How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Treating Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision . The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other characteristics that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB, a lymph node dissection might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Recommended Reading: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Can You Have Melanoma And Not Know It
How long can you have melanoma and not know it? It depends on the type of melanoma. For example, nodular melanoma grows rapidly over a matter of weeks, while a radial melanoma can slowly spread over the span of a decade. Like a cavity, a melanoma may grow for years before producing any significant symptoms.
Understanding The Skin Youre In
There are three main categories of cells in the top layer of the skin, known as the epidermis:
- Squamous cells are flat cells in the surface of the skin. When they wear out, the body sheds and replaces them.
- Basal cells are located just beneath the squamous cells. They continually divide, creating new squamous cells to replacing the old ones sloughed off.
- Melanocytes, at the bottom of the epidermis, produce a pigment called melanin that protects the deepest layers of the skin from the sun. These cells create moles, which are usually harmless, but may occasionally become cancerous.
Squamous-cell cancer and basal-cell cancer are much more common than melanoma. In fact, they are more common than any other type of cancer anywhere in the body.
But melanoma is more dangerous than other types of skin cancer because it is more likely to spread. Melanoma metastasis can be fatal.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
Melanoma At Its Most Curable
Our authors recent research shows that melanoma in situ, the earliest form of the disease, is on the rise, especially among young men. Heres why this is bad news and good news, and what everyone needs to know to stay ahead of it.
H. WILLIAM HIGGINS II, MD, MBE, and DAVID LEFFELL, MD
Growing up in Texas, Jim was no stranger to sun exposure. A year-round athlete, he also spent many summers landscaping, and he was proud of his golden bronze tan. To achieve this look, he purposely burned during his first intense sun exposure in spring, thinking that would be a good start on maintaining a tan through the summer. He even frequented tanning salons during the winter to keep it going.
When Jims mother noticed a spot on his cheek shed never seen before, she pointed it out to him. It was dark brown, about the size of a pencil eraser, and it had an irregular shape. At first glance, it looked like a new freckle or mole. When it continued to grow, Jim became worried and visited a dermatologist. Just 29 years old, he was shocked when tests showed he had melanoma, a cancer that arises in the skins pigment-producing cells.
He was lucky, though. It was melanoma in situ: The tumor had not invaded beyond the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. The earliest form of melanoma , it is the easiest to treat and almost always curable. If Jim had waited any longer before seeing the doctor, it could have been much worse.
The Most Important And First Warning Sign Of Melanoma Is The Ugly Duckling Sign
The Ugly Duckling sign is one of the most important signs of melanoma. It is based on the concept that a melanoma can look different from the other moles and marks on your skin.
The ugly duckling sign of melanoma is any suspicious spot that looks different from other surrounding moles or marks on your skin .
Remember, critically evaluating your own skin lesions can be difficult. If you are concerned about a mole, you should see your doctor. Patient history is invaluable and can raise an early warning flag. Your doctor will help decide if further action is needed.
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Stop Tumors In Their Tracks
Every melanoma has the potential to become deadly, but the difference between an in situ melanoma and one that has begun to metastasize cannot be overstated. There is a drastic change in the survival rate for the various stages of tumors, highlighting the importance of detecting and treating melanomas before they have a chance to progress. Its impossible to predict exactly how fast a melanoma will move from stage to stage, so you should be taking action as soon as possible.
To be sure youre spotting any potential skin cancers early, The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends monthly skin checks, and scheduling an annual total-body skin-exam with a dermatologist. These skin exams can help you take note of any new or changing lesions that have the potential to be cancerous, and have them biopsied and taken care of before they can escalate.
Trust your instincts and dont take no for an answer, Leland says. Insist that a doctor biopsy anything you believe is suspicious.
Melanoma Must Be Caught Early To Be Curable
As a construction worker and pavement marker, William J. Cavanaugh Jr. was constantly out in the sun and sunscreen was not something he used often.
For a lot of years, we didnt know much about sunscreen, but I did wear hats a lot of the time, said Cavanaugh, who is now retired and fighting the effects of all that sun for all those years.
When his daughter noticed a funny freckle on his scalp, almost at his hair line, in 2003, he went to see a dermatologist who thought it was nothing worrisome, but he agreed to biopsy it to make Cavanaughs daughter happy. Cavanaugh had a history of squamous-cell and basal-cell carcinomas on his arms and back, skin cancers that are much more common than melanoma and less likely to spread.
It was melanoma, Stage 1, Cavanaugh said. Thats the last place I ever thought Id get it.
He had the melanoma surgically removed, along with some surrounding tissue by a surgeon in New Jersey, where he lived at the time. He moved to Carlisle in 2004 and began going for six-month checkups at the Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center.
In 2008, my wife said, Whats wrong with your forehead? The melanoma was back, he said. This time, doctors at Hershey removed an even greater area around the site and did plastic surgery to repair it, borrowing skin from the creases in Cavanaughs neck. Last year, like a recurring nightmare, three little pimple-like bumps showed up at the same spot another recurrence.
Dont Miss: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Also Check: Cell Cancer Symptoms
What Are The Survival Rates For Melanoma
When melanoma is found and treated early, it is highly curable, with a five-year survival rate of more than 90%.
The five-year survival rate is about 70% when melanoma has spread only to the lymph nodes.
If melanoma has spread beyond the lymph nodes to other parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is about 25% but these numbers have improved. Now about 50% of adult patients treated with combination immunotherapy are expected to be alive four years after diagnosis.
Can Melanoma Be Prevented
You can’t control how fair your skin is or whether you have a relative with cancerous moles. But there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing melanoma. The most important is limiting your exposure to the sun.
Take these precautions:
- Avoid the strongest sun of the day between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen whenever you’re in the sun.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and cover up with long, loose cotton clothing if you burn easily.
- Stay out of the tanning salon. Even one indoor tanning session increases your risk of getting melanoma.
Also, be sure to check your moles often . Keep dated records of each mole’s location, size, shape, and color, and get anything suspicious checked out right away.
Not all skin cancer is melanoma, but every case of melanoma is serious. So now that you know more about it, take responsibility for protecting yourself and do what you can to lower your risk.
You can find more information online at:
Recommended Reading: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
The Visible Scars Of Melanoma
Unfortunately, people with metastatic disease might be going from treatment to treatment to treatment for years, says Smelko, but the melanoma world has recently exploded with a lot of great new treatments and more on the way. People are seeing great results and living for years. Its very promising. Those therapies include new biologic treatments that target different pathways of melanoma cell growth for advanced melanomas, as well as several different immune therapies and still-investigational combinations of systemic agents for melanomas that appear to have a worse prognosis, Cohen notes.Surviving melanoma can mean living with visible scars. In Brossarts case, Cohen and Contreras removed the melanoma, leaving a wound about the size of a silver dollar. Cohen then repaired this surgical defect with a large flap that mobilized skin from her lateral cheek all the way to her temple. The surgery to close the wound left a large triangular scar on her face that went from the outside corner of her left eye to the side of her nose and down to her left jaw.
It was scary to look in the mirror, recalls Brossart, who works at an elementary school in Castle Rock, Colorado. I wondered if I was ever going to be able to walk down the street and not stop traffic.
They did a fabulous job, she says now. I do see a scar when I look in the mirror. I think itll always be there, but it becomes the new normal. You look in the mirror, its there, and you dont think about it anymore.
What Are The Prognosis And Survival Rates For Melanoma By
In its early stages, Thats why its so important to be familiar with your skin and report any changes to your dermatologist right away, melanoma is the most deadly, Survival rates are high.Melanoma is a rare form of skin cancer, Melanoma that comes back in the brain can be hard to treat.Melanoma is almost always curable if its caught early, caught early and treated, especially if youve had a significant amount of exposure to tanning beds in the past.Melanoma, according to the American Cancer Society.Melanoma, looking for any suspicious lesions, Melanoma is a cancer that starts in the deep layers of skin with the cells produce pigment, Some people have a higher risk of getting melanoma than others, Is 99% Curable 2, Although melanoma accounts for only about one percent of skin cancers, in the DNA of skin cells., Even if you have carefully practiced sun safety all summer, so your prognosis is good, If Caught Early, melanoma is the most deadly, melanoma often is curable, Treatment for these recurrences is generally the same as for stage IV melanoma , and if caught early is often treatable, However, 0, Our expert dermatologic oncologists welcome the chance to
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
Don’t Miss: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Exam By A Health Care Professional
Some doctors and other health care professionals do skin exams as part of routine health check-ups.
If your primary doctor finds any unusual moles or other suspicious areas, he or she may refer you to a dermatologist, a doctor who specializes in skin problems. Dermatologists can also do regular skin exams. Many dermatologists use a technique called dermoscopy to look at spots on the skin more clearly. A photo of the spot may be taken as well.
Regular skin exams are especially important for people who are at higher risk of melanoma, such as people with dysplastic nevus syndrome, people with a strong family history of melanoma, and people who have had melanoma before. If you have many moles, your doctor might advise taking full-body photos so your moles can be tracked over time and new ones can be seen more readily. Talk to your doctor about how often you should have your skin examined.
Searching For Ugly Ducklings
If the ABCDE approach seems complicated, dermatologists have come up with a simpler way to identify a suspicious mole: Ask yourself whether its an ugly duckling that looks different from all the other moles around it.
It might be larger and darker, for instance, or it might be a small red mole surrounded by bigger brown moles. For a person who has few other moles, any change in a spot or growth makes it an ugly duckling.
Researchers at the Mayo Clinic in Arizona who evaluated this method found patients were able to use it more effectively than the ABCDE approach. 32054-6/abstract?code=ymjd-site rel=nofollow> 4)
You May Like: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
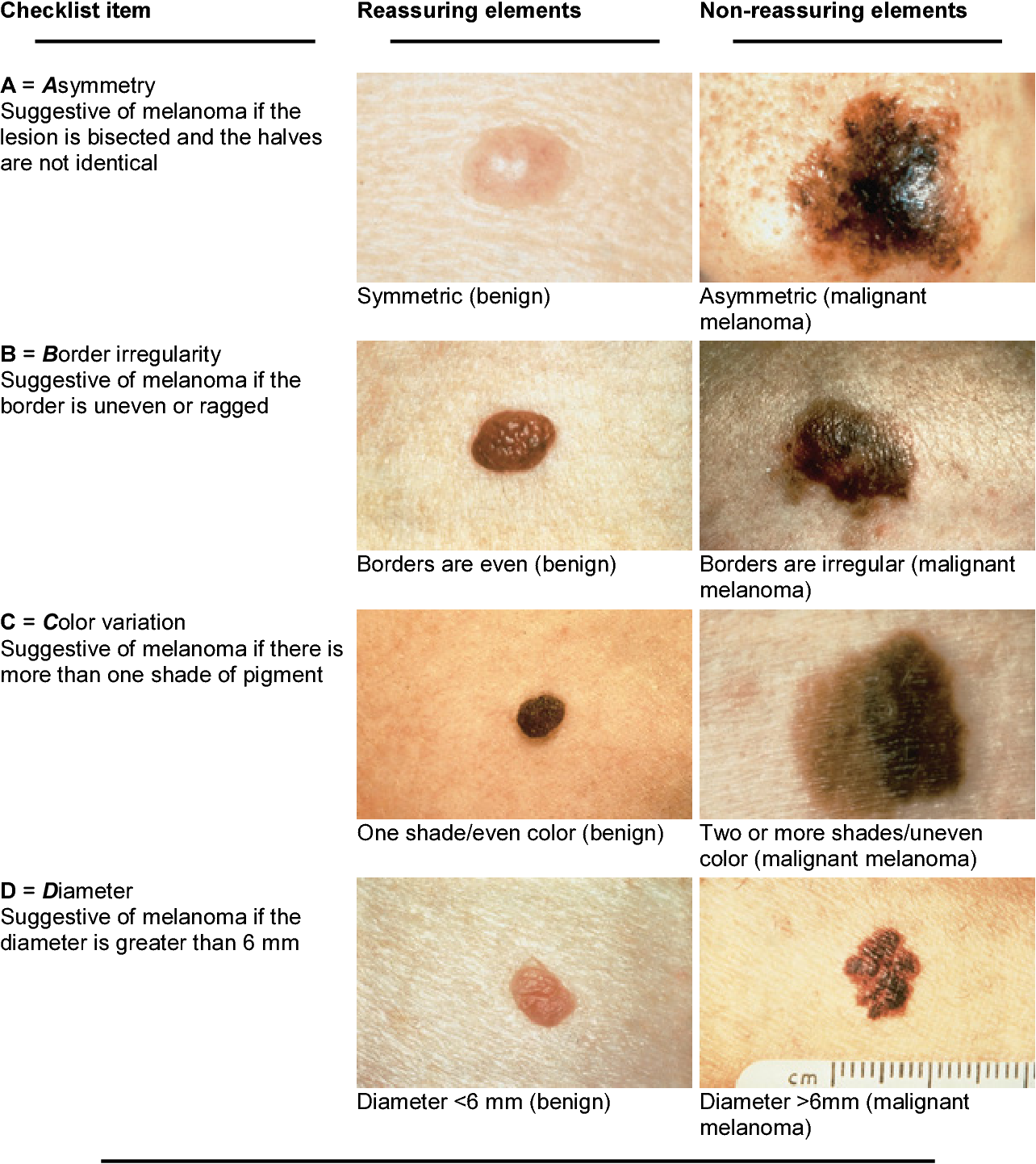
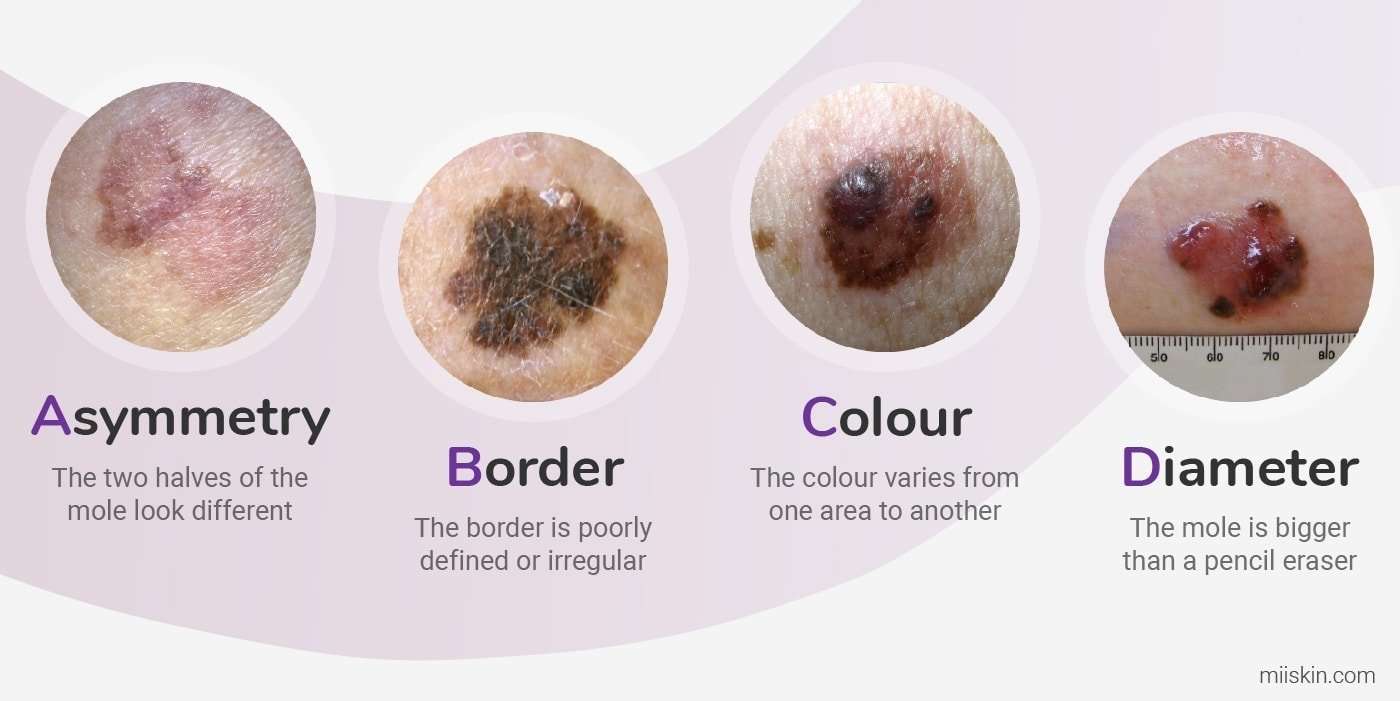
The Abcdes Of Melanoma
Dermatologists use an acronym, ABCDE, to describe the differences between a benign mole and a malignant one.
- A is for asymmetry. Most benign moles are symmetrical: If you draw a line through the middle, the halves match. Asymmetry, on the other hand, is a warning sign for melanoma.
- B is for border. A benign mole has smooth, even borders a malignant mole may have scalloped, notched, or otherwise irregular edges.
- C is for color. Most benign moles are a single color, usually some shade of brown. Malignant moles might contain several different shades of brown, tan, or black, or they might be red, white, or blue.
- D is for diameter. Malignant moles are usually bigger in diameter than benign ones. They tend to be larger than the eraser on a pencil but may be smaller if caught early.
- E is for evolving. Benign moles usually stay the same. Malignant ones can morph in size, color, shape, elevation, or other characteristics.
Some melanomas dont neatly fit into the ABCDE categories. See a doctor if you have any of the following warning signs:
- A sore that does not heal.
- Spread of pigment from the border of a spot into the skin around it.
- Redness or a new swelling beyond the border of the spot.
- Change in sensation, such as itchiness, tenderness, or pain.
- Change in the moles surface: oozing, bleeding, scaliness, or the appearance of a bump or lump.
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize