Are There Any Other Health Issues Related To Uv Radiation
In addition to skin cancer, exposure to UV rays can cause other health problems:
- UV rays, either from the sun or from artificial sources like tanning beds, can cause sunburn.
- Exposure to UV rays can cause premature aging of the skin and signs of sun damage such as wrinkles, leathery skin, liver spots, actinic keratosis, and solar elastosis.
- UV rays can also cause eye problems. They can cause the cornea to become inflamed or burned. They can also lead to the formation of cataracts and pterygium , both of which can impair vision.
- Exposure to UV rays can also weaken the immune system, so that the body has a harder time fending off infections. This can lead to problems such as reactivation of herpes triggered by exposure to the sun or other sources of UV rays. It can also cause vaccines to be less effective.
Some people are more sensitive to the damaging effects of UV radiation. Some medications can also make you more sensitive to UV radiation, making you more likely to get sunburned. And certain medical conditions can be made worse by UV radiation.
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
Donât Miss: Can Skin Cancer Be Inherited
Skin Cancer From Sun Exposure: How It Happens
Heres how you can get skin cancer from sun exposure:
- The suns light contains several types of UV radiation. Two types of this radiationUVA and UVBreach the earths surface.
- UVB rays cause sunburns, while UVA rays cause accelerated skin aging. Although UVB rays have a greater impact on the likelihood of skin cancer both types of radiation contribute to skin cancer formation.
- Essentially, both types of UV radiation penetrate your cells and cause damage to their DNA. This damage is replicated with the cells reproduction, and it is cumulative.
- If your cells accumulate too much DNA damage from this radiation, they may start growing and reproducing too rapidly.
- The out-of-control growth that develops is known as skin cancer.
Although the likelihood of metastasis varies depending on the type of skin cancer in question, most skin cancers can eventually spread from the skin to other organs. This is why early detection is so important.
You May Like: Do Skin Cancer Spots Appear Suddenly
What Changes In The Skin Occur Due To Exposure To The Sun
Exposure to sun causes most of the wrinkles and age spots on our faces. People think a glowing complexion means good health, but skin color obtained from being in the sun can actually speed up the effects of aging and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
Sun exposure causes most of the skin changes that we think of as a normal part of aging. Over time, the sunâs ultraviolet light damages the fibers in the skin called elastin. When these fibers break down, the skin begins to sag, stretch, and lose its ability to go back into place after stretching. The skin also bruises and tears more easily in addition to taking longer to heal. So while sun damage to the skin may not be apparent when youâre young, it will definitely show later in life. The sun can also cause issues for your eyes, eyelids, and the skin around the eyes.
Changes in the skin related to sun exposure:
- Precancerous and cancerous skin lesions caused by loss of the skinâs immune function.
- Fine and coarse wrinkles.
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
How Can Uv Light Cause Skin Cancer

Every time UV light hits our skin, it can damage some of the DNA inside our skins cells. This happens every time we:
-
Spend time in the sun without sun protection
-
Use indoor tanning equipment
The body tries to repair this damage. When the body can no longer repair all the damage, changes called mutations develop in our skins cells. The mutated cells, which are cancer cells, can multiple quickly. As these cells pile up, a tumor develops.
When a tumor forms in skin cells called squamous cells, we get SCC of the skin. These cells are found in the outermost layer of our skin, which is called the epidermis. The following picture shows you where these cells live.
Recommended Reading: When To Get Skin Cancer Screening
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells that is divided into two main types: melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. Non-melanoma skin cancer grows slowly in the upper layers of the skin and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
The second, and more dangerous, type of skin cancer is melanoma skin cancer. Melanomas can spread to other organs in the body, and in 2020 it was estimated that over 320,000 people worldwide were diagnosed with melanoma skin cancer.
Melanoma can spread to other organs in the body. It often spreads to nearby lymph nodes first, before spreading to other vital organs. If this happens, it becomes much harder to treat. That means it is very important to look out for signs of melanoma and catch it at an early stage.
What About Tanning Beds
Some people think that getting UV rays from tanning beds is a safe way to get a tan, but this isnt true.
Both IARC and NTP classify the use of UV-emitting tanning devices as carcinogenic to humans.
The US Food and Drug Administration , which refers to all UV lamps used for tanning as sunlamps, requires them to carry a label that states, Attention: This sunlamp product should not be used on persons under the age of 18 years.
The FDA also requires that user instructions and sales materials directed at consumers carry the following statements:
- Contraindication: This product is contraindicated for use on persons under the age of 18 years.
- Contraindication: This product must not be used if skin lesions or open wounds are present.
- Warning: This product should not be used on individuals who have had skin cancer or have a family history of skin cancer.
- Warning: Persons repeatedly exposed to UV radiation should be regularly evaluated for skin cancer.
The FDA has also proposed a new rule to ban the use of indoor tanning devices by anyone under age 18, to require tanning facilities to inform adult users about the health risks of indoor tanning, and to require a signed risk acknowledgment from all users. Some US states have already banned indoor tanning by all people younger than 18, while others have banned use by younger teens and children.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer On Top Of Head
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors Of Skin Cancer
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by ultraviolet radiation produced by the sun, but other risk factors also are linked to these skin cancers. Risk factors listed below can increase the risk for skin cancer.
Ultraviolet radiation: Too much exposure to UV radiation is a risk factor for skin cancer. The main source of such radiation is sunlight and tanning lamps and booths.Race: People with fair skin, freckling or red or blond hair have a higher risk. The risk of skin cancer is much higher for whites than for dark-skinned African Americans.Moles: Certain types of moles, including some large moles, increase the chance of getting melanoma.Family history: People with a family history of skin cancer are at increased risk . A person who has already had melanoma is at a higher risk of getting another melanoma.Exposure to chemicals: Exposure to large amounts of arsenic, a heavy metal used in making some insecticides, increases the risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer.Radiation: Radiation treatment increases the risk of developing nonmelanoma skin cancer in the area that was treated.Gender: Men are more likely to develop skin cancer than women.Age: More than 50 percent of all melanomas occur in people older than 50 years of age.
How To Spot Skin Cancer
For melanoma skin cancer, any change to your skin can be a concern and people are advised to regularly check their entire body for new or changed moles. The commonly used guidelines include looking for the ABCD signs:
- Asymmetry two halves of the mole differ in shape
- Borders edges may be irregular or blurred, sometimes show notches
- Colour may be uneven, different shades of black, brown and pink
- Diameter most melanomas are at least 6mm across
The more common non-melanoma skin cancer is not connected to moles and is often less dangerous than melanoma. Nevertheless, people should look out for non-melanoma skin cancer signs:
- Scab/sore that wont heal
- Scaly/crusty patch of skin that is red/inflamed
- Flesh coloured lump that wont go away and grows
- Volcano like growth with rim and crater
To find out more about the symptoms and how to spot skin cancer, go to the NHS website.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Non Melanoma Skin Cancer
Do Some People Have A Higher Risk Of Developing Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Cancer
Yes. The key risk factors for getting this skin cancer are listed below. A risk factor is anything that increases your risk of developing a disease.
While having one or more risk factors for SCC of the skin increases your risk of developing it, some people who get this skin cancer dont seem to have any risk factors. People of all colors get this skin cancer, including people of African, Asian, and Latin descent.
If you find a spot on the skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist to find out what it is. Youll find out how this skin cancer is diagnosed and treated at, Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Diagnosis and treatment.
1 American Academy of Dermatology. Indoor tanning fact sheet. Last accessed January 31, 2019.
2 Omland SH, Ahlstrom MG, et al. Risk of skin cancer in patients with HIV: A Danish nationwide cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 79:689-95.
ImagesGetty Images
ReferencesAnadolu-Brasie R, Patel AR, et al., Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 86-114.
Nadhan KS, Chung CL, et al. Risk factors for keratinocyte carcinoma skin cancer in nonwhite individuals: A retrospectiveaAnalysis. J Am Acad Dermatol , doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.038.
Omland SH, Ahlstrom MG, et al. Risk of skin cancer in patients with HIV: A Danish nationwide cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 79:689-95.
What Causes Basal And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
While many risk factors for basal and squamous cell skin cancers have been found, its not always clear exactly how these factors might cause cancer.
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet rays from sunlight, as well as from man-made sources such as tanning beds.
UV rays can damage the DNA inside skin cells. DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes help control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth in check by slowing down cell division or causing cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA changes that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control.
Researchers dont yet know all of the DNA changes that result in basal or squamous cell skin cancer, but they have found that in many skin cancers the cells have changes in tumor suppressor genes.
These are not the only gene changes that play a role in the development of skin cancer. There are many others as well.
You May Like: What Does Vulvar Melanoma Look Like
If You Have One Of The Two Types Of Non
- A sore that crusts, bleeds, or oozes without scabbing over and healing for a period of several weeks
- One patch of skin appears tight and shiny like a scar
- A red, raised patch with or without itching
- A dip in the skin with a raised border
- A shiny, pearl-like bump
The terms basal cell and squamous cell refer to the layer of the skin where a doctor diagnoses a carcinoma, which means the skin contains cancer cells. Basal cell skin cancer means that cancer is present in the skins epidermis. Squamous cell skin cancer resides in the skins subcutaneous layer.
How Uv Radiation Increases Skin Cancer Risk
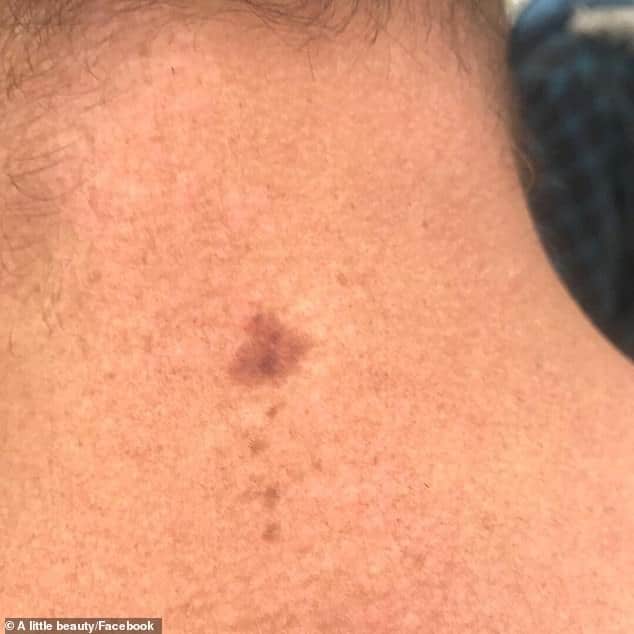
When your skin is unprotected from the sun, ultraviolet radiation can damage your DNA. If the body is unable to repair this damage the cell can begin to divide and grow in an uncontrolled way. This growth can eventually form a tumour.
UV radiation is made up of UVA and UVB rays which can penetrate the skin and cause permanent damage, contributing to melanoma and other skin cancers, sunburn, skin ageing and eye damage:
- UVA penetrates deeply into the skin causing genetic damage to cells, photo-ageing and immune-suppression.
- UVB penetrates the top layer of the skin causing damage to the cells. UVB is responsible for sunburn a significant risk factor for skin cancer, especially melanoma.
Get to know your skin and consult your doctor if you notice any changes or new spots.
Its also important to remember that damage is not always visible, damage starts long before a sunburn or tan occurs, and is permanent and cumulative much of the DNA damage to skin cells is impossible to repair by our body.
Don’t Miss: How To Make Skin Glow
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- What are the long-term effects of sun exposure?
- What type of skin cancer do I have?
- What caused my skin cancer?
- How do I protect myself from the suns UV rays?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Ultraviolet radiation is necessary because it provides vitamin D to help you survive, but its also harmful with overexposure. You can take care of your skin and prevent skin cancer from ultraviolet radiation by wearing sunscreen outdoors and staying out of the sun when its at its brightest in the middle of the day. Nearly 80% of a persons lifetime sun exposure occurs before age 18. You can become a good role model and foster skin cancer prevention habits for your family by taking preventive measures when you go outside.
- American Cancer Society. Ultraviolet Radiation. Accessed 11/16/2022.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Multiple pages reviewed. Accessed 11/16/2022.
- Environmental Protection Agency. The UV Index Scale. Accessed 11/16/2022.
- Skin Cancer Foundation. Multiple pages reviewed. Accessed 11/16/2022.
- Tung R, Vidimos A. Melanoma. In: Carey WD, ed. Cleveland Clinic: Current Clinical Medicine 2010, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier 2010:section 3.
- World Health Organization. Multiple pages reviewed.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
What Really Causes Skin Cancer
Exposure to the sun does not cause skin cancer , but do you know what does? Ive got your ironic right here, Alanis Morissette: What really causes skin cancer is
Sunscreen!
Those crafty globalists arent too bright, but what does that say about all the people who blindly believe all the things they somehow manage to convince so many of? Those 3-letter deities that you are not to question. WHO, you might ask?
Exactly.
Heres a couple more questions, which well address in a minute:
If the sun causes skin cancer, how did our ancestors get enough vitamin D from sunlight without getting skin cancer? And, Do any vitamins or supplements help to prevent or reduce the risks of cancer?
Read Also: What Does Insight 2 Melanoma Mean
How Does The Sun Change My Skin
Exposure to the sun causes:
- Pre-cancerous and cancerous skin lesions – due to decreases in the skin’s immune function
- Discolored areas of the skin, called mottled pigmentation
- Sallowness — a yellow discoloration of the skin
- Telangiectasias — the dilation of small blood vessels under the skin
- Elastosis — the destruction of the elastic and collagen tissue
Are There Different Types Of Radiation In Sunlight
Yes. The types of radiation include:
- visible light, which gives us the colours we see
- infrared radiation which gives us the warmth we feel
- ultraviolet radiation
Except in extreme situations, neither visible light nor infrared radiation from sunlight causes health problems. However, ultraviolet radiation can cause harmful effects to the skin.
There are three basic types of ultraviolet radiation:
Also Check: Can Kids Get Skin Cancer
Does Sunlight Cause Skin Cancer
Health Canada states that one of the main causes of skin cancer is ultraviolet light, which is produced by the sun and tanning equipment.
Skin cancer is an occupational concern for people who work under the sun. The risk however, may be reduced through awareness of the problem, and by taking measures to prevent exposure to sunlight.
People At Particular Risk
Children and adolescents are particularly vulnerable to the harmful effects of UVR due to their skin and eye structure. Sunburns in childhood lead to a higher risk of skin cancer in later life. Also, a larger amount of UVR can reach and damage their retina.
Fair-skinned people suffer more from sunburn and have a higher risk of skin cancer than dark-skinned people however, darker-skinned people also develop skin cancers. Consideration of eye damage is important for everyone.
People at increased risk include those with a high number of naevi, those taking photosensitizing medication, and those with a family history of skin cancer.
Outdoor workers exposed occupationally to solar UVR levels face an increased risk of developing non-melanoma skin cancers.
Recommended Reading: How Would I Know If I Have Skin Cancer