What Happens If Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It typically affects people above the age of 50 and those who have weakened immune systems. In most cases, Merkel cell carcinoma begins as a skin-toned growth that may bleed easily. The bumps or nodules may also have blue, purple, or red coloring. Because the Merkle cells are near nerve endings, this form of cancer has numerous health risks, and if left untreated, Merkle cell cancer may spread to the brain, lungs, or bones, becoming fatal.
Do You Know The 4 Main Types Of Skin Cancer
As the sun shines in spring and the days lengthen toward summer, tis the season for sunscreen. Using a sunscreen of SPF 15 or higher is one of the best ways to protect yourself against skin cancer, which affects more than 3.3 million people in the U.S. each year.
Its also a good time to practice good skin habits like staying in shade during the hottest part of the day, keeping skin covered with clothing, and checking your skin for irregularities. Which brings up the question: Are you familiar with the 4 main types of skin cancer?
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma Bad
Basal Cell Carcinomas And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
While melanoma often gets the most coverage, there are two other major types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Often grouped together as non-melanoma skin cancers, these two types are much more common than melanoma cancer. Although they are unlikely to spread to other parts of the body, they may cause disfigurement if not treated early.
Basal cell carcinomas are abnormal, uncontrolled growths or lesions that arise in the skins basal cells, which line the deepest layer of the outermost layer of the skin. They often look like open sores, red patches, pink growths, shiny bumps or scars and usually are caused by sun exposure.
Warning signs include:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas, similar to a scar
- Raised reddish patches that may be itchy
- Small, pink or red, translucent, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown or black areas
- Pink growths with raised edges and a lower area in their center, which may contain abnormal blood vessels
- Open sores that dont heal or that heal and then return
- Basal cell cancers are often fragile and might bleed after shaving or after a minor injury. If you have a sore or a shaving cut that doesnt heal after a week, it would be wise to contact your doctor.
- Rough or scaly red patches, which may crust or bleed
- Raised growths or lumps, sometimes with a lower area in the center
- Open sores that dont heal or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Are All Moles Cancerous
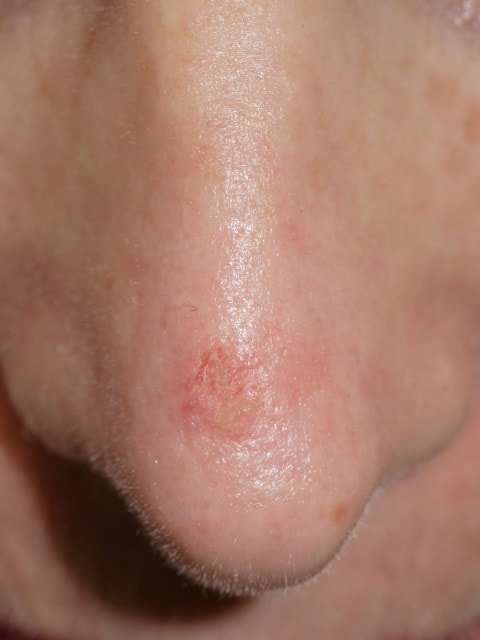
Most moles are not cancerous. Some moles are present at birth, others develop up to about age 40. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles.
In rare cases, a mole can turn into melanoma. If you have more than 50 moles, you have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your skin is the largest organ in your body. It needs as much attention as any other health concern. What may seem like an innocent cosmetic imperfection, may not be. Performing regular skin self-checks is important for everyone and is especially important if you are a person at increased risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is also color-blind. If you are a person of color, skin cancer can happen to you. Check your skin every month for any changes in skin spots or any new skin growths. Consider taking skin selfies so you can easily see if spots change over time. If youre a person of color, be sure to check areas more prone to cancer development, such as the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, your genital area and under your nails. Takes steps to protect your skin. Always wear sunscreen with SPF of at least 30 every day of the year. Wear UV-A/UV-B protective sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeve shirts and pants. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin check.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/19/2021.
References
You May Like: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Main Types Of Skin Cancers
The 4 main types of skin cancer include:
- Sore that does not heal or heals and returns
- Brown or black discolored stripe under a nail
Imaging tests
You May Like: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- T cell lymphoma of the skin
- Sebaceous gland cancer
These are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skin’s natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma is a rare condition. It’s often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who don’t have HIV. It’s a cancer that starts in the cells that form the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment is surgery or radiotherapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin
T cell lymphoma of the skin can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. It’s a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer.
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, and it is considered very low risk for metastasizing and spreading to other parts of the body. It is typically very slow-progressing and is usually diagnosed and treated in very early stages. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can be locally destructive to the tissues where it grows, and it can invade deeper structures such as nerves, cartilage, and even bone. In most cases, basal cell carcinoma develops on the face, ears, neck, head, shoulders, hands, and other areas that receive frequent sun exposure. The tumors may look like raised bumps on the skin that are usually smooth and pearly/shiny in appearance. Blood vessels can sometimes be seen within the lesions, and in some cases, a wound may form and bleed easily.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
Basal Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin And Actinic Keratosis Often Appear As A Change In The Skin
Not all changes in the skin are a sign of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, or actinic keratosis. Check with your doctor if you notice any changes in your skin.
Signs of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include the following:
- A sore that does not heal.
- Areas of the skin that are:
- Raised, smooth, shiny, and look pearly.
- Firm and look like a scar, and may be white, yellow, or waxy.
- Raised and red or reddish-brown.
- Scaly, bleeding, or crusty.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin occur most often in areas of the skin exposed to the sun, such as the nose, ears, lower lip, or top of the hands.
Signs of actinic keratosis include the following:
- A rough, red, pink, or brown, scaly patch on the skin that may be flat or raised.
- Cracking or peeling of the lower lip that is not helped by lip balm or petroleum jelly.
Actinic keratosis occurs most commonly on the face or the top of the hands.
What Types Of Skin Cancers Are Deadly
Skin cancers are some of the most complex and serious conditions treated by dermatologists, and the U.S. Dermatology Partners team takes our role in preventing and treating all types of skin cancers very seriously. While some forms of skin cancer are not typically life-threatening, without proper treatment, there are serious health risks associated with all forms of skin cancer. According to Dr. Jessica Dorsey of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Cedar Park, Texas, Most skin cancers are slow-growing and unlikely to spread to other parts of the body, but without treatment, just about any form of skin cancer has the potential to be destructive or even fatal. Keep reading to learn more about the importance of regular screenings to catch skin cancer in the earliest stages and prevent the severe repercussions of untreated skin cancers.
Don’t Miss: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Other Cancers On The Face
A few other rare skin cancers that might happen on the face:
- Lymphoma of the skin is an uncommon type of white blood cell cancer.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma is cancer caused by a herpes virus in immunosuppressed patients that causes skin lesions on the face. They look like painless purplish spots.
- Skin adnexal tumors is a rare cancer type that starts in hair follicles or skin glands.
- Sarcomas are tumors of the connective tissuesspecifically the fat, nerves, bone, skin, and muscles 80% of which occur in the face, head, or neck.
- Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma is an uncommon soft-tissue sarcoma that can happen on the face.
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the U.S.
Other skin cancer facts:
- Around 20% of Americans develop skin cancer sometime in their life.
- Approximately 9,500 Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer every day.
- Having five or more sunburns in your life doubles your chance of developing melanoma. The good news is that the five-year survival rate is 99% if caught and treated early.
- Non-Hispanic white persons have almost a 30 times higher rate of skin cancer than non-Hispanic Black or Asian/Pacific Islander persons.
- Skin cancer in people with skin of color is often diagnosed in later stages when its more difficult to treat. Some 25% of melanoma cases in African Americans are diagnosed when cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Rarer Types Of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, and Merkel cell cancer make up the vast majority of all skin cancer cases. However, there are several other rare types of skin cancer:
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma can affect the skin, blood, lymph nodes, and internal organs. It presents as a dry, itchy red rash.
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans causes a tumor in the deep layers of the skin and starts out as a patch of firm skin that raises over time. The tumors have a high rate of recurring or returning once treated.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma is a rare cancer caused by an infection with human herpesvirus-8 . It causes abnormal tissue growth under the skin, and looks like red and purple lesions. Those with a compromised immune system, such as people who are HIV-positive, are more at risk.
- Sebaceous carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually affects the skin on or around the eyelid. It presents as a small, round, painless tumor on the upper or lower eyelid.
- Skin adnexal tumors are very rare tumors that grow in the sebaceous glands or hair follicles. They are often misdiagnosed as benign growth, and almost always require a pathologist to diagnose.
- Soft tissue sarcomas are cancerous growths that can develop in the deep layers of skin, as well as the bodys fat, muscle, nerves and blood vessels.
Taking Care Of Yourself
After you’ve been treated for basal cell carcinoma, you’ll need to take some steps to lower your chance of getting cancer again.
Check your skin. Keep an eye out for new growths. Some signs of cancer include areas of skin that are growing, changing, or bleeding. Check your skin regularly with a hand-held mirror and a full-length mirror so that you can get a good view of all parts of your body.
Avoid too much sun. Stay out of sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s UVB burning rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen. The suns UVA rays are present all day long — thats why you need daily sunscreen. Make sure you apply sunscreen with at least a 6% zinc oxide and a sun protection factor of 30 to all parts of the skin that aren’t covered up with clothes every day. You also need to reapply it every 60 to 80 minutes when outside.
Dress right. Wear a broad-brimmed hat and cover up as much as possible, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
Continued
Also Check: What Does Cancer Tissue Look Like
Basic Information About Skin Cancer
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the skin, it is called skin cancer.
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States. Some people are at higher risk of skin cancer than others, but anyone can get it. The most preventable cause of skin cancer is overexposure to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or from artificial sources like tanning beds.
Most skin cancers are caused by too much exposure to ultraviolet rays. To lower your risk of getting skin cancer, you can protect your skin from UV rays from the sun and from artificial sources like tanning beds and sunlamps.While enjoying the benefits of being outdoors, people can decrease skin cancer risk by using sun protection. Protect yourself by staying in the shade, wearing protective clothing, and applying and re-applying a broad spectrum sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 15 or higher.Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare Skin Cancer On The Rise
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that affects about 2,000 people in the United States each year.
Though its an uncommon skin cancer, cases of Merkel cell carcinoma have increased rapidly in the last couple of decades.
This type of cancer starts when cells in the skin, called Merkel cells, start to grow out of control.
Merkel cell carcinomas typically grow quickly and can be difficult to treat if they spread.
They can start anywhere on the body, but Merkel cell carcinomas commonly affect areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, and arms.
They may look like pink, red, or purple lumps that are firm when you touch them. Sometimes, they can open up as ulcers or sores.
Risk factors include:
Also Check: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment