Familial Renal Oncocytoma And Birt
Individuals affected with familial renal oncocytoma can develop bilateral, multifocal oncocytoma or oncocytic neoplasms in the kidney. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome is a hereditary cutaneous syndrome. Patients with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome have a dominantly inherited predisposition to develop benign tumors of the hair follicle , predominantly on the face, neck, and upper trunk, and these individuals are at risk of developing renal tumors, colonic polyps or tumors, and pulmonary cysts.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the stage and grade of the tumor.
The treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage and grade of the tumor.
- Where the tumor is.
- Whether the patient’s other kidney is healthy.
- Whether the cancer has recurred.
Most transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis and ureter can be cured if found early.
Having One Kidney Does Not Affect The Length Of Your Life Nor Does It Affect The Type Of Life You Will Have
How long will i live with kidney cancer. Cancer cells that have spread from. The percentage of people who after treatment will live at least five years after diagnosis is only 8. People with kidney failure may have many distressing symptoms but these can usually be managed with appropriate medication.
But specialists are getting better at helping patients to live longer after their diagnosis. The kidney is part of the body system that removes waste products from your body. Five years survival rate for stage 4 cancer ie.
A colonoscopy remains the best test to find precancerous and cancerous colon polyps. This slow-growing cancer may linger for a long time before symptoms appear. I think Im a little anxious about my kidneys as my grandfather died of kidney cancer.
It seems that the treatment plan has developed in recent years which may turn into a better outlook for patients now being diagnosed with this cancer. A healthy person who donates a kidney can live a normal life with the one kidney that is left. Sometimes it isnt diagnosed until after it has spread.
The liver has several important functions. You likely will not have kidney problems especially in the first few years after kidney removal. Life expectancy prognosis and outlook after kidney removal can vary.
But the operation is major surgery for the donor as well as the recipient. More information about hospice can be found below in the Related Resources section of this fact sheet. Having to do with the kidneys.
Read Also: Late Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma
Advanced Or Recurrent Kidney Cancer Treatment
For people with advanced kidney cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, treatment with a drug may be recommended along with surgery, or instead of surgery. Some of these drugs are given to you as a pill that you take by mouth others are given as an injection. Much progress has been made in recent years, and people with advanced kidney cancer are living much longer than ten years ago.
- Medicine is often used for advanced kidney cancer that has spread to other parts of the body or where surgery cannot be done.
- Immunotherapy uses the bodys defense system to stop or slow the growth of cancer cells
- Monoclonal antibodies attack a specific part of cancer cells
- Checkpoint inhibitors help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells
- Vaccines give an overall boost to the immune system
Staging Kidney Cancer With The Tnm System
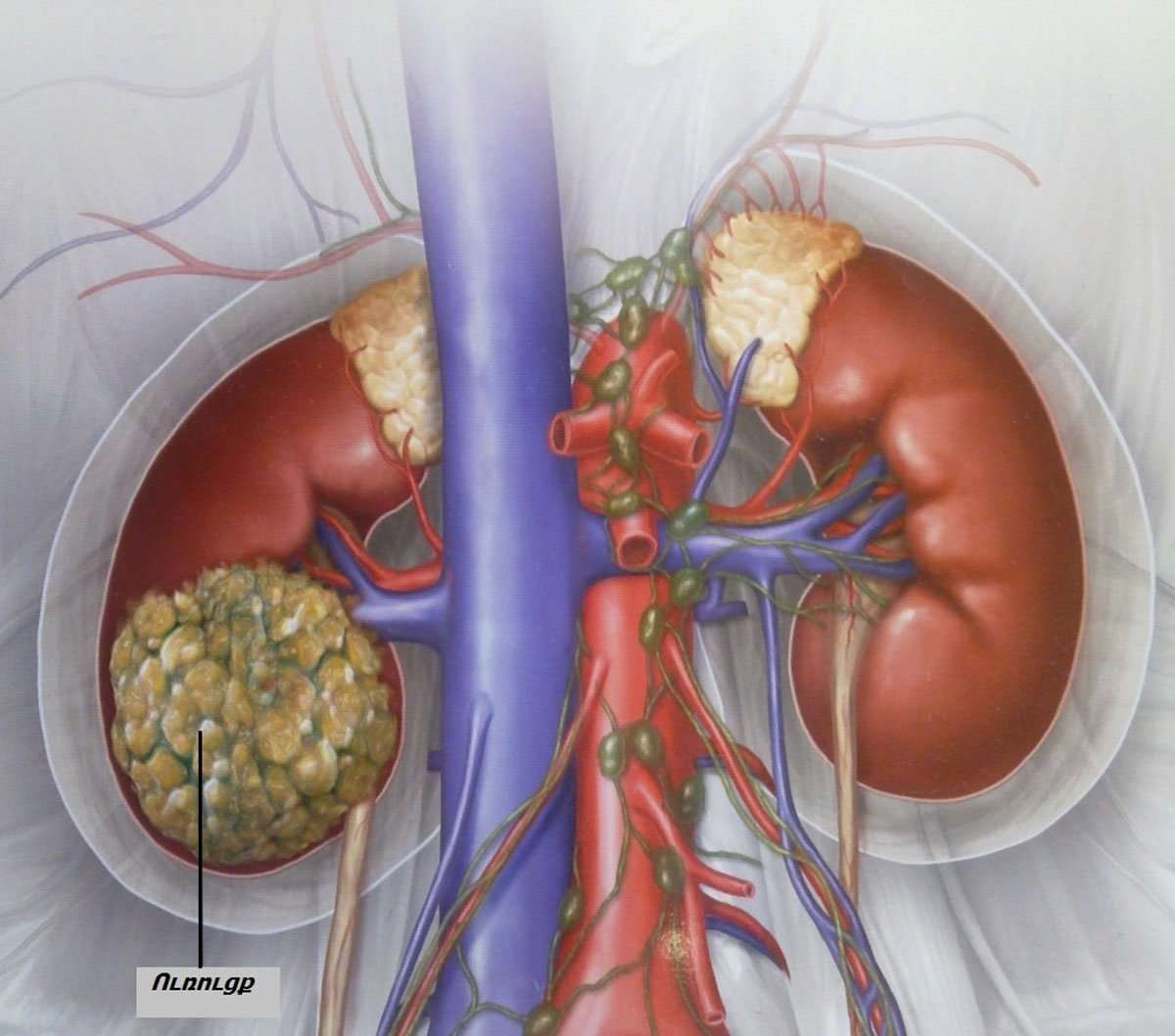
The American Cancer Society describes stages of kidney cancer in more detail using the American Joint Committee on Cancers TNM system. In this system, T stands for tumor, N for lymph nodes and M for metastasis.
- T for tumor is T1, T2, T3 or T4.
- A T1 tumor measures 7 cm or smaller in width.
- A T2 tumor is larger than 7 cm.
- A T3 tumor may be any size and has grown into a major kidney blood vessel or into the tissues on the outside of the tumor, but it hasnt reached the adrenal gland.
- A T4 tumor has grown into the adrenal gland.
The ACS describes kidney cancer using the TNM system in this way:
- Stage 1 is T1, N0, M0.
- Stage 2 is T2, N0, M0.
- Stage 3 is T3, N0, M0 or T1-T3, N1, M0.
- Stage 4 is T4, any N, M0 or any T, any N, M1.
Read Also: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, also known as ccRCC or conventional renal cell carcinoma, is a the most common form of kidney cancer. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is named after how the tumor looks under the microscope. The cells in the tumor look clear, like bubbles.
In adults, ccRCC makes up about 80% of all renal cell carcinoma cases. ccRCC is more common in adults than children. Renal cell carcinoma makes up 2% to 6% of childhood and young adult kidney cancer cases.”
One Type Of Standard Treatment Is Used:
Surgery
One of the following surgical procedures may be used to treat transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis and ureter:
- Nephroureterectomy: Surgery to remove the entire kidney, the ureter, and the bladder cuff .
- Segmental resection of the ureter: A surgical procedure to remove the part of the ureter that contains cancer and some of the healthy tissue around it. The ends of the ureter are then reattached. This treatment is used when the cancer is superficial and in the lower third of the ureter only, near the bladder.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
The Role Of Insulin Mrna Binding Protein
Insulin mRNA binding protein-3 is an onco-fetal mRNA-binding protein recently described as an independent prognostic marker for distant metastasis in RCC and is associated with poorer survival . In hepatocellular carcinoma, IMP3 has been associated with cell motility and trans-endothelial migration . A member of the highly conserved protein family associated with mRNA transport, translation and turnover, IMPs can modulate cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion . Its expression is almost exclusively limited to embryonic development, and it is undetectable in most adult tissues. However, it has recently been found to be significantly expressed in malignant adult tissue, including RCC .
Xie et al. assessed the correlation between computed tomography vascularity, and IMP3 and demonstrated an association between high IMP-3 expression and RCC bone metastasis in in situ and cell line studies. Nonetheless, more investigations on the diagnostic potential of biomarkers for RCC bone metastasis and the functional significance of IMP-3 in RCC vascularity and tumor progression are warranted.
Natural History Of Bone Metastasis In Rcc
Bone metastases in RCC are mainly osteolytic, thereby decreasing bone integrity, inducing bone pain and resulting in significant morbidity for patients with associated skeletal-related events . Such morbidities include pathologic fractures, bone pain requiring radiotherapy, impending fracture needing surgical intervention, spinal cord and nerve root compressions and hypercalcemia . The SREs can significantly decrease functional independence with loss of autonomy and impair quality of life .
In a study of 803 patients with mRCC treated in a tertiary center between 1998 and 2007, Woodward et al. found that 32% of patients presented with or later developed bone metastases. The mean number of SREs experienced by those with bone metastasis over the disease course was 2.4. Furthermore, 80% received radiotherapy for bone pain, and 28% experienced spinal cord/nerve root compression .
Don’t Miss: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Treatments For Cancer In Your Bones
Some treatments shrink the cancer. Others protect your bones from the damage the cancer can cause. And some therapies ease your symptoms to help you feel better.
Targeted therapy. These medicines go after substances that help cancer cells grow and survive. Theyâre designed to kill cancer without harming healthy cells.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors target proteins that help cancer cells and their blood vessels grow. These drugs include:
Bevacizumab is another type of targeted therapy. It blocks a protein called VEGF, which helps tumors grow new blood vessels.
mTOR inhibitors target the mTOR protein, which helps cancer cells grow. They include everolimus and temsirolimus .
Immunotherapy. Also called biologic therapy, these medicines use substances made in a lab or by your body to fight kidney cancer. There are a few types:
- Interleukin-2
- Checkpoint inhibitors, such as nivolumab
Radiation. In this treatment, a machine beams high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells inside your body. It can relieve pain in your bones. It also can prevent weak bones from breaking. If you already have a fracture, killing cancer cells with radiation will help it heal faster.
Surgery to remove cancer from your bone can relieve pain, prevent fractures, and make it easier for you to move around.
Drugs to strengthen bones. A few medicines can make bones stronger, and prevent pain and fractures.
How Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Spread
It occurs in one of three ways: Cancer cells spread into the tissue around the tumor in your kidney. The cancer moves from your kidney into your lymph system, which has vessels throughout the body. Kidney cancer cells enter the bloodstream and are carried and deposited to another organ or location in your body.
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
Moffitt Cancer Centers Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma
At Moffitt Cancer Center, our multispecialty team of cancer experts takes a highly individualized approach to squamous cell carcinoma treatment. We offer the latest diagnostic and treatment options, and we work closely with each patient to offer customized guidance and help ensure the best possible outcome. For instance, there are many steps a patient can take to improve his or her own squamous cell carcinoma prognosisregardless of the general survival ratesuch as:
- Performing self-examinations from head to toe, including parts of the body that are not regularly exposed to UV rays, at least monthly, and promptly reporting any suspicious or unusual changes in skin texture or appearance to a physician
- Seeing a physician for a professional skin cancer examination yearly
- Avoiding exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays while outdoors, preventive measures include seeking shade, wearing sunglasses and a brimmed hat, covering up with clothing and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with both UVA and UVB protection
- Never using indoor tanning beds
Recurrent Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell cancers typically develop resistance to treatment. Resistant cancer may return locally in the area of the kidney, or in other parts of the body such as the lungs or bones. Its important to understand that not all sites of recurrence are the same. Different cancer causing mutations may lead to resistance in different locations of the body and some of these resistant cancers can be effectively treated by surgical removal while areas continue to respond to systemic treatment.
Standard treatment for recurrent cancer is with the checkpoint inhibitor combinations if not already used, otherwise combinations of other precision cancer medicines, immunotherapy, or participation in a clinical trial utilizing new, innovative therapies may provide the most promising treatment. There are several medications approved for the treatment of advanced or recurrent RCC.
Doctors can perform NGS – biomarker testing on a biopsy sample to help determine whether surgery may be beneficial and to identify cancer driving mutations that could be treated with newer precision cancer medicines available through clinical trials.
- Systemic therapy is cornerstone of treatment with checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy.
- TKI therapy is preferred if checkpoint inhibitor has already been used.
- NGS – biomarker testing to determine if isolated metastases can be surgically removed and to determine clinical trial participation.
Read Also: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
Stage Iii Renal Cell Cancer Treatment
Stage III renal cell cancer is defined by the American Joint Committee on Cancer’s TNM classification system:
- T1, N1, M0
Treatment information for patients whose disease has the following classification:
- T3a, N0, M0
Radical resection is the accepted, often curative, therapy for stage III renalcell cancer. The operation includes removal ofthe kidney, adrenal gland, perirenal fat, and Gerota’s fascia, with or withouta regional lymph node dissection. Lymphadenectomy is commonly employed, butits effectiveness has not been definitively proven. External-beam radiationtherapy has been given before or after nephrectomy without conclusive evidence thatthis improves survival when compared with the results of surgery alone however, it may be ofbenefit in selected patients with more extensive tumors.
Inpatients with bilateral stage T3a neoplasms ,bilateral partial nephrectomy or unilateral partial nephrectomy withcontralateral radical nephrectomy, when technically feasible, may be a preferredalternative to bilateral nephrectomy with dialysis or transplantation.
In patients who arenot candidates for surgery, arterial embolization can provide palliation.
Treatment information for patients whose disease has the following classification:
- T3b, N0, M0
In patients who are not candidates forsurgery, arterial embolization can provide palliation.
Treatment information for patients whose disease has the following classifications:
- T1, N1, M0
- T3b, N1, M0
- T3c, N1, M0
Standard treatment options:
The Role Of Akt/integrin
In previous evidence, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase /protein kinase B signaling pathway, which is engaged in the development and progression of many malignancies, may be disrupted by varying integrin signaling . Primary RCC cells can recognize increased levels of pro-migratory and pro-adhesive factors, like fibronectin and collagen I. These are highly concentrated in bone tissue and can promote RCC bone metastasis. Aside from adherence to ECM compounds, increased integrin 5 levels and downstream signaling via AKT can help tumor cells and facilitate their migration to bone , suggesting that integrin 5 may be a prognostic marker of RCC bone metastasis. In other tumors, an integrin 5 inhibitor being tested as cancer therapy in a phase II trial prevented tumor cell invasion and metastasis .
Read Also: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
Interplay Between Bone And Rcc
The local interactions between tumor cells and bone form a vicious cycle underlying the development of skeletal metastases . The bone marrow is favored by certain tumor cells that have a biological proclivity for it for instance, bone marrow produces factors like CXCL12, which has a chemotactic role on cancer cells. On the other hand, cancer cells express the chemokine receptors, CXCR4 and CXCR7 . Activated osteoclasts resorb bone and release growth factors, like bone morphogenetic proteins, transforming growth factor- , insulin-like growth factor and fibroblast growth factor, and others that stimulate metastatic tumor cell growth . In turn, cancer cells secrete prostaglandins, parathyroid hormone, parathyroid hormone-related peptide , activated vitamin D, interleukin-6 and TNF. These increase RANKL expression on osteoblasts and bone marrow stromal cells and stimulate osteoclast number, survival and activity, promoting osteolytic metastases .
How Does It Spread
If a cancerous tumor is discovered in one of your kidneys, the usual treatment is to surgically remove part or all of the affected kidney.
If the tumor is not removed, its more likely that the cancer will spread to either your lymph nodes or other organs. The spread of cancer is called metastasis.
In the case of RCC, the tumor can invade a large vein leading out of the kidney. It can also spread to the lymph system and other organs. The lungs are especially vulnerable.
Also Check: Melanoma Cancer Prognosis
Survival Rates For Kidney Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Your doctor is familiar with your situation, so ask how these numbers may apply to you.
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of kidney cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of kidney cancer is 80%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 80% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
You May Like: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
Survival Rates By Tnm Stage
The first approach is based on the TNM stage statistical survival times are matched to the stage of the disease.
| TNM Lung Cancer Stage | |
|---|---|
| M1c | 6.3 months |
By contrast, the one-year survival rate for stage 4 lung cancer was reported in one study to be between 15% and 19%, meaning this portion of patients with metastatic disease lived for at least a year.
Transitional Cell Cancer Of The Renal Pelvis And Ureter Is Also Described As Localized Regional Metastatic Or Recurrent:
Localized
The cancer is found only in the kidney.
Regional
The cancer has spread to tissues around the kidney and to nearby lymph nodes and blood vessels in the pelvis.
Metastatic
The cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Recurrent
The cancer has recurred after it has been treated. The cancer may come back in the renal pelvis, ureter, or other parts of the body, such as the lung, liver, or bone.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate