Common Places For Melanoma To Spread
Melanoma can spread from the original site on your skin and form a tumor in any organ or body tissue, but its most likely to metastasize to the lymph nodes, liver, brain, lungs, and less commonly, the bones. Melanoma really likes the brain and the liver, says Lisa Zaba, M.D., dermatologic oncologist at Stanford Medical Center in San Jose, CA. If you notice any of the following red flags, it might mean your melanoma has spread and warrants a call to your doctor right away.
Treatment Options: Mohs Surgery
Minor cases of skin cancer can often be treated with a simple excision, but in about half of all cases more significant intervention is needed. In these more significant cases, most dermatologic practices either offer Mohs surgery in-house or refer patients for Mohs surgery to a practice offering the procedure. While Mohs surgery effectively treats non-melanoma skin cancer 95 percent of the time or more, the side effects of Mohs surgery can be significant with bleeding, pain, and healing time being the most common. Theres also a need for reconstructive surgery in about 1 third of cases.
Alternative Treatment Options: Radiation Therapy
For Squamous and Basal cell cancer, Mohs surgery is often not the only viable treatment option. The invasive nature of Mohs surgery coupled with the possibility of scarring and the need for antibiotics following the procedure makes some patients uneasy.
If you are searching for a non-invasive alternative, youll want to learn more about Image Guided Superficial Radiotherapy . IG-SRT uses Ultrasound Imaging and Superficial Radiotherapy to treat Basal and Squamous cell cancers with a precise, measured dose of radiation delivered directly under the patients skin surface. It is completely non-invasive and has less of an effect on the patients daily life post-treatment, with no scarring, no need for antibiotics, and no requirement to stop taking certain medications prior to the procedure.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Melanoma Life Expectancy
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma include:
- Unprotected exposure to ultraviolet rays
- Light-colored hair, skin, or eyes
- History of skin cancer
- The pathologists report
- Recurrence after treatment
Treatment for squamous cell carcinoma usually involves surgery to remove the lesion. The surgical options include:
- Excision: The physician cuts out the tumor with a scalpel, along with a small margin of healthy skin around the tumor.
- Curettage and electrodesiccation: Used in small lesions, the physician scrapes away cancer cells, then cauterizes the skin to prevent bleeding.
- Mohs surgery: The surgeon removes layers of skin and examines them under a microscope to determine if cancer is present. This process continues until no cancer cells are visible.
Rarely, squamous cell carcinoma is treated with chemotherapy , radiation therapy , and immunotherapy when it has metastasized to other areas of the body.
Skin Cancer Undiagnosed For Over 10 Years
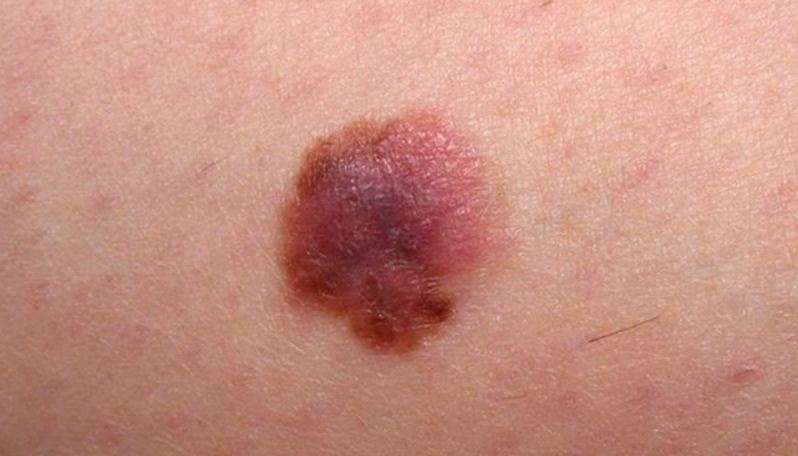
The patient had neglected his illness for more than 10 years, says a case report in the International Open Access Journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons .
The patient was a man, 48, living in a U.S. city. The medical attention was sought out due to the insistence of a family member, continues the paper.
The cancer was basal cell carcinoma that had grown to 10 centimeters on his scalp. Somehow this patient didnt mind living with an ulcerating, oozing and bleeding growth on his head.
Had he not sought treatment, he could have lived many more years barring death from an unrelated cause such as a heart attack or car accident.
With that all said, there is no data on what the record is for how long a person lived with an undiagnosed skin cancer.
Certainly you can imagine there must be many cases of people all over the world, living in undeveloped societies with scant medical care, let alone skin cancer awareness, whove been living for over 20 years with a slowly growing bump or patch.
This would describe basal cell carcinoma.
But a person will not get away for too long with an undiagnosed melanoma, as it WILL spread and cause symptoms of that spread, such as respiratory problems or ongoing severe headaches .
Dr. Musick says that the following are common ways that skin cancer shows up:
red bump that bleeds easily a scab or wound that just wont heal slowly enlarging pink or red patch of skin a dark irregularly-bordered bump or spot
Steven Musick, MD
.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
The 4 Stages Of Melanoma
Two main things determine the stage of melanoma: The thickness or depth of the tumor and how far it has spread when its diagnosed, explains David Polsky, M.D., dermatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City. In stages 0, 1, and 2, the melanoma is limited to the skin. In stage 3, its spread to the lymph nodes, small structures throughout your body that help filter fluids and fight infection. In the most advanced stage, stage 4, melanoma cells have broken away from the original tumor, traveled through the body and formed a new tumor somewhere else.
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the U.S.
Other skin cancer facts:
- Around 20% of Americans develop skin cancer sometime in their life.
- Approximately 9,500 Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer every day.
- Having five or more sunburns in your life doubles your chance of developing melanoma. The good news is that the five-year survival rate is 99% if caught and treated early.
- Non-Hispanic white persons have almost a 30 times higher rate of skin cancer than non-Hispanic Black or Asian/Pacific Islander persons.
- Skin cancer in people with skin of color is often diagnosed in later stages when its more difficult to treat. Some 25% of melanoma cases in African Americans are diagnosed when cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
You May Like: Web Md Skin Cancers
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
How Does Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
Cancer can spread from where it started to other parts of the body.
When cancer cells break away from a tumor, they can travel to other areas through either the bloodstream or the lymph system. If they travel through the lymph system, the cancer cells may end up in lymph nodes. Most of the escaped cancer cells die or are killed before they can start growing somewhere else. But one or two might settle in a new area, begin to grow, and form new tumors. This spread of cancer to a new part of the body is called metastasis.
In order for cancer cells to spread to new parts of the body, they have to go through several changes. They must become able to break away from the original tumor and attach to the outside wall of a lymph or blood vessel. Then they must move through the vessel wall to flow with the blood or lymph to a new organ or lymph node.
When cancer does spread to lymph nodes, it usually spreads to nodes near the tumor itself. These are the nodes that have been doing most of the work to filter out or kill the cancer cells.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Where Else Does Melanoma Spread To
When melanoma advances to stage 3, it means the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes or the skin around the primary tumor and lymph nodes. In stage 4, the cancer has moved to other areas far beyond the lymph nodes, like your internal organs. The most common places melanoma spreads to are the:
- lungs
- brain
- stomach, or abdomen
These growths will cause different symptoms, depending on which areas it has spread to. For example, you may feel breathless or constantly cough if the cancer has spread to your lungs. Or you may have a long-term headache that wont go away if it has spread to your brain. Sometimes the symptoms for stage 4 melanoma may not appear for many years after the original tumor was removed.
Talk to your doctor if youre feeling new pains and aches or symptoms. Theyll be able to help diagnose the cause and recommend treatment options.
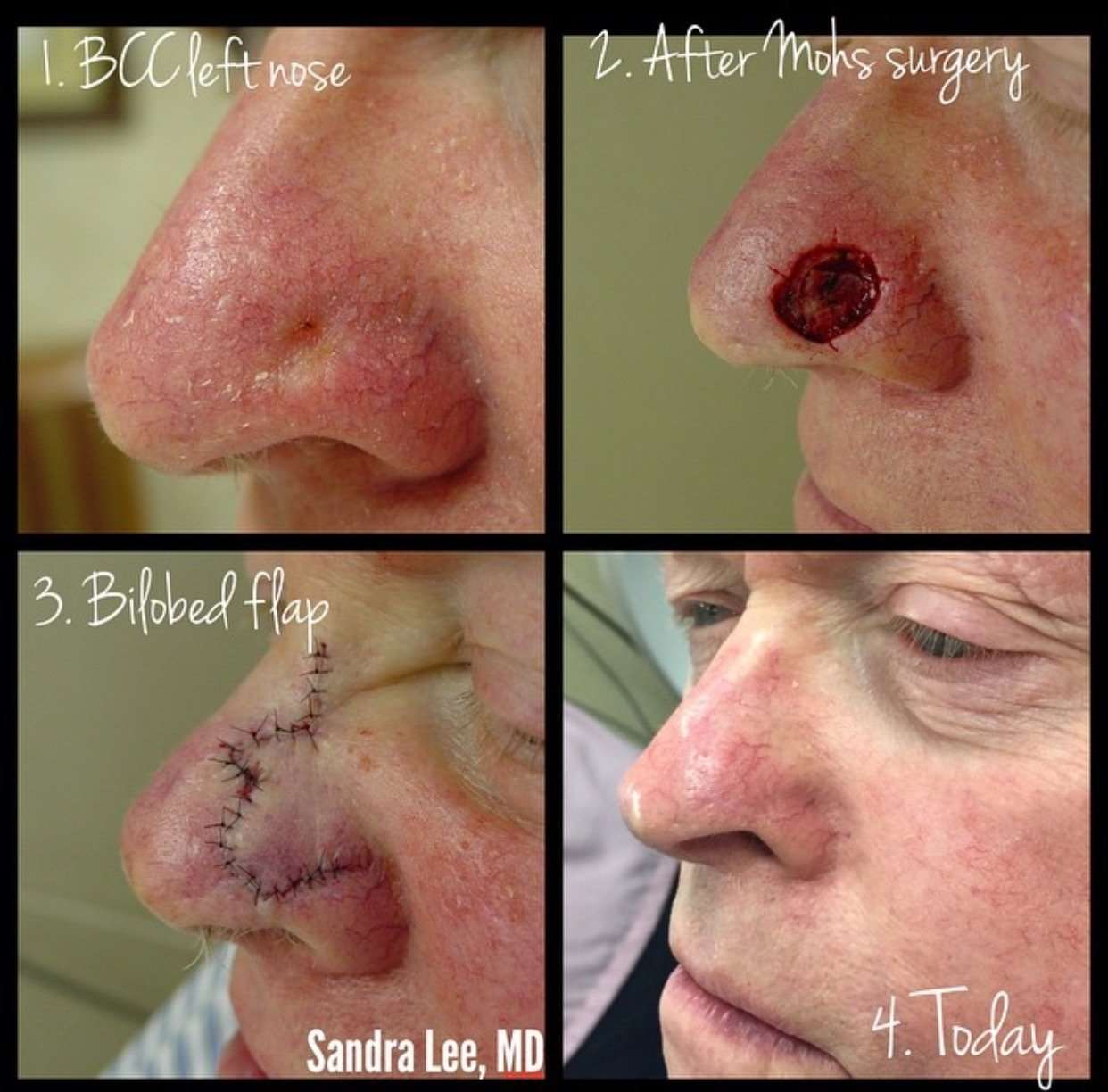
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
|
After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft Skin Tissue transplantation is the removal of various tissues, such as skin cells, corneas, cartilage, or bone, from a body and then inserting that tissue into the same or another person who has… read more or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
Also Check: Body Cancer Symptoms
Comparing Metastatic Melanoma Cells In Lymph Versus Blood
Most studies of cancer cell metastasis in people have focused on cells circulating in the blood. Thats because its much easier to collect patient blood samples than it is to collect samples of lymph, the clear fluid that carries immune cells through vessels of the lymphatic system, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found that human melanoma cells injected into lymph nodes in the mice were more likely to form distant tumors than melanoma cells injected into blood.
To study the role of lymph in metastasis, lead investigator Jessalyn Ubellacker, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in Dr. Morrisons lab, figured out how to collect melanoma cells from lymph in mice. This allowed the team to do the first side-by-side comparison of melanoma cells spreading through lymph and through blood in the same animal, Dr. Morrison said.
Next the team found that melanoma cells in lymph experienced less oxidative stress than melanoma cells in blood. That offered a potential explanation for why melanoma cells from lymph nodes were surviving better and better able to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Further experiments showed that melanoma cells in blood are vulnerable to ferroptosisa form of cell death that occurs when lipids damaged by oxidative stress build up in the outer membrane of a cell. By contrast, melanoma cells from lymph nodes were protected from ferroptosis.
How Is Cancer In Lymph Nodes Found
Normal lymph nodes are tiny and can be hard to find, but when theres infection, inflammation, or cancer, the nodes can get larger. Those near the bodys surface often get big enough to feel with your fingers, and some can even be seen. But if there are only a few cancer cells in a lymph node, it may look and feel normal. Lymph nodes deep in the body cannot be felt or seen. So doctors may use scans or other imaging tests to look for enlarged nodes that are deep in the body. Often, enlarged lymph nodes near a cancer are assumed to contain cancer.
The only way to know whether there is cancer in a lymph node is to do a biopsy. Doctors may remove lymph nodes or take samples of one or more nodes using needles. The tissue thats removed is looked at under the microscope by a pathologist to find out if there are cancer cells in it. The pathologist prepares a report, which details what was found. If a node has cancer in it, the report describes what it looks like and how much was seen.
When a surgeon operates to remove a primary cancer, they may remove one or more of the nearby lymph nodes as well. Removal of one lymph node is considered a biopsy, but when many lymph nodes are removed, its called lymph node dissection. When cancer has spread to lymph nodes, theres a higher risk that the cancer might come back after surgery. This information helps the doctor decide whether more treatment, like chemo, immunotherapy, targeted therapy or radiation, might be needed after surgery.
Also Check: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Fast Breast Cancer Grows
One main reason for why people ask about how fast breast cancer grows, or its doubling time, is when they consider how long to wait to begin treatment. This growth rate also is important to understand if you have a lump and have been advised to simply observe it over time.
In general, the growth of breast cancer can be quite variable, but several studies provide at least an estimate of what may be happening.
Unless your healthcare provider is extremely confident that a lump is benign, it should be evaluated right away rather than waiting.
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread
Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It is estimated that melanoma kills, on average, over 10,000 people in the United States every year.
The first sign of flat melanoma is usually a new spot or an existing mole or freckle that changes in appearance. Some changes can include:
- A spot that has grown in size
- A spot where the edges are looking irregular versus smooth and even
- A spot that has a range of colors such as brown, black, blue, red, white or light gray.
- A spot that has become itchy or is bleeding
According to Dr. Andrew Duncanson, board-certified dermatologist at Forefront Dermatology, It is important to know that melanoma can appear on areas of the skin not normally exposed to the sun such as under the arm, chest, and buttocks. It can also appear in areas that you are not able to see easily on your own including the ears, scalp, back of legs, and bottom of feet. I always recommend to my patients to look for the ugly duckling spot the new spot that doesnt look like any others. Additionally, ask a family member to look over the hard to see areas monthly, while also getting an annual skin cancer exam by a board-certified dermatologist to detect skin cancer early.
Recommended Reading: How Do Carcinomas Spread
How Does A Doctor Know The Stage Of A Patient’s Melanoma
When your dermatologist found a spot on your skin that looked like a skin cancer, your dermatologist performed a skin biopsy. This involved giving you an injection to numb the area and then removing all the spot.
The skin that your dermatologist removed was then sent to a lab, where another doctor looked at it under a microscope. This doctor saw melanoma cells.
When a doctor, who is either a dermatopathologist or pathologist, sees melanoma cells, this doctor also tries to determine the stage of the melanoma. When its possible to figure out the stage, the doctor includes this information in your biopsy report. This is a report that the doctor writes and sends to your dermatologist. It explains what the doctor saw under the microscope.
Because the doctor sees only the skin that your dermatologist removed, your dermatologist also uses the findings from your complete skin exam and physical to help determine the stage of the melanoma.
Sometimes, more information is needed to determine the stage.