancerous
Most moles are not cancerous. Some moles are present at birth, others develop up to about age 40. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles.
In rare cases, a mole can turn into melanoma. If you have more than 50 moles, you have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your skin is the largest organ in your body. It needs as much attention as any other health concern. What may seem like an innocent cosmetic imperfection, may not be. Performing regular skin self-checks is important for everyone and is especially important if you are a person at increased risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is also color-blind. If you are a person of color, skin cancer can happen to you. Check your skin every month for any changes in skin spots or any new skin growths. Consider taking skin selfies so you can easily see if spots change over time. If youre a person of color, be sure to check areas more prone to cancer development, such as the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, your genital area and under your nails. Takes steps to protect your skin. Always wear sunscreen with SPF of at least 30 every day of the year. Wear UV-A/UV-B protective sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeve shirts and pants. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin check.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/19/2021.
References
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Recommended Reading: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment
Lip Skin Cancer Pictures Symptoms Signs Treatment
Learn all about lip skin cancer symptoms and treatments used for it. Skin cancer is a malignant growth of the external surface or epithelial layer of the skin. The lower lip is approximately 12 times more likely to be affected, owing to its greater exposure to sunlight.
Lip cancer occurs most often on the lower lip and is seen overwhelming in fair-skinned males over the age of 50. This may be because these men are in occupations with a lot of sun exposure, such as construction or farming. Smoking is also thought to contribute to lip cancer. Tobacco and alcohol use can affect the risk of lip and oral cavity cancer.
Lip and oral cavity cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the lips or mouth. Aside from metastases to other parts of the body, lip cancer also results in altered body image because of the presence of tumor on the lips. This significantly reduces the self-esteem of the patient. Metastasis to the oral cavity also yields difficulty in drinking, eating, talking or breathing.
Treatment for cancer of the lip is much the same as for skin cancer. However, new research has shown that heat can kill some cancer cells and that type of treatment, called hyperthermia, is sometimes used. Most people recover from lip cancer. Only about 4 in 2.5 million people in the United States dies from lip cancer.
What Are Possible Complications Of Skin Cancer In A Child
Possible complications depend on the type and stage of skin cancer. Melanoma is more likely to cause complications. And the more advanced the cancer, the more likely there will be complications.
Complications may result from treatment, such as:
-
Loss of large areas of skin and underlying tissue
-
Scarring
-
Problems with the area healing
-
Infection in the area
-
Return of the skin cancer after treatment
Melanoma may spread to organs throughout the body and cause death.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
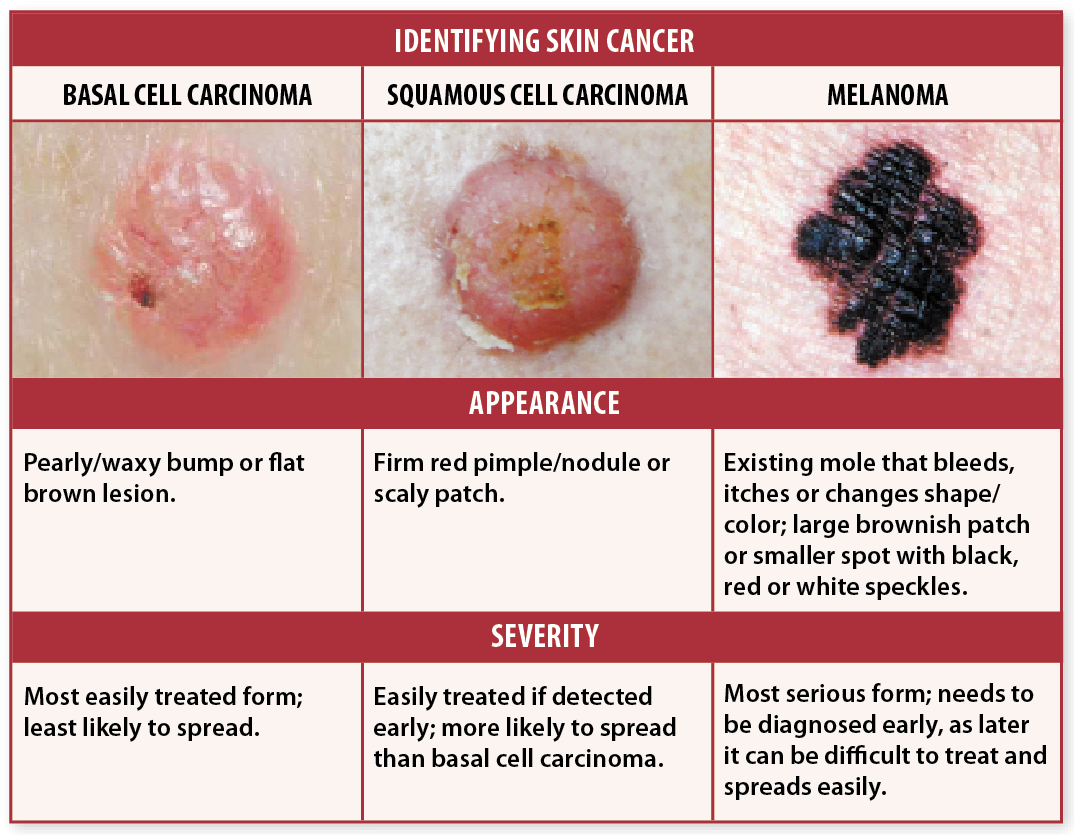
What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
There are 3 main types of skin cancer:
-
Basal cell carcinoma. The majority of skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma. Its a very treatable cancer. It starts in the basal cell layer of the skin and grows very slowly. The cancer usually appears as a small, shiny bump or nodule on the skin. It occurs mainly on areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck, arms, hands, and face. It more often occurs among people with light-colored eyes, hair, and skin.
-
Squamous cell carcinoma. This cancer is less common. It grows faster than basal cell carcinoma, but its also very treatable. Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as nodules or red, scaly patches of skin, and may be found on the face, ears, lips, and mouth. It can spread to other parts of the body, but this is rare. This type of skin cancer is most often found in people with light skin.
-
Melanoma. This type of skin cancer is a small portion of all skin cancers, but it causes the most deaths. It starts in the melanocyte cells that make pigment in the skin. It may begin as a mole that turns into cancer. This cancer may spread quickly. Melanoma most often appears on fair-skinned people, but is found in people of all skin types.
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
Also Check: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Can I Do To Prevent Skin Cancer In My Child
The American Academy of Dermatology and the Skin Cancer Foundation advise you to:
-
Limit how much sun your child gets between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Put it on the skin of children older than 6 months of age who are exposed to the sun.
-
Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, even on cloudy days. Reapply after swimming.
-
Use extra caution near water, snow, and sand. They reflect the damaging rays of the sun. This can increase the chance of sunburn.
-
Make sure your child wears clothing that covers the body and shades the face. Hats should provide shade for both the face, ears, and back of the neck. Wearing sunglasses will reduce the amount of rays reaching the eye and protect the lids of the eyes, as well as the lens.
-
Dont let your child use or be around sunlamps or tanning beds.
The American Academy of Pediatrics approves of the use of sunscreen on babies younger than 6 months old if adequate clothing and shade are not available. You should still try to keep your baby out of the sun. Dress the baby in lightweight clothing that covers most surface areas of skin. But you also may use a small amount of sunscreen on the babys face and back of the hands.
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Read Also: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
How To Spot An Scc
SCC of the skin can develop anywhere on the body but is most often found on exposed areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation like the face, lips, ears, scalp, shoulders, neck, back of the hands and forearms. SCCs can develop in scars, skin sores and other areas of skin injury. The skin around them typically shows signs of sun damage such as wrinkling, pigment changes and loss of elasticity.
SCCs can appear as thick, rough, scaly patches that may crust or bleed. They can also resemble warts, or open sores that dont completely heal. Sometimes SCCs show up as growths that are raised at the edges with a lower area in the center that may bleed or itch.
Abcde Melanoma Detection Guide
A is for Asymmetry
Look for spots that lack symmetry. That is, if a line was drawn through the middle, the two sides would not match up.
B is for Border
A spot with a spreading or irregular edge .
C is for Colour
Blotchy spots with a number of colours such as black, blue, red, white and/or grey.
D is for Diameter
Look for spots that are getting bigger.
E is for Evolving
Spots that are changing and growing.
These are some changes to look out for when checking your skin for signs of any cancer:
- New moles.
- Moles that increases in size.
- An outline of a mole that becomes notched.
- A spot that changes colour from brown to black or is varied.
- A spot that becomes raised or develops a lump within it.
- The surface of a mole becoming rough, scaly or ulcerated.
- Moles that itch or tingle.
- Moles that bleed or weep.
- Spots that look different from the others.
Don’t Miss: Whats Cancer Look Like
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
When Is A Mole A Problem
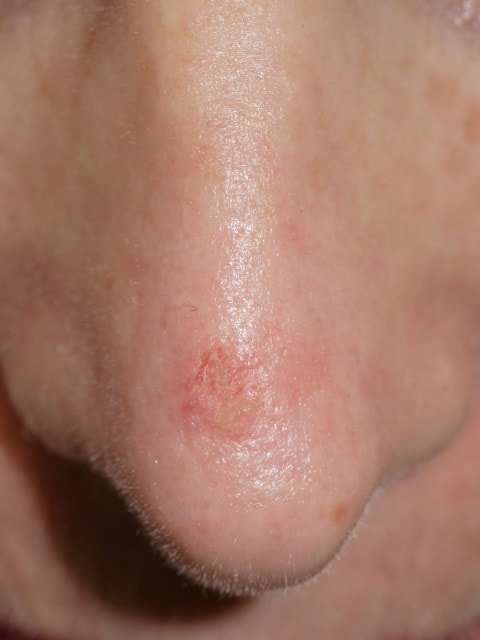
If a new or existing mole begins to change shape, color, size, or becomes flaky, crusty, or begins to bleed, it’s time to make an appointment with your dermatologist to get it checked out. A mole can turn into melanoma on rare occasions. In early melanoma, the shape of a mole becomes asymmetrical and uneven.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that is most often found on the head. This type of cancer starts in basal cells, which are tasked with making new skin cells to push the old ones toward the surface of the skin. Nodular basal cell carcinoma is responsible for 60%-80% of all basal cell carcinomas. In the United States, its estimated that 4.3 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed every year, with 2.5 to 3.4 million of those cases being nodular basal cell carcinoma.
This type of cancer appears as a pearl-like papule that is round and surrounded by threadlike red lines on the skin made up of tiny blood vessels. The risk of developing nodular basal cell carcinoma can be increased by spending a lot of time out in the sun, living in high-altitude and sunny locations, and radiation therapy.
Other risk factors include:
- Prolonged exposure to arsenic
- Certain rare genetic disorders such as basal cell nevus syndrome
Although this type of cancer is common, it is highly treatable, and the five-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
The second most common form of cancer in the skin is squamous cell carcinoma. At first, cancer cells appear as flat patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, reddish, or brown surface. These abnormal cells slowly grow in sun-exposed areas. Without proper treatment, squamous cell carcinoma can become life-threatening once it has spread and damaged healthy tissue and organs.
The Abcdes Of Melanoma
The first five letters of the alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the warning signs of melanoma.
A is for Asymmetry. Most melanomas are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the lesion, the two halves dont match, so it looks different from a round to oval and symmetrical common mole.
B is for Border. Melanoma borders tend to be uneven and may have scalloped or notched edges, while common moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
C is for Color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually a single shade of brown, a melanoma may have different shades of brown, tan or black. As it grows, the colors red, white or blue may also appear.
D is for Diameter or Dark. While its ideal to detect a melanoma when it is small, its a warning sign if a lesion is the size of a pencil eraser or larger. Some experts say it is also important to look for any lesion, no matter what size, that is darker than others. Rare, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
E is for Evolving. Any change in size, shape, color or elevation of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in it, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs, or anything NEW, CHANGING or UNUSUAL on your skin see a dermatologist promptly.
A is for Asymmetry
D is for Diameter or Dark
E is for Evolving
E is for Evolving
Also Check: Stage Iii Melanoma
Why Does Skin Cancer Occur In More Non
Scientists dont fully know why people of skin with color develop cancer in non-sun-exposed areas, such as their hands and feet. They think that the sun is less of a factor though. However, dermatologists still see plenty of UV sunlight-induced melanomas and squamous cell skin cancer in people of color, in skin tones ranging from fair to very dark.
What Is Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Skin cancer is a disease that occurs when your skin cells grow abnormally, usually from too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
This uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells forms a tumour in the skin. Tumours are either benign , or malignant .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer: each year, more than 13,000 Australians are diagnosed with a melanoma and almost 980,000 new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers are treated. Skin cancer is mostly preventable, and there are effective treatment options available.
Skin cancers are named according to the cells in which they form. There are 3 main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma begins in the lower segment of cells of the epidermis your outer layer of skin. These tend to grow slowly, and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma grows from the flat cells found in the top layer of your epidermis. SCC can grow quickly on the skin over several weeks or months. Bowens disease is an early form of SCC that hasnt grown beyond the top layer of skin.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes cells that give your skin its colour. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer but is considered the most serious because it can spread quickly throughout the body.
BCC and SCC are also called non-melanoma skin cancers. BCC represents more than 2 in 3 non-melanoma skin cancers, and around 1 in 3 are SCC. There are other types of non-melanoma skin cancers, but they are rare.
Recommended Reading: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome