What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell cancers are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals. Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do not heal or go away on their own.
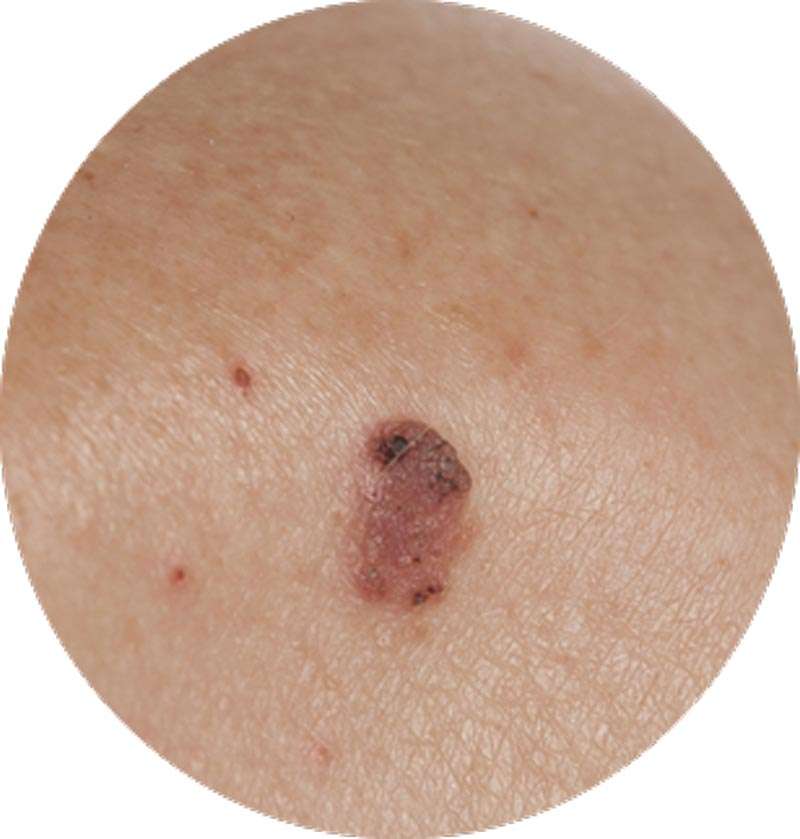
Melanoma Skin Cancer Growth Rate
Melanoma skin cancer is the most dangerous and aggressive type of skin cancer, but it is significantly less common than other, non-melanoma types of skin cancer like Squamous cell carcinoma and Basal cell carcinoma. Melanoma skin cancer has a rapid growth rate, which is what makes it so dangerous it can turn life-threatening in just six weeks and poses a high risk of spreading to other parts of the body if left untreated. The early form of squamous cell carcinoma is known as Bowens disease.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
It is usually possible to completely remove an SCC. The best type oftreatment for you will depend on the size of the SCC and where it is.
Usually, the doctor will remove an SCC using simple skin surgery. Theywill then look at the area under a microscope to check all the cancer has beenremoved. If it has spread, you might need radiotherapy afterwards.
Other ways of removing the SCC are:
- scraping it off then sealing the base of the wound with an electric needle or liquid nitrogen
- using a laser to burn the SCC away
- freezing it off
- Applying creams, liquids or lotions directly onto the SCC. Sometimes the doctor will shine a light on the area to make the medicine work
After treatment, you will need follow-up appointments with your doctor. You will be at greater risk of developing another skin cancer, so its more important than ever to protect your skin from the sun.
You May Like: What Is Triple Negative Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Is Advanced Scc
When a squamous cell carcinoma of the skin has spread extensively or aggressively, or has resisted multiple treatments and repeatedly recurred, it is considered to be advanced.
These tumors include:
- Locally advanced SCC: Tumors that are large or have penetrated deep into underlying tissues, muscles or nerves. These SCCs can be disfiguring and/or can compromise these underlying structures.
- Metastatic SCC: Tumors that have spread beyond the original location to other parts of the body. These SCCs can be life-threatening.
If youve been diagnosed with advanced SCC, your doctor may recommend an evaluation by a multidisciplinary team to explore treatment options. The team may include your dermatologist and/or Mohs surgeon, along with physicians and surgeons from other specialties. After surgery to remove the tumor and, if necessary due to metastasis, local lymph nodes, options may include a combination of treatments, based on the complexity of the disease and your overall health. The regimen can include:
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. Your doctor will want you to check your skin at least once a month. It will be very important to protect yourself from getting too much sun.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your skin cancer doctor. At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. Your doctor will ask about symptoms and check you for signs of the cancer coming back or a new skin cancer. Other exams and tests may also be done.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
Don’t Miss: Do You Need Chemo For Melanoma
What Can I Do To Manage Or Prevent Scc
- Prevent skin cancer:
- Wear sunscreen when outdoors. Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15 and UVA and UVB protection. Reapply after you swim or sweat. If you need to be in the sun, wear a hat and long-sleeved shirts and pants to cover your skin.
- Stay out of the sun between 10 am and 4 pm. This is when the sun is the strongest and most damaging to your skin.
- Do not use tanning booths. These can damage your skin as much as the sun.
- Examine your skin monthly. Watch for growths or moles that change size, shape, or color.
Skin Cancer Undiagnosed For Over 10 Years
The patient had neglected his illness for more than 10 years, says a case report in the International Open Access Journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons .
The patient was a man, 48, living in a U.S. city. The medical attention was sought out due to the insistence of a family member, continues the paper.
The cancer was basal cell carcinoma that had grown to 10 centimeters on his scalp. Somehow this patient didnt mind living with an ulcerating, oozing and bleeding growth on his head.
Had he not sought treatment, he could have lived many more years barring death from an unrelated cause such as a heart attack or car accident.
With that all said, there is no data on what the record is for how long a person lived with an undiagnosed skin cancer.
Certainly you can imagine there must be many cases of people all over the world, living in undeveloped societies with scant medical care, let alone skin cancer awareness, whove been living for over 20 years with a slowly growing bump or patch.
This would describe basal cell carcinoma.
But a person will not get away for too long with an undiagnosed melanoma, as it WILL spread and cause symptoms of that spread, such as respiratory problems or ongoing severe headaches .
Dr. Musick says that the following are common ways that skin cancer shows up:
red bump that bleeds easily a scab or wound that just wont heal slowly enlarging pink or red patch of skin a dark irregularly-bordered bump or spot
Steven Musick, MD
.
Read Also: What Does Stage 2 Melanoma Look Like
How Long Does It Take For A Squamous Cell Skin Cancer To Spread
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
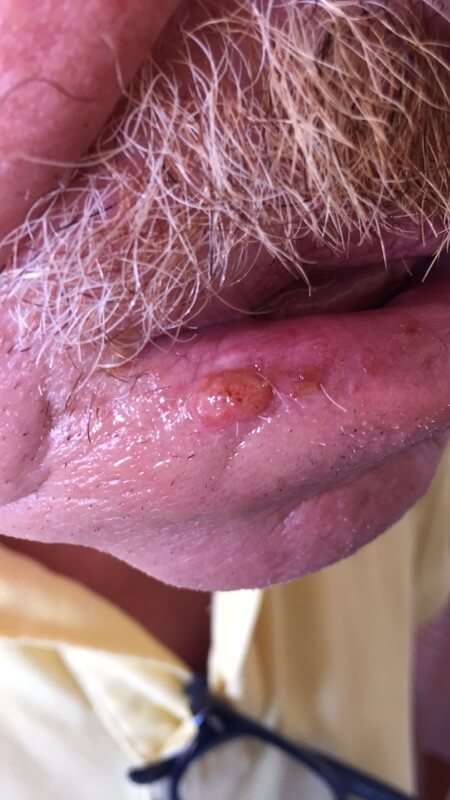
The first sign of an SCC is usually a thickened, red, scaly spot thatdoesnt heal. You are most likely to find an SCC on the back of your hands,forearms, legs, scalp, ears or lips. If its on your lips, it can look like asmall ulcer or patch of scaly skin that doesnt go away.
An SCC may also look like:
- a crusted sore
- a sore or rough patch inside your mouth
- a red, raised sore around your anus or genitals
An SCC will probably grow quickly over several weeks or months.
You May Like: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Metastatic Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Do You Need Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Because just about all squamous cell carcinoma is usually localized it is typically not treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is used for widespread cancer cell eradication, not localized growths. Chemotherapy could be used for a very small percentage of these cases, typically if the cancer has spread.
About 95 percent of squamous cell carcinomas are detected early, and this makes them easy to treat. All treatment options are highly successful, but Mohs micrographic surgery is the most successful while taking the least amount of healthy skin.
Don’t Miss: How Likely Is Skin Cancer
How To Tell If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
Many doctors will order a PET or CT scan once a squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis has been reached to ensure the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body and is contained within the layers of the skin. Your doctor may also test your lymph nodes near the tumor site.
Diagnostic services, staging services and a comprehensive range of treatments are all available at Moffitt Cancer Center, and referrals are not required. To learn more about squamous cell carcinoma stages and the treatment options for each, call or submit a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
Stage Iii Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The tumor cells may be of any size at the original site. A stage III SCC has begun to invade the nearby lymph nodes on the side of the body of the original cancerous growth. This new growth is still under 3 cm in size. It may also have grown into the facial bones like the bones surrounding the eye or your jaw bone.9 It has not affected any other organs.10
Also Check: How Fast Does Melanoma Develop
How Skin Cancer Progresses
All cancer starts in one part of your body. With SCC, it starts in your skin. From there, cancer cells can spread.
How far your cancer has spread is known as its stage. Doctors assign skin cancers a stage number between 0 and 4.
Stage 4 means your cancer has spread beyond your skin. Your doctor might call the cancer advanced or metastatic at this stage. It means your cancer has traveled to one or more of your lymph nodes, and it may have reached your bones or other organs.
The stage of your cancer and where it is located will help your doctor find the right treatment for you. At stage 4 your cancer may not be curable, but it is still treatable.
Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinomas are usually slow growing, but occasionally SCCs grow in subtle ways and may be quite extensive and advanced by the time of diagnosis.
The general stages of a Squamous Cell Carcinoma are:
- T – stands for the main tumour .
- N – stands for spread to nearby lymph nodes .
- M – is for metastasis .
If a Squamous Cell Carcinoma is advanced the outcome can vary and this may affect your treatment choices.
A small number of Squamous Cell Carcinomas, especially those diagnosed late or were not treated are fatal.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Subungual Melanoma Grow
Understanding Your Stage Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage. If you have squamous cell skin cancer, your doctor may also recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan, or testing lymph nodes near the tumor to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
Do You Need Chemo For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Larger squamous cell cancers are harder to treat, and fast-growing cancers have a higher risk of coming back. In rare cases, squamous cell cancers can spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. If this happens, treatments such as radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and/or chemotherapy may be needed.
Don’t Miss: What Is Precancerous Skin Cancer
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
95% of Squamous Cell Carcinomas in Australia are the result from skin damage caused by
- Cumulative long-term sun exposure
- Intermittent overexposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun
Most Squamous Cell Carcinomas occur on parts of the body exposed to the sun especially the face, ears, neck, bald scalp, shoulders, and back, but many can be found in areas that are only burned or exposed occasionally such as the abdomen or upper thighs
It is not possible to pinpoint a precise, single cause for a specific tumour, especially tumours found on a sun-protected area of the body or in an extremely young individual. Some Squamous Cell Carcinoma can also result from less common causes such as:
- contact with arsenic,
- exposure to ionising radiation such as X-rays
- open sores that resist healing,
- chronic inflammatory skin conditions, and
- as complications of burns and scars.
Prognosis For Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If carcinoma of the tongue is localized , 5-year survival is > 75%. For localized carcinoma of the floor of the mouth, 5-year survival is 75%. Lymph node metastasis decreases survival rate by about half. Metastases reach the regional lymph nodes first and later the lungs.
For lower lip lesions, 5-year survival is 90%, and metastases are rare. Carcinoma of the upper lip tends to be more aggressive and metastatic.
Don’t Miss: What Is Grade 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
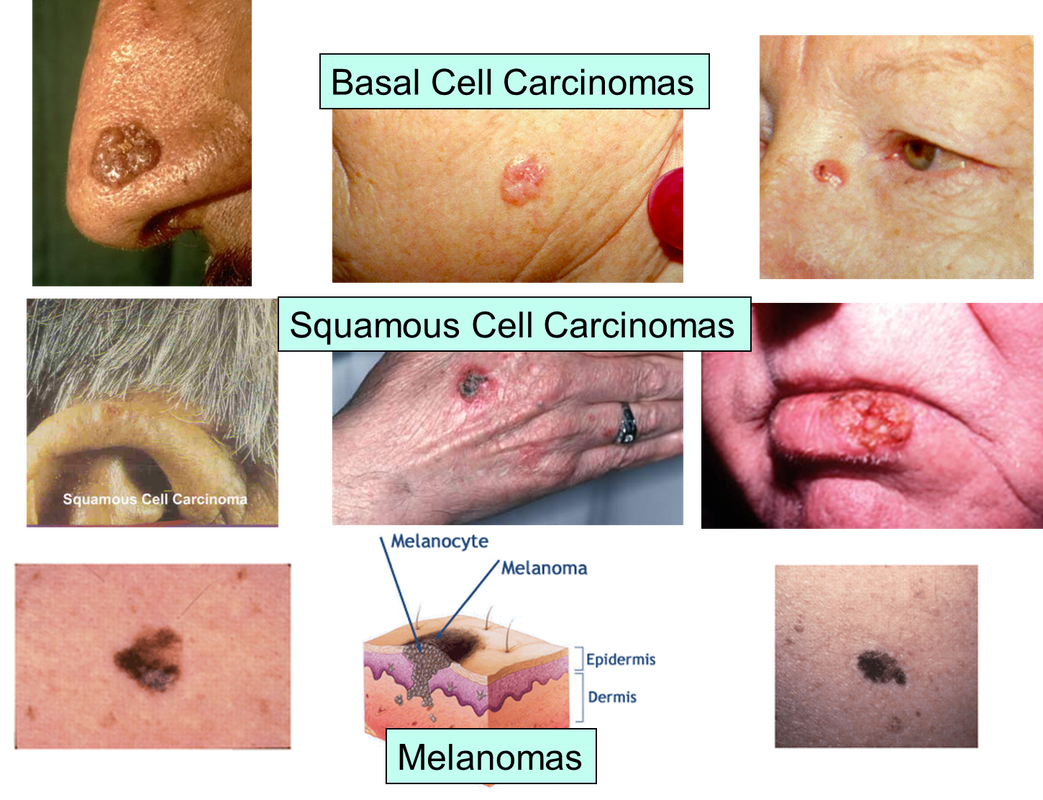
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
Answer: How Quickly Does Scc Grow
While SCC is a diagnosis, there are also types of SCCs that are more infiltrative than others, so those can grow faster and deeper. It’s not necessary to know which one you have for treatment purposes. The most important thing to know is that you DO have confirmed SCC and now you need to get treatment for it. Once I know a patient has a confirmed skin cancer, we try to get them their appointment to resolve it within 2 months. There’s no point in delaying it further and letting it grow. “This answer has been solicited without seeing this patient and cannot be held as true medical advice, but only opinion. Seek in-person treatment with a trained medical professional for appropriate care.”
Don’t Miss: How Fast Does Melanoma Grow
Moffitt Cancer Centers Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma
At Moffitt Cancer Center, our multispecialty team of cancer experts takes a highly individualized approach to squamous cell carcinoma treatment. We offer the latest diagnostic and treatment options, and we work closely with each patient to offer customized guidance and help ensure the best possible outcome. For instance, there are many steps a patient can take to improve his or her own squamous cell carcinoma prognosis regardless of the general survival rate such as:
- Performing self-examinations from head to toe, including parts of the body that are not regularly exposed to UV rays, at least monthly, and promptly reporting any suspicious or unusual changes in skin texture or appearance to a physician
- Seeing a physician for a professional skin cancer examination yearly
- Avoiding exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays while outdoors, preventive measures include seeking shade, wearing sunglasses and a brimmed hat, covering up with clothing and using a broad spectrum sunscreen with both UVA and UVB protection
- Never using indoor tanning beds
If youd like to learn more about the squamous cell carcinoma survival rate, the experts at Moffitt can put this information into the proper context for you and help you take appropriate steps to achieve the best possible outcome. Call or complete a new patient registration form online. We see patients with and without referrals.