For More Information About Skin Cancer
National Cancer Institute, Cancer Information Service Toll-free: 4-CANCER 422-6237TTY : 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
Media file 1: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
Media file 2: Skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma.
Media file 3: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 5: Skin cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Continued
Media file 6: Skin cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Exams And Tests For Skin Cancer
If you think a mole or other skin lesion has turned into skin cancer, your primary care provider will probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface. Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are thought to be skin cancer, may then be checked. Tests for skin cancer may include:
- The doctor may use a handheld device called a dermatoscope to scan the lesion. Another handheld device, MelaFind, scans the lesion then a computer program evaluates images of the lesion to indicate if it’s cancerous.
- A sample of skin will be taken so that the suspicious area of skin can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy is done in the dermatologist’s office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you may undergo further testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest X-ray, and other tests as needed. This is only needed if the melanoma is of a certain size.
Continued
Also Check: Is An Itchy Neck A Sign Of Cancer
Why Does Skin Cancer Occur In More Non
Scientists dont fully know why people of skin with color develop cancer in non-sun-exposed areas, such as their hands and feet. They think that the sun is less of a factor though. However, dermatologists still see plenty of UV sunlight-induced melanomas and squamous cell skin cancer in people of color, in skin tones ranging from fair to very dark.
Skin Cancer Types: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
What is squamous cell carcinoma of the skin?A common type of skin cancer, squamous cell skin cancer can develop from a pre-cancerous skin growth called an actinic keratosis .
Is it contagious? No
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
When Is A Mole A Problem
If a new or existing mole begins to change shape, color, size, or becomes flaky, crusty, or begins to bleed, it’s time to make an appointment with your dermatologist to get it checked out. A mole can turn into melanoma on rare occasions. In early melanoma, the shape of a mole becomes asymmetrical and uneven.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that is most often found on the head. This type of cancer starts in basal cells, which are tasked with making new skin cells to push the old ones toward the surface of the skin. Nodular basal cell carcinoma is responsible for 60%-80% of all basal cell carcinomas. In the United States, its estimated that 4.3 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed every year, with 2.5 to 3.4 million of those cases being nodular basal cell carcinoma.
This type of cancer appears as a pearl-like papule that is round and surrounded by threadlike red lines on the skin made up of tiny blood vessels. The risk of developing nodular basal cell carcinoma can be increased by spending a lot of time out in the sun, living in high-altitude and sunny locations, and radiation therapy.
Other risk factors include:
- Prolonged exposure to arsenic
- Certain rare genetic disorders such as basal cell nevus syndrome
Although this type of cancer is common, it is highly treatable, and the five-year relative survival rate is 100%.
What Happens If Melanoma Is Left Untreated
Even though this form of skin cancer impacts a relatively low percentage of patients, melanoma skin cancers make up the majority of skin cancer deaths. Melanoma lesions often look like moles, freckles, or sunspots, and they may even develop within an existing mark on your body. Unlike other forms of skin cancer that are slow to progress and unlikely to spread to other areas, melanoma advances quickly and can form or spread anywhere on the body. In order to diagnose melanoma in the earliest stages, patients need to remember the ABCDEFs of melanoma, as discussed above.
Also Check: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
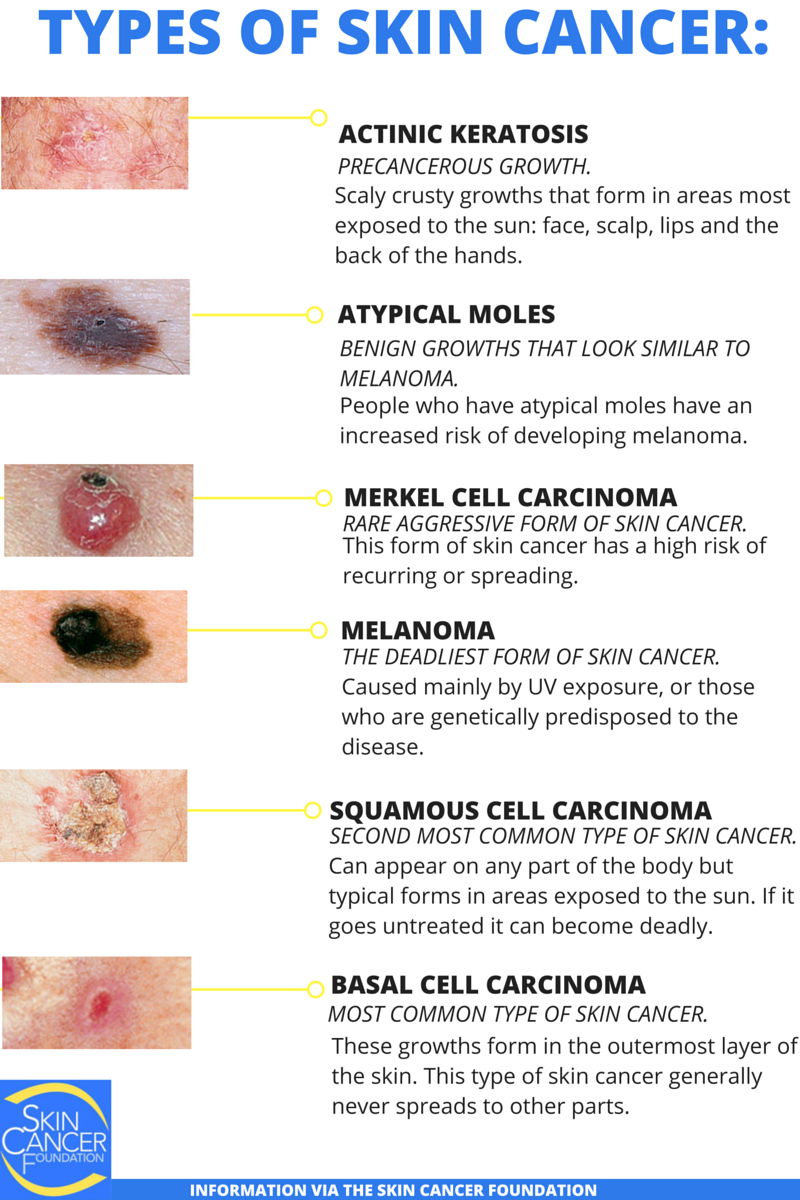
Skin Cancer Pictures By Type
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer. There are several different types of skin cancer with Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Bowens Disease, Keratoacanthoma, Actinic Keratosis and Melanoma most commonly occurring.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, and least dangerous whereas melanoma is the most dangerous type.
Below you will find skin cancer pictures of these six types, but remember that skin cancer should be diagnosed by a doctor. Comparing your skin lesion to skin cancer images found online cannot replace medical examination.
If you have any pigmented mole or non-pigmented mark on your skin that looks different from the other marks or moles on your skin, that is new or that has undergone change, is bleeding or wont heal, is itching or in any way just seems off, visit your doctor without delay dont lose time comparing your mole or mark with various pictures of skin cancer.
If you want to be proactive about your health, you may want to photograph areas of your skin routinely including individual moles or marks to familiarise yourself with the appearance of your skin . A skin monitoring app may be a useful tool to assist in that process.
MIISKIN PROMO
Don’t Miss: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Are All Moles Cancerous
Most moles are not cancerous. Some moles are present at birth, others develop up to about age 40. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles.
In rare cases, a mole can turn into melanoma. If you have more than 50 moles, you have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your skin is the largest organ in your body. It needs as much attention as any other health concern. What may seem like an innocent cosmetic imperfection, may not be. Performing regular skin self-checks is important for everyone and is especially important if you are a person at increased risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is also color-blind. If you are a person of color, skin cancer can happen to you. Check your skin every month for any changes in skin spots or any new skin growths. Consider taking skin selfies so you can easily see if spots change over time. If youre a person of color, be sure to check areas more prone to cancer development, such as the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, your genital area and under your nails. Takes steps to protect your skin. Always wear sunscreen with SPF of at least 30 every day of the year. Wear UV-A/UV-B protective sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeve shirts and pants. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin check.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/19/2021.
References
Knowledge Is Your Best Defense
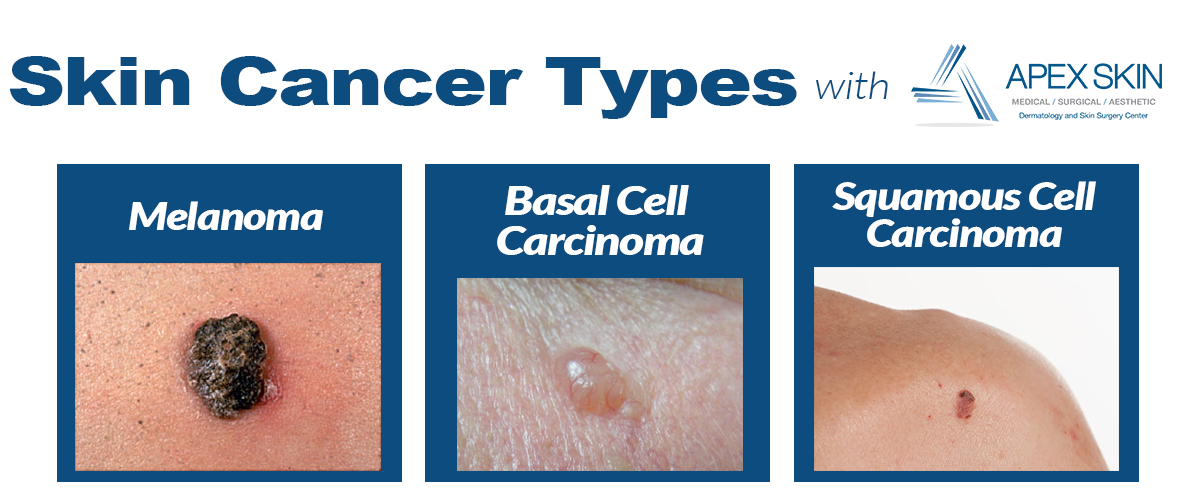
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of abnormal cells in the epidermis, the outermost skin layer, caused by unrepaired DNA damage that triggers mutations. These mutations lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. The main types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma .
The two main causes of skin cancer are the suns harmful ultraviolet rays and the use of UV tanning beds. The good news is that if skin cancer is caught early, your dermatologist can treat it with little or no scarring and high odds of eliminating it entirely. Often, the doctor may even detect the growth at a precancerous stage, before it has become a full-blown skin cancer or penetrated below the surface of the skin.
Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Identifying Skin Cancer: 37 Photos You Need To See
As we head into summer, its time to kick your safe skin practices into high gear. All individuals should apply a broad spectrum SPF every day, and watch their local UV forecast for daily updates when outside activities are planned.
Why? Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. One in five Americans will be diagnosed with the disease in his or her lifetime. There are more new cases of skin cancer every year than breast, prostate, lung and colon cancers combined, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although family history and your natural skin pigmentation play a role in your risk, the number-one thing that causes skin cancer is exposure to UV rays.
Erin Gilbert, M.D., Ph.D., a spokesperson for the Skin Cancer Foundation, offered these guidelines to weather.com in 2014: Avoid the sun when its at its peak wear sun-protective clothes, such as a hat always wear a broad-spectrum SPF. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or after swimming or sweating.
Its a myth that most sun damage occurs in childhood, so theres nothing you can do about it as an adult, Dr. Gilbert said.
Twenty-three percent of sun damage happens before youre 18, but it is cumulative. Its never too late to start protecting yourself, she said. Your melanoma risk doubles if youve had more than five severe sunburns at any age. Dont let a sunburn or a tan deter you from seeing your dermatologist or wearing sun screen the next day.
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Are Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin , and are often related to sun exposure.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer cells. To learn more about cancer and how it starts and spreads, see What Is Cancer?
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun damage DNA in your skin, causing abnormal cells to form. These abnormal cells rapidly divide in a disorganized manner, forming a mass of cancer cells.
Another cause of skin cancer is frequent skin contact with certain chemicals, such as tar and coal.
Many other factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. See question, Who is most at risk for skin cancer?
Also Check: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Cells Involved In Skin Cancer
Skin cancer begins in your skins top layer that is in the epidermis. The epidermis is a thin layer on your skin, a protective cover of skin cells that the body continually sheds. The epidermis consists of three types of cells and they include:
- Squamous cells: It lies below the outer surface of your skin and function as the skins inner lining.
- Basal cells: It produces new skin cells, stays beneath the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: It produces melanin, the pigment that gives skin its normal color. It is located in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanocyte produces more melanin when you are exposed to the sun to help protect the deeper layers of the skin.
Tracking Changes To Your Skin With An App
Some people find it helpful to photograph areas of their skin such as the back or individual lesions to be able to better spot any future changes.
Over the past years, smartphone apps that can help consumers track moles and skin lesions for changes over time have become very popular and can be a very helpful tool for at-home skin checks.
This page does not replace a medical opinion and is for informational purposes only.
Please note, that some skin cancers may look different from these examples. See your doctor if you have any concerns about your skin.
It might also be a good idea to visit your doctor and have an open talk about your risk of skin cancer and seek for an advice on the early identification of skin changes.
* Prof. Bunker donates his fee for this review to the British Skin Foundation , a charity dedicated to fund research to help people with skin disease and skin cancer.
Make a difference. Share this article.
Also Check: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Squamous cell carcinoma also appears in areas most exposed to the sun and, as indicated in the pictures below, often presents itself as a scab or sore that doesnt heal, a volcano-like growth with a rim and crater in the middle or simply as a crusty patch of skin that is a bit inflamed and red and doesnt go away over time.
Any lesion that bleeds or itches and doesnt heal within a few weeks may be a concern even if it doesnt look like these Squamous cell carcinoma images.
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100 non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call a basal cell cancer a rodent ulcer.
There are a number of different types of BCC. Each type can look and behave differently. They include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
You May Like: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate