How Can Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Be Prevented
Currently, Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant skin cancer that has no preventive measures. However, the following factors may help reduce the risk for the condition:
- Avoid or minimize sun exposure
- Limit the use of tanning beds and tanning parlors
- Smoking cessation
- If it is caused by certain underlying disorders, then treating the underlying disorder may help in the treatment and early cure of BCC of skin
Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its metastasizing potential and high possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary
Can You Treat It Naturally
Luckily, the BCC is a type of cancer that may be treated naturally. The treatment options like hydrogen peroxide, baking soda and apple cider vinegar can eradicate the cancerous cells, while the vitamin C and vitamin E can help to heal your damaged skin.
1. Hydrogen Peroxide
The hydrogen peroxide can be used for the treatment of the cancer through oxygenation. The peroxide is able to naturally break down into its parts one is the oxygen. The extra oxygen can create an environment which is unsuitable for those cancer cells, so they will naturally die off. If you want to use this treatment, soak one cotton swab in a hydrogen peroxide and then you should rub the cancerous growth until that area is saturated and white. It can sting. After this, place a soaked cotton pad with hydrogen peroxide over that area and let it dry. You need to apply the treatment once a day.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
The apple cider vinegar is very rich in nutrients, it contains many beneficial enzymes and potassium. These nutrients can help the body to regenerate the soft tissue. Also, it can aid in alkalizing your body, so the system is able to fight the cancer naturally. You can implement the treatment with ACV as both oral supplement and a topical application. You can swab the affected area every day, or you can soak one cotton pad with apple cider vinegar and let it dry on your affected area. You should drink 1 to 2 tbsps. of apple cider vinegar diluted in eight ounces of distilled water.
What Is The Treatment For Primary Basal Cell Carcinoma
The treatment for a BCC depends on its type, size and location, the number to be treated, patient factors, and the preference or expertise of the doctor. Most BCCs are treated surgically. Long-term follow-up is recommended to check for new lesions and recurrence the latter may be unnecessary if histology has reported wide clear margins.
Recommended Reading: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCCs usually develop on parts of the body that are often exposed to the sun, like the head, face, shoulders, arms and lower legs.
They often start with a subtle change in the skin, like a small bump or a flat red patch.
Signs of a BCC to look for include:
- a pearly spot or lump
- a scaly, dry area that is shiny and pale or bright pink in colour
- a sore that doesnt heal
- a sore that bleeds
See your doctor if you notice any new spots or an existing spot that changes size, shape or colour. Visit the Cancer Councils website for tips on how to check your skin.
Baking Soda Hydrogen Peroxide
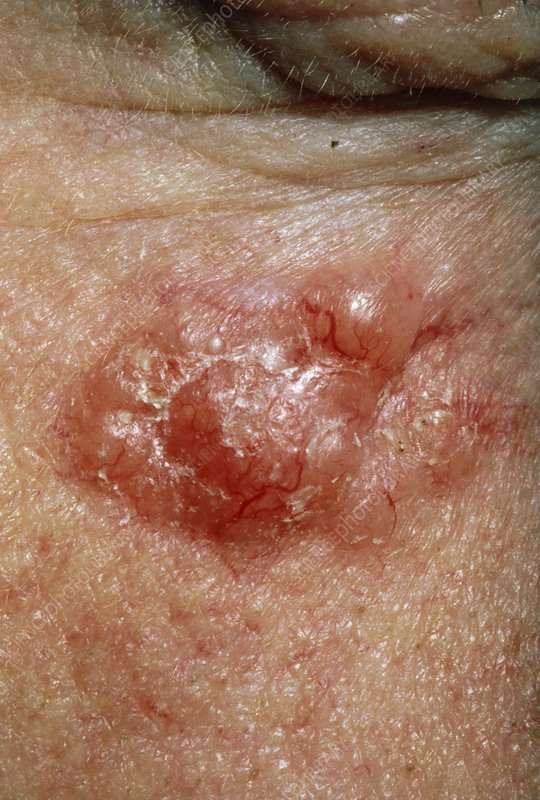
For around 2yrs I had a sore on my head that wouldn’t heal, it was risen around the edge and depressed in the middle, kinda like a crater. I had a bad habit of picking it and assumed that was why it wouldn’t heal so I decided to leave it alone and I put a paste of water and bicarbonate of soda on it at night for a few weeks and it cleared up in no time even although I would forget to put the bicarb on for days at a time.
A few months later a similar eruption appeared nearer the crown of my head and shortly after that another smaller one near it. This time I used 3% Hydrogen Peroxide as I could put it on throughout the day without the hassle of the caked bicarb in my hair. It felt like a needle being stabbed into my brain the first few times I done it, I got such a shock but it only lasted a minute or two and by the third of fourth application I didn’t feel anything. Both sores cleared up within two weeks.
I’ve read with great interest some of the remedies here. I’ve just had a punch biopsy by a local skin doctor the results of which gave the diagnosis of Multifocal and Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma.
I went out and bought some of the ingredients that were mentioned and seemed to be most effective, like: Raw Organic Apple Cider Vinegar, Milk Thistle, 3% Hydrogen Peroxide, Vitamin C Crystals, Iodine and Colloidal Silver. Any good recipes, using these ingredients?
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Cancer Prognosis
Basal Cell Carcinoma Home Remedy And Other Natural Treatment
Basal cell carcinoma is skin cancer. This type of cancer has shown increasing number of the people who are affected with it. People with white skin are more likely to get basal cell carcinoma. The main reason for this disease is the high UV radiation which comes from the sunlight . You should avoid the sum when is hottest. Also you should not go out at the midday if you are not having any type of work. Protect your skin with cream when you are exposed to the sun. Also you should wear protective clothes to avoid the sunburns. There are many types of medicines that you can use it. We recommend you to use the following Basal Cell Carcinoma home remedy and natural cures:
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Read Also: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
What Are The Clinical Features Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is a locally invasive skin tumour. The main characteristics are:
- Slowly growing plaque or nodule
- Skin coloured, pink or pigmented
- Varies in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration
BCC is very rarely a threat to life. A tiny proportion of BCCs grow rapidly, invade deeply, and/or metastasise to local lymph nodes.
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
Also Check: Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
How Dermatologists Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
When possible, BCC is treated with a procedure called surgical removal. If you have an early BCC, this can often be performed in your dermatologists office while you remain awake. The following explains the types of surgical removal used to treat BCC, along with other treatment options.
Surgical removal: Three types of surgical removal are used to treat BCC. The type of surgical removal you receive depends largely on the type of BCC you have, where its located, and how deeply it goes.
Heres what involved with each type of surgical removal:
Freezing or light therapy: While surgical removal is often the preferred way to treat BCC, one of these following procedures may be recommended for some patients.
-
Freezing: The procedure is called cryotherapy , and it can be performed during an office visit. Cryotherapy involves spraying an extremely cold substance, such as liquid nitrogen, on the BCC to destroy the tumor.
-
Light therapy: The medical name for this procedure is . Its a two-part procedure. First, a solution that makes your skin more sensitive to light is applied to the cancer and a bit of skin around it. Youll sit with this solution on your skin for one to several hours.Once your skin is ready, it will be treated with a blue or red light to kill the cancerous cells.Light therapy can effectively treat some early BCCs, but you may need repeat treatments.
For a few patients, this may be the only treatment prescribed.
How Is Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. These cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes or other organs, but they can grow quite large and invade small nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the basal cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are often nodular and do not have nerve involvement. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed. An aggressive growth pattern on the pathology evaluation and perineural invasion are also features of high-risk basal cell cancers.
Recommended Reading: 2nd Stage Cancer
Answer: Risk Of Not Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a locally destructive type of skin cancer that is notorious for recurrence when not adequately treated. It can become quite disfiguring if left untreated, especially when located in cosmetically sensitive areas such as the nose. Typically this type of skin biopsy is performed for diagnosis and is not adequate treatment for a skin cancer. Biopsies sample a portion of the lesion, leaving some behind. This type of sampling biopsy is not intended to remove the entire lesion. It is not advisable to leave a known skin cancer untreated as it will likely grow and become more of a problem to remove in the future. Mohs micrographic surgery allows for 100% margin control and is tissue-sparing, which means it offers the highest cure rate while preserving as much normal tissue as possible.
What Is The Likely Outcome For Someone Who Has Bcc
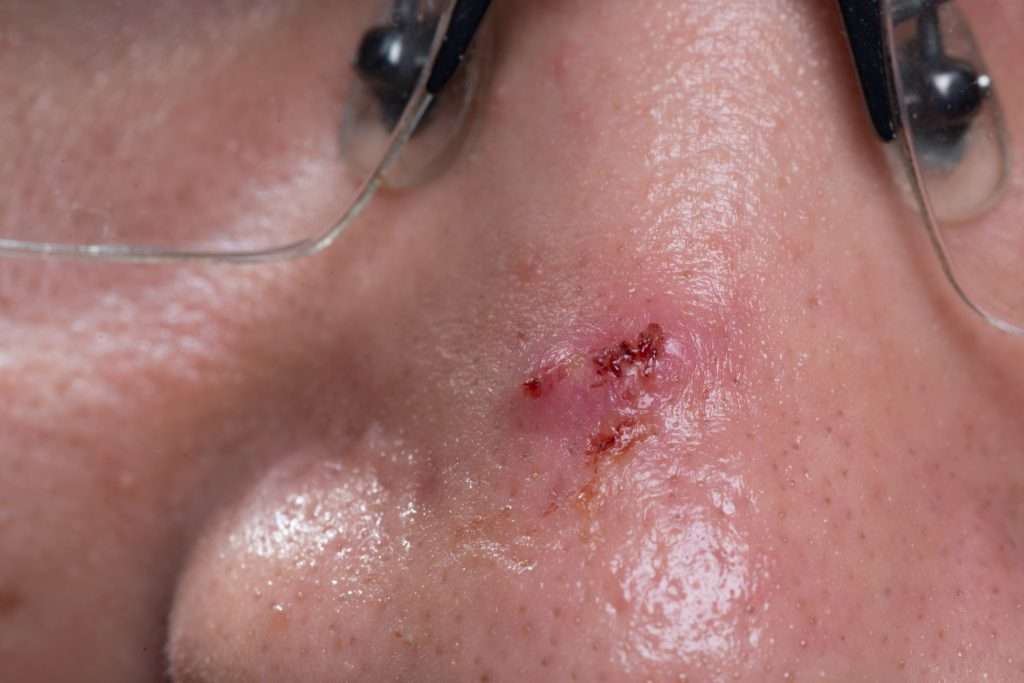
When found early and treated, this skin cancer can often be removed. However, this skin cancer can return. You also have a higher risk of developing another BCC or other type of skin cancer.
Thats why self-care becomes so important after treatment for BCC. Youll find the self-care that dermatologists recommend at, Basal cell carcinoma: Self-care.
ImageGetty Images
ReferencesBichakjian CK, Armstrong A, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 78:540-59.
Bichakjian CK, Olencki T, et al. Basal cell skin cancer, Version 1.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016 14:574-97.
Cameron MC, Lee E, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: Epidemiology pathophysiology clinical and histological subtypes and disease associations. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019 80:303-17.
Cameron MC, Lee E, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: Contemporary approaches to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019 80:321-39.
Nouri K, Ballard CJ, et al. Basal cell carcinoma. In: Nouri K, et al. Skin Cancer. McGraw Hill Medical, China, 2008: 61-81.
Xie P, Lefrançois P. Efficacy, safety, and comparison of sonic hedgehog inhibitors in basal cell carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018 79:1089-100.
10/21/21
You May Like: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Choosing To Stop Treatment Or Choosing No Treatment At All
For some people, when treatments have been tried and are no longer controlling the cancer, it could be time to weigh the benefits and risks of continuing to try new treatments. Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Some people, especially if the cancer is advanced, might not want to be treated at all. There are many reasons you might decide not to get cancer treatment, but its important to talk to your doctors and you make that decision. Remember that even if you choose not to treat the cancer, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms.
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100 non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call a basal cell cancer a rodent ulcer.
There are a number of different types of BCC. Each type can look and behave differently. They include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
Recommended Reading: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cause Complications
The most common complication of basal cell carcinoma is recurrence. BCCs commonly recur, even after successful treatment. In some cases, BCC may reappear in the same place. It can also be disfiguring, especially if not treated promptly.
A diagnosis of BCC increases the chance of developing other types of skin cancer. This includes melanoma, which can metastasize and is the most life-threatening form of skin cancer.
Rare, aggressive forms of BCC can invade the body beyond the skin. It can destroy bone, nerves, and muscles. In rare cases it can metastasize to other parts of the body, including key organs, and become life-threatening.
Recommended Reading: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
How Is Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Diagnosed
Some of the tests that may help in diagnosing Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin include:
- Complete physical examination with detailed medical history evaluation
- Examination by a dermatologist using a dermoscopy, a special device to examine the skin
- Woods lamp examination: In this procedure, the healthcare provider examines the skin using ultraviolet light. It is performed to examine the change in skin pigmentation
- Skin or tissue biopsy: A skin or tissue biopsy is performed and sent to a laboratory for a pathological examination, who examines the biopsy under a microscope. After putting together clinical findings, special studies on tissues and with microscope findings, the pathologist arrives at a definitive diagnosis
- Differential diagnosis of other tumors should be ruled out hence, a skin tissue biopsy is an important diagnostic tool
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
How To Recognize Diagnose And Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. In fact, it is estimated that about 2 million Americans hear the words, You have basal cell carcinoma, each year.
For most, basal cell carcinoma is treatable and not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body. However, early detection is vital. Below, we will review what basal cell carcinoma looks like, how it is diagnosed, and how it is treated.
Also Check: Immunotherapy For Malignant Melanoma
How Doctors Treat Basal Cell Carcinomas
Dermatologists usually remove basal cell carcinomas with liquid nitrogen. Painless and efficient, the procedure freezes the cancerous skin and, when performed by a doctor, leaves healthy skin intact. Larger basal cell carcinomas, especially when they occur on the forehead or nose, may require minor plastic surgery with careful attention to wound care for several weeks to achieve a cosmetically acceptable result.
Dont try removing basal cell carcinomas with liquid nitrogen at home. And dont use certain natural remedies like bloodroot salve , either. Bloodroot is caustic, and burns into the healthy layers of the skin. Treating yourself with bloodroot hurts, and will leave a scar. Even worse, if you happen to apply the herbal remedy to a melanoma or other spreading cancer, you risk trapping bits and pieces of the cancer underneath the scar tissue bloodroot salve leaves on your skin. Underneath the scar, these more serious forms of skin cancer may go undetected until treatment requires extensive surgery.
Dont Miss: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn