When Does Lung Cancer Begin
A different question looks at when the lung cancer first began. People may think of a stressful time in their life, or a specific chemical exposure, and wonder if it could have been the cause of their cancer. There isnt a precise answer, but there are some theories.
One idea is to look at the patterns of mutation. A 2017 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine suggested that it takes along time for a lung cancer to develop, perhaps decades, especially for lung adenocarcinomas.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
BCCs grow slowly and the prognosis is typically excellent. If left untreated, the basal cell carcinoma will continue to grow deeper and wider into the skin and may involve the nerves, muscle, or bone underneath the skin. When basal cell carcinomas have grown significantly, they will cause disfigurement. Even though they grow slowly, its essential to make an appointment with a dermatologist as soon as you discover a change in your skin.
Alternative Treatment Options: Radiation Therapy
For Squamous and Basal cell cancer, Mohs surgery is often not the only viable treatment option. The invasive nature of Mohs surgery coupled with the possibility of scarring and the need for antibiotics following the procedure makes some patients uneasy.
If you are searching for a non-invasive alternative, youll want to learn more about Image Guided Superficial Radiotherapy . IG-SRT uses Ultrasound Imaging and Superficial Radiotherapy to treat Basal and Squamous cell cancers with a precise, measured dose of radiation delivered directly under the patients skin surface. It is completely non-invasive and has less of an effect on the patients daily life post-treatment, with no scarring, no need for antibiotics, and no requirement to stop taking certain medications prior to the procedure.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
When Can Lung Cancer First Be Detected
Talk about doubling size raises the question of when lung cancer can first be detected. Lung cancer is most treatable in the early stages. Unfortunately, its still the case that most people have an advanced-stage tumor when they are diagnosed.
Its thought that the average size at which lung cancers can be detected on a chest X-ray is 10 mm to 20 mm. But on chest CT, tumors as small as 6 mm can often be seen.
The difference is clear. Medical providers now know that while screening chest X-rays didnt save lives, screening chest CT scans clearly do save lives.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
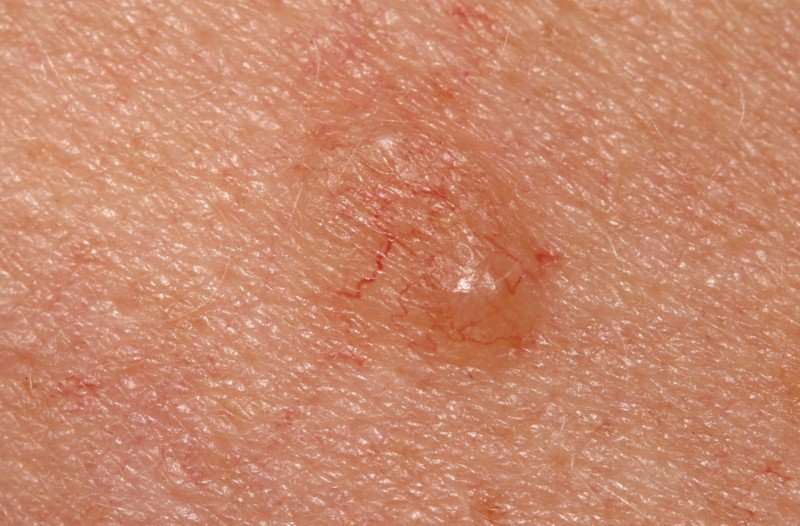
First, your dermatologist may ask you if you have noticed any changes in any existing moles, freckles or other skin spots or if youve noticed any new skin growths. Next, your dermatologist will examine all of your skin, including your scalp, ears, palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, around your genitals and between your buttocks.
If a skin lesion is suspicious, a biopsy may be performed. In a biopsy, a sample of tissue is removed and sent to a laboratory to be examined under a microscope by a pathologist. Your dermatologist will tell you if your skin lesion is skin cancer, what type you have and discuss treatment options.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 4
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
You May Like: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
Can Better Detection Mean A Cure
With better screening, some people want to know if theres a certain tumor size that suggests the lung cancer can be cured. In 2017, researchers created a simulation model. They found that the most aggressive NSCLCs would need to be diagnosed at only 10 mm in size in males and 15 mm in females. The average size of a lung tumor at diagnosis without screening is 33 mm.
Cancer Stage Determines Risk Of Spreading And Line Of Treatment
A cancer of the upper layers of the skin in the epidermis, SCC is the second most common form of skin cancer after basal cell carcinoma and affects an estimated 1 million new people every year in the United States alone. Cancer staging is done for SCC with the intention of categorizing the size of cancer and to judge how much it has grown. And theres a clear line of treatment and way forward for each stage.1
With skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma, the likelihood of cancer spreading to other parts of the body is very low and early diagnosis and treatment usually tackles the problem before it spreads. SCC, however, is a little trickier. While the risk of spreading is still quite small, there is a relatively higher chance of it progressing depending on what stage the cancer is at. For those with weakened immune systems, say, people whove had organ transplants or anyone infected with HIV, the risk is a little higher. Also, when the cancer is in the head and neck region, it may have a slightly higher risk of recurring or spreading.2
The actual stage of this form of cancer is determined based on the TNM protocol devised by the American Joint Commission on Cancer.3
- T : The size/extent of the tumor
- N : Whether it has spread to lymph nodes
- M : Whether it has spread to other parts of the body
Read Also: What Does Skin Cancer On The Outer Ear Look Like
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prevention
Anyone who has had one Squamous Cell Carcinoma has an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same skin area or nearby. That is usually because the skin has already suffered irreversible sun damage.
Thus, it is crucial to pay particular attention to any previously treated site, and any changes noted should be shown immediately to your Doctor at the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas on the nose, ears, and lips are especially prone to recurrence.
Even if no suspicious signs are noticed, regularly scheduled follow-up visits including total-body skin exams are an essential part of post-treatment care every 6 months.
To prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma make sure you follow the recommendations below:
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Are You At Risk
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is also our bodys first line of defense. There are numerous factors which may increase your risk of skin cancer:
- Genetics: Individuals with fair complexions are at the greatest risk. Your risk is also increased if your parents, children, or siblings have had skin cancer.
- Sun Exposure: Over the course of a lifetime, exposure to the sun can lead to a higher risk of skin cancer. Tanning beds and other false sunlight are no exception.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression therapy following organ transplants, chemotherapy, AIDS, and other treatments can put you at a significant risk for skin cancer.
- Lifespan: Human life expectancy has increased from forty-two years in 1904 to close to eighty years today. As a result, the number of skin cancers being seen around the world is increasing.
You May Like: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Turn Into Melanoma
You May Like: Stage Iii Melanoma
How Does Skin Cancer Become A Life
You may wonder how cancer on the surface of your skin becomes a life-threatening cancer. It seems logical to think you could just scrape off the skin with the cancer cells or even remove the cancerous skin lesion with a minor skin surgery and thats all that would be needed. These techniques are successfully used if cancer is caught early.
But if skin cancer isnt caught early, something thats just on my skin can grow and spread beyond the immediate area. Cancer cells break away and travel through the bloodstream or lymph system. The cancer cells settle in other areas of your body and begin to grow and develop into new tumors. This travel and spread is called metastasis.
The type of cancer cell where cancer first started called primary cancer determines the type of cancer. For example, if malignant melanoma metastasized to the lungs, the cancer would still be called malignant melanoma. This is how that superficial skin cancer can turn into life-threatening cancer.
Factors Other Than Growth Rate
The chance that a tumor will spread often depends on factors other than the growth rate or doubling time.
Previously, it was thought that a tumor had to reach a certain size, first spread to lymph nodes, and then onward from there. We know now that this simply isnt the case. Instead, it may be specific mutations in the tumor, or the normal cells around it, that allow new cancer cells to grow in that organ or tissue.
First, the cancer cells need to escape. Normal cells have molecules that hold them together. Different mutations in cancer cells can make it easier or harder to break loose. Then they have to travel through either the blood, lymphatic system, or airways.
Spreading through the lymphatic system takes longer, but spread through the bloodstream can seed cancer cells to other parts of the body much faster and sometimes, long before the tumor is found. Tumor cells in the bloodstream are common even in very early-stage NSCLC.
Most of the cancer cells that arrive in a new body location will die off. For growth to occur, the cells need a blood supply as well as a change in the environment so that the immune system doesnt attack them. To do this, they need to communicate with normal cells nearby. It could be that some lung cancer cells develop new mutations that allow them to establish blood supply in a new region more easily, rather than growing in size and spreading via lymph nodes.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Recurrence
Doctors at the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic have seen a significant increase in the number of patients in their twenties and thirties are being treated for Basal Cell Carcinoma over the last 17 years.
Men with Basal Cell Carcinoma have outnumbered women with the disease, but more women are getting Basal Cell Carcinomas than in the past.
Regular checks at the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic should be performed so that not only the site previously treated, but the entire skin surface can be examined, and mapped digitally and compared to the images taken at subsequent skin checks.
Basal Cell Carcinomas on the scalp and nose are especially troublesome, with higher rates of recurrence and with these recurrences typically taking place within the first two to three years following surgery.
Should a cancer recur, your Doctor might recommend a different type of treatment. Some methods, such as Mohs micrographic surgery, may be highly effective for recurrences.
Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgery is the preferred method of treatment for basal cell cancer. Radiation is an alternative when surgery is not desirable because of cosmetic concerns or medical reasons. Many early stage small basal cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, which is a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Excision, curettage and desiccation, and cryosurgery can also be used to remove the cancer while sparing normal tissue. Large tumors and tumors with nerve or lymph node involvement are not suitable for Mohs surgery and require a multimodality approach to treatment with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy. Larger tumors require reconstruction, which can be done at the time of surgery if margin status is clear.
Patients with high-risk tumors should meet with a radiation therapist to discuss postoperative radiation. In patients with high-risk tumors who are not surgical candidates, systemic treatment with chemotherapy that inhibits the Hedgehog pathway of tumor progression has been shown to be effective. Such cases require multidisciplinary care by a team of surgeons, radiation oncologists and medical oncologists.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Also Check: Well Differentiated Meaning
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Screening
Diagnosis and management of Squamous Cell Carcinoma is best performed via a Full Body Scan. In the first incidence, this process includes
- Digitally Mapping a patients entire body for any suspicious skin damage or lesion
- Followed by a detailed Dermoscopic Examination by a trained skin cancer Specialist
- Recording and combining all images and skin metrics into the patient record
Our expert Doctors at Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic will then clearly identify and diagnose any skin cancers. Having a digital molemap or a baseline of all your skins sun damage for all family members with
- any suspicious sun damage,
- those with a large number of moles, or
- have been diagnosed with melanoma is recommended.
Any changes can be more easily spotted and understood.
Dont Miss: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rates
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Also Check: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Answer: Basal Cell Carcinoma Growth Rate Difficult To Generalize
Well, typically BCCs grow very slowly, but there are occasions when they grow fast. If a persons immune system is compromised , BCC can grow faster. If the cancer has been there for 5 years, typically its bigger than a dime, but again its hard to say. Each persons BCC grow as different rates. Im a Mohs surgeon and have seen thousands of BCCs.
How Quickly Does Skin Cancer Appear On The Body
Have you noticed the appearance of a sudden, unusual growth on your skin? Certain types of skin cancer, like melanoma, can show up very quickly and without warning. So, how can you know if its truly a cause for concern? The only way to determine if a skin growth is cancerous is by getting a skin cancer screening from a qualified provider. The expert dermatology team at Advanced Dermatology offers skin cancer screenings to detect many types of skin cancer and can offer a variety of appropriate treatment solutions at our practice locations in Katy, League City, Pearland, and Sugar Land, TX. So, reach out to us for a screening as soon as you notice an irregular spot.
How long does it take skin cancer to appear?
There’s no set timeline for skin cancer growth and appearance. While some skin cancer lesions appear suddenly, others grow slowly over time. For example, the crusty, pre-cancerous spots associated with actinic keratoses can take years to develop. Other forms of skin cancer, like melanoma, can appear very suddenly, while at other times, the lesions can vanish and reappear.
Where is skin cancer commonly found on the body?
Signs of skin cancer
The specific symptoms can vary based on each individual type of skin cancer. During a skin cancer screening performed in one of our Houston, TX area offices, our dermatologists look for the following types of cancer:
Get a skin cancer diagnosis in Houston, TX
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy