Skin Cancer Radiation Treatment Faqs
How do you protect yourself from Skin Cancer?< br />
The biggest thing you can do is limit your exposure to the sun, but here are some tips that can help:
- Use sunscreen regularly, and it should be the kind that can protect against UVB light and UVA rays and an SPF of 30
- Reapply often when outside and especially after swimming or sweating.
- Wear sunglasses
- Avoid tanning beds as they will increase the risk of skin cancer
- See your dermatologist every year for a skin exam
Can I get skin cancer anywhere on my skin?
Most skin cancer happens on skin that is exposed to the sun most often such as your head, neck, chest, and arms. However, it is possible to get skin cancer on parts of your body that rarely or ever see sun such as genitals, but that is much more rare.
Are there side effects to treating skin cancer with Radiation?
Will my cancer come back? Or will I get more skin cancers?
People who have already had one skin cancer have a higher risk of developing additional skin cancers in the future, so anyone who has been diagnosed with one basal cell carcinoma should be especially watchful for signs of recurrence. Most recurrences happen within three to five years of a patients original diagnosis.
Possible Side Effects Of Radiation
Side effects of radiation are usually limited to the area getting radiation, and can include:
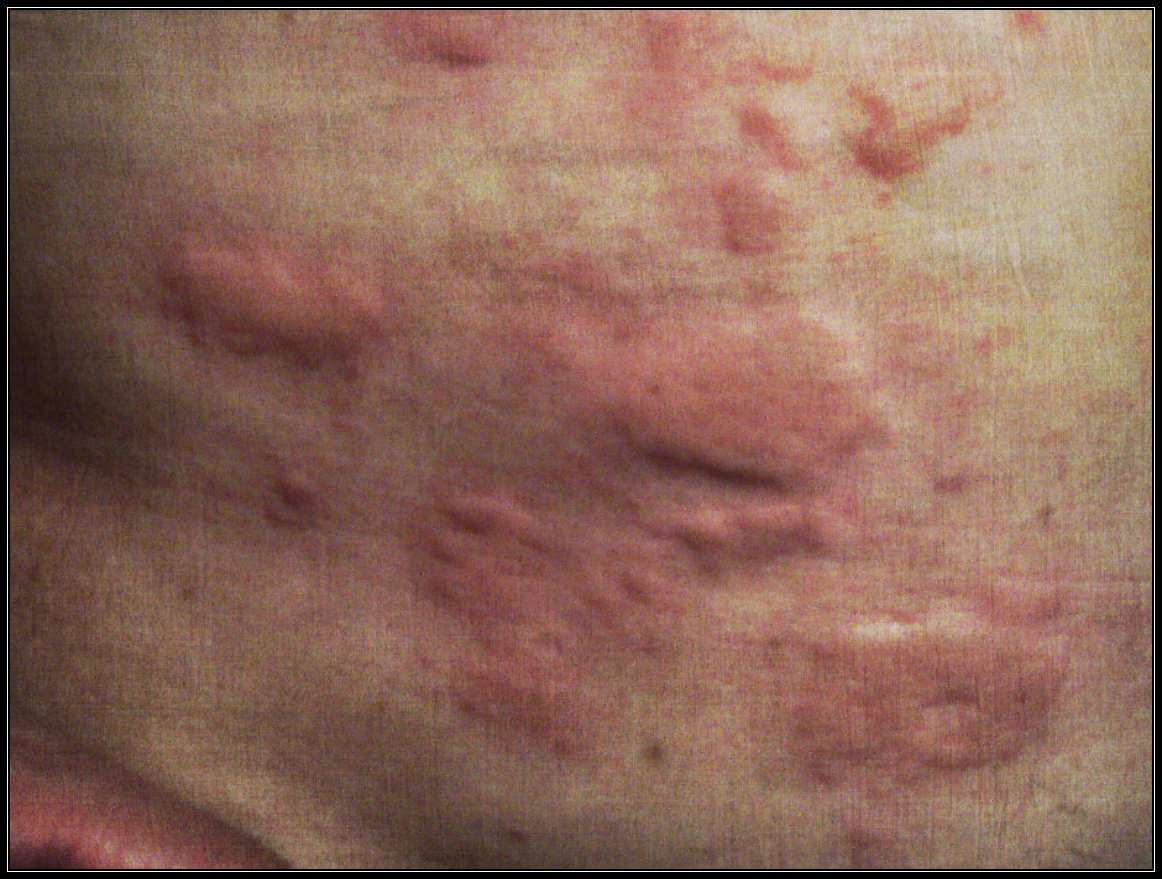
- Skin irritation, ranging from redness to blistering and peeling
- Changes in skin color
- Hair loss in the area being treated
- Damage to saliva-making glands and teeth when treating cancers near these structures
With longer treatment, these side effects may get worse.
After many years, new skin cancers sometimes develop in areas previously treated by radiation. For this reason, radiation usually is not used to treat skin cancer in young people. Radiation is also not recommended for people with certain inherited conditions , who may be at higher risk for new cancers, or for people with connective tissue diseases , which radiation might make worse.
Attention Thinking And Memory Problems
Many patients who received RT to the head and neck and/or chemotherapy experience attention, thinking, or short-term memory problems . Other causes for cognitive problems are pain, side effects of medications, emotional state, and other medical problems. Cognitive problems can manifest in the following symptoms or behavioral changes: trouble concentrating, focusing, or paying attention, mental fog or disorientation, difficulty with spatial orientation, memory loss or difficulty remembering things, especially names, dates, or phone numbers, problems with understanding, difficulties with judgment and reasoning, and impaired ability to calculate and organize, and impaired language skills. These include difficulties to organize ones thoughts, find the right word, or balance a checkbook: problems in multitasking, processing information slower, behavioral and emotional changes, such as irrational behavior, mood swings, inappropriate anger or crying, and socially inappropriate behavior, and severe confusion.
Management of these cognitive problems includes: medications, including stimulants, cognition-enhancers, antidepressants, narcotics blockers, occupational therapy and vocational rehabilitation, and cognitive rehabilitation and cognitive training.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Mayo
Radiotherapy For Skin Cancer
Radiotherapy uses high energy x-rays to kill cancer cells. There are 2 main types of radiotherapy, external and internal radiotherapy .
External beam radiotherapy directs radiotherapy beams at the cancer from a machine. This is different to internal radiotherapy which means giving radiotherapy to the cancer from inside the body.
You usually have external radiotherapy for non melanoma skin cancer. But in some cases, your doctor might use brachytherapy instead. But this is less common.
How Fertility Might Be Affected
For women: Talk to your cancer care team about how radiation might affect your fertility . Its best to do this before starting treatment so you are aware of possible risks to your fertility.
Depending on the radiation dose, women getting radiation therapy in the pelvic area sometimes stop having menstrual periods and have other symptoms of menopause. Report these symptoms to your cancer care and ask them how to relieve these side effects.Sometimes menstrual periods will return when radiation therapy is over, but sometimes they do not.
See Fertility and Women With Cancer to learn more.
For men: Radiation therapy to an area that includes the testicles can reduce both the number of sperm and their ability to function. If you want to father a child in the future and are concerned about reduced fertility, talk to your cancer care team before starting treatment. One option may be to bank your sperm ahead of time.
See Fertility and Men With Cancer to learn more.
Also Check: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
If Youre Getting Radiation Therapy To The Brain
People with brain tumors often get stereotactic radiosurgery if the cancer is in only one or a few sites in the brain. Side effects depend on where the radiation is aimed. Some side effects might show up quickly, but others might not show up until 1 to 2 years after treatment. Talk with your radiation oncologist about what to watch for and when to call your doctor.
If the cancer is in many areas, sometimes the whole brain is treated with radiation. The side effects of whole brain radiation therapy may not be noticeable until a few weeks after treatment begins.
Radiation to the brain can cause these short-term side effects:
- Headaches
- Trouble with memory and speech
- Seizures
Some of these side effects can happen because radiation has caused the brain to swell. Medicines are usually given to prevent brain swelling, but its important to let your cancer care team know about headaches or any other symptoms. Treatment can affect each person differently, and you may not have these particular side effects.
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function. You may also have an increased risk of having another tumor in the area, although this is not common.
Talk with your cancer care team about what to expect from your specific treatment plan.
Stage Iv Patients With Brain Metastases
Purpose: Radiation therapy in Stage IV patients with brain metastases is primarily used to control the growth of or shrink melanoma tumors in the brain, in a precise manner.
How it Works: SRS uses several powerful beams of radiation located at different angles around the head which come together to focus precisely on the tumor. Gamma Knife is one of the most advanced forms of SRS. The knife is formed by many intersecting beams of gamma radiation that deliver a concentrated dose to a precise area of the brain. This noninvasive procedure is the preferred treatment for metastatic brain tumors that were previously considered inoperable or at a very high risk for standard brain surgery.
Which Patients: Radiation may be given to Stage IV patients with brain metastases.
How Its Given:
- Prior to the operation, imaging techniques including CT scans and MRIs are used to pinpoint tumor location.
- One treatment session is often all that is required. Gamma knife radiosurgery is available at many major medical centers.
Effectiveness: SRS is most effective when there are only a few small metastases. Typically, patients who have too many brain metastases to be suitable for SRS may be treated with whole-brain radiation .
Side Effects: SRS has fewer side effects than more diffuse radiation but still can cause hair loss, hearing loss, memory problems, and speech problems, depending on the location of the brain tumor.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
When Radiation Therapy May Be The Best Skin Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy provides a safe, effective treatment for basal and squamous cell carcinoma in many cases. It may be the best treatment option for:
- Patients have skin cancer in delicate sites on the face, such as those around the nose, eyes, ears, or lips, where surgical defects may harm the area or cause undesirable cosmetic damage.
- Patients who have skin cancer that has been treated but has come back in the same location.
- Patients with high-risk squamous cell and basal cell lesions that have close positive margins, nerve invasion, high growth rate, or the possibility of nodal involvement.
- Patients who have large skin cancer tumors that cover a large area.
- Older adults .
- Patients who have poor overall health or underlying medical conditions that could lead to complications from surgery.
- Patients on blood thinners or other medications that interfere with surgery.
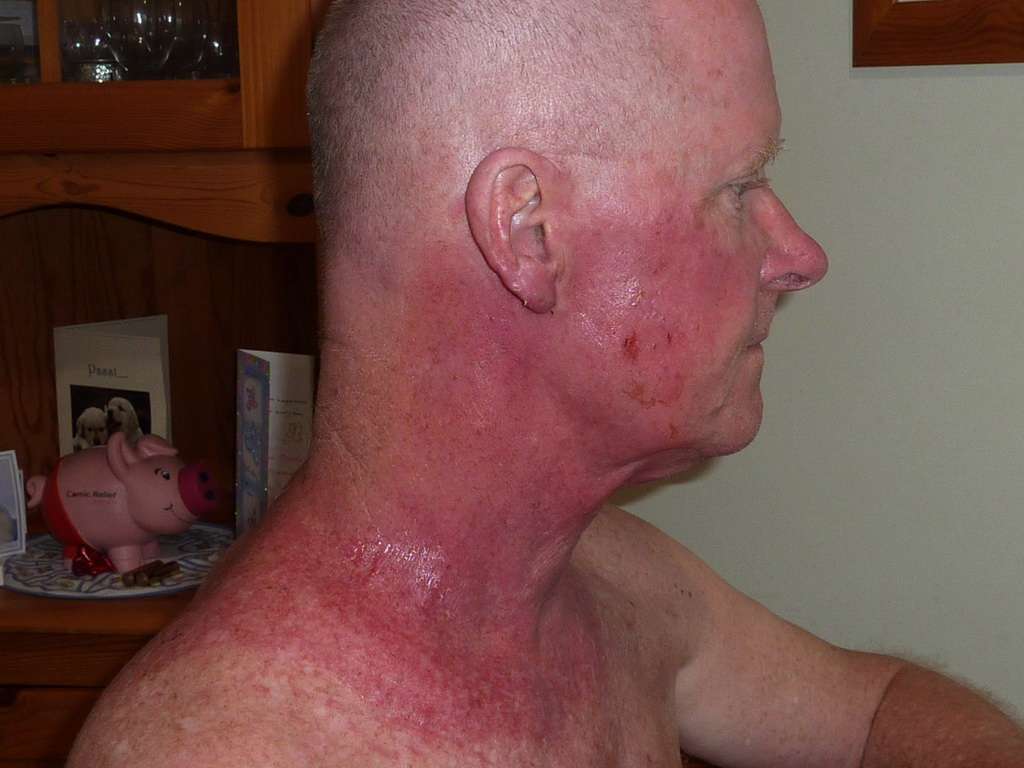
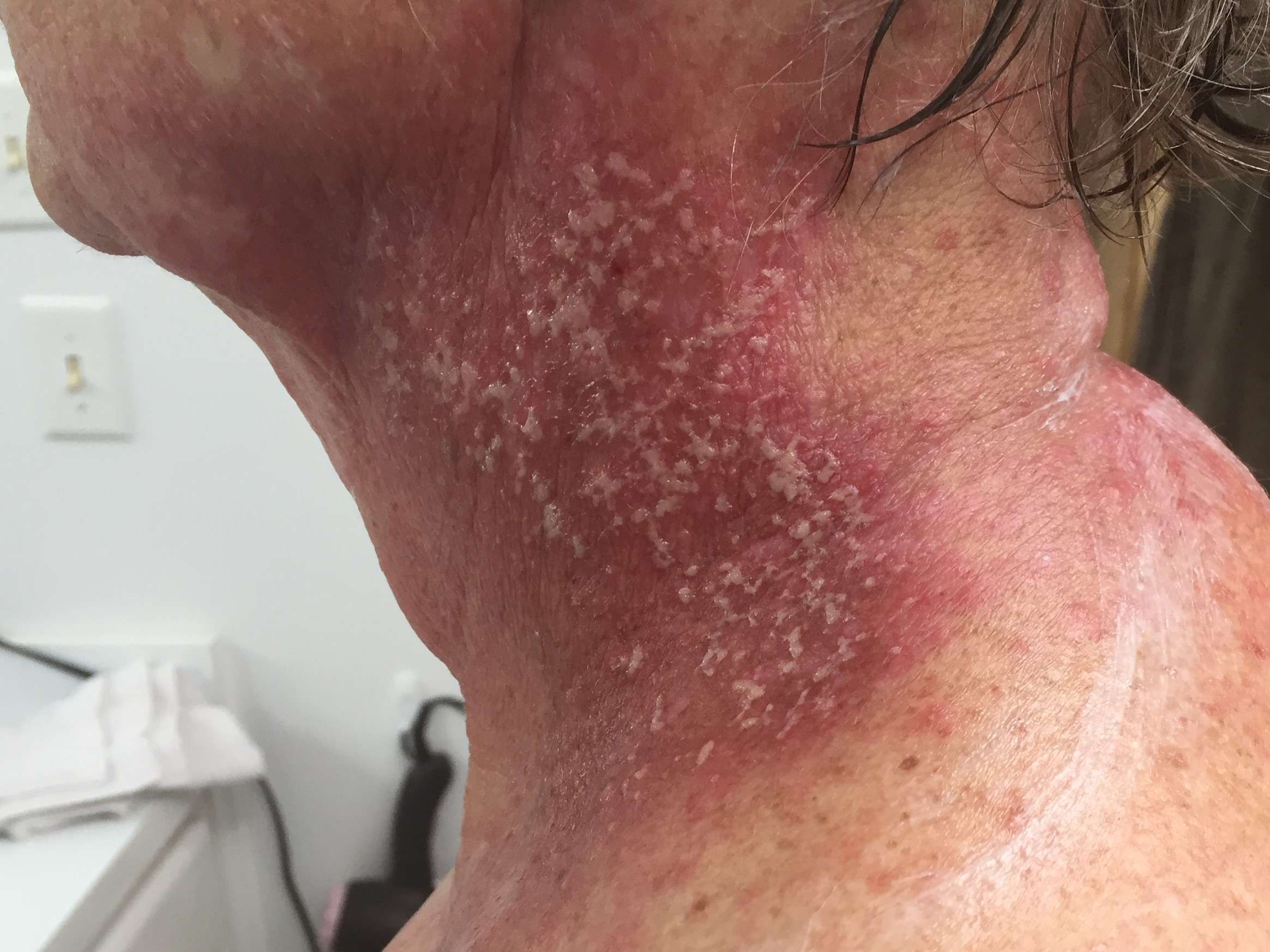
What Is Radiation Recall
Radiation recall is a rash that looks like a severe sunburn. It is rare and happens when certain types of chemotherapy are given during or soon after external-beam radiation therapy.
The rash appears on the part of the body that received radiation. Symptoms may include redness, tenderness, swelling, wet sores, and peeling skin.
Typically, these side effects start within days or weeks of radiation therapy. But they can also appear months or years later. Doctors treat radiation recall with medications called corticosteroids. Rarely, it may be necessary to wait until the skin heals before continuing chemotherapy.
Don’t Miss: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Possible Side Effects Of Radiation Treatment For Prostate Cancer
The radiation used to destroy cancer cells can also hurt normal cells in the nearby area. Side effects from radiation treatment are related to the area of the body being treated. Patients start to have side effects a few weeks into their treatment. While side effects may be unpleasant, there are treatments to help deal with them. Most side effects are temporary and slowly start to go away once treatment is done.
You will be seen by your radiation oncology providers often during treatment. These visits are a chance to ask questions and to talk about any side effects and how to best manage them. You can also call your providers to speak about any side effects.
Facts About Skin Cancer
- The skin is the bodyâs largest organ. Its job is to protect internal organs against damage, heat and infection. The skin is also the most exposed organ to sunlight and other forms of harmful ultraviolet rays.
- More than 1 million cases of basal and squamous cell skin cancers will be diagnosed in the United States this year. These cancers can usually be cured. 65,000 cases of melanoma will be diagnosed this year.
- More than 7,000 men and 3,710 women will die from the disease this year.
- Melanoma is 10 times more common among Caucasians than in African-Americans.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
What Are The Risks Of Radiation Therapy
The electrons used for external-beam radiation therapy for skin cancer do not go deeper than the skin.1,2 This limits the side effects of radiation therapy.2 Nevertheless, there are many possible side effects of radiation. They include:2,4,6
- Skin irritation or sunburn-like reaction
- Changes in skin color
- Nerve damage
- Joint problems
Brain radiation therapy can cause problems such as memory loss, headaches, trouble thinking, and reduced sexual desire.4
When Is Radiation Therapy Used As A Primary Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgery is the preferred treatment for most cases of skin cancer. However, the tumor size or location may make surgery impossible. Surgery may not be an option because of co-existing medical conditions. If surgery is not possible, radiation therapy can be an alternative.2,4,5 When radiation therapy is used to treat skin cancer, it is typically reserved for patients older than 60 years. The reason is that future skin cancers may develop at the radiation site.
Radiation therapy can be a primary treatment for:2,5-7
- Large non-melanoma skin cancer
- Kaposi sarcoma lesions on the skin, mouth, or throat
- Merkel cell carcinoma that has returned or is likely to recur
The approximate 5-year recurrence rates after radiation therapy for non-melanoma skin cancer are:8,9
- Basal cell carcinoma : 4% to 16%
- Squamous cell carcinoma : 4% to 10%
Also Check: Stage 2 Carcinoma
What Are Side Effects
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are the two most common types of cancer treatment. They work by destroying these fast-growing cells. But other types of fast-growing healthy cells also can be damaged along with cancer cells, causing adverse reactions, or side effects.
Side effects can range from tiredness and nausea to hair loss and blood clotting problems. Because each person responds a little differently to treatment and it’s hard for doctors to predict exactly how the body will react, they’ll closely watch someone who is being treated for cancer. Doctors weigh the amount and severity of side effects against the benefits of treatments.
Fortunately, most side effects are temporary. As the body’s normal cells recover, these problems start to go away. There are also good supportive treatments that can lessen the side effects.
Side effects vary:
- Some can be merely unpleasant, while others can be much more serious.
- Some show up right away, while others develop over time.
- Some teens have just a few, while others have many over the course of treatment.
If Youre Having Radiation Therapy To The Pelvis
Radiation therapy to the pelvis can cause side effects such as:
- Bladder problems
- Fertility problems
- Changes in your sex life
You might also have some of the same problems people get from radiation to the abdomen, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation.
Bladder problems
Radiation to the pelvis can cause problems with urination, including:
- Pain or burning sensations
- Blood in the urine
- An urge to urinate often
Most of these problems get better over time, but radiation therapy can cause longer-term side effects as well:
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Radiation Therapy Side Effects
Radiation not only kills or slows the growth of cancer cells, it can also affect nearby healthy cells. Damage to healthy cells can cause side effects.
Many people who get radiation therapy have fatigue. Fatigue is feeling exhausted and worn out. It can happen all at once or come on slowly. People feel fatigue in different ways and you may feel more or less fatigue than someone else who is getting the same amount of radiation therapy to the same part of the body.
Other radiation therapy side effects you may have depend on the part of the body that is treated. To see which side effects you might expect, find the part of your body being treated in the following chart. Many of the side effects in the list link to more information in the Side Effects section. Discuss this chart with your doctor or nurse. Ask them about your chances of getting each side effect.
Can We Avoid That Damage
So why do we not just space out the treatments more and give the healthy cells are time? We could, but that would also provide the skin cancer cells more time to repopulate. Therefore we continue the treatments knowing that even though the healthy skin is being affected, it will ultimately heal over time and eventually repair the damage.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
Less Common Bladder Symptoms After Radiation
- a small amount of urine leakage especially if you laugh, sneeze, exercise, or cough
- pain when passing urine
- passing blood clots
- difficulty passing urine, because the radiation treatment can make the tube that drains urine from the bladder narrower. This is known as a stricture.
Contact your doctor if any of these symptoms occur, because treatment is available to alleviate them.
Surgery Vs Radiation Therapy For Skin Cancer
Historically, surgery has been the most common way to treat non-melanoma skin cancer, particularly for minor, early-stage cases. Since basal and squamous cell carcinomas tend to start small, are slow-growing, and frequently do not spread right away, surgery may offer the best treatment.
For these reasons, surgery is often an excellent option. Through various surgical procedures, including Mohs surgery, cryosurgery, and curettage with electrosurgery, a physician can quickly remove the cancer before it grows, spreads, or causes additional damage. The effectiveness of each surgical approach is different, but all have very high curative rates.
At the same time, radiation therapy provides an excellent treatment option for skin cancer, either as an alternative to surgery or an adjunctive treatment in combination with surgery.
In many cases, radiation therapy may be used in place of or in combination with surgical options. Depending on a patients specific medical situation, overall health, age, and preferences, radiation therapy may be the best option available.
If youve got basal or squamous cell carcinoma, youll want to talk to your doctor and cancer team about the options that are best suited for your particular case. Several highly effective treatments are available, and your best choice will depend on your circumstances and preferences.
Factors to consider when choosing a treatment for skin cancer include:
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
Looking After Your Skin During Radiotherapy Treatment
Your radiotherapy team will tell you how to care for your skin during and after treatment.
Tips for looking after your skin:
- Gently wash your skin with warm water
- Dont use perfume, perfumed soaps or lotions on the area as it can irritate the skin
- Pat your skin dry using a soft towel, do not rub
- Dont shave the area being treated speak to your radiotherapy team if you really need to remove the hair, it may be better to use a hair trimmer instead
- Dont use any creams or dressings on the treatment area unless advised by your doctor or radiographer
What Questions Should I Ask Before Radiation Therapy
Questions to ask your doctor about radiation therapy include:11
- What is the goal of radiation therapy for me?
- What are the other options for treating my cancer?
- How will the radiation be delivered? How often and for how long will I need treatments?
- What short-term side effects should I expect?
- What are the long-term side effects of radiation treatment?
- How likely is it that the cancer returns or spreads without radiation therapy? How likely is recurrence or metastasis with radiation therapy?
- How often should I have follow-up exams with my dermatologist to check for cancer recurrence or a second skin cancer?
Also Check: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy