How Veterinarians Diagnose Pyoderma In Dogs
In order to diagnose your dog with pyoderma, your veterinarian will need to start with a physical exam. Based on the presence of certain lesionssuch as pustules the veterinarian may be comfortable diagnosing your pet based on what he or she determines from the physical exam. Diagnostic testing is usually necessary, and may include:
- Skin cytology: A veterinarian will take an impression smear or tape sample of the affected areas of skin and look at it under a microscope. This is a non-invasive test that allows the veterinary staff to look for bacteria and yeast.
- Skin scraping: This can be used to look for mites, such as Sarcoptes scabiei or the Demodex species under the microscope.
- Culture and sensitivity: A swab of the affected skin area may be sent to a diagnostic laboratory for fungal and/or bacterial culture and sensitivity testing. Results typically take several days and enable vets to pinpoint the exact types of bacteria and/or fungus that are the root causes of the infection.
- Your vet will also prescribe the medication that will work best to treat that specific infection. Ringworm culture may be performed in-house at your veterinary clinic. Bacterial culture and susceptibility are recommended if your pet has recurrent skin infections, or the infection is deep and severe.
Causes Of Bacterial Infection Of The Skin In Dogs
Pyoderma can be associated with many different conditions and veterinarians often struggle to find the exact cause. The following conditions are often related.
- Any chronic form of dermatitis
- Fungal or yeast infection
- Endocrine imbalance that reduces lymphocyte counts like Cushings disease , and hypothyroidism
Treatment Of Fungal Dermatitis & Staph Infection In Dogs
Yeast dermatitis infections can be treated with oral or topical treatments, or a combination of both based on the severity of your dogs condition. These medications are highly effective, though they must be given for a prolonged period .
These drugs can have potential side effects on the liver that will require close monitoring with routine blood tests.
Staph infections are typically treated with oral antibiotics. Antibacterial shampoo or topical ointments can be used for these types of skin conditions. Depending on the severity of the infection, treatment may take several weeks to have an effect.
Because staph infections can be passed between dogs and from dogs to humans, extra care should be taken when handling and treating your dog.
Discuss any supplements or medications your dog is currently taking with your veterinarian so he or she can choose the best treatment for your pets individual circumstances while helping to reduce the risk of a potential interaction between drugs.
Note: The advice provided in this post is intended for informational purposes and does not constitute medical advice regarding pets. For an accurate diagnosis of your pet’s condition, please make an appointment with your vet.
Is your dog showing signs of a bacterial or fungal skin infection? Contact our Greensboro vets right away to schedule an appointment for testing. Our vets are experienced in diagnosing a number of conditions and illnesses.
Don’t Miss: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help With Skin Cancer
Herbal Remedy For Bacterial Skin Infections In Dogs
For a skin infection that’s NOT deep-rooted i.e. a superficial scrape, cut, or abrasion, natural remedies work well.
While studying natural remedies for dogs, I made careful notes of some holistic treatments recommended by Dr. Randy Kidd that you can try. See below:
Choose one or more of the following herbs and brew into a tea:
Calendula has antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties. It’s an excellent herb to choose as it also speeds up healing and encourages tissues growth. Calendula contains salicylic acid as a pain-relieving agent also found in Asprin.
Aloe the fresh juice of aloe is especially useful for wounds and burns including sunburn. Take the leaf of a raw aloe plant and squeeze the juice directly onto the wound.
Chamomile Chamomile speeds wound healing and work particularly well for inflamed cuts. It can also calm a dog’s anxiety when applied topically.
Lavender aids in healing while easing aches and pains.
Mullein promotes healing and soothes inflamed areas.
Plantain The leaf acts as a drawing agent when used as a poultice. Suitable for removing foreign bodies that may be deep in wounds.
St-John’s-wort eases pain, speed healing of wounds, especially good with bruises, and mild burns.
Yarrow – Stops bleeding from oozing wounds and is an excellent healing herb.
Symptoms Of Skin Infection In Dogs
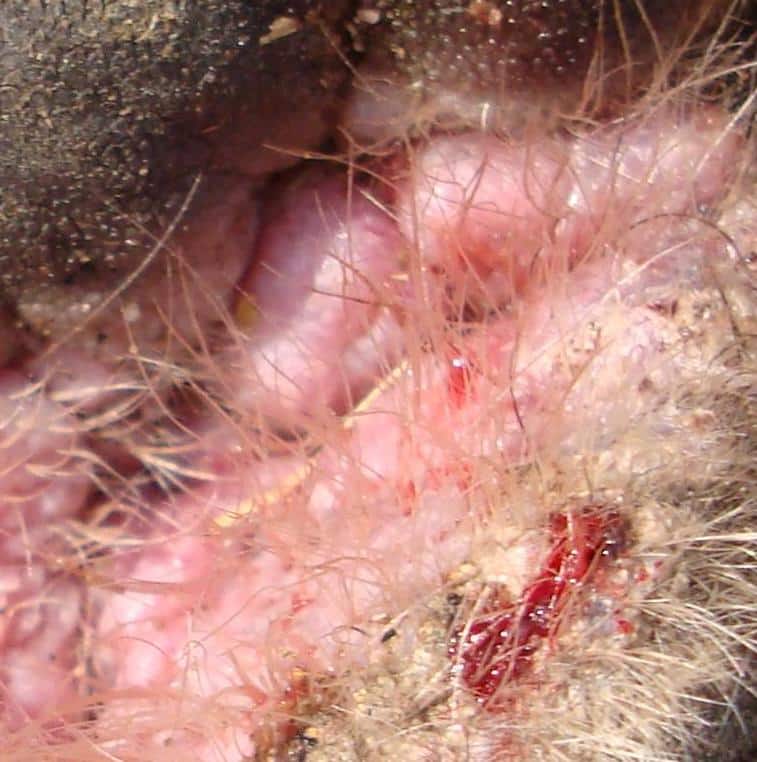
Clinical signs associated with a skin infection in dogs can vary depending on the specific cause, but early manifestations of the skin condition can be similar regardless of the cause. Commonly seen symptoms are itchiness, hair loss, and generalized discomfort. Skin flaking and crusting can also be seen in some cases of skin infection.
Generalized redness, erythema, and skin inflammation can also be observed in dogs with skin infections. Untreated and severe cases will eventually emit a pungent or foul odor, and can even be fatal to highly susceptible and immunocompromised animals.
Don’t Miss: Blue Lagoon Iceland Skin Care
Best Practices In Sbf Therapy
Recently, guidelines for antimicrobial therapy for canine superficial bacterial folliculitis were published . These recommendations emphasized the need for demonstration of cocci from lesional skin by cytology as a powerful adjunctive diagnostic test . It is good practice to perform impression cytology as an in-clinic test while diagnosing skin infections. Appropriate techniques have been described for both specimen collection and examination to optimize the value of this diagnostic procedure .
Bacterial culture for canine pyoderma is never contraindicated and is, in fact, encouraged in patients with chronic or recurrent pyoderma due to the increased frequency of isolation of antibiotic resistant staphylococci in veterinary medicine over the past decade. Careful consideration for bacterial culture should also be given to dogs that have received repetitive antibiotic therapy. When bacterial culture is indicated for a patient, generally a 48- to 72-hour washout period after antibiotic therapy is desirable. It is, however, acceptable to collect samples for bacterial culture and susceptibility testing from pyoderma lesions at any time, regardless of the current use of topical or systemic antibiotic .
How Are Bacterial Infections In Dogs Treated
If your dog has a bacterial infection, it would be best for your dog to see your vet. They can prescribe them antibiotics to help clear this infection. If they have a skin infection or wound, your vet may also want to send home shampoos or ointments for you to also use on your dog. Make sure that you follow the direction from your vet to help your dog quickly recover from their bacterial infection.
For a really bad infection, your vet may take a sample of their skin, urine, or discharge from their ears or eyes. They can send these samples to the lab to see what bacteria is growing and what bacteria will treat these infections.
If your dog has recently been diagnosed with a bacterial infection, or if your think that your dog has a bacterial infection, it would be best for your vet to help them get better. Your vet can prescribe medication to help quickly clear this infection. In severe cases, your dog may need a culture to make sure that they do not have a resistant bacterial infection. With the proper treatment and care, your dog can quickly recover from these infections.
Your veterinarian may also recommend doing routine lab work, such as blood work or a urinalysis to identify any underlying causes of infeciton. It is important to have a baseline so when your dog does become ill, we have something to compare to. Routine blood work is a benefit and should be considered as your pet ages.
Meet The Author
Don’t Miss: Does Merkel Cell Carcinoma Bleed
Do I Have To Be Concerned About Recurrent Staph Infection In My Dog
Absolutely. A recent concern in the veterinary community has been the emergence of methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococcal bacteria that have become resistant to commonly-used antibiotics. Round after round of antibiotics to treat the infection can lead to bacterial mutation, and multiple antibiotic resistance. While antibiotic resistant infections once were seen only among humans, they are now seen in dogs as well.
Preventing Future Skin Infections In Dogs
It is best to prevent a bacterial skin infection before it occurs. Reed Animal Hospital provides pet owners with suggestions for prevention and proactive prevention for your dogs health. Dog owners should be vigilant in their awareness of potential symptoms of skin infections to help maintain their dogs good health. This includes frequent bathing and cleaning under any folds where infections can grow. Food allergies need to be addressed right away, as these can cause skin irritation that may eventually lead to an infection. Ask our team if any medication, shampoos, or a change in diet can reduce your dogs risk of a bacterial or viral skin infection.
Read Also: How Deep Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Go
What Is The Prognosis For My Pet’s Condition
The prognosis for uncomplicated pyoderma in the majority of cases is good to excellent. Most cases of pyoderma resolve with oral antibiotics and/or topical therapy. Chronic or recurrent cases may require additional testing to determine if there is an underlying condition contributing to the bacterial skin infection. Routine bathing with medicated shampoos can minimize recurrences.
How Do We Diagnose Pyoderma
Pyoderma is diagnosed by history and clinical examination, and supported by cytologic findings.
Cytology is important for several reasons it:
- Identifies coexistent staphylococcal and Malassezia infections in order to resolve the infections, both need to be treated
- Confirms the presence of bacteria and white blood cells
- Helps to differentiate pyoderma from other cutaneous diseases that mimic, or may coexist with, pyodermas, such as pemphigus foliaceus.
Samples can be obtained for cytology in several ways.
- Clear tape is an excellent way to collect materials from feet and skin folds, as well as from collarettes. See Step by Step: Using Clear Tape for Cytologic Evaluation of Pyoderma.
- Direct impression smears can be obtained from moist lesions and pustule exudate, allowed to dry, and then stained.
- A dry #10 blade can collect crusts from very dry lesions, which are then placed on a slide and minced into sterile saline. Once dried, the slide can be stained and examined.
Culture and sensitivity is recommended for all generalized deep pyodermas and if treatment with 2 different classes of oral antibiotic, repeated courses of a previously effective antibiotic, or one injection of cefovecin18 fail to resolve any superficial or deep infections .
Don’t Miss: How To Detect Melanoma Skin Cancer
Ways To Diagnose A Bacterial Skin Infection
There are several ways to diagnose a bacterial skin infection. The most accurate way to diagnosis this condition is to culture the skin. A skin culture is becoming a more common procedure in the veterinary clinic. During this procedure, a sterile cotton tip applicator is applied to the skin and the sample swab is placed into a tube and submitted to an outside laboratory. The culture is used for bacterial growth and the laboratory will isolate and identify the bacteria. These isolates are then challenged with individual classes of antibiotics. Based on the growth response to a given antibiotic the bacteria will be classified as resistant or susceptible . This data will help the veterinarian choose the best antibiotic for the affected individual. A veterinarian can simply choose an antibiotic without a skin culture however, this choice may or may not help your pet.
What Are The Common Symptoms Of Dog Skin Conditions
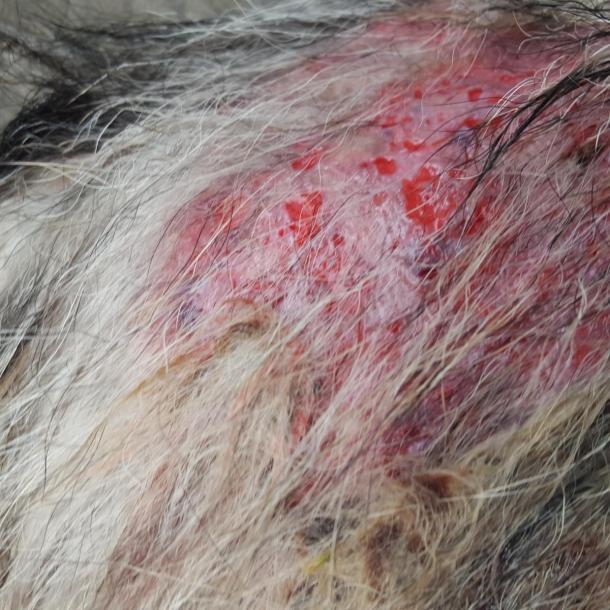
The only way to know whether your dog is healthy or not is to observe changes in their appearance and behavior. If you notice something out of the ordinary, consult a vet.
When it comes to skin conditions, it’s best to check your pet every couple of days and look for obvious symptoms – such as your pet scratching more than usual.
You should be on your toes whenever you introduce a new food or during the allergy season so that you can notice the potential allergic reactions in time. Note down all the changes you see – and report them to your veterinarian.
The more information your vet has, the sooner they can get a complete and accurate diagnosis of your dog’s skin infection or allergy.
So, what are the most common symptoms you should be on the lookout for here?
Here’s a quick overview:
Of all the listed symptoms, itching is the most common – and the most difficult to spot. Your dog can have an occasional itch under normal circumstances – that’s perfectly fine.
So, how can you know when something more serious is going on?
Frequent or prolonged itching are some of the most obvious symptoms of dog skin conditions that call for concern. If you notice your pet is often rubbing its head against an object, scratching with its paws, or licking paws, you should consult a vet.
Read More:Heart Murmurs In Dogs: What Does It Mean For Your Pet?
Also Check: How Do You Get Basal Cell Carcinoma
Rule Out Internal Causes Of Your Dog’s Skin Condition
Consider if the reason your dog is itching is due to a more serious health condition that may need a very specific treatment.
Dog skin conditions and problems can be caused by serious diseases like cancer, Cushing’s disease, autoimmune disease, hyperthyroidism or hormone imbalances in the canine’s body.
While they usually do not cause itching in dogs, they may be interrelated with the above-mentioned skin infections in dogs.
As there are numerous causes of skin lesions in dogs, it is important to determine the underlying cause to help guide treatment recommendations. Dr. Alison Diesel, DVM
This is why it’s important to seek veterinary care quickly.
You can use the best dog skin infection treatment products while you’re waiting to get an appointment.
But your vet will give your dog a thorough examination to see if there is any underlying conditions that lead to these dog skin conditions in the first place.
Underlying Conditions To Skin Infections
Bacterial skin infections can often develop due to an underlying condition that causes the skin to become more fragile. All skin conditions, many immunologic or metabolic abnormalities can lead to secondary skin infection. An example of this would be in a dog that suffers from allergic skin disease allergic skin disease, regardless of what the dog is allergic to, is incredibly itchy that can lead to skin trauma and thus infection. In addition, their skin microbiota is modified and more prone to let bad bacteria overgrow. Certain breeds may be more susceptible to bacterial infections as they are predisposed to certain underlying conditions, for example in the case of breeds predisposed to developing allergies, Labrador Retrievers, Shar Peis, Boxers and Boston Terriers are amongst the breeds more likely to be affected.
Also Check: Are White Spots On Your Skin Cancer
A Healthy Dog Will Be Able To Fight Infections And Skin Rashes But If You Suspect Bacterial Infections Its Best To Consult With A Veterinarian
- How to diagnose bacterial skin infection in dogs?
A dogs skin is very sensitive, and it can take a lot for a dog to develop a bacterial skin infection. This is why its important that you get your dog to the vet if you suspect one, as they will be able to diagnose the issue and prescribe treatment options. If you notice any of these symptoms on your dog:
- Redness or swelling around an area of hair loss
- Dry patches of fur on their back or hips
- Small scabs appear over areas where there were previously no rashes
* Itchy areas of fur that feel rough and bumpy * Redder than normal skin, especially around ears or on the face * Dry flaky patches on their skin when they were clean before these are usually caused by bacterial infections.
Final words
Bacterial skin infections are common in dogs but can be easily treated by a veterinarian. If your dog shows signs of a bacterial skin infection, take him to the vet as soon as possible so he can be properly diagnosed and treated with antibiotics. The sooner your pet receives treatment for his bacterial skin condition, the better off he will be because if left untreated it could lead to more serious problems like internal organ damage or even death
Which Bacteria Cause Pyoderma In Dogs
The major canine skin pathogen is S pseudintermedius 11 however, Staphylococcus schleiferi, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa have also been identified in canine pyoderma.
S aureusa human pathogenhas been identified in a low percentage of dogs. However, this bacterium has received a great deal of attention due to its methicillin resistance in humans and potential role as a zoonotic agentdogs infected with methicillin-resistant S aureus most likely acquired the infection from a human.
S pseudintermedius, while not as virulent, shares many characteristics with S aureus, including:
- Enzyme and toxin production
- Ability to adhere to matrix adhesive proteins
- Ability to form biofilms.
Methicillin-resistant S pseudintermedius is unlikely to cause human infection, unless a person is very young, very old, or immunocompromised.
S schleiferi was first identified from human clinical specimens in 1988, and has now been identified as a cause of pyoderma and otitis externa in dogs.12-14
P aeruginosawhile not commonhas been identified on the skin of dogs, particularly in lip fold pyodermas and postgrooming folliculitis.15-16
Identifying the particular Staphylococcus species involved in skin infections, and its antimicrobial sensitivity, is important with regard to determining whether the dog is infected with a methicillin-resistant strain.
Don’t Miss: Can Skin Cancer Go Away On Its Own
Treatment For A Bacterial Infection
First, bathe your dog with a good quality medicated shampoo that contains an antibacterial agent.
I found a great medicated shampoo to try is Derma Treat.
Derma-Treat has antibacterial, antiseptic, and antifungal properties that treats many skin irritations in dogs.
Derma-Treat is highly regarded by holistic MDs and has even been voted as the professional groomers’ ultimate choice for severe cases of skin problems where nothing else seems to
Baths should be given twice a week for the first 2 weeks, then scale down to once a week for a month and finally just once a month.
Antibiotics and/or ear-drops may be prescribed by your veterinarian for a bacterial skin infection. But be warned, if you just treat the infection with antibiotics alone, and don’t determine the root cause, it may come back time and time again.