How Dangerous Is Melanoma Its All A Matter Of Timing
Skin cancer holds the unfortunate distinction of being the worlds most common cancer. Though its prevalence around the globe is disturbing, there is some good news: When caught early, skin cancers are highly curable.
You might already know that catching a cancer early means a more favorable prognosis. But it can be difficult to comprehend just how big a difference early detection makes with melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Melanoma should never be underestimated, but treating a tumor early rather than after it is allowed to progress could be lifesaving.
Leland Fay, 46, understands better than most the seriousness of this distinction. When the Monument, Colorado native was diagnosed with melanoma in 2012, he was given a bleak prognosis due to the advanced stage of the tumor it had already reached stage IV.
Leland hadnt thought much of the little black mole on his head a few months earlier, when a dermatologist froze it off during a routine exam. But the mole resurfaced, bigger than it had been originally. After a biopsy and imaging tests, doctors told Leland it was melanoma, and that it had already spread. He could have as few as six weeks to live.
To fully comprehend the significance of timing, it can be helpful to understand exactly what happens to a melanoma when it advances to a later stage, and what it means when a melanoma spreads beyond the original tumor site.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Staging
Staging is the process of determining whether cancer has spread and, if so, how far. The stage of the disease may affect the treatment plan.
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage. In rare cases, your doctor may recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin
Stages are numbered in Roman numerals between 0 and IV.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
High risk features for primary tumor staging
- Depth/invasion: > 2 mm thickness , Clark level IV, Perineural invasion
- Anatomic: Primary site ear
- Location: Primary site hair-bearing lip
- Differentiation: Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
It’s common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful.
It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.
All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Read Also: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Most Melanoma Does Not Start In A Preexisting Mole
Melanoma can develop in a preexisting mole, says Dr. Marghoob, but nearly 70% of skin melanomas do not. Rather, they occur in normal skin. Moles themselves are not cancerous, and it is extremely rare for a mole to transform into a melanoma, says Dr. Marghoob. That said, he adds, having many moles helps identify people who are at an increased risk for developing melanoma somewhere on their skin.
Since most melanoma develops on normal skin, Dr. Marghoob stresses the importance of protecting the entire surface of the body, including areas with many moles and areas without any moles. Some people use sunblock only where they have moles because they think the moles themselves are dangerous, adds Dr. Marghoob. Stay safe by applying broad-spectrum sunblock with an SPF of at least 30, wearing sun-protective clothing, or using a combination of the two approaches.
What Are The Screenings And Tests For Oral Cancer
As part of an ordinary check-up or as a result of patient concerns, your primary care physician or dentist will review your symptoms and conduct a physical inspection of your mouth and throat. If the signs are indicative of cancer, they will refer you to a specialist doctor or dentist who is trained to deal with various diseases of the mouth and throat.
This specialist will carry out another physical exam and may take a tissue sample to be analyzed in a laboratory. This tissue sample, or biopsy, is the only way to know for certain whether a problem spot is cancerous.
Once cancer is diagnosed, in order to find out how far the cancer has progressed, a doctor can order one or more tests. These tests include x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, endoscopies, and PT scans. Each of these tests shows the doctor where the cancer is and whether it has moved to other parts of the body. Some scans, such as the endoscopy , can only target small areas of the body while others, like the MRI, can take a detailed picture of the entire body.
You May Like: How Fast Can Melanoma Spread
What Do The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer Look Like
Early stage skin cancer may resemble a small spot or discolored blemish significantly smaller than the size of a fingernail. It may be reddish or brown, though sometimes white with flaking skin cells surrounded by a small blotch of darker skin.
If you have concerns about the recent appearance of unusual spots on your skin, schedule an appointment right away with a board-certified dermatologist.
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells. Skin cancer develops when mutations occur in the DNA of skin cells. The mutations can quickly cause cells to grow out of control and turn into a mass of cancer cells, which then attack healthy cells.
The most common cause of skin cancer is prolonged overexposure to the sun, sometimes over a period of years, but skin cancer can also develop on areas of your skin not exposed to sunlight.
There are three main types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Other, rare forms of skin cancer also exist.
Skin cancer starts in the epidermis, which is the top layer of your skin. This top layer contains three main types of cells:
Research has shown that patients with skin of color are less likely to survive melanoma. Late detection is one of the critical reasons for this higher mortality rate. On average, 2 people die of skin cancer in the United States every hour, reports the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
Also Check: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Learn More About Stages Of Skin Cancer
All stages of skin cancer can be serious. Delaying treatment can cause unwanted complications, and in some cases, death. Fortunately, treatments with high success rates are now available and can help you restore your confidence, balance, and health. Contact Advanced Skin Canser and Dermatology Center in Wolcott, CT to schedule your consultation today. Well be happy to answer all your questions and recommend the best treatment options!
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
You May Like: Stage 3b Melanoma Survival Rate
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Questions to ask your dermatologist may include:
- What type of skin cancer do I have?
- What stage is my skin cancer?
- What tests will I need?
- Whats the best treatment for my skin cancer?
- What are the side effects of that treatment?
- What are the potential complications of this cancer and the treatment for it?
- What outcome can I expect?
- Do I have an increased risk of additional skin cancers?
- How often should I be seen for follow-up checkups?
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinomas are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals. Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do not heal or go away on their own.
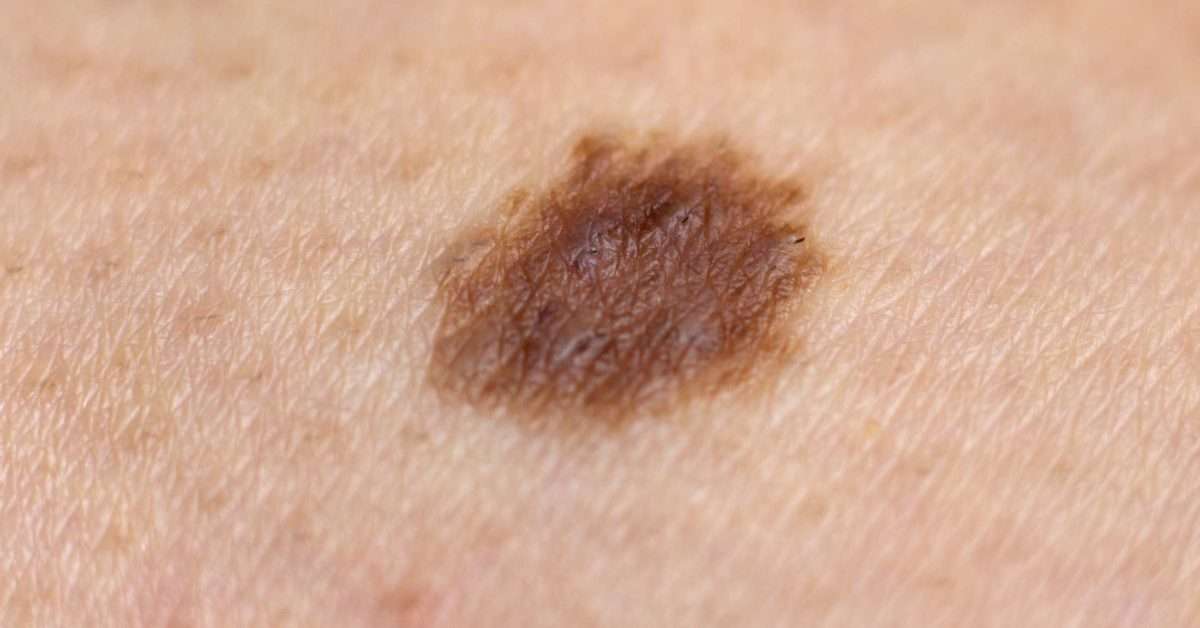
Abcde Melanoma Detection Guide
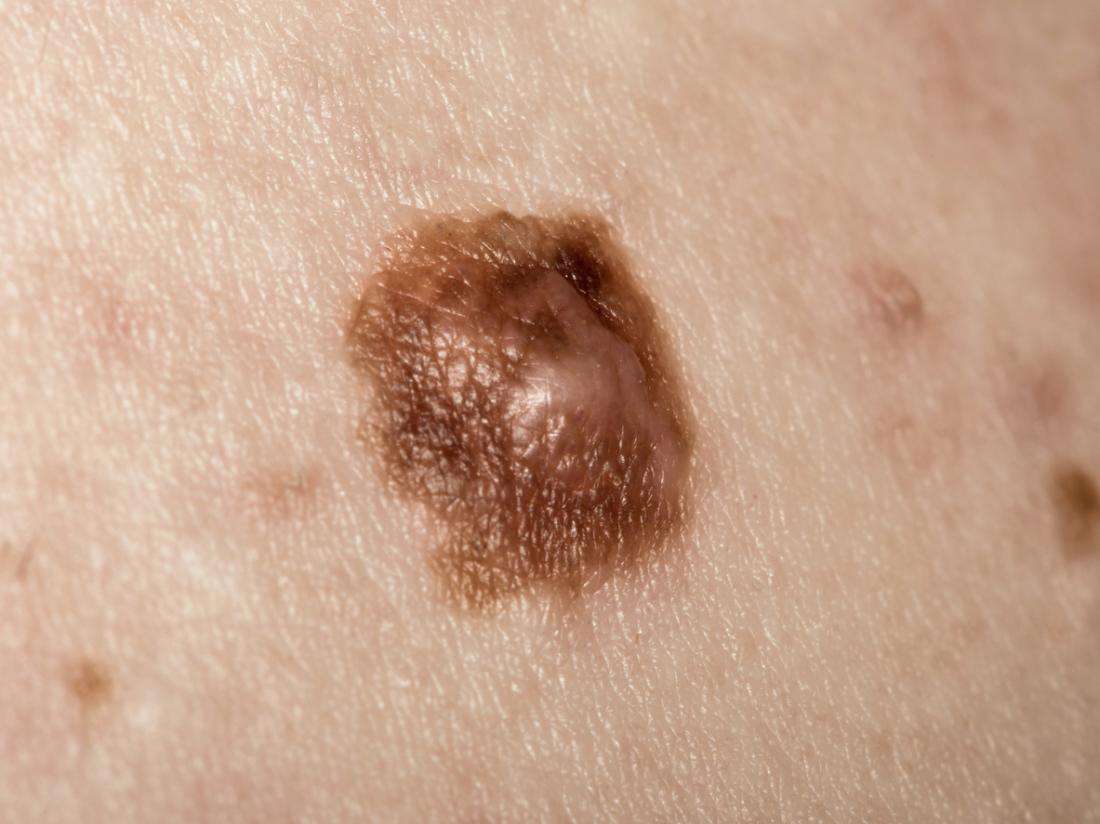
A is for Asymmetry
Look for spots that lack symmetry. That is, if a line was drawn through the middle, the two sides would not match up.
B is for Border
A spot with a spreading or irregular edge .
C is for Colour
Blotchy spots with a number of colours such as black, blue, red, white and/or grey.
D is for Diameter
Look for spots that are getting bigger.
E is for Evolving
Spots that are changing and growing.
These are some changes to look out for when checking your skin for signs of any cancer:
- New moles.
- Moles that increases in size.
- An outline of a mole that becomes notched.
- A spot that changes colour from brown to black or is varied.
- A spot that becomes raised or develops a lump within it.
- The surface of a mole becoming rough, scaly or ulcerated.
- Moles that itch or tingle.
- Moles that bleed or weep.
- Spots that look different from the others.
Read Also: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
A Primer On Skin Cancer
Malignant melanoma, especially in the later stages, is serious and treatment is difficult. Early diagnosis and treatment can increase the survival rate. Nonmelanoma skin cancers include basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Both are common and are almost always cured when found early and treated. People who’ve had skin cancer once are at risk for getting it again they should get a checkup at least once a year.
Are All Moles Cancerous
Most moles are not cancerous. Some moles are present at birth, others develop up to about age 40. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles.
In rare cases, a mole can turn into melanoma. If you have more than 50 moles, you have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your skin is the largest organ in your body. It needs as much attention as any other health concern. What may seem like an innocent cosmetic imperfection, may not be. Performing regular skin self-checks is important for everyone and is especially important if you are a person at increased risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is also color-blind. If you are a person of color, skin cancer can happen to you. Check your skin every month for any changes in skin spots or any new skin growths. Consider taking skin selfies so you can easily see if spots change over time. If youre a person of color, be sure to check areas more prone to cancer development, such as the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, your genital area and under your nails. Takes steps to protect your skin. Always wear sunscreen with SPF of at least 30 every day of the year. Wear UV-A/UV-B protective sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeve shirts and pants. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin check.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/19/2021.
References
Don’t Miss: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun damage DNA in your skin, causing abnormal cells to form. These abnormal cells rapidly divide in a disorganized manner, forming a mass of cancer cells.
Another cause of skin cancer is frequent skin contact with certain chemicals, such as tar and coal.
Many other factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. See question, Who is most at risk for skin cancer?
You May Like: Web Md Skin Cancers
Many Melanomas Dont Require Immediate Treatment
Many people have this concept that all melanomas are extremely rapidly growing cancers, says Dr. Marghoob. They think that waiting even one day after the diagnosis of melanoma can be fatal.
While some subtypes of melanoma do grow extremely fast, says Dr. Marghoob, most early melanomas dont require immediate treatment, allowing ample time to detect, treat, and cure them. Dr. Marghoob advises checking your skin on a monthly basis. If you notice a changing spot on your skin, dont delay in getting it checked out by a dermatologist, he says. And if your doctor does think you may have a melanoma, know that for most people its not necessary to rush to treatment. Most people can take the time they need to meet with doctors and understand their options.