Red Flag #: Swollen Lymph Nodes
If melanoma spreads, it often goes to the lymph nodes first, says Melinda L. Yushak, M.D., assistant professor of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta. The cancer cells will first travel to the nodes closest to the original tumor, she says. Lymph nodes are located throughout your entire body, but large clusters are found in the neck, underarms, chest, abdomen, and groin. If the cancer has made its way to the lymph nodes, it usually wont be painful, but theyll feel swollen or even hard to the touch, Dr. Zaba says.
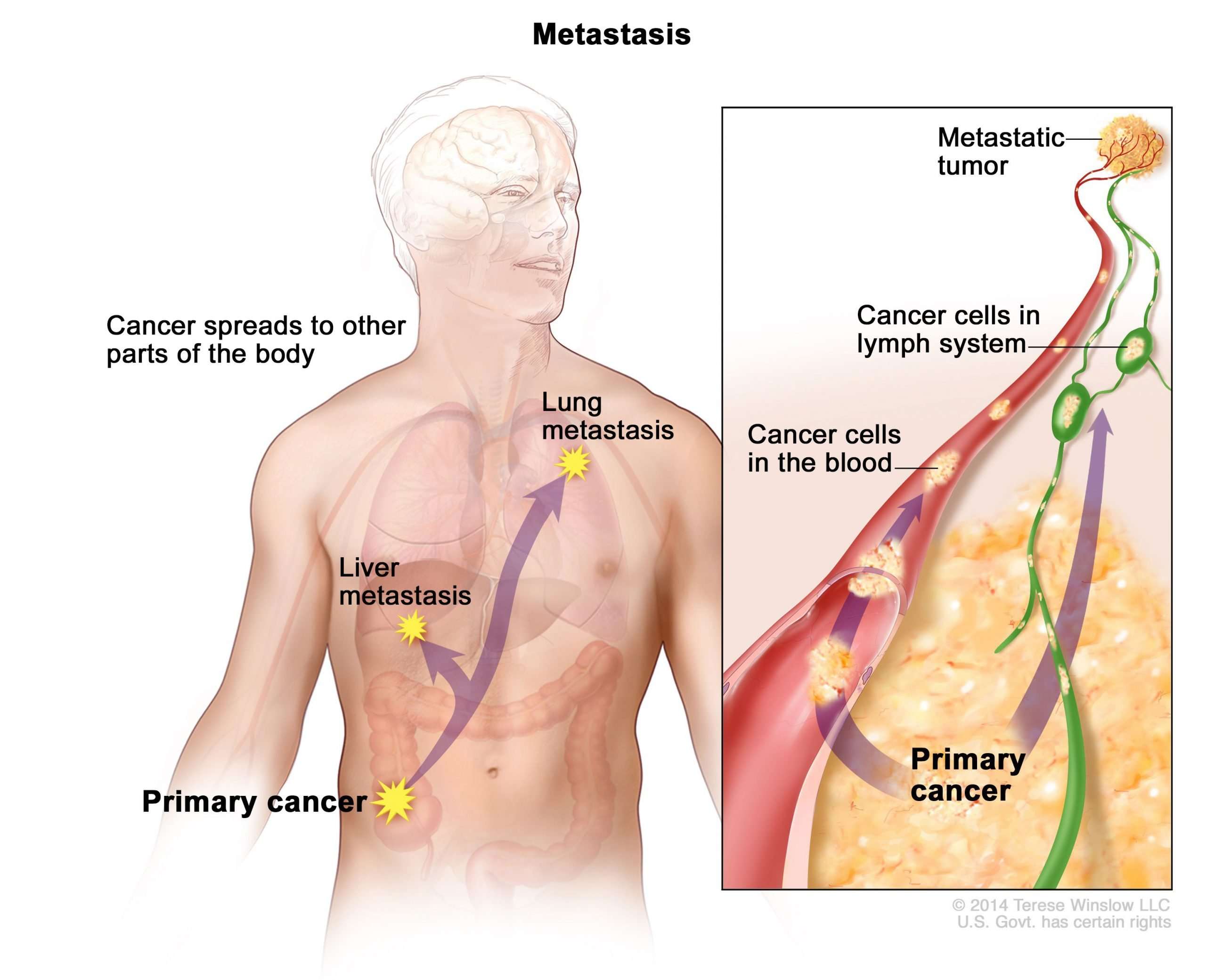
The Spread Of Melanoma Metastasis
If you or a family member or friend have recently been diagnosed with melanoma, you may be wondering, just where and why can melanoma spread?
With surgery, melanoma confined to the skin has a 5-year survival rate in 98% of cases. Unfortunately, if the lesion recurs , gets thicker, or spreads from the skin to the lymph nodes or distant organs, it becomes much more dangerous. This occurs in stage III and IV melanoma and is called melanoma metastasis.
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. For years after treatment, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to see if the cancer has come back.
At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. After 5 years, they may be done once a year.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
Recommended Reading: Does The Sun Cause Skin Cancer
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. When it spreads to other places in your body, it’s called metastatic, or advanced. You may also hear your doctor refer to it as stage IV melanoma.
Melanoma often spreads to:
Although in many cases metastatic melanoma canât be cured, treatments and support can help you live longer and better. Doctors have therapies that have greatly increased survival rates. And researchers are working to find new medications that can do even more.
Remember: You still have control over the decisions you make about your treatment and your life. It’s important to have people you can talk to about your plans, your fears, and your feelings. So find support and learn about your treatment options. That will help you make the most of your life.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
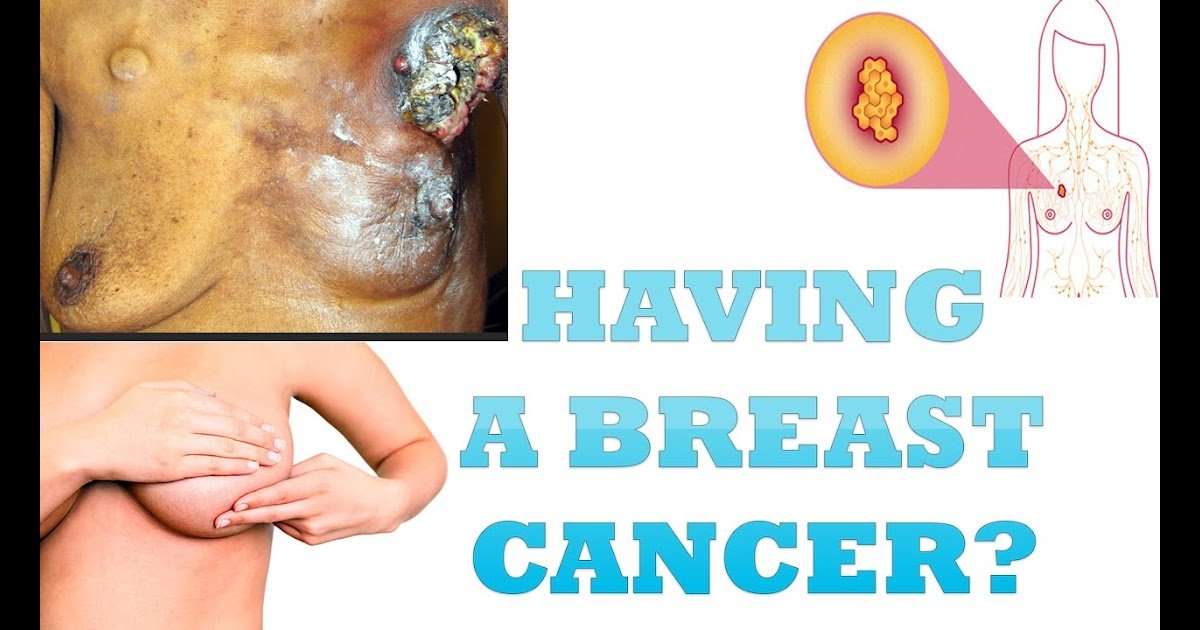
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
You May Like: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer
You May Like: How Fast Can You Get Skin Cancer From The Sun
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system. There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
Your doctor will check your skin to look for melanoma. If your doctor thinks that you have melanoma, he or she will remove a sample of tissue from the area around the melanoma. Another doctor, called a pathologist, will look at the tissue to check for cancer cells.
If your biopsy shows melanoma, you may need to have more tests to find out if it has spread to your lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Recognizing The Signs And Symptoms
The most noticeable sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole or birthmark. People should be aware of any pigmented areas on the skin that appear abnormal in color, shape, size, or texture.
People with stage 4 melanoma may also have ulcerated skin, which is skin with tiny breaks on the surface. These ulcerations can bleed.
Another sign is swollen or hard lymph nodes, which a doctor can confirm by carrying out a physical examination. Other tests include blood tests and imaging scans to confirm the presence of cancer and check how much it has spread.
Dont Miss: How Quickly Can Melanoma Metastasis
What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma That Has Spread
Melanoma that has spread from the skin to other areas of the body is known as metastatic melanoma. However, since melanoma often first presents itself as an abnormal mole, many people with this malignancy can receive a diagnosis before the cancer has spread. This mole may be asymmetrical, have an uneven border, have an inconsistent color, be large or change over time. A melanoma may also appear as a sore or itchy bump, a tender nodule or a patch of skin that is scaly or bleeding. In some cases, early signs of melanoma are not present. For example, if the cancer starts in a mucous membrane rather than on the skin, a mole may not be present.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer
Red Flag #: Headaches Or Visual Changes
Just like the liver, not everyone will notice symptoms of melanoma spreading to the brain. But when symptoms do show up, its usually in the form of headaches, problems with eyesight, paralysis on one side of the body, or seizures. If someone simply has a headache, that doesnt mean they have advanced stage melanoma, Dr. Yushak says. But if its a headache thats not going away after a week, and you never have headaches, then thats something that definitely needs to be checked out.
When A Mole Is Not A Mole: How To Tell If It Might Be Melanoma
Summertime is for swimming, sunbathing, hiking and barbequing. Something that virtually all of the best summer activities have in common is that theyre all done in the sun. While you probably try your best to put sunscreen on before spending time outside, there are always times where you forget or dont realize youll be exposed for a significant amount of time. Without fail, mysterious spots always seem to appear at the end of each summer. Many of these spots are really just harmless moles or freckles, but sometimes they can be something much worse.
Before you start checking your body in a panic, remember your ABCDEs:
Read Also: How Long Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Take To Spread
What Does A Normal Vs An Abnormal Mole Look Like
Normal moles are usually round or oval and smaller than a pencil eraser. They are one consistent color , with a clear border. Most people have less than 50 moles. You can be born with moles, develop them with age or even have some disappear.
Cancerous, or malignant, moles may vary greatly in appearance. To help identify moles that might indicate melanoma, think of the letters A-B-C-D-E:
- A | Asymmetry: Mole is an irregular shape, such as if one side looks different than the other
- B | Border: Mole has irregular, ragged, notched or scalloped borders
- C | Color: Mole has more than one color or uneven shading
- D | Diameter: Mole is bigger than a pencil eraser
- E | Evolution: Mole changes in some way
Talk to your doctor, if you notice any skin changes that seem unusual.
What Increases Your Risk
A risk factor for melanoma is something that increases your chance of getting this cancer. Having one or more of these risk factors can make it more likely that you will get melanoma. But it doesn’t mean that you will definitely get it. And many people who get melanoma don’t have any of these risk factors.
Risk factors for melanoma include:footnote 1
- Too much exposure to the sun’s UV rays. This includes:
- Having had blistering sunburns at any time of life.
- Getting intense sun exposure every now and then.
Don’t Miss: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
It’s common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful. It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Staging
Staging is the process of determining whether cancer has spread and, if so, how far. The stage of the disease may affect the treatment plan.
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage. In rare cases, your doctor may recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin
Stages are numbered in Roman numerals between 0 and IV.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
High risk features for primary tumor staging
- Depth/invasion: > 2 mm thickness , Clark level IV, Perineural invasion
- Anatomic: Primary site ear
- Location: Primary site hair-bearing lip
- Differentiation: Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
Also Check: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
What Are The Symptoms
You may not have any symptoms in the early stages of melanoma. Or a melanoma may be sore, or it may itch or bleed.
Any change in the shape, size, or color of a mole may be a sign of melanoma.
Melanoma may look like a flat, brown or black mole that has uneven edges. Melanomas usually have an irregular or asymmetrical shape. This means that one half of the mole doesn’t match the other half. They may be any size but are usually 0.25 in. or larger.
Melanomas can be found anywhere on your body. Most of the time, they are on the upper back in men and women and on the legs of women.
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
Recommended Reading: What Is Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
How Dangerous Is Melanoma Its All A Matter Of Timing
Skin cancer holds the unfortunate distinction of being the worlds most common cancer. Though its prevalence around the globe is disturbing, there is some good news: When caught early, skin cancers are almost always curable.
You might already know that catching a cancer early means a more favorable prognosis. But it can be difficult to comprehend just how big a difference early detection makes with melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Melanoma should never be underestimated, but treating a tumor early rather than after it is allowed to progress could be lifesaving.
Leland Fay, 46, understands better than most the seriousness of this distinction. When the Monument, Colorado native was diagnosed with melanoma in 2012, he was given a bleak prognosis due to the advanced stage of the tumor it had already reached stage IV.
Leland hadnt thought much of the little black mole on his head a few months earlier, when a dermatologist froze it off during a routine exam. But the mole resurfaced, bigger than it had been originally. After a biopsy and imaging tests, doctors told Leland it was melanoma, and that it had already spread. He could have as few as six weeks to live.
To fully comprehend the significance of timing, it can be helpful to understand exactly what happens to a melanoma when it advances to a later stage, and what it means when a melanoma spreads beyond the original tumor site.
Mouse Models Mimic Metastasis Of Human Melanoma
Metastasis is a highly inefficient process in that the vast majority of cancer cells that try to migrate die before they ever have an opportunity to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found previously that one factor limiting the survival of melanoma cells circulating in the blood is that the cells experience a high level of oxidative stress. Oxidative stressan imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the bodycauses chemical reactions that can damage proteins, DNA, and lipids in cells and disrupt normal cell processes. However, precisely how oxidative stress kills circulating melanoma cells was not known.
For their studies, the team used a mouse model of metastasis created by transplanting melanoma cells from humans beneath the skin of specially bred mice with weakened immune systems. These mice were used to avoid having the transplanted human cells seen as foreign and attacked by the immune system. The team also used a second mouse model created by transplanting mouse melanoma cells into mice with normal immune systems.
Comparing these two mouse models let the researchers control for potential effects of the immune system on the spread of melanoma, Dr. Salnikow explained.
The study was supported in part by NCIs Patient-Derived Models of Cancer program, which promotes the development of animal models that more closely mirror how tumor cells behave in humans.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Latest Treatment For Melanoma
The 4 Stages Of Melanoma
Two main things determine the stage of melanoma: The thickness or depth of the tumor and how far it has spread when its diagnosed, explains David Polsky, M.D., dermatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City. In stages 0, 1, and 2, the melanoma is limited to the skin. In stage 3, its spread to the lymph nodes, small structures throughout your body that help filter fluids and fight infection. In the most advanced stage, stage 4, melanoma cells have broken away from the original tumor, traveled through the body and formed a new tumor somewhere else.
What Is Fine Needle Aspiration
It’s a type of biopsy that you can get done in your doctorâs office. It checks large lymph nodes near the skinâs surface and near the melanoma to see if the cancer spread there.
Your doctor will feel the area around your melanoma to find the lymph node or nodes, numb that spot, and use a very thin needle syringe to remove a little bit of your lymph node. It shouldnât hurt much, and it wonât leave a scar.
One drawback of a fine needle aspiration biopsy is that if it doesnât collect a big enough sample, you might need to get surgery for a second biopsy.
Don’t Miss: What Does Sebaceous Carcinoma Look Like