What Is Meant By A Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy For Melanoma
Melanomas are rapidly spreading tumors. The first lymph node that a melanoma travels to is called the sentinel lymph node. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a type of surgery in which a few lymph nodes nearest to the melanoma are removed and examined for the presence of melanoma cells. It is a minimally invasive surgery with a low risk of side effects. Sentinel lymph node biopsy or SLNB helps the doctor know about the stage of melanoma to plan appropriate treatment for the patient. It also helps the doctor to know the patients chances of recovery .
During a sentinel lymph node biopsy:
- A dye or a tracer material is injected into the site of the tumor or mass that help stain the sentinel nodes during the procedure.
- The stained path from the tumor to the sentinel lymph nodes is mapped using an instrument that detects the tracer.
- The surgeon removes the sentinel lymph nodes and sends them for lab examination.
If the sentinel lymph node biopsy detects cancer cells, the surgeon removes all local lymph nodes or destroys them with radiation therapy or do both, the surgery as well as radiation therapy.
How Does Distant Recurrence Occur
Many patients find it hard to understand how they can be apparently cancer free one day and be diagnosed with recurrent cancer the next. If surgery got all of the cancer out and chemotherapy and radiation were supposed to have mopped up the rest, how can recurrence even happen?
In most cases, even the smallest breast cancer detected has been growing for some time before it was caught. During this period of growth, the cancer cells multiplied and divided over and over again, and some cancer cells may splinter off from the main tumour and escaped into the surrounding blood and lymphatic vessels. Cells that spread to lymph nodes can certainly be trapped in those lymph nodes and removed at the time of surgery, but cells can also go into the circulatory system. Even early-stage cancers that originally had no lymph node involvement can recur and develop metastatic disease.
While its less common, cancer cells can bypass lymphatics and lymph nodes and travel via surrounding blood vessels. Cancer cells can continue to circulate and go anywhere the blood vessels will take them, or they can home in on other organs in the body, where they take up residence and continue to grow and divide in that one particular spot.
If and when cancer comes back, the cancer cells that escaped the breast are to blame. Obviously if your recurrence is ten years after your diagnosis, we assume that the cells have been dormant all that time and missed the treatments aimed at dividing cells.
Breast Cancer With Possible Spread To Lymph Nodes In Neck
Hi, I have been really worried. Last year I was diagnosed with BC Her2+ and I had chemo Fec-T and radiotherapy. I started zolendronic acid on Friday and I am still on Herceptin. Yesterday I went for an ultrasound to my neck. The radiologist spoke of finding 3 enlarged lymph nodes I think at the base of my neck. I am so worried it has come back and that prognosis will be poor. Has anyone had anything similar? IN other ways I am feeling well. Thank you. Xx
Hi Sunny-day
Im sorry to hear that the radiologist found some enlarge lymph nodes on your recent ultrasound. Its understandable that youre cconcerned about what these may be and what they may mean given that youve had breast cancer.
I would say that we seem to have a lot of posts here on the forum at the moment from people who have swollen lymph nodes so try to stay positive and remember that there could be a number of reasons other than cancer for this problem.
Have you spoken to your GP or Consultant about these findings? Its certainly worth giving them a call to talk things through and see if they feel further investigation is needed.
Keep in touch and let us know how you get on.
Best wishes,
Dont Miss: Where Can Breast Cancer Lumps Be
Also Check: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Melanoma
Cancer In Nearby Lymph Nodes
Sometimes cancer is found in lymph nodes that are near to where the cancer started. For example, breast cancer cells may travel to lymph nodes in the armpit or above the collar bone .
If a surgeon removes a primary cancer, they often remove some of the nearby lymph nodes. The lymph nodes are examined to see if there are any cancer cells in them.
The risk of the cancer coming back may be higher if the nearby lymph nodes contain cancer cells. Your doctors may suggest you have more treatment after surgery to reduce the risk.
Cancer in lymph nodes that are further away is called secondary cancer. Cancer found in nearby lymph nodes is usually treated differently to cancer in lymph nodes that are further away from the primary cancer.
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
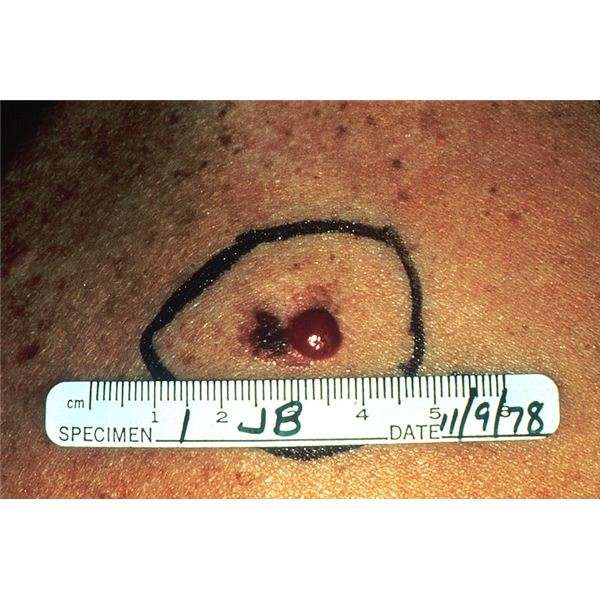
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
Read Also: What Is Liver Cell Carcinoma
Melanocyte As The Source Cell Of Melanoma
Melanoma is known to be more aggressive than most other cancers. Introduction of the Ras oncogene into normal melanocytes resulted in significantly more metastasizing melanomas than similar introduction into normal fibroblasts or epithelial cells . This provides evidence that an intrinsic feature of the melanocyte might be responsible for the rapid development of metastatic disease. Since melanocytes are derived from the neural crest, they are characterized by expression of the motility-associated genes that not only mediate the neural crest but also tumor cell migration. Some of those genes are transcription factor Slug, endothelin receptor B, ERBB3, CD44 and Nodal . Alternatively, the melanogenesis process that defines the melanocyte, might be the culprit . Formation of melanin consists of transformation of l-tyrosine to melanin pigment through several oxidativereduction reactions . Melanogenesis thus forms oxidative environment and some of its intermediates are directly toxic and mutagenic. Melanin scavenges biomolecules and oxygen. All these processes might significantly enhance the effects of typical oncogenes. Inhibition of melanogenesis should therefore decrease melanoma aggressiveness and act as an enhancer of current therapy protocols . We have recently shown that the inhibition of melanogenesis by phenylthiourea and d-penicillamine enhanced cytoxicity of cyclophosphamide and IL-2-activated lymphocytes against melanoma cells .
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. For years after treatment, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to see if the cancer has come back.
At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. After 5 years, they may be done once a year.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
You May Like: Where To Get Checked For Melanoma
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- How far has the melanoma spread under my skin?
- Has it spread anywhere else?
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Most Melanoma Does Not Start In A Preexisting Mole
Melanoma can develop in a preexisting mole, says Dr. Marghoob, but nearly 70% of skin melanomas do not. Rather, they occur in normal skin. Moles themselves are not cancerous, and it is extremely rare for a mole to transform into a melanoma, says Dr. Marghoob. That said, he adds, having many moles helps identify people who are at an increased risk for developing melanoma somewhere on their skin.
Since most melanoma develops on normal skin, Dr. Marghoob stresses the importance of protecting the entire surface of the body, including areas with many moles and areas without any moles. Some people use sunblock only where they have moles because they think the moles themselves are dangerous, adds Dr. Marghoob. Stay safe by applying broad-spectrum sunblock with an SPF of at least 30, wearing sun-protective clothing, or using a combination of the two approaches.
Recommended Reading: What Are The 2 Types Of Skin Cancer
Prognosis And Survival For Melanoma Skin Cancer
If you have melanoma skin cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for melanoma skin cancer.
When Would A Patient Have A Slnb
Most patients have a SLNB when they have their melanoma surgery.
The melanoma surgery differs from the skin biopsy. You had a skin biopsy when your dermatologist removed what looked like a melanoma from your skin.
For patients with melanoma, the next step after a skin biopsy is usually melanoma surgery. During melanoma surgery, the goal is to remove any remaining cancer. If your melanoma is thin, your dermatologist may perform the melanoma surgery in a medical office or surgical suite while you are awake.
Patients who have an early, thin melanoma do not need to have a SLNB.
If the melanoma is thick or has spread, you may be treated in an operating room. A SLNB is also performed in an operating room.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
When Would A Doctor Recommend A Slnb
Your doctor may recommend a SLNB if you have an increased risk of melanoma spreading to a lymph node. Melanoma has a greater risk of spreading to the nearest lymph nodes when it:
-
Grows to a certain thickness in the skin
-
Has cells that are dividing quickly
-
Breaks open
A doctor can tell if melanoma has any of these risks by reading your biopsy report.
A SNLB is only recommended when you have a high risk of melanoma spreading and your doctor did not feel any enlarged lymph nodes when examining you.
If your doctor felt any enlarged lymph nodes, you need different testing.
How Can You Tell If A Mole Is Cancerous
This ABCDE guide can help you determine if a mole or a spot may indicate melanoma or other skin cancers: A is for asymmetrical shape. One half is unlike the other half. B is for border. Look for moles with irregular, notched or scalloped borders. C is for color. Look for growths that have changed color, have many colors or have uneven color.
Recommended Reading: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Slow Growing
When Melanoma Cant Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this. General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
What If I Have Metastatic Melanoma Symptoms
Whether you have a suspicious mole or are experiencing some symptoms of advanced-stage melanoma, it is important to consult with a physician to receive an accurate diagnosis, as many other conditions can cause similar symptoms. At Moffitt Cancer Center, we provide a comprehensive range of screening, diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services for patients with melanoma and other types of cancer. Within our Cutaneous Oncology Program, our multispecialty team includes surgeons, dermatologists, medical oncologists and other experts who work together as a tumor board to ensure our patients receive the best possible treatment and care.
If you would like to schedule an appointment at Moffitt to discuss your metastatic melanoma symptoms, call or fill out a new patient registration form online. We do not require a referral to schedule an appointment.
- BROWSE
You May Like: What Is Stage 4 Melanoma Cancer
Common Places For Melanoma To Spread
Melanoma can spread from the original site on your skin and form a tumor in any organ or body tissue, but its most likely to metastasize to the lymph nodes, liver, brain, lungs, and less commonly, the bones. Melanoma really likes the brain and the liver, says Lisa Zaba, M.D., dermatologic oncologist at Stanford Medical Center in San Jose, CA. If you notice any of the following red flags, it might mean your melanoma has spread and warrants a call to your doctor right away.
Symptoms Of Metastatic Melanoma Other Than A Mole
Other symptoms of this type of cancer may not appear until a later stage, when the melanoma has metastasized to another area of the body. Metastatic melanoma most often spreads to the lymph nodes, brain, bones, liver or lungs, and the additional symptoms experienced at this late stage will depend on where the melanoma has spread. For example:
- Lungs A persistent cough or shortness of breath
- Brain Headaches or seizures
- Lymph nodes Swelling of the lymph nodes
- Liver Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
- Bone Bone pain or unusual fractures
Read Also: Can You Cure Stage 4 Melanoma
How Is Melanoma Staged
Melanoma stages are assigned using the TNM system.
The stage of the disease indicates how much the cancer has progressed by taking into account the size of the tumor, whether its spread to lymph nodes, and whether its spread to other parts of the body.
A doctor can identify a possible melanoma during a physical exam and confirm the diagnosis with a biopsy, where the tissue is removed to determine if its cancerous.
But more sophisticated technology, such as PET scans and sentinel lymph node biopsies, are necessary to determine the cancers stage or how far its progressed.
There are five stages of melanoma. The first stage is called stage 0, or melanoma in situ. The last stage is called stage 4. Survival rates decrease with later stages of melanoma.
Its important to note that survival rates for each stage are just estimates. Each person with melanoma is different, and your outlook can vary based on a number of different factors.
How Fast Melanoma Spreads
Some forms of melanoma can spread quickly, though the exact timeline will depend on your individual health situation. The timeline can be impacted by factors like your age, family history, any underlying medical conditions you may have, as well as what kind of melanoma you have.
During the diagnosis process, your dermatologist will determine what stage your cancer is at. The stage of your melanoma indicates what kind of treatment youll need.
Melanoma can spread quickly and be difficult to treat at later stages, so its important to seek treatment immediately after diagnosis, even if youre only at Stage 0 or Stage 1.
Protect the skin youre in.
Skincare is healthcare
Don’t Miss: What Does Skin Carcinoma Look Like
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma, also called malignant melanoma or cutaneous melanoma, is a type of skin cancer. It develops when there is an uncontrolled growth of the cells that give the skin its tan or brown color . Usually, the melanoma tumors are brown or black since most melanoma cells can make melanin. Some melanomas, however, do not make melanin. Such melanoma tumors can appear pink, tan, or even white.Melanoma can occur on the skin of any part of the body. They usually start developing on the chest and back in men and on the legs in women. Melanomas also commonly occur on the neck and face. The less common sites for melanomas include the eyes, mouth, genitals, and anal area. Although melanomas are far less common than the other types of skin cancers, they are more dangerous since they spread rapidly to other parts of the body . Thus, they need to be diagnosed and treated at early stages.