How Can I Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma
The best way to prevent basal cell carcinoma is to limit sun exposure:
-
Stay out of the sunsit in the shade, try to avoid the sun between 10:00 am and 4:00 pm
-
Don’t sunbathe or use tanning beds
-
Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and hats with broad brims
-
Use sunscreen thats at least 30 sun protection factor it’s important to use more sunscreen every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating
See a doctor if you see a change in a skin growth that doesn’t go away after a few weeks.
How Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The most important way to prevent BCC is to avoid sunburn. This is especially important in childhood and early life. Fair skinned individuals and those with a personal or family history of BCC should protect their skin from sun exposure daily, year-round and lifelong.
- Stay indoors or under the shade in the middle of the day
How Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer Treated When It Grows Deep Or Spreads
While this skin cancer tends to grow slowly, early treatment is recommended. Without treatment, BCC can grow deep, destroying what lies in its way. This can be disfiguring. The medical term for this is advanced basal cell carcinoma.
Its also possible for BCC to spread to other parts of your body, but this is rare. When the cancer spreads, it typically travels first to the lymph nodes closest to the tumor. From there, it tends to spread through the blood to bones, the lungs, and other parts of the skin. When this skin cancer spreads, it is called metastatic basal cell carcinoma.
For cancer that has grown deep or spread to the closest lymph nodes, treatment may involve:
-
Surgery to remove the tumor
-
Follow-up treatment with radiation to kill any remaining cancer cells
For some patients, medication that works throughout the body may be an option. Medication may also be used to treat cancer that:
-
Returns after surgery or radiation treatments
-
Has spread to another part of the body
Two such medications have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Both come in pill form and are taken every day. A patient only stops taking the medication if the cancer starts to grow, or the side effects become too severe.
The two medications are:
-
Sonidegib
-
Vismodegib
In clinical trials, these medications have been shown to stop or slow down the spread of the cancer and shrink the cancerous tumors in some patients.
Cemplimab may be an option if sonidegib or vismodegib:
Don’t Miss: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
In addition to basal cell carcinoma, this autosomal dominant disorder can result in the early formation of multiple odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies. Various tumors such as medulloblastomas, meningioma, fetal rhabdomyoma, and ameloblastoma also can occur.
Odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies may be seen. Mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, particularly the patched gene, are causative.
Go to Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome to see more complete information on this topic.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
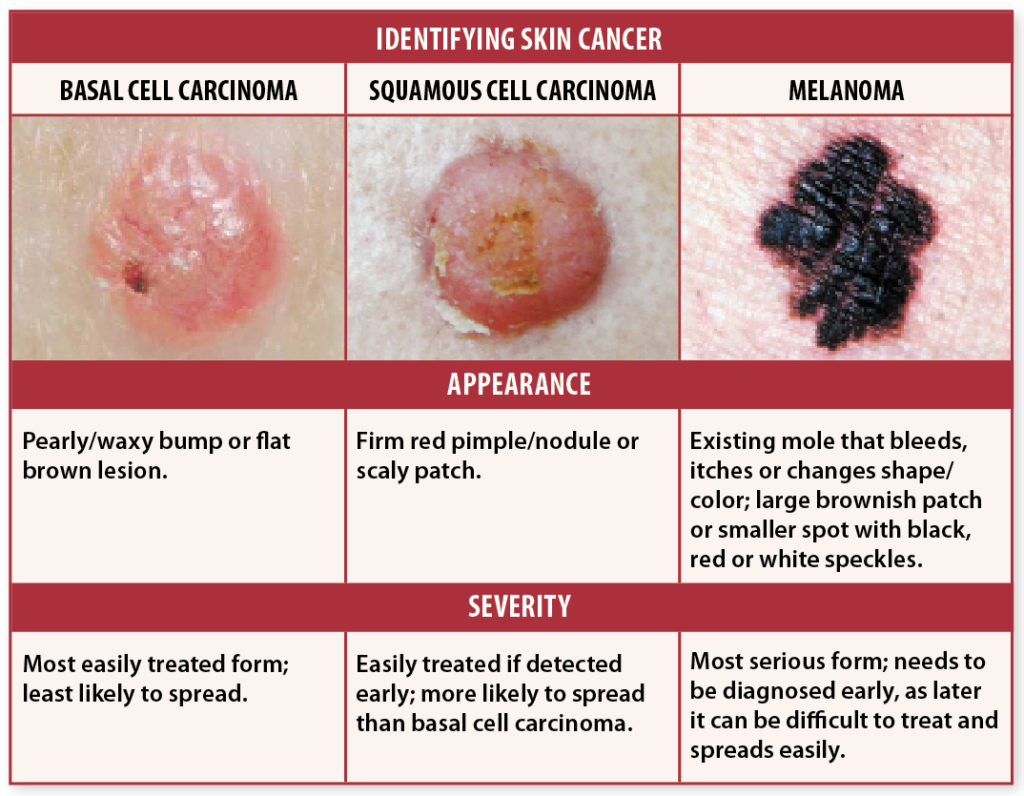
Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in how they look. They usually occur on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp or ear.
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Proby for her permission and the photography.
You should see your doctor if you have:
- a spot or sore that doesn’t heal within 4 weeks
- a spot or sore that hurts, is itchy, crusty, scabs over, or bleeds for more than 4 weeks
- areas where the skin has broken down and doesn’t heal within 4 weeks, and you can’t think of a reason for this change
Your doctor can decide whether you need any tests.
-
Cancer and its management J Tobias and D HochhauserBlackwell, 2015
-
Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology VT De Vita, TS Lawrence and SA RosenbergWolters Kluwer, 2018
Also Check: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
Basal cell carcinoma is very treatable when diagnosed early. This is why seeing a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis is imperative. During your appointment, your dermatologist will examine your skin carefully and ask questions about your health, symptoms, and medications.
If your dermatologist sees a spot that appears cancerous, he/she will perform a skin biopsy. A biopsy is a simple procedure that dermatologists can quickly and easily perform to remove the spot. Once the spot is safely removed, your dermatologist will examine it under a microscope to determine if cancerous basal cells are present.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to accurately diagnose basal cell carcinoma. The biopsy or pathology report will disclose what type of basal cell carcinoma you have and how deeply the cancer has grown.
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
Mohs micrographically controlled surgery involves examining carefully marked excised tissue under the microscope, layer by layer, to ensure complete excision.
- Very high cure rates achieved by trained Mohs surgeons
- Used in high-risk areas of the face around eyes, lips and nose
- Suitable for ill-defined, morphoeic, infiltrative and recurrent subtypes
- Large defects are repaired by flap or skin graft
Read Also: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Looking After Your Skin After Treatment
After treatment, you may need follow-up appointments with your dermatologist or GP to see if you need any further treatment.
If you had surgery, you may need to have any stitches removed at your GP surgery a few weeks later.
After treatment:
- see a GP if an existing patch starts to bleed, change in appearance or develops a lump do not wait for your follow-up appointment
- see a GP if you notice any worrying new patches on your skin
- make sure you protect your skin from the sun wear protective clothing and use a sunscreen with a high sun protection factor of at least 30
Page last reviewed: 21 May 2019 Next review due: 21 May 2022
Taking Care Of Yourself
After you’ve been treated for basal cell carcinoma, you’ll need to take some steps to lower your chance of getting cancer again.
Check your skin. Keep an eye out for new growths. Some signs of cancer include areas of skin that are growing, changing, or bleeding. Check your skin regularly with a hand-held mirror and a full-length mirror so that you can get a good view of all parts of your body.
Avoid too much sun. Stay out of sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s UVB burning rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen. The suns UVA rays are present all day long — thats why you need daily sunscreen. Make sure you apply sunscreen with at least a 6% zinc oxide and a sun protection factor of 30 to all parts of the skin that aren’t covered up with clothes every day. You also need to reapply it every 60 to 80 minutes when outside.
Dress right. Wear a broad-brimmed hat and cover up as much as possible, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
Continued
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Carcinoma Lung Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is usually a growth on your skin that is:
-
Small, shiny, firm, and raised
-
Almost clear to pink in color
-
Full of visible tiny blood vessels
-
Sometimes, with a thickened, pearly white outer border
It can also appear as:
-
Raised bumps that may break open and form scabs in the center
-
Flat pale or red patches that look like scars
-
Sores that bleed, form a scab, and heal over
Tumors are usually slow growing but can grow as much as a half inch in a year.
What Does Bcc Look Like
BCCs can look like open sores, red patches, pink growths, shiny bumps, scars or growths with slightly elevated, rolled edges and/or a central indentation. At times, BCCs may ooze, crust, itch or bleed. The lesions commonly arise in sun-exposed areas of the body. In patients with darker skin, about half of BCCs are pigmented .
Its important to note that BCCs can look quite different from one person to another. For more images and information on BCC signs, symptoms and early detection strategies, visit our BCC Warning Signs page.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference to what they can look like. If you see something new, changing or unusual on your skin, schedule an appointment with your dermatologist.
An open sore that does not heal
A shiny bump or nodule
A reddish patch or irritated area
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
Also Check: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Is The Best Treatment For A Basal Cell Carcinoma
Pro Tip
If treated when small, basal cell carcinomas are easily removed. Dr. MacCormack
If you think you may have skin cancer, make an appointment with a dermatologist . They will examine the lump or sore and also the rest of your body for any other suspicious spots.
If skin cancer is suspected, the doctor will want to scrape or cut off a small piece of the lesion so it can be examined and tested for basal cell carcinoma cells in a laboratory.
If a biopsy confirms BCC, the dermatologist will likely offer several treatment options. Possibilities include in-office surgical procedures to remove the lesion, radiation therapy, or certain medications.
The type of treatment will depend on the size and location of the tumor, plus patient preference where possible. Your dermatologist will help you decide which approach is right for you.
Where Can You Get It
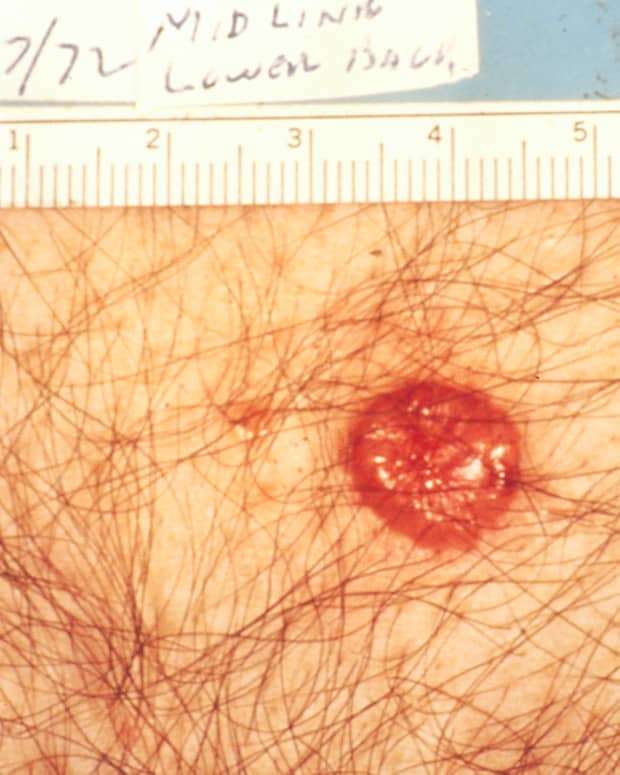
Any kind of skin cancer is more likely to show up on areas exposed to the sun. Most of the time, advanced BCC affects you from the neck up. But itâs possible to get it other places, like your genitals.
Advanced BCC more commonly affects these areas:
- Eye or eyelid
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Thereâs ongoing research into what works best for advanced BCC. Your doctor might suggest joining a clinical trial if other treatments arenât successful. Thatâs a study that looks at new kinds of drugs or treatment methods.
Also Check: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Signs Of Bcc
BCC usually forms on skin that has been exposed to the sun. Tumors on the head, ears, nose, and neck are common. Most tumors are not painful. The following are common signs of a BCC:
- Shiny, waxy, pale or pink bumps or growths that may have blood vessels on the surface
- Red, scaly patches
- Open sores that may bleed and do not heal
Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The skin consists of three layers. The top layer, called the epidermis, is where most skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma, arise.
This information is about basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinomas are most commonly found on the face, neck, hands, or other parts of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun.
The first sign of basal cell carcinoma is an unusual growth on your skin. You may notice a waxy lump or a small, smooth, shiny, or pale growth. Or there may not be a lump at all, but instead you notice a flat spot that looks slightly different from the rest of your skin.
Some basal cell carcinomas develop so slowly that you only notice them after theyve been there for a while.
Basal cell carcinoma can appear in one of several ways:
- a small, smooth, shiny, or pale growth
- a waxy-looking lump
Don’t Miss: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The various types of basal cell carcinoma can take many different forms. Often, it may seem like a small bump that grows very slowly. Other symptoms are a:
- Pink, reddish spot that dips in the center
- Scaly patch, especially near the ears
- Sore that resembles a pimple, but that either doesnt heal or heals but keeps returning
- Round growth that can be pink, red, brown, tan, black, or skin-colored
- Scar-like skin that isnt from an injury
Its important to note that the color and shape of the tumor may not be uniform. The spot may be flat or raised, it can be dipped in the center or not, and it can even appear shiny. Often, BCCs do not cause pain, but the area can be numb, sensitive, or itchy. Its hard to self-diagnose a basal cell carcinoma because they can take so many different shapes. If you have a concerning spot, its best to schedule a dermatological appointment right away.
Is It Time For Your Annual Skin Check
One of the best ways to prevent basal cell carcinoma is to take steps to protect your skin from the sun, including daily sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade whenever possible. If you have a high risk of developing skin cancer, then make sure that you dont miss your yearly skin check-up with your dermatologist.
Are you experiencing any symptoms that concern you? Schedule an appointment with the dermatologists at the Center for Surgical Dermatology. Were now accepting patients for telemedical appointments!
You May Like: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. Also known as BCC, this skin cancer tends to grow slowly and can be mistaken for a harmless pimple, scar, or sore.
Common signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma
This skin cancer often develops on the head or neck and looks like a shiny, raised, and round growth.
To help you spot BCC before it grows deep into your skin, dermatologists share these 7 warning signs that could be easily missed.
If you find any of the following signs on your skin, see a board-certified dermatologist.
Dna Mismatch Repair Proteins
DNA mismatch repair proteins are a group of proteins that physiologically stimulate G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis. Failure of MMR proteins to detect induced DNA damage results in the survival of mutating cells. MMR protein levels have been found to be higher in nonmelanoma skin cancers than in normal skin, and there is also some evidence of MMR dysregulation.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How To Recognize Diagnose And Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. In fact, it is estimated that about 2 million Americans hear the words, You have basal cell carcinoma, each year.
For most, basal cell carcinoma is treatable and not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body. However, early detection is vital. Below, we will review what basal cell carcinoma looks like, how it is diagnosed, and how it is treated.
What Does Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
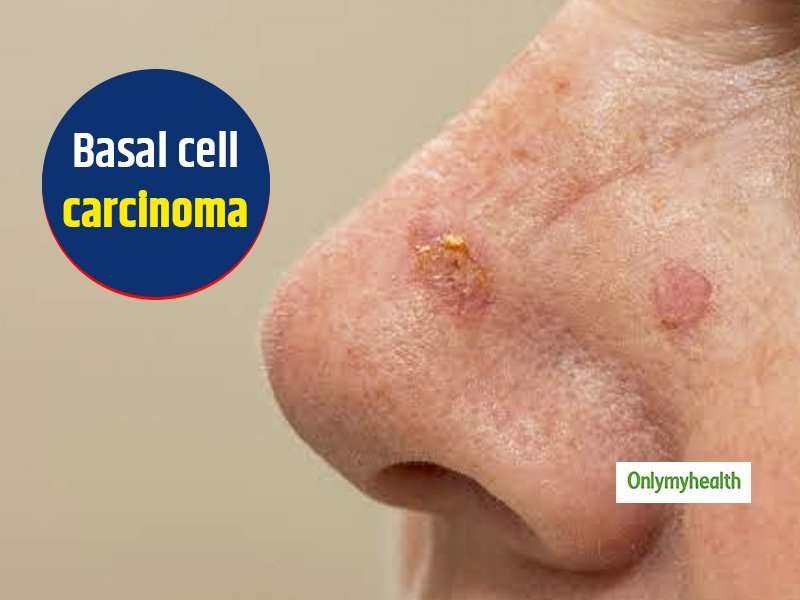
One of the defining features of morpheaform BCC is its shape. These tumors tend to be less regular and do not have well-defined edges. They often have long strands that extend off the main tumor node. This means the tumors can grow into other layers of the skin, or nearby muscles or other structures. The irregular shape of these tumors can make them difficult to treat.2
Don’t Miss: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
What Is A Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that occurs when there is damage to the DNA of basal cells in the top layer, or epidermis, of the skin. They are called basal cells because they are the deepest cells in the epidermis. In normal skin, the basal cells are less than one one-hundredth of an inch deep, but once a cancer has developed, it will spread deeper.
Skin: Condition: Infomation Superficial Bccs
- Curettage and cautery the skin is numbed with local anaesthetic and the BCC is scraped away and then the skin surface is sealed by heat .
- Cryotherapy freezing the BCC with liquid nitrogen.
- Creams these can be applied to the skin. The two most commonly used are 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod.
- a special cream is applied to the BCC which is taken up by the cells that are then destroyed by exposure to a specific wavelength of light. This treatment is only available in certain dermatology departments .
Surgical excision is the preferred treatment, but the choice of other treatments depends on the site and size of the BCC, the condition of the surrounding skin and number of BCC to be treated as well as the overall state of health of each person to be treated.
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Using sunscreen Sunscreens Sunburn results from a brief overexposure to ultraviolet light. Overexposure to ultraviolet light causes sunburn. Sunburn causes painful reddened skin and sometimes blisters, fever… read more : At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An evidence-based approach to basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is relatively common. Patients often first present to the primary care provider with complaints of an abnormal skin lesion. When diagnosed early, it has an excellent prognosis, but if there is a delay in diagnosis, the tumor can advance and lead to significant morbidity. Basal cell cancer is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes a dermatologist, mohs surgeon, plastic surgeon, nurse practitioner, primary care provider, and a dermatopathologist. Basal cell carcinomas typically have a slow growth rate and tend to be locally invasive. Tumors around the nose and eye can lead to vision loss. In most cases, surgical excision is curative. However, because recurrences can occur, these patients need long-term follow up.
Also Check: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis