Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
The causes and risk factors for squamous cell cancer are similar to those for basal cell. Getting too much ultraviolet light causes precancerous skin growths called actinic keratoses . These may develop into squamous cell cancers. AKs may appear as dry, scaly growths in areas of the body that get a lot of sunthe face, ears, hands, arms and legs. AKs may burn or itch.
Signs of squamous cell skin cancer include:
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Diagnosis Of Skin Cancer
It is important to check your skin regularly and check with your doctor if you notice any changes.
In the majority of cases, your GP will examine you, paying attention to any spots that may look suspicious. Your GP may perform a biopsy . In some cases your GP may refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist, if necessary.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell is the most common type of . Getting too much ultraviolet light from the sun or from a tanning bed can harm skin cells and cause basal cell skin cancer. When the damage comes from the sun, basal cell cancer takes years to develop. It usually shows up after age 50. It can develop faster if you use a tanning bed. If you have a light complexion and you burn easily, you are at higher risk for getting this skin cancer.
Signs of basal cell cancers include:
-
A dome-shaped skin growth that grows slowly. You may be able to see tiny blood vessels near the surface.
-
A pale, waxy growth that looks like a scar
-
A shiny, scaly patch that’s pink or red
- A sore that bleeds and crusts but does not heal
To diagnose basal cell skin cancer, doctors take off a small piece of a suspicious growth and check it under a microscope. This procedure is a biopsy. Basal cell cancers are very treatable because they grow slowly and rarely spread. They are almost always curable. Treatment options include:
-
Cryosurgeryfreezing the growth with liquid nitrogen
-
Curettage and electrodessicationscraping away the growth and then destroying any remaining cancer cells with an electrical current
-
Medicated creams
-
Mohs surgeryremoving the cancer and some cells around it layer by layer and using a microscope to check the cells for cancer. If need be, more layers are removed and checked. This continues until the doctor finds no more cancer cells.
- Surgical removal
What Happens If Precancers Go Untreated
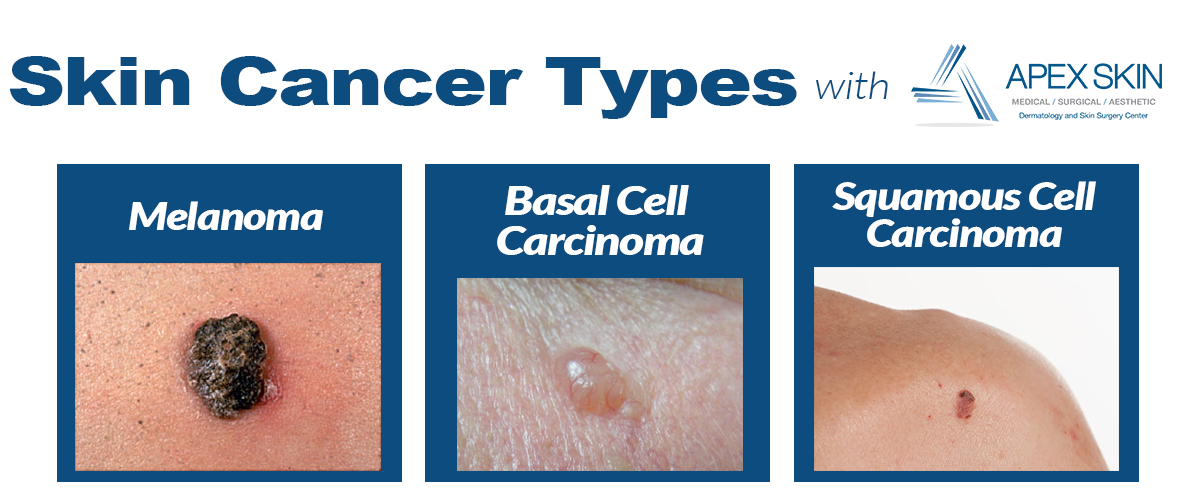
As the name suggests, precancers are damaged skin cells that arent considered cancerous, but if they are left untreated, these lesions are at high risk to become skin cancer. There are two main types of precancerous skin conditions: actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi. Actinic keratosis looks like a rough, scaly patch of the skin that is usually red or brown. This condition may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
Nevi are moles, and dysplastic nevi is a term that means a mole is abnormal. Dysplastic nevi may develop into melanoma without proper treatment. While precancerous skin cancers are not malignant on their own, the potential to develop into life-threatening forms of this condition means they need to be evaluated regularly.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Is Zinc Oxide Sunscreen Good For Skin
There are two types of sunscreen: physical and chemical sunscreens. Physical sunscreens, or mineral sunscreens, work by blocking and scattering UV rays before they penetrate your skin.
Chemical sunscreens on the other hand function by absorbing UV rays before they cause damage to your skin. Both types of sunscreen are safe and effective, though you want to choose one that is comfortable and wearable enough to use daily.
Zinc oxide is a type of mineral-based sunscreen that blocks UV light. For people with sensitive skin or someone wanting a more natural sunscreen, zinc oxide sunscreens are essential in their skincare toolkit.
One of the major downsides of physical sunscreens is the all too common whitecast, or the unblendable layer of sunscreen, that they can cause. While searching for a mineral sunscreen, youll want to look for an option that is lightweight and leaves a satin-y finish on your skin, like the Sdara Zinc Oxide Sunscreen.
Recommended Reading: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
When To Seek Medical Care For Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or have had extensive sun exposure, periodically check their entire body for suspicious moles and lesions.
Have your primary health care provider or a dermatologist check any moles or spots that concern you.
See your health care provider to check your skin if you notice any changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas .
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist or cancer specialist will talk to you about symptoms of metastatic disease that might require care in a hospital.
What Happens If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Like basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma is relatively common, slow-growing, and at low risk to metastasize in most cases. This form of skin cancer is also likely to develop on the areas of the body that are exposed to sunlight like the face, hands, neck, shoulders, and lower legs, especially for people who have a history of sunburns. Unlike the smooth appearance of basal cell carcinoma lesions, squamous cell carcinoma tumors often appear as rough, thickened, scaly patches of skin. The growths may appear wart-like or like a donut shape. Squamous cell carcinoma lesions may form sores and bleed often or develop into a large, thick, and firm mass. Squamous cell carcinoma typically impacts people over the age of 50. While the condition does spread slowly, the risk that squamous cell carcinoma will spread to other parts of the body is higher than that of basal cell carcinoma. Additionally, these have the potential to arise suddenly and grow rapidly in some cases.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Common In Sun
Squamous cell carcinoma, also called squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20 percent of cases.
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores.
Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis .
These cancers might look like:
- A firm, red bump
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A sore that heals and then reopens
People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin.
Other risk factors include:
- Having light eyes, blond or red hair, or freckles
- Being exposed to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Having a history of sunburns
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having the genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum
RELATED: 10 Things You May Know Cause Skin Cancer
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
First, your dermatologist may ask you if you have noticed any changes in any existing moles, freckles or other skin spots or if youve noticed any new skin growths. Next, your dermatologist will examine all of your skin, including your scalp, ears, palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, around your genitals and between your buttocks.
If a skin lesion is suspicious, a biopsy may be performed. In a biopsy, a sample of tissue is removed and sent to a laboratory to be examined under a microscope by a pathologist. Your dermatologist will tell you if your skin lesion is skin cancer, what type you have and discuss treatment options.
Recommended Reading: Is Carcinoma Curable
What Happens If Melanoma Is Left Untreated
Even though this form of skin cancer impacts a relatively low percentage of patients, melanoma skin cancers make up the majority of skin cancer deaths. Melanoma lesions often look like moles, freckles, or sunspots, and they may even develop within an existing mark on your body. Unlike other forms of skin cancer that are slow to progress and unlikely to spread to other areas, melanoma advances quickly and can form or spread anywhere on the body. In order to diagnose melanoma in the earliest stages, patients need to remember the ABCDEFs of melanoma, as discussed above.
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
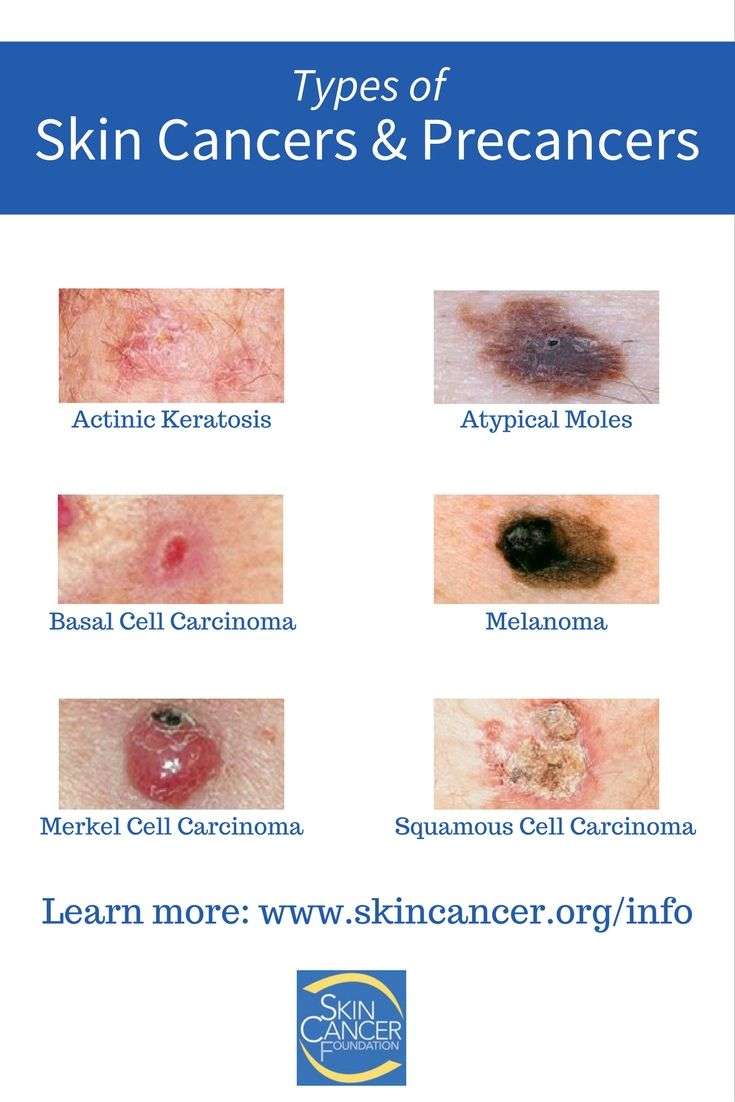
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Also Check: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Types Of Skin Cancers Are Deadly
Skin cancers are some of the most complex and serious conditions treated by dermatologists, and the U.S. Dermatology Partners team takes our role in preventing and treating all types of skin cancers very seriously. While some forms of skin cancer are not typically life-threatening, without proper treatment, there are serious health risks associated with all forms of skin cancer. According to Dr. Jessica Dorsey of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Cedar Park, Texas, Most skin cancers are slow-growing and unlikely to spread to other parts of the body, but without treatment, just about any form of skin cancer has the potential to be destructive or even fatal. Keep reading to learn more about the importance of regular screenings to catch skin cancer in the earliest stages and prevent the severe repercussions of untreated skin cancers.
Rarer Types Of Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
There are other less common types of skin cancer. These include:
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- T cell lymphoma of the skin
- Sebaceous gland cancer
These are all treated differently from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is very rare. Treatment is with surgery or radiotherapy, or both. This usually works well, but sometimes the cancer can come back in the same place. And sometimes it spreads to nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Sebaceous gland cancer
Sebaceous gland cancer is another rare type of skin cancer affecting the glands that produce the skin’s natural oils. Treatment is usually surgery for this type of cancer.
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Kaposis sarcoma is a rare condition. It’s often associated with HIV but also occurs in people who don’t have HIV. It’s a cancer that starts in the cells that form the lining of lymph nodes and the lining of blood vessels in the skin. Treatment is surgery or radiotherapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
T cell lymphoma of the skin
T cell lymphoma of the skin can also be called primary cutaneous lymphoma. It’s a type of non Hodgkin lymphoma. There are a number of different types of treatment for this type of cancer.
Read Also: Metastatic Skin Cancer Pictures
Different Types Of Cancer Start In The Skin
Skin cancer may form in basal cells or squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer. They are also called nonmelanoma skin cancer. Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that sometimes becomes squamous cell carcinoma.
Melanoma is less common than basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
This summary is about basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. See the following PDQ summaries for information on melanoma and other kinds of cancer that affect the skin:
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Cancer
SCC often occurs in areas exposed to UV radiation, such as the face, ears, and hands. However, it can also appear in the mouth, in the anal area, and on the genitals.
In its early stages, SCC often presents itself as a scaly, reddish patch of skin. As it progresses, it can turn into a raised bump that continues to grow. The growth may also crust or bleed. In the mouth, this cancer will take on the appearance of a mouth ulcer or a white patch.
In some cases, youll notice a new growth on a preexisting scar, mole, or birthmark. Any existing lesions or sores that arent healing can also indicate SCC.
Make an appointment with your doctor or dermatologist right away if you notice any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for preventing complications.
Also Check: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Does Sunscreen Prevent Skin Damage
Sunscreen significantly reduces UV ray exposure which reduces the risk of you getting skin cancer. As a sweet additional benefit, wearing sunscreen also slows down the aging process caused by the sun and keeps your skin youthful and glowing.
Everyone and we really mean everyone should be wearing sunscreen daily. Regardless of whether you spend all day indoors, or are working outside all day, you are being exposed to the sun and its UV rays.
Reducing your skins exposure to the sun as much as possible is also key in preventing sun damage. Wearing clothes that cover your skin, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, will help protect your skin from the sun.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Also Check: Is Melanoma In Situ Malignant
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2 cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued