Which Type Of Skin Cancer Is The Most Dangerous
Melanoma vs Non-melanoma skin cancer
There are two main categories of skin cancer: melanoma and non-melanoma. Between these types, melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer, although non-melanoma skin cancers are the most common.
Non-melanoma skin cancers refer mostly to basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma two types of skin cancer that are, in most cases, treatable without becoming life-threatening.
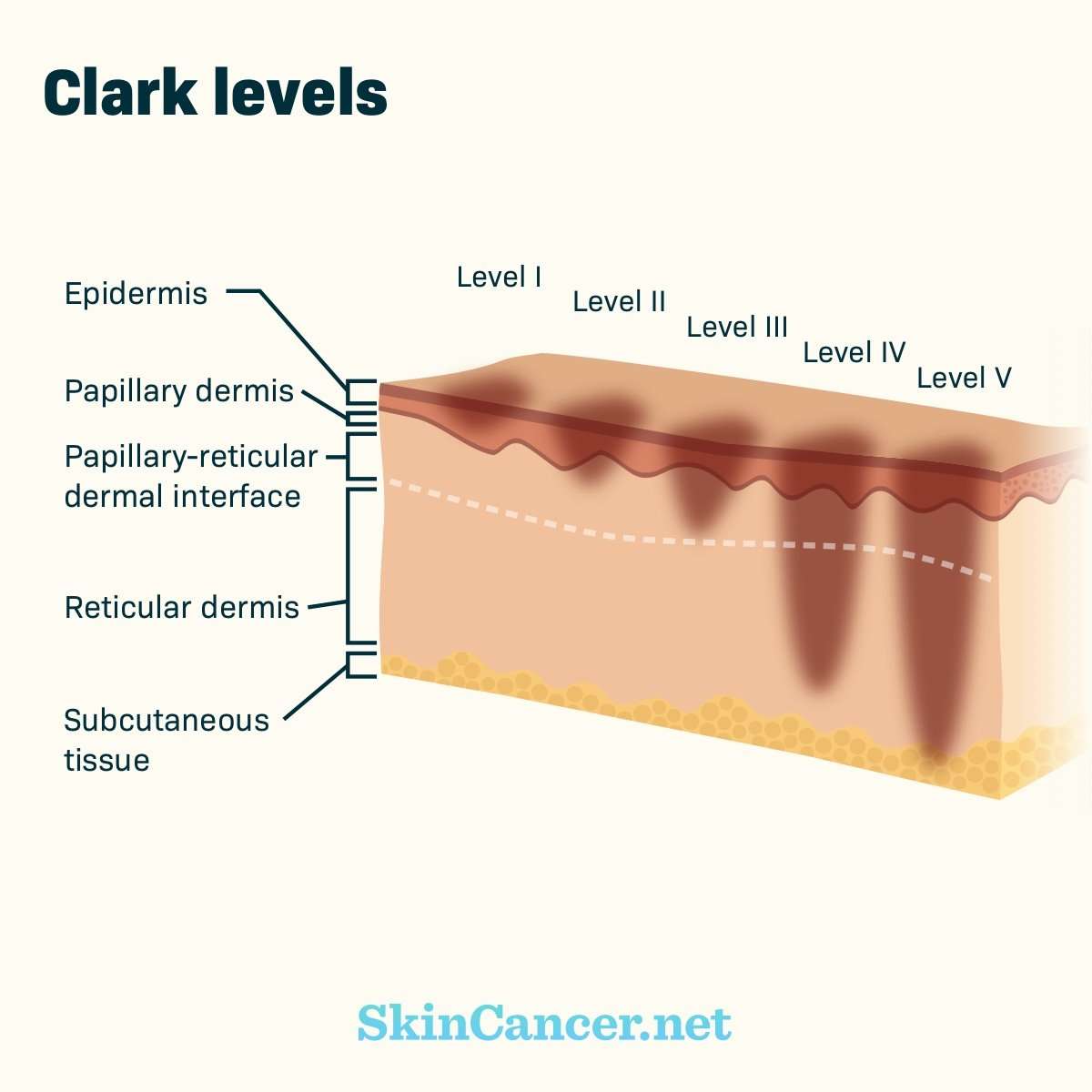
Melanoma skin cancer begins in melanocyte cells in the deepest layer of skin, also known as the hypodermis or subcutaneous tissue, while non-melanoma cancers are found in the upper and middle layers of skin, called the epidermis and dermis, respectively.
What Are The Signs Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer can be a portion or spot of skin that does not heal. If you scrape your knee, it will usually heal within a month. Skin cancer will not heal.
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, typically a new growth, or a change in an existing growth or mole.
- Basal cell carcinoma might appear as a small, smooth, pearly or waxy bump on the face, ears, and neck or as a flat, pink/red- or brown-colored lesion on the trunk or arms and legs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma can appear as a firm, red nodule, or as a rough, scaly flat lesion that might itch, bleed, and become crusty. Both basal cell and squamous cell cancers mainly occur on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, but can occur anywhere.
- Melanoma usually appears as a brown-pigmented patch or bump. It might resemble a normal mole, but usually has a more irregular appearance. Thinking of the ABCDE rule tells you what signs to watch for:
- Asymmetry: irregular shape
- Border: blurry or irregularly shaped edges
- Color: mole with more than one color
- Diameter: larger than a pencil eraser
- Evolution: enlarging, changing in shape, color, or size.
Be alert to pre-cancerous skin lesions that can develop into non-melanoma skin cancer. They appear as small scaly, tan or red spots, and are most often found on surfaces of the skin chronically exposed to the sun, such as the face and backs of the hands.
Determining If The Cancer Has Spread
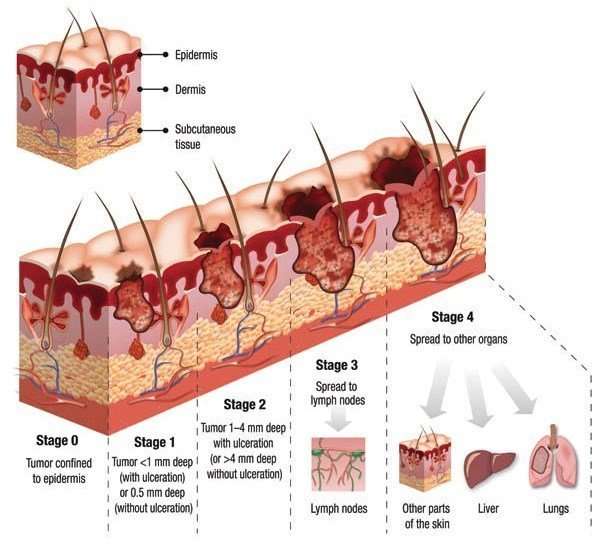
As part of your diagnosis, your doctor will also determine what stage the cancer is in. The different stages refer to whether and how far the cancer has spread in your body, on a Roman numeral scale of I to IV. A stage I cancer is small and contained to the body part where it originated, whereas a stage IV cancer has spread aggressively to other parts of the body.
Depending on the type of skin cancer that a person has, it may be more or less likely that it has spread through the body. For instance, basal cell skin cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin where it starts. However, melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas are more likely to spread into other regions of the body. Cases of melanoma, in particular, may call for further tests to determine the specific stage theyre in.
Your doctor may evaluate multiple factors in order to stage the cancer. Using biopsies and imaging tests, your doctor may take a look at:
-
The size and thickness of the tumor, and whether it has grown into surrounding tissues
-
Nearby lymph nodes, to check for signs of cancer spread
Recommended Reading: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Support Groups And Counseling
Living with skin cancer presents many new challenges for you and for your family and friends. You will probably have many worries about how the cancer will affect you and your ability to “live a normal life,” that is, to care for your family and home, to hold your job, and to continue the friendships and activities you enjoy.
Many people with a skin cancer diagnosis feel anxious and depressed. Some people feel angry and resentful others feel helpless and defeated. For most people with skin cancer, talking about their feelings and concerns helps. Your friends and family members can be very supportive. They may be hesitant to offer support until they see how you are coping. Don’t wait for them to bring it up. If you want to talk about your concerns, let them know.
Continued
Some people don’t want to “burden” their loved ones, or prefer talking about their concerns with a more neutral professional. A social worker, counselor, or member of the clergy can be helpful. Your dermatologist or oncologist should be able to recommend someone.
Many people with cancer are profoundly helped by talking to other people who have cancer. Sharing your concerns with others who have been through the same thing can be remarkably reassuring. Support groups for people with cancer may be available through the medical center where you are receiving your treatment. The American Cancer Society also has information about support groups throughout the U.S.
Skin Cancer Pictures By Type
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer. There are several different types of skin cancer with Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Bowens Disease, Keratoacanthoma, Actinic Keratosis and Melanoma most commonly occurring.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, and least dangerous whereas melanoma is the most dangerous type.
Below you will find skin cancer pictures of these six types, but remember that skin cancer should be diagnosed by a doctor. Comparing your skin lesion to skin cancer images found online cannot replace medical examination.
If you have any pigmented mole or non-pigmented mark on your skin that looks different from the other marks or moles on your skin, that is new or that has undergone change, is bleeding or wont heal, is itching or in any way just seems off, visit your doctor without delay dont lose time comparing your mole or mark with various pictures of skin cancer.
If you want to be proactive about your health, you may want to photograph areas of your skin routinely including individual moles or marks to familiarise yourself with the appearance of your skin . A skin monitoring app may be a useful tool to assist in that process.
MIISKIN PROMO
Read Also: Tumor Calcification
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Australia has one of the highest rates of skin cancer in the world. Anyone can be at risk of developing skin cancer, though the risk increases as you get older.
The majority of skin cancers in Australia are caused by exposure to UV radiation in sunlight.
Some factors that increase your risk of skin cancer include:
-
sunburn
Skin Color And Being Exposed To Sunlight Can Increase The Risk Of Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesnt mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk.
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight over long periods of time.
- Having a fair complexion, which includes the following:
- Fair skin that freckles and burns easily, does not tan, or tans poorly.
- Blue, green, or other light-colored eyes.
- Red or blond hair.
Although having a fair complexion is a risk factor for skin cancer, people of all skin colors can get skin cancer.
Older age is the main risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
Don’t Miss: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
For More Information About Skin Cancer
National Cancer Institute, Cancer Information Service Toll-free: 4-CANCER 422-6237TTY : 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
Media file 1: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
Media file 2: Skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma.
Media file 3: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 5: Skin cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Continued
Media file 6: Skin cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.
What Is The Tnm System
The TNM system uses the results from x-rays, scans, biopsies and other tests to provide information about a persons cancer.
This is recorded in three categories represented by the letters TNM, each followed by a number or letter showing the extent of the cancer:
T shows how large the tumour or primary cancer is and whether it has spread into nearby tissues. The numbers 1 to 4 are used to provide information about this.
N shows whether the cancer has spread into any nearby lymph nodes and how many nodes are involved. 0 means no lymph nodes are affected, while the numbers 1 to 3 show that nodes are involved and indicate how many.
M shows whether the cancer has spread from where it started to other parts of the body, which is known as metastasis. 0 means no spread and 1 means it has spread.
Don’t Miss: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
How To Check Your Skin
- Make sure you check your entire body, as skin cancers can sometimes occur on parts of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet, between fingers and toes and under nails.
- Undress completely and make sure you have good light.
- Use a mirror to check hard to see spots, like your back and scalp, or get a family member, partner or friend to check for you.
What Are The Stages Of Melanoma
Cancerstaging is how doctors describe the extent of cancer in your body. Staging is defined by the characteristics of the original melanomatumor and if/how far it has spread in your body.
Melanoma is divided into stages using five Roman numerals and up to four letters that indicate a higher risk within each stage. The stage is determined mostly by specific details about the tumor and its growth that are tallied in a system called TNM. Read more about the TNM system.
Your stage is important because cancer treatment options and prognoses are determined by stage.
Recommended Reading: Braf Melanoma Treatment
Skin Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Skin
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common in skin that is often exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands.
Skin Cancer Symptoms And Signs
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and has a predilection for sun-exposed skin. Tumors may appear as a pearly or waxy bumps usually with visible blood vessels , or as a flat scaly reddish patch with a brown border, or as a hard or scar-like lesion . Frequently BCCs can be itchy, often bleed, or in more advanced cases, ulcerate.
Don’t Miss: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Melanoma: The Deadliest Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, because it tends to spread if its not treated early.
This cancer starts in the melanocytes cells in the epidermis that make pigment.
About 100,350 new melanomas are diagnosed each year.
Risk factors for melanoma include:
- Having fair skin, light eyes, freckles, or red or blond hair
- Having a history of blistering sunburns
- Being exposed to sunlight or tanning beds
- Living closer to the equator or at a higher elevation
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles or unusual-looking moles
- Having a weakened immune system
Melanoma can develop within a mole that you already have, or it can pop up as a new dark spot on your skin.
This cancer can form anywhere on your body, but it most often affects areas that have had sun exposure, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. Melanomas can also develop on the soles of your feet, palms of your hands, or fingernail beds.
Signs to watch out for include:
- A mole that changes in color, size, or how it feels
- A mole that bleeds
RELATED: The Difference Between Chemical and Mineral Sunscreen
Preparing For Your Appointment
If you have any concerns about the health of your skin, it is important to share them with your doctor. After making an appointment, there are steps you can take to prepare yourself and make the most of your time with your doctor.
Here are some things to consider and be prepared to discuss before visiting the clinic or hospital:
-
What symptoms are you experiencing ?
-
When did you first notice your symptoms?
-
Have there been any major changes or stressors in your life recently?
-
What medications and/or vitamins are you taking?
-
What questions do you have for your doctor?
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Most Common Forms Of Skin Cancer
Three types of skin cancer are the most common:
-
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body. Basal cells, which are round, form the layer just underneath the epidermis, or outer layer of the skin.
-
Squamous cell carcinoma spreads more often than basal cell carcinoma, but still is considered rare. Squamous cells, which are flat, make up most of the epidermis.
-
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer. It occurs when melanocytes, the pigment cells in the lower part of the epidermis, become malignant, meaning that they start dividing uncontrollably. If melanoma spreads to the lymph nodes it may also reach other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs or brain. In such cases, the disease is called metastatic melanoma.
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor or dermatologist will first conduct a physical examination by looking at your skin to identify any suspicious spots using a dermatoscope .
Its not always possible to tell from looking at it whether a spot or lump is cancerous or not. So your doctor or dermatologist may take a skin biopsy. This is where part of, or all of, your spot is removed and sent for further study under a microscope.
Some smartphone apps allow you to photograph your skin and compare photos over time. While they can be a good reminder to check your skin and record details, they shouldnt replace a visit to the doctor. See a doctor if youre concerned about any spots or moles on your skin.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Tests Or Procedures That Examine The Skin Are Used To Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
The following procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patients health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Skin exam: An exam of the skin for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape, or texture.
- Skin biopsy: All or part of the abnormal-looking growth is cut from the skin and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. There are four main types of skin biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A sterile razor blade is used to shave-off the abnormal-looking growth.
- Punch biopsy: A special instrument called a punch or a trephine is used to remove a circle of tissue from the abnormal-looking growth. Enlarge Punch biopsy. A hollow, circular scalpel is used to cut into a lesion on the skin. The instrument is turned clockwise and counterclockwise to cut down about 4 millimeters to the layer of fatty tissue below the dermis. A small sample of tissue is removed to be checked under a microscope. Skin thickness is different on different parts of the body.
- Incisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove part of a growth.
- Excisional biopsy: A scalpel is used to remove the entire growth.