What Are The Risk Factors For Subungual Melanoma
The following factors increase the risk for Subungual Melanoma:
- Injury to the toes or fingers
- Nevus is a non-cancerous pigmented tumor. While most nevi never become cancerous , a small number of atypical/dysplastic nevi may turn cancerous. When such dysplastic nevi run in families, the condition is called dysplastic nevus syndrome. Individuals with this condition have a 10% increased risk of developing melanoma. Despite the above and irrespective of the condition, whether the nevi are present since birth, or are normal, or atypical the more the number of moles, the greater is the risk
- Previous history of melanoma or a history of melanoma in parents/siblings
- An inherited condition called xeroderma pigmentosum, where the ability of the cells to repair sun-induced damage to genetic material is impaired
- Weakened immune system, as a result of infections , drugs , and the presence of cancers
Note: Current studies have shown that the development of Subungual Melanoma is not related to sun-exposure . However, this factor has not yet been conclusively proven. In general, sun-exposure is an important risk factor for melanoma formation.
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one’s chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Surgery And Prognosis Of Subungual Melanoma
Three cases with melanoma in situ and 2 cases with dermal invasion underwent conservative surgery , whereas 17 cases underwent amputation. Case 14 did not receive any surgery. The mean follow-up period of the cases with the conservative surgery was 8.8 months and that of amputation was 32.4 months. There was no local recurrence after surgery. Only one patient received palliative treatment and died of multiple distant metastases at 20 months after amputation.
How Is Subungual Melanoma Treated
The choice of treatment for Subungual Melanoma depends on how far the cancer has progressed. This is estimated through staging of the melanoma. Some of the factors taken into consideration during staging include:
- The thickness of the melanoma : Tumors can be thin, intermediate, or thick, depending on how deep into the skin they have penetrated. The thinner the tumor, the better the chances of a cure
- Presence of any ulceration over the tumor
- Spread of melanoma to lymph nodes or other internal organs
The melanoma is sorted into one of four stages depending on how far it has progressed, with I and II being early stages, III and IV being later stages, where melanoma has spread to sites beyond the skin. While early stage melanomas can be treated by surgery alone, the later stages of the disease often require a combination of treatment measures.
Treatment options for melanoma include:
Surgery:
Chemotherapy:
Immunotherapy:
Targeted therapy:
Radiation therapy:
Also Check: Melanoma 3b
What Are The Consequences Of Subungual Melanoma
Subungual melanoma is invariably diagnosed late and so the 5-year survival rate ranges between 16% and 87% based on the stage of the cancer. With advanced stages, the survival rate drops. Different factors affect the survival rate of subungual melanoma, such as:
- Breslow thickness  A good survival indicator for subungual melanoma .
- Tumor metastases  Distant metastases to the lymph node or liver
- Tumor stage
Some of the risk factors considered in diagnosing subungual melanoma are compiled as ABCDEF guidelines. The guidelines are useful to identify lesions that need to be excised. The guidelines are:
- Ethnic origin and age  Chinese, Japanese, African-American or Native Americans are more susceptible to subungual melanoma.
- Black-brown band with irregular border
- Change in rate of growth and size or lack of improvement with treatment
- Digit  usually one affected digit, such as big toe, thumb, or index finger
- Extension of discolored pigmentation e.g. Hutchinson sign
- Family history of cases of melanoma is recorded<
In order to accurately diagnose subungual melanoma, it is important to follow the above guidelines, compare the lesions with earlier photographic evidence, and immediately excise suspicious lesions. The tissue pathology of the nail shows an increased number of melanocytes. The metastatic cases exhibit a 2- to 3-fold increase in the number of melanocytes compared with benign cases.
There are 2 clear ways to confirm subungual melanoma.
Health & Wellness7 Nail Symptoms Explained: Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
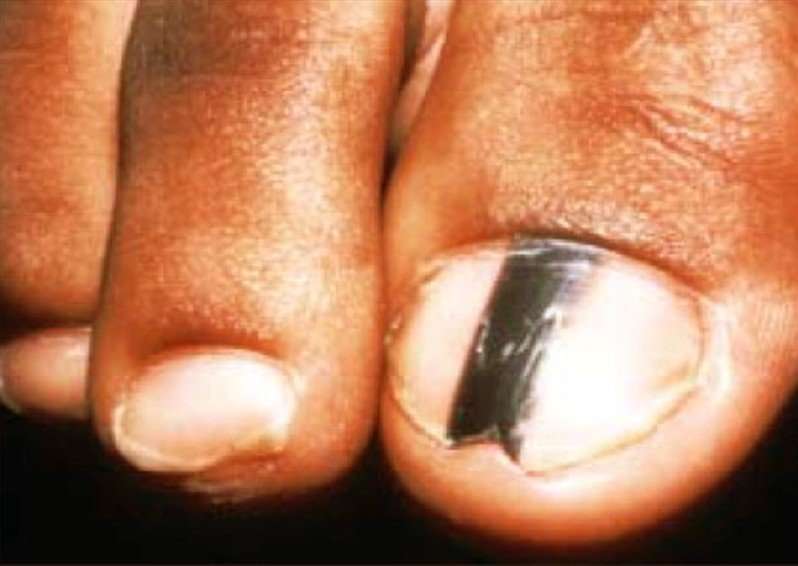
Some doctors say nail melanoma often develops on the thumb of ones dominant hand, or big toe of ones dominant side, but Patel has seen it on all digits and believes all of the nails are equally potentially affected.
This type of melanoma is more driven by genetics and family history than sun exposure, but people should still follow sun-safe practices, he added:
- Be careful about UV exposure, including at the nail salon. Wear fingerless gloves with an ultraviolet protection factor or apply sunscreen to your hands at least 15 minutes before a gel manicure.
- When outside, apply sunscreen to the whole body, including around your nails and on your hands.
- Wear sunscreen and possibly gloves during your daily commute: If youre a driver who has your hands out in a one-and-a-half-hour commute, youre getting UV radiation exposure right to the backs of the hands and the nails, Patel said. Some of these things sound crazy, but the cumulative exposure over time .
- Remove nail polish before going to your annual skin check so a doctor can see your nails.
With Jasko’s family history of melanoma, doctors cant say how much of a role her regular UV exposure at the nail salon played. She now paints her nails with regular polish and skips the gel manicures. She also gets her skin checked every four months and is doing well.
Also Check: 3b Melanoma
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Subungual Melanoma
Diagnosing and treating subungual melanoma is much more involved.
Once your doctor performs the initial assessment and determines you might have subungual melanoma, theyll commonly suggest a nail biopsy.
A nail biopsy is the primary diagnostic tool available for making a definitive diagnosis. A dermatologist or nail specialist will remove some or all of the nail for examination.
If theres a diagnosis of cancer, depending on the severity and how early it was found, treatment can include:
- surgery to remove the affected nail
- amputation of the knuckles of the finger or toe
- amputation of the entire finger or toe
What Are The Symptoms & Signs Of Subungual Melanoma
The initial signs of subungual melanoma are streaks or black-brown bands on the nail bed. The pigmentation may be irregular. Subsequently, the nail thickens, may split or is completely damaged resulting in swelling, pain, pus secretion and discoloration of the surrounding region.
A characteristic sign of subungual melanoma is the spread of melanin pigment from the nail to the surrounding skin.
Read Also: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
How Can Subungual Melanoma Be Prevented
The exact cause or risk factors for Subungual Melanoma have not been identified yet. Hence, currently, it is not possible to prevent the condition.
A few steps to diagnose the condition during its early stages may include:
- Perform self-examination of your skin, from head to toe, once a month
- Get a professional skin exam from a healthcare provider, once a year
- All individuals with melanoma should undergo skin examinations regularly even after treatment, at least once a year throughout their lives
- Close monitor of individuals receiving immunosuppressants for various reasons, or those with poor immune system
Causes Of Subungual Melanoma
Unlike most melanomas, subungual melanoma doesnt stem from sun exposure. Technically, it occurs when theres increased melanin production and repeated injuries of the fingers or toe nails are considered a risk factor. Genetics likely also factor in, Potozkin says, but specific causes of subungual melanoma arent yet understood.
Any cancer is the unregulated growth of cells, Potozkin says. Melanoma is the unregulated growth of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cell in the body. The scary thing with melanoma is that it has the tendency to metastasize and spread to other parts of the body. So, if diagnosis is delayed, it can be a life-threatening skin cancer.
Also Check: Is An Itchy Neck A Sign Of Cancer
What Causes Subungual Melanoma
Most cases of skin melanoma are caused by sun exposure. This is why dermatologists warn against tanning and unprotected sun exposure. However, subungual melanoma isnt usually caused by the sun. Most cases seem to be caused by injury or trauma. It also tends to affect middle-aged and older adults with darker skin.
Additionally, subungual melanoma is more prevalent in the nails of your thumbs and big toes.
Melanoma Survivor Shares Her Story After Countless Skin Cancer Surgeries
Jasko, now 22, who will soon graduate from the University of Illinois at Chicago, first became aware of the unusual spot in 2016 when she was a senior in high school. Shed been getting her nails done once or twice a month for a couple of years, complete with acrylics artificial nails applied on top of her natural nails plus a gel polish that was cured with UV light.
When the acrylics were removed during one particular visit, the technician pointed out what seemed to be a bruise on her right thumb nail. It looked like a perfectly straight thin vertical line drawn with a pencil from the top to the bottom of her nail, with a purplish tint to it, Jasko recalled.
She didnt think much about it. But about a week later, her nail became infected, swollen and red, which led her to see her doctor. The infection didnt alarm him, but the mysterious streak on her nail did.
Jasko was immediately referred to a dermatologist who told her she needed to undergo a biopsy that same day at Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago.
It was overwhelming because everything happened so quick, Jasko said. It was so scary My mom was like, I cant believe that I never even thought that it could be in your nail.
The nail infection which was unrelated to the melanoma, but led Jasko to see a doctor may have saved her life, doctors told her.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 2 Survival Rate
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Subungual melanoma is most common in non-Caucasians, with both men and women having equal risk. Like other forms of melanoma, subungual melanoma can also spread to other parts of the body and is lethal. The key to diagnosis and early treatment is awareness. All healthcare workers, including nurses, should routinely examine the nails and maintain a high index of suspicion for any pigmented lesion on the nails. The only way to reduce the high mortality is an early referral to a dermatologist for a biopsy. Further, the nurse should educate patients on examining their skin and nails for unusual changes. Finally, both the nurse and the pharmacist should educate the public about using sunscreen when going outdoors and wearing protective clothing when going outdoors. Sunglasses are also recommended as the UV rays of the sun can damage the retinal cells.
Outcomes
For early lesions, the outcomes are good, but for advanced lesions, the outcomes are poor. Disease-free survival is not affected by the type of surgery on the nail. The earlier the diagnosis, the better the survival.
This Is Why A New Though Tiny Spot Or Speck Should Not Be Ignored Even If It Looks Normal
Melanoma
Ultimately I believe genetics will help determine the behavior of these, but until we have that data we have to look at patterns, explains Dr. Gordon.
In general, survival rate of melanomas depends on depth of the cancer.
This depth is determined by a dermapathologist who examines a biopsy of the suspicious spot, which includes a surrounding margin of skin also taken out, under a microscope.
The rule of thumb is that the height of the melanoma above the surface of the skin is equal to its depth below the skin surface.
Dr. Gordon explains, In general, smaller lesions the thinner they are and the better outcomes people have.
Some melanomas will grow in a spreading pattern on the skin , but some will grow in a deep pattern that are more aggressive .
There is no easy way to decipher the spread of melanoma until it is biopsied and sometimes until further tests are performed.
Dr. Gordons interests include medical dermatology, particularly the treatment and prevention of melanoma and other skin cancers in athletes. For 2016, 2017 and 2018 Texas Monthly Magazine selected her as one of the Texas Super Doctors Rising Stars.
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. Shes also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
You May Like: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Also Check: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Symptoms Of Subungual Melanoma
The symptoms of subungual melanoma are often difficult to diagnose, because their incidence is in a relatively unknown place. Subungual melanomas often appear as a dark line below the nail. However, since the predisposition of the condition happens in people with dark color skin, such lines underneath the nails are usually normal and benign. In the event that the stripe changes shape or color, or if a new stripe appears, it is advisable to consult the medical professional. Other indications of advanced subungual melanoma are damaged nail beds, or skin hyperpigmentation. The first signs and symptoms of subungual melanoma are often the development of a new pigmented growth or unusual appearance on the skin or nails.
Melanomas can grow in areas of the body with little or no exposure to the sun. They are named occult melanomas. When melanoma arises in people with darker skin, it is more likely to happen in a hidden area of the body. Subungual melanoma begins under the nail, and it can affect hands or feet. The first sign of a subungual melanoma is usually a brown or black coloration, often confused with a contusion.
How Do You Treat Subungual Melanoma
Most often, subungual melanoma is misdiagnosed as infection due to a hematoma , a fungal infection, trauma, or a mole on the skin. This affects the survival outcome.
Basic treatment of subungual melanoma involves tumor excision. Initially, an excision nail biopsy helps to diagnose the condition. When the cancer becomes invasive, amputation is the preferred option. Often, the extent of excision is determined by the tumorÂs Breslow thickness. Digit-sparing amputation improves survival rate and reduces recurrence.
Lymph nodes, if they are palpable, should be analyzed with imaging. Biopsy may or may not be carried out. If the disease is identified, lymph nodes need to be dissected. Lymph node biopsies are performed on lesions that are 1mm to 4 mm in thickness. If the thickness exceeds 4 mm, brain MRI scans and CT-PET imaging is used to stage the tumor.
Immunotherapy and radiotherapy are utilized only in specific cases. Radiotherapy is used on lymph nodes with large lymphadenectomy.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups. Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems. After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the suns UV radiation. As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times. It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
What Is A Melanoma And How Common Is It
A melanoma is a malignant tumour arising from the pigment producing cell of the skin, the melanocyte. The number of cases of malignant melanoma worldwide is increasing faster than any other form of cancer amongst Caucasians . When compared to other forms of skin cancer, the disease is relatively uncommon . However in the UK, like much of the world, the incidence of cutaneous melanoma continues to rise accounting for the majority of skin cancer deaths. It has been calculated that the lifetime risk for an individual developing the disease is 1:120 for men and 1:95 for women . Currently there are around 8500 new cases annually in the UK with around 1800 melanoma related deaths . Cutaneous melanoma can develop on any skin and mucosal surface. The lower limb is the location of around 30% of all primary cutaneous melanomas, with women are more highly represented in this group, and foot and ankle lesions representing around 3-15% of all cutaneous melanomas .
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
How Is The Diagnosis Of Nail Unit Melanoma Made
Subungual melanoma may be suspected clinically because of a wide new or changing pigment band in a single nail. The dermatoscopic examination may reveal more details showing pigmented lines of varying colour, width and spacing. These lines tend to lose their usual tendency to run parallel to each other along the length of the nail. Ungual melanoma forms a non-pigmented lump under the nail plate, eventually resulting in its destruction.
The diagnosis of melanoma is confirmed by biopsy of the nail matrix and nail bed. It can be a difficult diagnosis requiring examination by expert dermatopathologists. The pathologist should report whether the melanoma is in-situ or invasive. The description of invasive melanoma should include its thickness in millimetres and what level of tissue has been invaded.
If the clinical diagnosis is a subungual haematoma , the nail may be observed for a few weeks. Normal-appearing nail should then be seen growing behind the mark. Dermoscopy is helpful, as haematoma does not conform to the band-like pattern of subungual melanoma. However, it must be remembered that melanoma may bleed.
Other diagnoses that are often considered include onychomycosis , paronychia, pyogenicgranuloma and squamous cell carcinoma. See also subungual melanoma pathology.