How Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer Treated
If a diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma is considered then referral to a specialist is usually recommended. If the diagnosis is confirmed, either a small biopsy or full removal of the lesion will be planned. For larger lesions, there are a variety of treatments which include:
- a form of light therapy
- scraping, burning or freezing lesions
- sometimes, the use of X-ray treatment
For larger lesions, particularly those in awkward areas on the head and neck sometimes a form of surgery called Mohs surgery is performed.
How Widespread Is Bcc
Basal cell carcinoma is quite common, and the number of reported cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 3.6 million Americans are diagnosed with BCC each year.
- More than one out of every three new cancers are skin cancers, and the vast majority are BCCs.
- The diagnosis and treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancers, including BCC and squamous cell carcinoma , increased up to 77 percent between 1994 and 2014.
Reviewed by:
Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Appear Suddenly
squamous cell cancerappear suddenly
. Then, do skin cancer spots appear suddenly?
Basal Cell CancerSigns include a new or growing bump that is skin colored, pink, or shiny. A growth can develop slowly or appear suddenly. Some growths have a blue or brown hue others may appear translucent. Other signs include an open sore that won’t heal or a reddish patch of skin that does not go away.
Beside above, what does squamous cell carcinoma look like? Squamous cell carcinomas may appear as flat reddish or brownish patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, or crusted surface. They tend to grow slowly and usually occur on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. Normal moles also develop from these skin cells.
Just so, is squamous cell carcinoma a fast growing cancer?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma SCC is generally a slow growing tumor that tends to grow without physical symptoms. However, some forms of this cancer may be fast growing and painful, especially when the lesions are large. They may become irritated and bleed.
How does squamous cell carcinoma start?
Squamous cell carcinoma usually starts out as a small, red, painless lump or patch of skin that slowly grows and may ulcerate. It usually occurs on areas of skin that have been repeatedly exposed to strong sunlight, such as the head, ears, and hands.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas can appear anywhere on the body but the most common sites are sun exposed areas such as the face and arms. Its important to keep a close eye on your skin to try and identify early basal cell carcinoma, as its easier to treat if identified early on.
Typical Basal cell carcinoma symptoms are:
- New skin lesion
- Change in colour of a lesion
The typical lesions to watch out for are as follows:
- Pink or translucent, shiny bumps or pearly nodules, sometimes with dark spots or black, blue, or brown surface
- Growths, pink in color, with raised edges and sunken center, usually with irregular blood spoke-wheel vessels on its surface
- Pale or yellow scar-like areas
- Elevated reddish patches
Stages Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
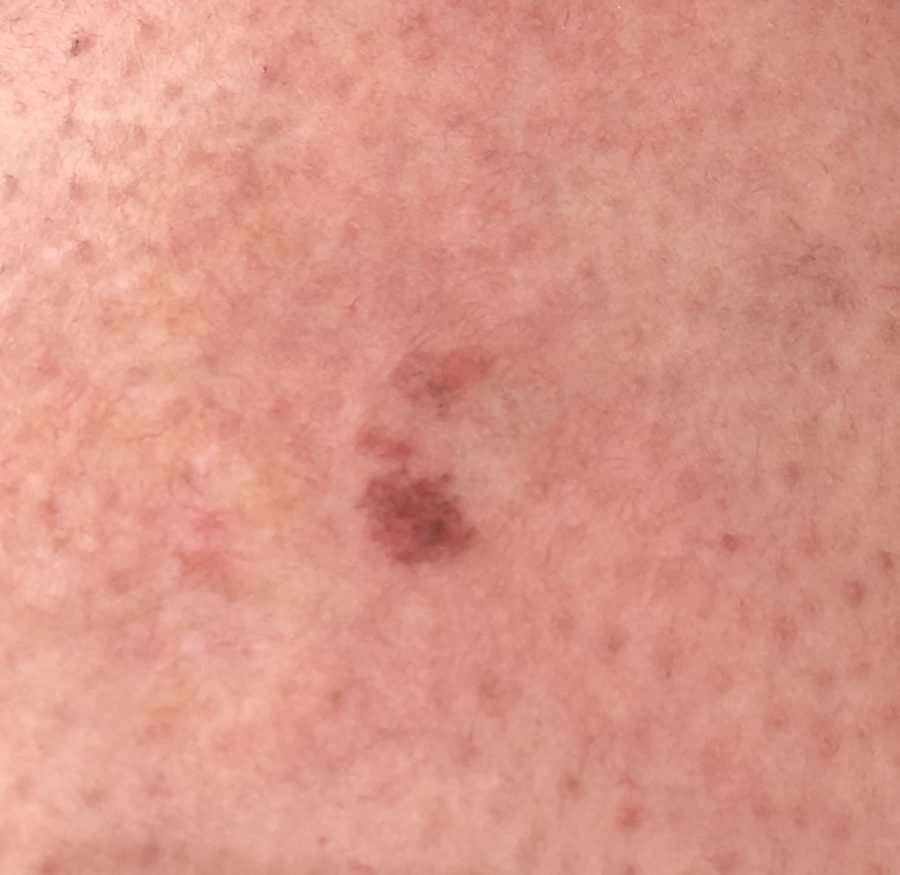
Basal Cell Carcinomas are usually slow growing, occasionally BCCs grow in subtle ways and may be quite extensive and advanced by the time of diagnosis. Some BCCs are aggressive and can grow and spread quickly.
If BCC cancer is advanced the outcome can vary and affect your treatment choices. A small number of Basal Cell Carcinomas cases can be fatal.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Which Is Worse Basal Cell Or Squamous Cell Cancer
Though not as common as basal cell , squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread . Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%5% of cases.
Melanoma typically begins as a mole and can occur anywhere on the body. Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as a firm red bump, a scaly patch, or open sore, or a wart that may crust or bleed easily. Basal cell carcinoma may appear as a small white or flesh-colored bump that grows slowly and may bleed.
Similarly, how long can you live with squamous cell carcinoma? Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
Besides, how serious is a squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive. Untreated, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body, causing serious complications.
What does squamous cell cancer look like?
Squamous cell carcinomas may appear as flat reddish or brownish patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, or crusted surface. They tend to grow slowly and usually occur on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. Normal moles also develop from these skin cells.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas.
The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white. The cancer may alternately bleed and form a scab and heal, leading a person to falsely think that it is a sore rather than a cancer.
Other types of basal cell carcinomas vary greatly in appearance. For example, the superficial type appears as flat thin red or pink patches, and the morpheaform type appears as thicker flesh-colored or light red patches that look somewhat like scars.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
In addition to basal cell carcinoma, this autosomal dominant disorder can result in the early formation of multiple odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies. Various tumors such as medulloblastomas, meningioma, fetal rhabdomyoma, and ameloblastoma also can occur.
Odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies may be seen. Mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, particularly the patched gene, are causative.
Go to Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome to see more complete information on this topic.
How Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Staged
In rare situations, such as when the original lesion is more than 2 millimeters thick, or when it has invaded the lower layers of the skin, a stage may be assigned. The stages range from zero to four higher numbers indicate more aggressive cancers. Most oncologists use the following scale:
- Stage 0 basal cell carcinoma These cancers are only present in the epidermis or the upper layer of the skin. They have not spread to any of the deeper layers or lymph nodes.
- Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma These cancers are smaller than 2 centimeters and have not spread to any nearby lymph nodes or organs, but may have one factor that increases the risk of spreading or recurrence .
- Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma These cancers are larger than 2 centimeters, and while they have not spread to other organs or lymph nodes, they have two or more factors that make them likely to return or spread.
- Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma These cancers have spread to local lymph nodes , but not to other organs.
- Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma These cancers have spread to several lymph nodes, bones or other organs, and they may be any size.
At Moffitt Cancer Center, we treat patients with all stages of basal cell carcinoma. Our skilled oncologists can determine whether a lesion is likely to spread and what treatments are expected to be most beneficial. No referral is necessary to meet with our team call or complete a new patient registration form online.
- BROWSE
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Is Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant cancer affecting the skin. It is a slow-growing tumor generally observed in older individuals, in both men and women
- This malignant carcinoma, which may be present as a lesion on the sun-exposed areas of the body, has the potential to metastasize to the lymph nodes
- Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is the most common type of BCC that is present as nodules on the skin, usually in the head and neck area
- Some nodules may grow to large sizes and ulcerate. They can also infiltrate into the adjoining soft tissues and nerves. Larger tumors also have a greater tendency to recur after treatment
- The cause of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is unknown, but factors such as chronic sun exposure, smoking, and ionizing radiation, etc., are known to contribute towards its development. Also, fair-skinned Caucasians have a greater risk than dark-skinned Africans and Asians
- Any combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures are used to treat Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin. Small-sized tumors and tumors that have not metastasized can be cured through appropriate skin surgery
- The prognosis for metastatic tumors depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor, health status of the individual, and treatment response. The prognosis may be guarded
You May Like: What Is The Worst Skin Cancer To Have
Is It A Pimple Or Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the type of skin cancer that most commonly may look like a pimple. The visible parts of basal cell carcinoma lesions are often small, red bumps that may bleed or ooze if picked at. This may look similar to a pimple. However, after its popped, a skin cancer will return in the same spot.
Also Check: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
A basal cell carcinoma is a stubborn, persistent spot that usually appears on areas that have been exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck, chest, arms and legs. The spot may take one of several forms: an open sore, a reddish irritated patch, a shiny red bump or nodule, a pink growth, or a small scar-like patch. In some people, the condition may resemble psoriasis or eczema. The spot will sometimes bleed, scab and heal up after a week or two, then bleed or become irritated again.
The main warning sign for basal cell carcinoma is that the spot doesn’t go away on its own. Patients often mistake basal cell carcinomas for minor injuries, says Dr. Christensen. They dont realize that an ordinary cut or scratch will heal within a month or so. So if something hasnt healed within a month, it should be examined by a dermatologist.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
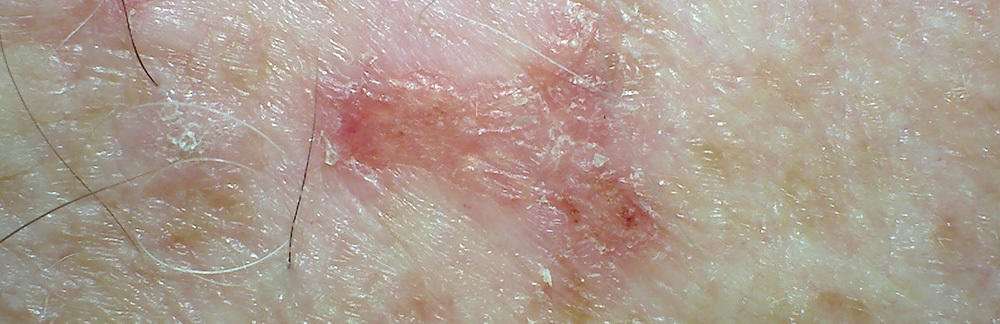
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Read Also: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment
What Does It Look Like
BCCs vary in their appearance. People often become aware of them as an area of discoloured skin, a lump, or area of skin that bleeds, scabs and then refuses to heal. Occasionally they are itchy. Usually BCCs are painless.
There are subtypes of BCC. The subtypes may have a different appearance and may require different treatment.
- Nodular BCC: Form a nodule with a pearly rim and may have a central crater. Fine blood vessels are visible within the nodule.
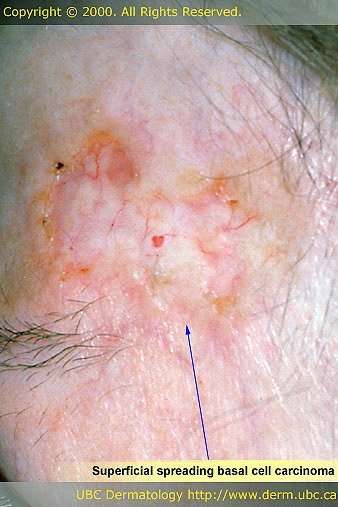
- Superficial BCC: Look like a scaly red patch on the skin with a thin translucent rolled border. Common on the upper trunck and shoulders.
- Morphoeic BCC: Also known as sclerosing BCC. This resembles a scar with a waxy appearance and indistinct margins it may be subtle. Often this type of BCC is much larger than it initally appears, it may invade deeply and infiltrate nerves .
- Basosqamous BCC: Mixed BCC and squamous cell carcinoma that is potentially more aggressive than other forms of BCC.
How Is Bcc Diagnosed
Inspection of your skin by your dermatologist can confirm whether or not a growth is suspicious for BCC. If your dermatologist determines that a growth is suspicious for BCC then a biopsy will be performed. This is a simple procedure performed in the office under local anesthesia. Your growth will then be sent to a pathology lab where thin sections from the growth will be examined under a microscope by a dermatopathologist . In the event your biopsy confirms BCC, your dermatologist will discuss treatment options.
Inspection of your skin at home with a weekly skin self-exam can help you identify a suspicious mole and help your dermatologist diagnose BCC early.
When inspecting your skin for any moles, growths, or spots, look for these signs.
| New |
|---|
Read Also: Melanoma Cancer Prognosis
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis
Occasionally a punch or shave biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis and to guide effective treatment. This diagnostic process involves a Doctor taking a tissue sample for biopsy by removing a portion of the lesion with a biopsy punch or by scraping the lesion with a curette .Usually a biopsy is sufficient to establish the diagnosis of a Basal Cell Carcinoma. In the rare case of suspected metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma, lymph nodes may be examined by the Doctor to see if the cancer has spread or by the use of imaging technologies like ultrasound, CT, or PET scanning.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer and each year there are more new cases of skin cancer than the combined cases of breast, prostate, lung and colon cancer. This translates to one in five Americans developing skin cancer over their lifetime. Of all skin cancer types, basal cell carcinoma is the most common type. According to the American Cancer Society, about 5.4 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed each year in America and basal cell carcinoma accounts for 80% of these cases.
We asked Dr. Rhett Kent, board-certified dermatologist and internal medicine physician with Forefront Dermatology, three of the most common questions surrounding basal cell carcinoma.
What does basal cell carcinoma look like?
Basal cell carcinomas are classically described as slowly growing, pearly papules. This reflects their smooth, shiny appearance. noted Dr. Kent. Although they are usually skin colored or pink, there are pigmented forms. Dilated blood vessels, ulceration, and a scar-like appearance are other clues to the diagnosis. Patients may find it difficult to distinguish these from benign skin growths. However, any new, growing and/or changing skin lesion is always concerning for skin cancer. When any of these features are present, it is important to bring them to the attention of your dermatologist urgently to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Where does basal cell carcinoma occur?
Can basal cell carcinoma spread?
Be Proactive
What Are The Different Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
People assume there is just a single type of squamous cell carcinoma, but there are actually several different types. Some are more likely to spread than others, but in general, most types share similar characteristics. The primary difference between the following types is related to the unique characteristics of the cancerous cells.
The primary types of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Adenoid/pseudoglandular squamous cell carcinoma
- Small cell keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma
- Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
Dont Miss: Brain Melanoma Treatment
Also Check: Well Differentiated Meaning
What Is The Difference Between Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body. Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prevention
Anyone who has had one Squamous Cell Carcinoma has an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same skin area or nearby. That is usually because the skin has already suffered irreversible sun damage.
Thus, it is crucial to pay particular attention to any previously treated site, and any changes noted should be shown immediately to your Doctor at the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas on the nose, ears, and lips are especially prone to recurrence.
Even if no suspicious signs are noticed, regularly scheduled follow-up visits including total-body skin exams are an essential part of post-treatment care every 6 months.
To prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma make sure you follow the recommendations below:
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: Skin Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes