Major Types Of Skin Cancers And Their Distribution In People Of Color
Skin cancer is mainly divided into two main categories as Non melanoma Skin Cancer and Melanoma Skin Cancer . Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . Each of these most common cancers viz. Basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , and melanoma is named after the type of skin cell from which it arises and has been linked to the varying degree of sun exposure .
NMSC greatly outnumber melanomas in incidence but fortunately most are much easier to treat and have much better long-term prognosis . They are less deadly than melanoma mainly due to their tendency to remain confined to their primary site of disease which makes their management much more straightforward. The devastating majority of keratinocyte malignancies progress in the areas of skin most exposed to UV such as on the face and arms . The BCC and the SCCs often carry a UV-signature mutation indicating that these cancers are caused by UV-B radiation via the direct DNA damage . Although Asians display relative protection from basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, incidence rates of these non melanoma skin cancers have been increasing over 3 to 8 percent annually in the past three decades . Features of different types of skin cancers are listed in .
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Melanoma The Most Serious Skin Cancer Is Killing Fewer People Likely Due To New Treatments
Consumer Reports has no financial relationship with any advertisers on this site.
Between 2013 and 2016, the mortality rate for melanoma declined by almost 18 percent despite continued increases in the incidence of melanoma, according to a recent study published online in the American Journal of Public Health.
Melanoma is by far the most serious type of skin cancer, and its also among the most common types of cancer in the United States. According to the American Cancer Society, just over 100,000 cases of melanoma are diagnosed every year.
In the new study, researchers analyzed melanoma incidence and melanoma death rates between 1986 and 2016. During that period, the incidence of melanoma among Caucasians increased by an average of 2.7 percent every year. For white men 50 and older , cases increased 3.4 percent each year.
Between 1986 and 2013, overall deaths from melanoma also increased by a total of 7.5 percent. But starting in 2013, that began to change. Even for men 50 and older, death rates declined 8.25 percent.
This very sharp drop over such a short time is unprecedented in cancer, says study author David Polsky, the Alfred W. Kopf professor of dermatologic oncology at NYU Langone Health and Perlmutter Cancer Center. Its an incredibly significant improvement over a three-year period, and it appears that the rates are continuing to go down.
Also Check: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Treating Stage 3 Melanoma
If the melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes , further surgery may be needed to remove them.
Stage 3 melanoma may be diagnosed by a sentinel node biopsy, or you or a member of your treatment team may have felt a lump in your lymph nodes.
The diagnosis of melanoma is usually confirmed using a needle biopsy .
Removing the affected lymph nodes is done under general anaesthetic.
The procedure, called a lymph node dissection, can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to a build-up of fluids in your limbs. This is known as lymphoedema.
Cancer Research UK has more information about surgery to remove lymph nodes.
Skin Cancer Undiagnosed For Over 10 Years
The patient had neglected his illness for more than 10 years, says a case report in the International Open Access Journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons .
The patient was a man, 48, living in a U.S. city. The medical attention was sought out due to the insistence of a family member, continues the paper.
The cancer was basal cell carcinoma that had grown to 10 centimeters on his scalp. Somehow this patient didnt mind living with an ulcerating, oozing and bleeding growth on his head.
Had he not sought treatment, he could have lived many more years barring death from an unrelated cause such as a heart attack or car accident.
With that all said, there is no data on what the record is for how long a person lived with an undiagnosed skin cancer.
Certainly you can imagine there must be many cases of people all over the world, living in undeveloped societies with scant medical care, let alone skin cancer awareness, whove been living for over 20 years with a slowly growing bump or patch.
This would describe basal cell carcinoma.
But a person will not get away for too long with an undiagnosed melanoma, as it WILL spread and cause symptoms of that spread, such as respiratory problems or ongoing severe headaches .
Dr. Musick says that the following are common ways that skin cancer shows up:
red bump that bleeds easily a scab or wound that just wont heal slowly enlarging pink or red patch of skin a dark irregularly-bordered bump or spot
Steven Musick, MD
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with approximately 80% of skin cancers developing from basal cells. The epidermis has three types of cells. The cells in the bottom layer of the epidermis are the basal cells.
Basal cells consistently divide to form new cells. These replace squamous cells, pushing old cells towards the skin’s surface, where they die and slough off. Cancers that start in this bottom/basal layer of skin cells are called basal cell carcinoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is usually triggered by damage from ultraviolet radiation. This is most commonly from either exposure to the sun or tanning beds. UV radiation can damage basal cells, causing them to change and grow uncontrollably.
Basal cell carcinoma can look different from person to person. It may present as an open sore, scaly patch, shiny bump, a red irritated patch, pink growth, waxy scar-like growth, or a growth that dips in the center. They can sometimes ooze, crust, or bleed
As it can vary in how it looks, it is essential to get any new growths, lesions, lumps, bumps, or changes of your skin checked by your doctor.
Recommendations For Prevention And Early Detection Of Skin Cancer In People Of Color
Prevention is better than cure and more than 90% of skin cancers are preventable . Because many people of color believe that they are not at risk of skin cancer, education through media and doctors offices is extremely important. People of color should perform regular self examination of their skin from head to the toe carefully every month. There are various types of skin tumors, many are benign which include moles , warts and lipomas etc that can develop from different types of skin cells . However, unusual moles, sores, lumps, blemishes, markings or changes in the way an area of the skin looks or feels may be a sign of melanoma or another type of skin cancer or a warning that it might occur. Know your ABCDEs can be a good guide for people of color to detect melanoma at an early stage .
How to Detect Melanoma Source:The Skin Cancer Foundation
You May Like: What Does Skin Cancer On Scalp Feel Like
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy may be used to treat skin cancer itself or to relieve pain from cancer that has spread.
- Radiation oncologists deliver external beam radiation therapy to the cancer from a machine outside your body.
- Skin cancer is often treated with superficial forms of radiation. That means the radiation only penetrates only a short distance below the surface.
- Doctors target the radiation beams at your tumor, giving more radiation to the skin cancer while keeping it away from underlying organs.
- Treatments are usually scheduled every day, Monday through Friday, for several weeks to accurately deliver radiation to the cancer.
- Treatments are painless and take less than half an hour each, start to finish.
- Your treatment schedule will depend on your cancer, but it usually requires daily treatments for one or more weeks.
- Radiation therapy is often given in addition to surgery, chemotherapy or biologic therapy.
Skin High Dose Rate Brachytherapy may be used to treat skin cancer and minimize the amount of radiation and side effects on nearby healthy tissues
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
Determining If The Cancer Has Spread
As part of your diagnosis, your doctor will also determine what stage the cancer is in. The different stages refer to whether and how far the cancer has spread in your body, on a Roman numeral scale of I to IV. A stage I cancer is small and contained to the body part where it originated, whereas a stage IV cancer has spread aggressively to other parts of the body.
Depending on the type of skin cancer that a person has, it may be more or less likely that it has spread through the body. For instance, basal cell skin cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin where it starts. However, melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas are more likely to spread into other regions of the body. Cases of melanoma, in particular, may call for further tests to determine the specific stage theyre in.
Your doctor may evaluate multiple factors in order to stage the cancer. Using biopsies and imaging tests, your doctor may take a look at:
-
The size and thickness of the tumor, and whether it has grown into surrounding tissues
-
Nearby lymph nodes, to check for signs of cancer spread
Also Check: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
When Do Signs And Symptoms First Appear
Typically, cancer signs and symptoms first appear when the cancerous tumor or mass has grown large enough that it begins to push against nearby organs and tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
This can lead to pain, a change in how the nearby organs function, or both. A brain tumor pressing against the optic nerve will affect vision, for example.
Some cancers are fast moving, such as liver and pancreatic cancers. Prostate cancer, however, is usually slow moving. This is why many older men with prostate cancer forego treatment theyre more likely to die with prostate cancer than because of it.
Screenings for certain cancers should be part of your normal preventive healthcare. These include cancers of the:
- prostate
- cervix
- skin
Your age, sex, family history, and your own medical history will dictate when routine screenings should begin and how often they should be done.
If youre concerned about symptoms associated with various cancers, then you shouldnt hesitate to see your doctor. You can connect to a physician in your area using the Healthline FindCare tool.
Recommended Reading: Where Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis To
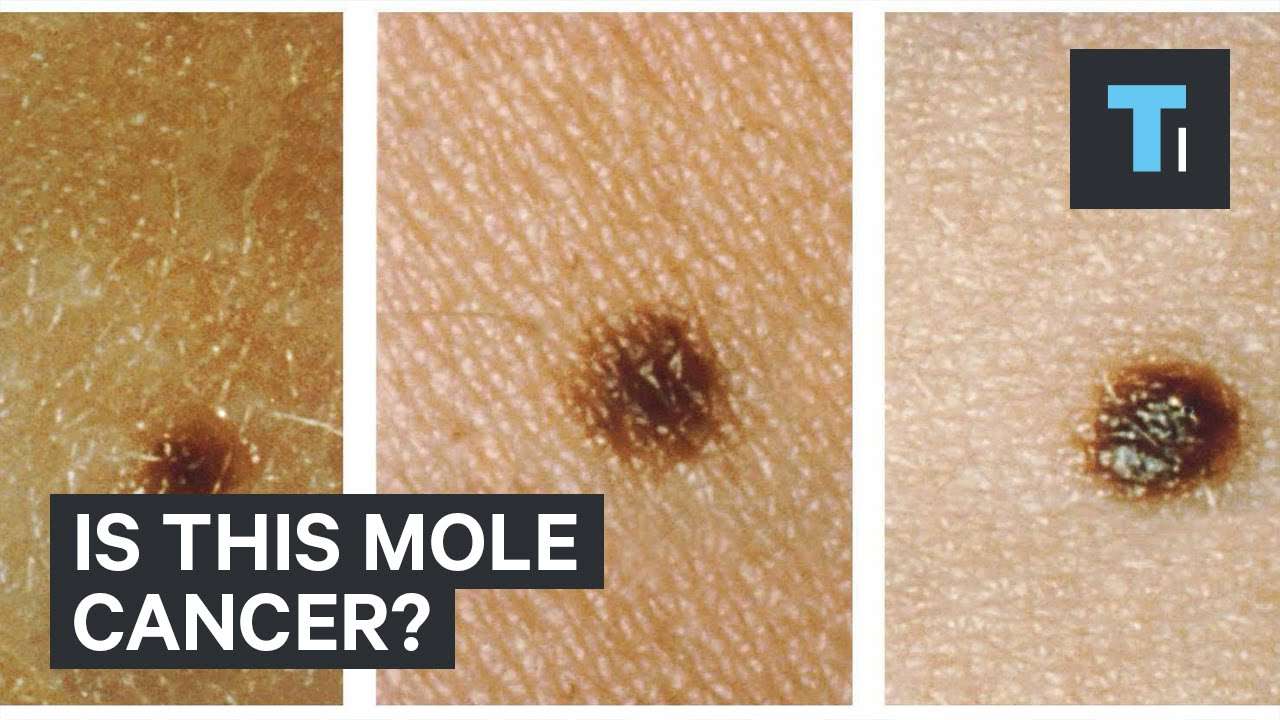
The Abcdes Of Melanoma
To help people find a possible melanoma on their skin, dermatologists created the ABCDEs of melanoma:
| A is for Asymmetry |
If you find a spot on your skin that has any of the ABCDEs of melanoma, see a board-certified dermatologist for a skin exam.
The following pictures can help you see how the ABCDEs of melanoma can appear on the skin.
Read Also: Squamous Cell Stage 4
Who Is At Risk For Developing Melanoma
Everyone is at some risk for melanoma, but increased risk depends on several factors. These are sun exposure, number of moles on the skin, skin type and family history .
How Do People Find Signs Of Melanoma On Their Own Skin
Performing a skin self-exam as often as recommended by your dermatologist is the best way. While examining your skin, you want to look for the following:
-
Mole that is changing in any way
-
Spot that looks different from the rest of the spots on your skin
-
Growth or spot on your skin that itches, bleeds, or is painful
-
Band of color beneath or around a nail
-
Sore that doesnt heal or heals and returns
The ABCDEs of melanoma can help you find changes to a mole, freckle, or other spot on your skin.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
When To Seek Medical Care For Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or have had extensive sun exposure, periodically check their entire body for suspicious moles and lesions.
Have your primary health care provider or a dermatologist check any moles or spots that concern you.
See your health care provider to check your skin if you notice any changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas .
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist or cancer specialist will talk to you about symptoms of metastatic disease that might require care in a hospital.
What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Forms Of Skin Cancer
After Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer is cured surgically in the dermatologist’s office. Of skin cancers that do recur, most do so within three years. Therefore, follow up with your dermatologist as recommended. Make an appointment immediately if you suspect a problem.
If you have advanced malignant melanoma, your oncologist may want to see you every few months. These visits may include total body skin exams, regional lymph node checks, and periodic chest X-rays and body scans. Over time, the intervals between follow-up appointments will increase. Eventually these checks may be done only once a year.
What Are Symptoms & Signs Of Skin Cancer
Symptoms of skin cancer include changes in skin lesions or moles, or the development of new moles that can be remembered by the ABCDEs:
- Asymmetry Irregularly shaped, each half looks different
- Border Jagged, uneven, irregular edges
- Color Mole is several different colors
- Diameter Size greater than ¼ inch
- Evolution Changes in size, shape, or color
Other symptoms of skin cancer include:
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Raised growths or lumps, sometimes with a depressed area in the center
- A pearly white bump
Also Check: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Both types of skin cancer occur when mutations develop in the DNA of your skin cells. These mutations cause skin cells to grow uncontrollably and form a mass of cancer cells.
Basal cell skin cancer is caused by ultraviolet rays from the sun or tanning beds. UV rays can damage the DNA inside your skin cells, causing the unusual cell growth. Squamous cell skin cancer is also caused by UV exposure.
Squamous cell skin cancer can also develop after long-term exposure to cancer-causing chemicals. It can develop within a burn scar or ulcer, and may also be caused by some types of human papillomavirus .
The cause of melanoma is unclear. Most moles dont turn into melanomas, and researchers arent sure why some do. Like basal and squamous cell skin cancers, melanoma can be caused by UV rays. But melanomas can develop in parts of your body that arent typically exposed to sunlight.
Your recommended treatment plan will depend on different factors, like the size, location, type, and stage of your skin cancer. After considering these factors, your healthcare team may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
Treating Stage 1 To 2 Melanoma
Treating stage 1 melanoma involves surgery to remove the melanoma and a small area of skin around it. This is known as surgical excision.
Surgical excision is usually done using local anaesthetic, which means you’ll be awake, but the area around the melanoma will be numbed, so you will not feel pain. In some cases, general anaesthetic is used, which means you’ll be unconscious during the procedure.
If a surgical excision is likely to leave a significant scar, it may be done in combination with a skin graft. However, skin flaps are now more commonly used because the scars are usually less noticeable than those resulting from a skin graft.
Read more about flap surgery.
In most cases, once the melanoma has been removed there’s little possibility of it returning and no further treatment should be needed. Most people are monitored for 1 to 5 years and are then discharged with no further problems.
Read Also: What Is Nodular And Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma