What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
Can You Have Melanoma For Years And Not Know
How long can you have melanoma and not know it? It depends on the type of melanoma. For example, nodular melanoma grows rapidly over a matter of weeks, while a radial melanoma can slowly spread over the span of a decade. Like a cavity, a melanoma may grow for years before producing any significant symptoms.
Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 /pd
The PD-1 receptor binds to PD-L1 and PD-L2, acts as a T-cell co-inhibitory molecule, and suppresses T-cell activation. Further than being expressed on the antigen-presenting cells, ligands are also expressed in many human tumors and in cells within the TME, in response to inflammatory stimuli. Yet, the utility of PD-L1 immunostaining as a predictive biomarker for anti-PD-1 treatment remains unclear.
Nivolumab is a high-affinity anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody that inhibits the binding between the PD-1 receptor and its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Nivolumab was approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. The blockade of the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands mediates immune responses and induces antitumor activity that reduces tumor progression. Nivolumab, with a PFS of 6.9 months, seems to be more efficient than monotherapies with ipilimumab, which display a median PFS of 2.9 months, or chemotherapy, with a median PFS of 2.2 months. The combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab achieved a median PFS of 11.5 months, superior than monotherapies, especially in patients with PD-L1 negative tumors.,
Other anti-PD-L1 molecules are used in Phase I/II trials, such as durvalumab in combination with other immunotherapies and targeted therapies , CK-301 , avelumab in combination with other immunotherapies , and atezolizumab in combination with other immunotherapies and targeted therapies .
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Laser Surgery Is Not Fda
Laser surgery is not currently used as a standard treatment for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It can, however, be an effective secondary treatment. Laser treatment is sometimes used after Mohs surgery to complete the removal of cancer cells. Lasers are effective at removing precancerous lesions, but have not been proven effective at treating cancer yet.
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
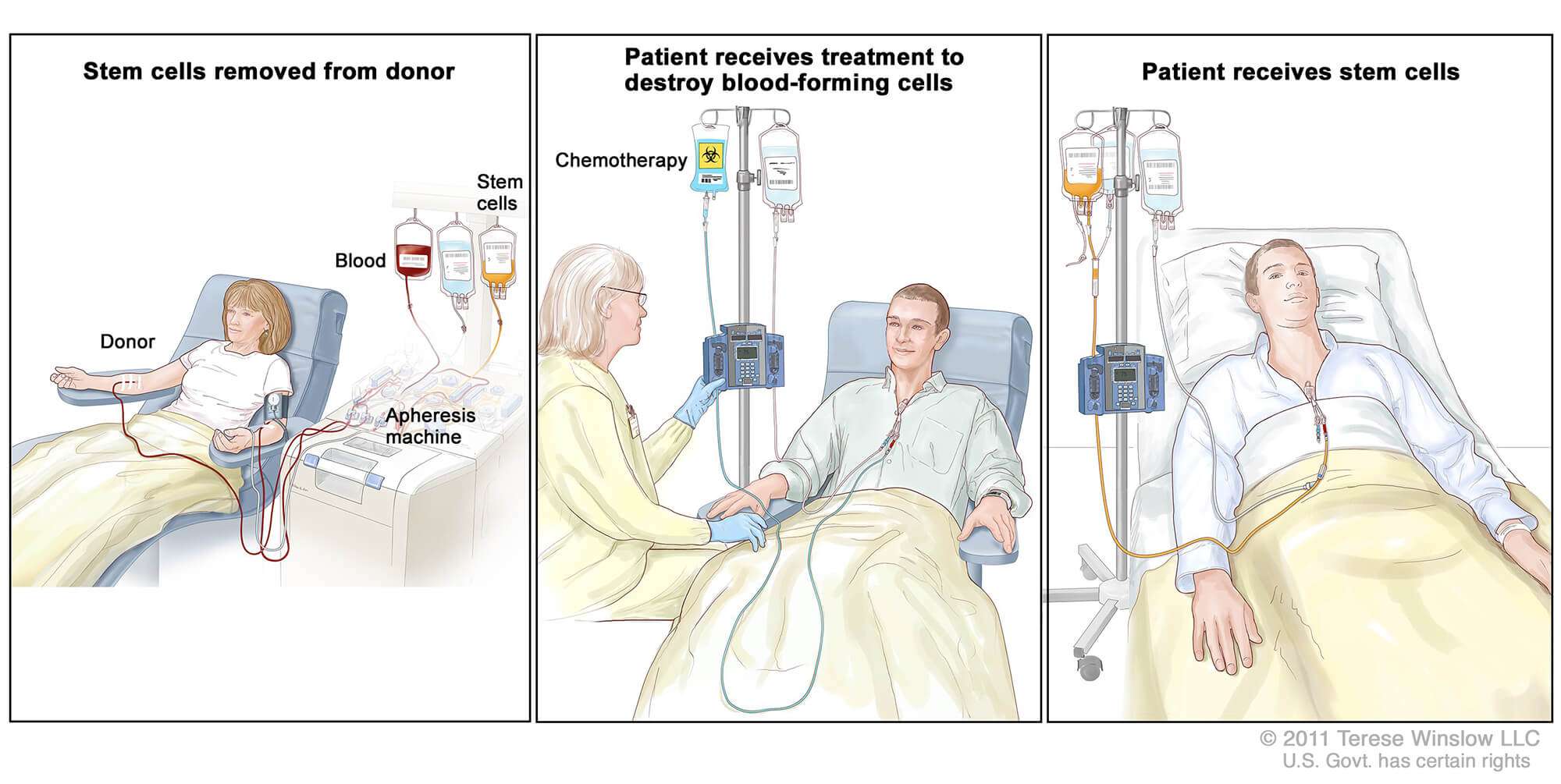
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
Don’t Miss: What Is Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment For Advanced Melanoma
A team of specialists will meet to discuss the best possible treatment for you. This is called a multidisciplinary team .
Your cancer doctor or nurse will explain the different treatments and their side effects. They will also talk to you about things to consider when making treatment decisions.
When melanoma has spread to other parts of the body, the aim of treatment is usually to control the cancer and help you live longer. It may also help improve your symptoms and quality of life. Controlling the cancer might mean shrinking the size of the cancer or stopping it growing for a time. Newer treatments mean many people are living a long time with advanced melanoma.
Depending on your situation, you may have one or more types of treatment.
The main treatments for advanced melanoma are:
- Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy drugs use the immune system to find and attack cancer cells. They help control or shrink the growth of advanced melanoma.
- Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy drugs work by targeting something in or around the cancer cell that is helping it grow and survive. They help control or shrink the growth of advanced melanoma.
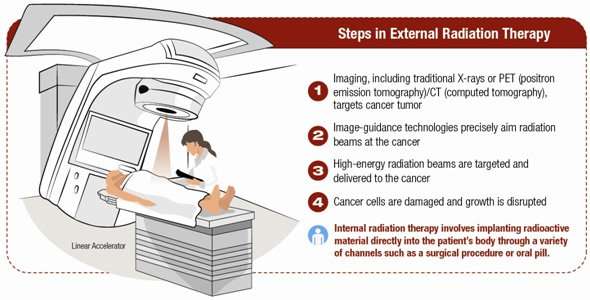
- Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy uses high-energy rays to destroy the cancer cells. It helps control symptoms if melanoma has spread to the brain, bones or skin.
Other treatments that are sometimes used are:
Metastases in the skin may sometimes be treated with:
You may have some treatments as part of a clinical trial.
See also
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Melanoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
You May Like: What Are The Chances Of Skin Cancer
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
Treating Stage Ii Melanoma
Wide excision is the standard treatment for stage II melanoma. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If an SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Historic Progress New Options More Hope
While melanoma is one of the most dangerous forms of skin cancer, promising new treatment options are improving quality of life and increasing survival rates for patients with advanced melanoma.
If youve been diagnosed, your treatment choices depend on the stage of the disease, the location of the tumor and your overall health. Options include:
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the melanoma returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another part of the body .
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin to learn as much as possible about the recurrence. After this testing is done, you and your doctor will talk about the treatment options. Often the treatment plan will include the treatments described above, such as surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and radiation therapy, but they may be used in a different combination or given at a different pace. Your doctor may suggest clinical trials that are studying new ways to treat this type of recurrent cancer. Whichever treatment plan you choose, palliative care will be important for relieving symptoms and side effects.
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system. There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
You May Like: How To Protect Your Self From Skin Cancer
Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma That Can Be Removed By Surgery
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage III melanoma that can be removed by surgery may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. Skin grafting may be done to cover the wound caused by surgery. Sometimes lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the lymph nodes at the same time as the surgery to remove the tumor. If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, more lymph nodes may be removed.
- Surgery followed by immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- Surgery followed by targeted therapy with signal transduction inhibitors if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- A clinical trial of immunotherapy with or without vaccine therapy.
- A clinical trial of surgery followed by therapies that target specific gene changes.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
You May Like: How Do You Spell Basal Cell Carcinoma
Ipilimumab For Advanced Melanoma
Ipilimumab can be effective for people with metastatic melanoma and stage III melanoma that cannot be removed completely with surgery. Ipilimumab works by blocking an immune molecule called CTLA-4.
In 2004, MSK patients were among the first in the world to receive ipilimumab treatment. MSK led the first clinical studies showing that ipilimumab could prolong the overall survival of people with metastatic melanoma. The US Food and Drug Administration approved the drug for general use in 2011. Clinical trials gave MSK patients the opportunity to receive ipilimumab years before the FDA approved it.
Diagnosis And Staging What It Means For You
How is melanoma diagnosed?
To diagnose melanoma, a dermatologist biopsies the suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab, where a dermatopathologist determines whether cancer cells are present.
After the disease is diagnosed and the type of melanoma is identified, the next step is for your medical team to identify the stage of the disease. This may require additional tests including imaging such as PET scans, CT scans, MRIs and blood tests.
The stage of melanoma is determined by several factors, including how much the cancer has grown, whether the disease has spread and other considerations. Melanoma staging is complex, but crucial. Knowing the stage helps doctors decide how to best treat your disease and predict your chances of recovery.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Test For Skin Cancer
Targeted Therapy For Advanced Melanoma
Targeted therapy is cancer treatment that focuses on specific molecules within cancer cells. The drugs work by blocking the function of abnormal molecules to slow the growth and spread of cancer, such as melanoma.
Targeted therapy is also systemic, and the drugs can be used with one another or in combination with other therapies.
Learn more about targeted therapy and how it works, as well as how combination therapy works.
Treatment Of Stage Ii Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage II melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it. Sometimes lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are done to check for cancer in the lymph nodes at the same time as the surgery to remove the tumor. If cancer is found in the sentinel lymph node, more lymph nodes may be removed.
- A clinical trial of new types of treatment to be used after surgery.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Read Also: Is Squamous Skin Cancer Deadly
Prognosis For Melanoma On The Nail
Like other forms of melanoma, subungual melanoma can metastasize to other parts of the body if left untreated.3,4 Because it can be difficult to see and is often mistaken for a bruise or other nail problem, this condition often goes undetected. However, checking your nails and showing any changes to your healthcare provider can help reduce your chances of an undetected subungual melanoma.