Continue Learning About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Dont Miss: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
When To Seek Medical Care
If you have developed a new bump on sun-exposed skin, or if you have a spot that bleeds easily or does not seem to be healing, then you should make an appointment with your primary care physician or with a dermatologist. You should also make an appointment if an existing spot changes size, shape, color, or texture, or if it starts to itch, bleed, or become tender.Try to remember to tell your doctor when you first noticed the lesion and what symptoms, if any, it may have . Also be sure to ask your parents, siblings, and adult children whether or not they have ever been diagnosed with skin cancer, and relay this information to your physician.
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- print page
- Bookmark for later
Cancer staging is a way of describing how extensive a cancer is. The stage is related to tumor size. It also relates to whether the cancer has spread from the original tumor to other parts of the body. The cancer stage helps you and your doctor to develop a treatment plan. It also provides information about survival. Squamous cell carcinoma stages use a system called TNM.1,2 This cancer staging system is used by most hospitals and medical systems.3 Once your doctor has categorized the T, N, and M, these values are combined to assign a cancer stage.2
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
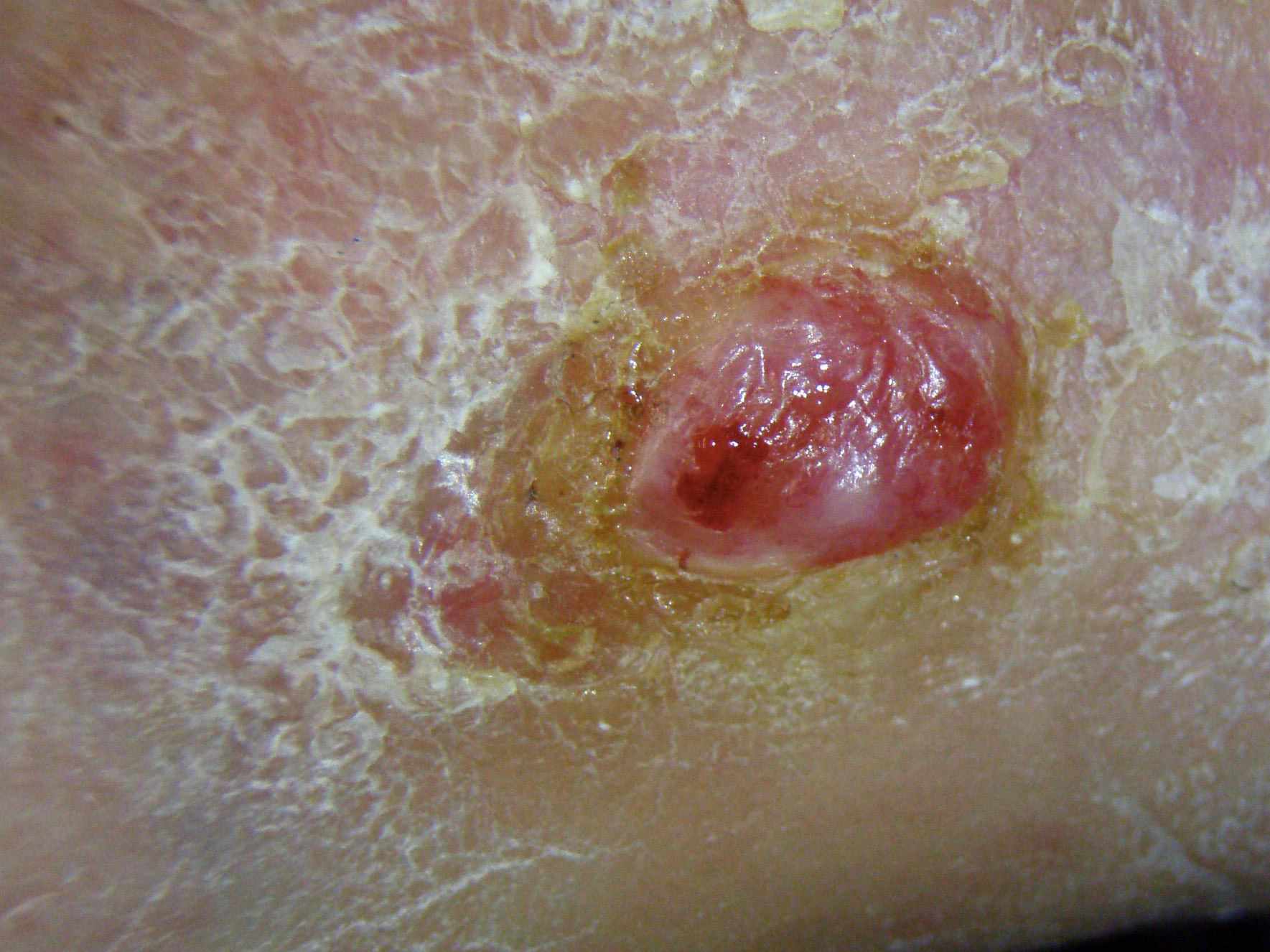
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The various types of basal cell carcinoma can take many different forms. Often, it may seem like a small bump that grows very slowly. Other symptoms are a:
- Pink, reddish spot that dips in the center
- Scaly patch, especially near the ears
- Sore that resembles a pimple, but that either doesnt heal or heals but keeps returning
- Round growth that can be pink, red, brown, tan, black, or skin-colored
- Scar-like skin that isnt from an injury
Its important to note that the color and shape of the tumor may not be uniform. The spot may be flat or raised, it can be dipped in the center or not, and it can even appear shiny. Often, BCCs do not cause pain, but the area can be numb, sensitive, or itchy. Its hard to self-diagnose a basal cell carcinoma because they can take so many different shapes. If you have a concerning spot, its best to schedule a dermatological appointment right away.
How Serious Is A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Id had a few skin cancers removed before, all basal cell carcinomas , the most common type. But when I was diagnosed with a squamous cell carcinoma on my scalp, it seemed different, and a little more scary. I asked C. William Hanke, MD, a Mohs surgeon at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Indiana and a senior vice president of The Skin Cancer Foundation, what we need to know about this second most common form of skin cancer.
Q: When people talk about nonmelanoma skin cancers, they tend to lump basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas together as the ones that are far less dangerous than melanoma. Should we take SCCs more seriously?
Dr. Hanke: Yes and no. BCCs hardly ever metastasize. Ive seen two cases in my entire career. But when SCCs that havent been treated early get big, then the chance of metastasis becomes real. Its uncommon, but its much more common than in BCC. We see it in our practice. But we dont want to scare people into thinking that just because they have squamous cell, Oh wow, Ive got a chance of metastasis. Remember, the rate is very low. Its just those big ones.
Q: OK, so its rare. But what happens when an SCC does spread?
Q: Whats the usual treatment for SCCs?
Q: How can we detect SCCs as early as possible?
Recommended Reading: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Staging For Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma usually do not spread to other parts of the body. On rare occasions, a persons lymph node may be removed to find out if the cancer has spread, which is called metastasis. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped organs that help fight infection. The doctor may recommend other tests to determine the extent of the disease, including blood tests, chest x-rays, and imaging scans of the lymph nodes and nerves, liver, bones, and brain, but this is uncommon.
When Should I Call The Doctor About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If you have never had skin cancer or if you have had SCC, contact your doctor if:
- You have any skin changes that cause you worry, including a new lump, mole, or sore that does not heal, or changes in a mole or spot you have had for some time.
- You need to schedule your yearly skin check appointment.
- You have any issues related to your treatment for SCC that worry you, such as excessive pain, bleeding or itching.
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Lung Cancer Doubling Time
Doctors may describe the doubling of a lung tumor in terms of either volume or metabolic doubling time. What they mean is, how long it takes for it to double in size. But there are more limitations, similar to what we have already seen, when estimating doubling time from models. Thats because:
- The models assume a continuous rate of growth, and this is not the case.
- Its hard to design studies in humans for ethical reasons. The results from animal or lab studies dont necessarily reflect what happens in people.
- There are limits to estimating tumor size based on imaging, such as a CT scan.
What Is Skin Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control.
Skin cancer cells can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, but this is not common. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the skin.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So if skin cancer spreads to another part of the body, its still called skin cancer.
The skin
Ask your doctor to use this picture to show you where your cancer is
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Cured
The majority of SCC tumors are found early and treated while they are still small. Treatment at an early stage can usually remove SCC.2
SCC is more likely than BCC to invade deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.2 This is uncommon. However, about 5% to 10% of SCC tumors are considered aggressive.2,4 It is more difficult to treat aggressive SCC. By one estimate, between 3,900 and 8,800 white individuals died from SCC in 2012.1 In the Midwest and southern United States, SCC may cause as many deaths as melanoma.1
Your dermatologist may recommend regular follow up for several years after treating any SCC. Most of the cases that return do so with 2 years of initial treatment.5
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Is More Serious Than Basal Cell Carcinoma
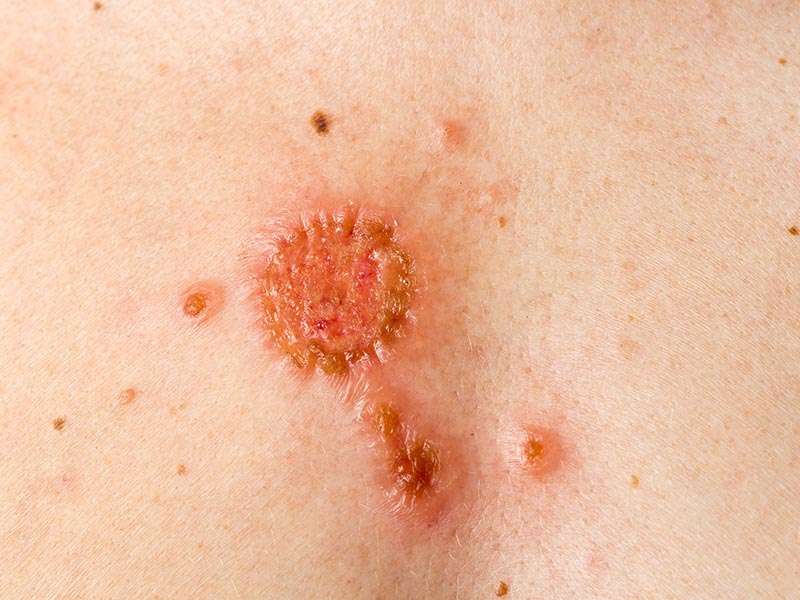
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is a less prevalent form of skin cancer compared to Basal Cell Carcinoma, which has about a million cases each year. However, it is a more dangerous skin cancer due to its potential to metastasize. It has a cure rate of 90% of treatments in its early stages. Treatment becomes more difficult once it has metastasized, which occurs in 1%-5% of cases.
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma Unique
Simple, small cancers can often be treated very well by a local dermatologist, according to Dr. Leffell. We rarely see the small cancers. We get referred to the cases that need special attention.
Dr. Leffell emphasizes that at Yale Medicine, the patient always comes first. We like to have a discussion with the patient about what happens after the skin cancer is removed, he says. We talk about what’s involved with plastic surgery and what’s involved with letting the area heal naturally. We prefer to take a minimalist approach and let the patient decide what they want us to do and how they want to let their skin heal.
If the decision is made to repair the wound using plastic surgery, we do that immediately in the office setting, Dr. Leffell says. Alternatively, allowing the wound to heal naturally is often a great option, and does not rule out doing plastic surgery down the road if needed, though that is very rarely the case.
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
You May Like: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Also Check: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isn’t yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, it’s important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
Prevention Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The American Academy of Dermatology makes the following recommendations to help reduce the chances of developing SCC:
- When possible, wear protective clothing to minimize direct sun exposure to the skin
- Seek shaded areas especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the suns ultraviolet radiation is most intense
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on all exposed skin. The sunscreen should be applied liberally and reapplied every 2 hours or more if excessively sweating or swimming.
- Avoid tanning beds
- Perform regular self-skin exams and note any changing moles or other skin lesions.
- Seek medical attention should you discover a new or changing skin growth.
Also Check: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Squamous cell carcinomas detected at an early stage and removed promptly are almost always curable and cause minimal damage. However, left untreated, they may grow to the point of being very difficult to treat.
A small percentage may even metastasize to distant tissues and organs. Your doctor can help you determine if a particular SCC is at increased risk for metastasis and may need treatment beyond simple excision.
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma. The choice of treatment is based on the type, size, location, and depth of penetration of the tumor, as well as the patients age and general health. Squamous cell carcinoma treatment can almost always be performed on an outpatient basis.
Also Check: Osteomyoma
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
Unlike other types of carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma can spread from its original site to the lymph nodes, e.g. in the neck or around the collarbone.
Squamous cells are thin, flat cells found in tissues that form the surface of the skin and the lining of body cavities, such as the mouth, nose and throat. Squamous cell carcinoma is a fairly slow-growing carcinoma. The doctor will try to find the original site from where the tumor metastasized . When physicians cannot locate a primary tumor, it is called an occult primary tumor. The chance of recovery depends on the number of lymph nodes containing cancer, the location of cancer in the neck and the patients general health.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
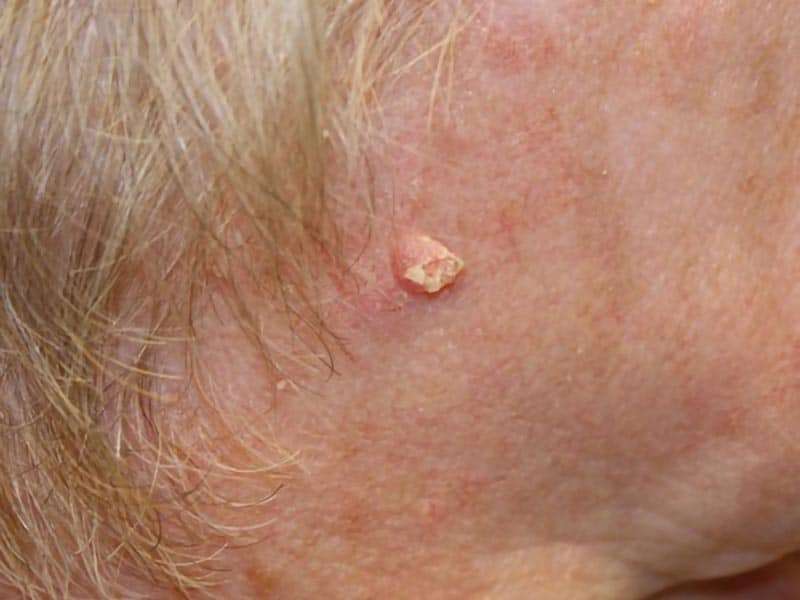
BCCs grow slowly and the prognosis is typically excellent. If left untreated, the basal cell carcinoma will continue to grow deeper and wider into the skin and may involve the nerves, muscle, or bone underneath the skin. When basal cell carcinomas have grown significantly, they will cause disfigurement. Even though they grow slowly, its essential to make an appointment with a dermatologist as soon as you discover a change in your skin.
Also Check: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell skin cancer tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell cancers occur four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell cancer can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell cancer that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell skin cancer can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell cancer of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
Answer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Growth
While it is said that most skin cancers grow slowly, the true answer is “it depends”. It depends on location of the skin cancer, your general health, the health of your skin and the cause of the skin cancer. Most squamous cell carcinomas arise in skin damaged by ultra violet light and, often, grow slowly. However, if the UV damage is severe or if the SCC arose from a burn or infection site, the cancer can grow rapidly and spread to other organs. Additionally, SCC, which grows contiguously will sometimes send “seeds” beyond the tissue containing the “roots”. These factors all have to be considered in determining how to deal with SCC. The best advice I can give you is to not delay and have this evaluated by a fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon. I hope I have answered your question. Best. jlr
Read Also: What Is The Worst Skin Cancer To Have