How Do I Know If I Need To See The Doctor If I Have A Mole Or A Discoloration On My Skin
When it comes to suspicious spots on your skin, warning signs of cancer can include itching, bleeding, pain, rapid growth or significant changes in size or color over a few months and should be checked out by a dermatologist. Having a yearly skin check can help ensure that any changes or warning signs on your skin are detected early.
Treatment Options For Skin Cancer On The Scalp
Treatment options for skin cancer on the scalp depend upon the type, depth, location, and size of the cancer. Small cancers may be removed completely during the initial biopsy of the skin. If the scalp cancer needs additional treatment, here are some other treatment options:
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancers. If there is skin cancer on the scalp or anywhere else on the body, knowing its type can help to understand treatment options and what to expect.
Skin Cancer General Characteristics
Skin cancers are malignant growths on the skin. They mostly arise from the upper layer of the skin epidermis. Skin cancers may develop anywhere on the skin, including the scalp, lips or under-nail skin.
Skin cancers are most common after 50 years of age, but they may occur at any time.
Any chronic skin growth or discoloration that increases in size with time is suspicious for a skin cancer.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Metastatic Melanoma
Seek Comprehensive Care If Your Skin Cancer Is Complicated To Treat
Complicated skin cancer may require the expertise of multiple specialists. Plastic surgeons may get involved when the cosmetic challenges are significant. An ocular surgeon or an oculoplastic specialist may be needed if you have an especially difficult-to-treat skin cancer close to the eye. A head and neck surgeon may join your care team if there is nerve involvement or if the cancer is too extensive for local anesthesia.
The beauty of a comprehensive cancer center like MSK is that the expertise is all here, says Dr. Lee. We have a multidisciplinary program especially for people with complex skin cancer. You can usually see all of your doctors on the same day and in the same location. The dermatology team works with you to coordinate your appointments with your schedule.
Where Does Skin Cancer Develop
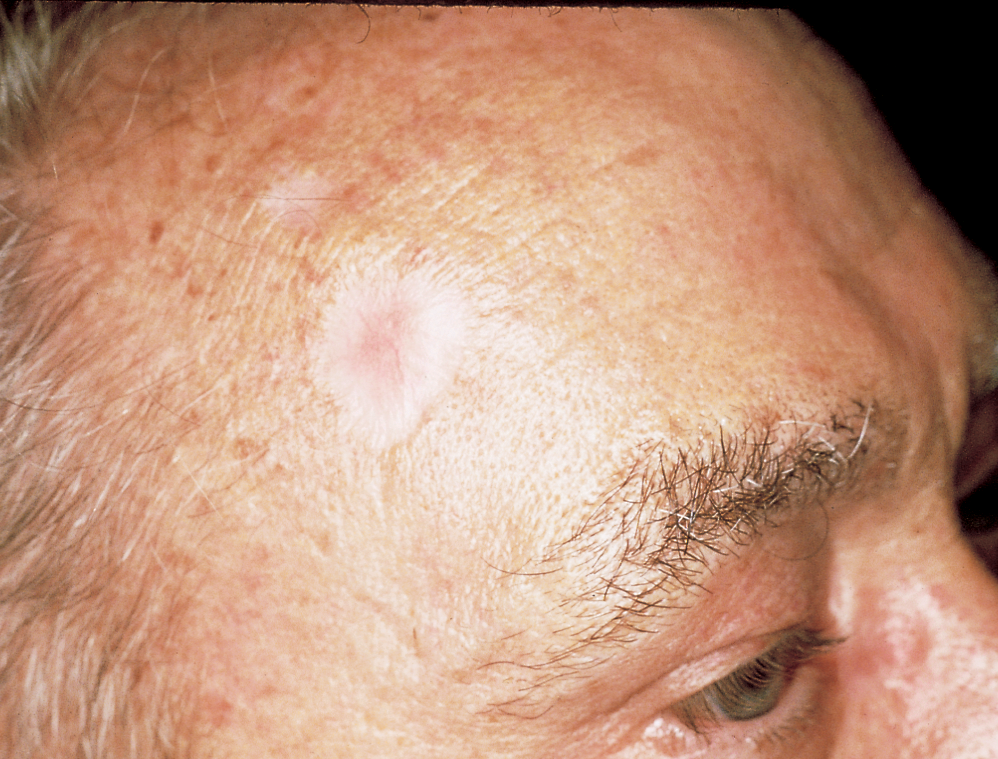
Skin cancer is most commonly seen in sun-exposed areas of your skin your face , ears, neck, arms, chest, upper back, hands and legs. However, it can also develop in less sun-exposed and more hidden areas of skin, including between your toes, under your fingernails, on the palms of your hands, soles of your feet and in your genital area.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
Stage Information For Skin Cancer
There are separate staging systems in the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancers AJCC Cancer Staging Manual for carcinoma of the eyelid and for cutaneous carcinoma of the head and neck. The cutaneous carcinoma staging system addresses cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and cutaneous basal cell carcinoma . The staging system for carcinomas of the eyelid addresses carcinomas of all histologies.
Regional lymph nodes should be routinely examined inall cases of SCC, especially for the following:
- High-risk tumors appearingon the lips, on the ears, and in the perianal and perigenital regions.
- High-risk areas of thehand.
- Sites of chronic ulceration or inflammation,or burn scars.
- Sites of previous radiation therapy treatment.
BCC rarely metastasizes, so a metastatic workup isusually not necessary.
There are several factors that correlate with poor prognosis for recurrence and metastasis. They apply primarily to patients with SCC and an aggressive subset of nonmelanoma skin carcinoma, but rarely to patients with BCC, and include the following:
- Extranodal extension.
| Laser therapy |
What Are The Risk Factors For Skin Cancer
The most common risk factors for skin cancer are as follows.
- Ultraviolet light exposure, either from the sun or from tanning beds. Fair-skinned individuals, with hazel or blue eyes, and people with blond or red hair are particularly vulnerable. The problem is worse in areas of high elevation or near the equator where sunlight exposure is more intense.
- A chronically suppressed immune system from underlying diseases such as HIV/AIDS infection or cancer, or from some medications such as prednisone or chemotherapy
- Exposure to ionizing radiation or chemicals known to predispose to cancer such as arsenic
- Certain types of sexually acquired wart virus infections
- People who have a history of one skin cancer have a 20% chance of developing second skin cancer in the next two years.
- Elderly patients have more skin cancers.
Most basal cell carcinomas have few if any symptoms. Squamous cell carcinomas may be painful. Both forms of skin cancer may appear as a sore that bleeds, oozes, crusts, or otherwise will not heal. They begin as a slowly growing bump on the skin that may bleed after minor trauma. Both kinds of skin cancers may have raised edges and central ulceration.
Signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinomas include:
Signs and symptoms of squamous cell carcinomas include:
- Persistent, scaly red patches with irregular borders that may bleed easily
- Open sore that does not go away for weeks
- A raised growth with a rough surface that is indented in the middle
- A wart-like growth
Don’t Miss: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
Skin Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Skin
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most common in skin that is often exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, and hands.
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
Surgical Procedures For Basal & Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal or squamous cell skin cancers may need to be removed with procedures such as electrodessication and curettage, surgical excision, or Mohs surgery, with possible reconstruction of the skin and surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer can be aggressive, and our surgeons may need to remove more tissue. They may also recommend additional treatments for advanced squamous cell cancer, such as medications or radiation therapyenergy beams that penetrate the skin, killing cancer cells in the body.
Basal cell cancer is less likely to become aggressive, but if it does, our doctors may use surgery and other therapies to treat it.
What Are Possible Complications Of Skin Cancer In A Child
Possible complications depend on the type and stage of skin cancer. Melanoma is more likely to cause complications. And the more advanced the cancer, the more likely there will be complications.
Complications may result from treatment, such as:
-
Loss of large areas of skin and underlying tissue
-
Scarring
-
Problems with the area healing
-
Infection in the area
-
Return of the skin cancer after treatment
Melanoma may spread to organs throughout the body and cause death.
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Carcinoma Lung Cancer
Early Detection And Treatment Of Skin Cancer
ANTHONY F. JERANT, M.D., University of California, Davis, School of Medicine, Sacramento, California
JENNIFER T. JOHNSON, M.D, Eisenhower Army Medical Center, Fort Gordon, Georgia
CATHERINE DEMASTES SHERIDAN, M.D, Buedingen Army Health Clinic, Buedingen, Germany
TIMOTHY J. CAFFREY, M.D, Commander, Vicenza Army Health Clinic, Vicenza, Italy
Am Fam Physician. 2000 Jul 15 62:357-368.
One in six Americans develops skin cancer at some point. Skin cancer accounts for one third of all cancers in the United States. Most patients with skin cancer develop nonmelanoma skin cancer. This group of cancers includes basal cell carcinoma, the most common neoplasm worldwide, and squamous cell carcinoma. Fortunately, mortality associated with nonmelanoma skin cancer is unusual. However, malignant melanoma accounts for 75 percent of all deaths associated with skin cancer.
Melanoma, the eighth most common malignancy in the United States, is the cancer with the most rapidly increasing incidence. One in 1,500 Americans born in 1935 were likely to develop melanoma, compared with one in 105 persons born in 1993.1 In contrast to nonmelanoma skin cancer, which typically affects older persons, the frequency of melanoma peaks between 20 and 45 years of age.
The rising incidence of skin cancer over the past several decades may be primarily attributed to increased sun exposure associated with societal and lifestyle shifts in the U.S. population and to depletion of the protective ozone layer.3
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
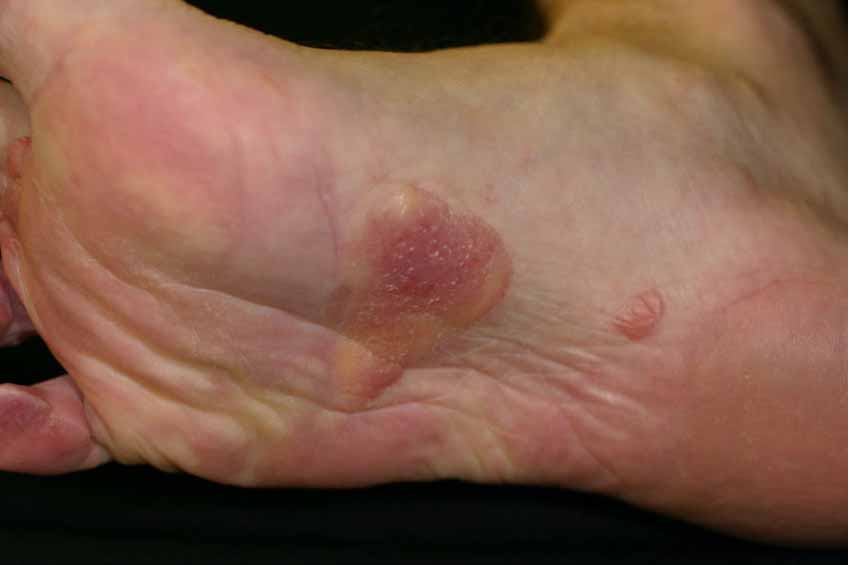
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 3
Skin Cancer On The Face: Types And Prevention
Casey Gallagher, MD, is board-certified in dermatology. He is a clinical professor at the University of Colorado in Denver, and co-founder and practicing dermatologist at the Boulder Valley Center for Dermatology in Colorado.
Because it is exposed to the sun more than other parts of the body, the skin on your face is especially vulnerable to skin cancer. And skin cancer on the face can be mistaken for other conditionssuch as age spots, pimples, scarring, acne, styes, and cysts.
Skin cancers that tend to occur more often on the face include actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The face is also a common site of melanoma and there are several other lesser-common skin cancers that can affect the face. The risk of getting skin cancers on the face increases with high amounts of sun exposure and other ultraviolet light exposure.
About 75% of non-melanoma skin cancers occur on the head or neck.
Skin cancer occurs when cells in the skin’s layers become damaged in ways that cause them to look and act differently than the normal healthy cells around them and start to grow out of control. UV rays play a major role in damaging cells by causing gene mutations.
You can watch for signs of skin cancer on your face by paying attention to new or odd-looking spots or feeling growths, splotches, or moles.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
Recommended Reading: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Read Also: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Alternative And Complementary Therapies For Skin Cancer
Once skin cancer is diagnosed, the only acceptable treatment is medical care. Alternative approaches may be useful in cancer prevention and in combating nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and headaches from chemotherapy, radiation, or immunotherapy used to treat advanced skin cancer. Be sure to discuss any alternative treatments you are considering using with your cancer doctor.
Skin Cancer Symptoms And Signs
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and has a predilection for sun-exposed skin. Tumors may appear as a pearly or waxy bumps usually with visible blood vessels , or as a flat scaly reddish patch with a brown border, or as a hard or scar-like lesion . Frequently BCCs can be itchy, often bleed, or in more advanced cases, ulcerate.
Don’t Miss: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
How Can Women Do A Skin Cancer Body Check At Home
Start by looking in a full-length mirror and use a handheld mirror as well. Then check each part of your body for rapid changes in color, size, shape or border of growths. Start at your scalp and move to your toes, using both mirrors. The American Academy of Dermatology has instructions on its website. They recommend that you do these checks every six to eight weeks.
Dermatologists recommend annual skin exams for adults, especially if you’ve had significant sun damage, tanning bed use or a family history of melanoma. Self-checks should not replace your yearly exam by a dermatologist.
How Skin Cancer Is Treated
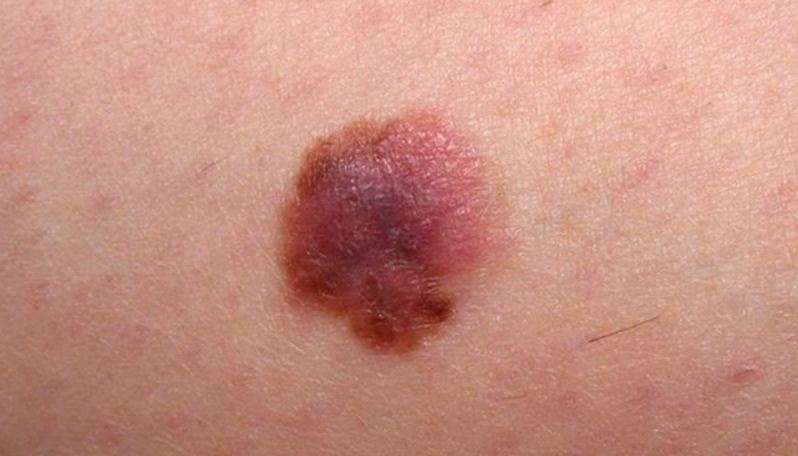
Treatments for skin cancer depend on the type of cancer, the stage, the size and location of the tumor, and its features. For basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas, surgery or electrodesiccation and cautery of the cancer is often all that is needed. Mohs surgery is an additional option to reduce scarring. The treatment of melanoma also includes surgery, but typically with a wider excision. Depending on the cancer stage, additional treatments such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy may be needed.
A team of doctors will work with you to determine your best skin cancer treatment plan. The team may include specialists such as a surgical oncologist, medical oncologist, radiation oncologist, dermatologist, plastic surgeon, and pathologist.
Verywell / Emily Roberts
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize