What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat melanoma. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
Most early stage melanomas can be treated with surgery alone. More advanced cancers need other treatments.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage of the cancer
- The results of lab tests on the cancer cells
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the melanoma or help in some way
- Your age
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Diagnosis Of Metastatic Melanoma
Your care team may use several tests to diagnose metastatic melanoma.
If theres evidence of a primary tumor, a biopsy may be taken. For this, a small section of suspected cancerous skin is removed with a razor, scalpel or small punch tool. The removed tissue is examined under a microscope to determine whether its melanoma.
Additional tests are needed to determine whether the cancer is metastatic melanoma, or if theres no visible primary tumor. To test for metastatic melanoma, or melanoma that has spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body, your care team may perform the following tests.
- Lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy : Your doctor may perform a physical exam of your lymph nodes and check for swelling or physical masses. If no tumors are found , an SLNB may be done. For an SLNB, a radioactive dye is injected to locate the primary tumor. Then, the doctor will remove the lymph nodes that the dye traveled to and check them for melanoma.
- Computed tomography scan, positron emission tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging scan or ultrasound exam: Each of these scans is a noninvasive way to look inside your body and check for tumors.
- Blood chemistry studies: Cancer may cause elevated or abnormal levels of certain substances in your blood. A laboratory test can identify if your blood chemistry shows signs of a cancerous tumor.
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Brain
You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to your brain:
- headaches
- weakness of a part of the body
- fits
- personality changes or mood changes
- eyesight changes
-
J Tobias and D HochhauserJohn Wiley and Sons Ltd
-
TNM Staging ChartsLippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2009
-
Improving supportive and palliative care for adults with cancerNational Institute for Clinical Excellence , 2004
-
Oxford Textbook of Palliative MedicineEds D Doyle and othersOxford Universty Press, 3rd edition 2005
-
Cancer and its Management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley Blackwell, 2015
You May Like: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Can A Small Melanoma Be Stage 4
Tumor size But the American Joint Commission on Cancer reports that stage 4 melanoma tumors tend to be thicker more than 4 millimeters deep. However, because stage 4 melanoma is diagnosed once the melanoma has spread to distant lymph nodes or to other organs, the size of the tumor varies from person to person.
Tests That May Be Done
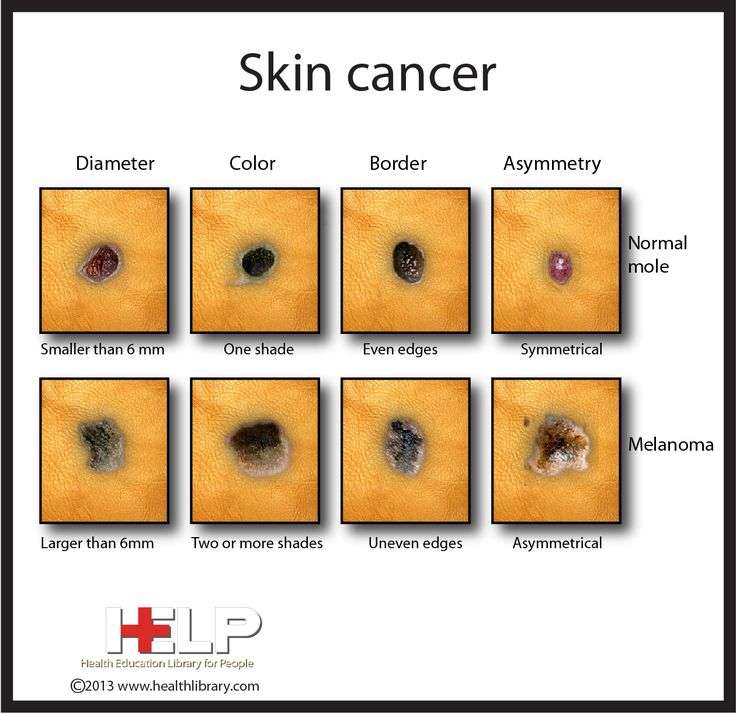
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers donât often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
You May Like: Well-differentiated Meaning
What Are The Symptoms Of Melanoma That Has Spread
Melanoma that has spread from the skin to other areas of the body is known as metastatic melanoma. However, since melanoma often first presents itself as an abnormal mole, many people with this malignancy can receive a diagnosis before the cancer has spread. This mole may be asymmetrical, have an uneven border, have an inconsistent color, be large or change over time. A melanoma may also appear as a sore or itchy bump, a tender nodule or a patch of skin that is scaly or bleeding. In some cases, early signs of melanoma are not present. For example, if the cancer starts in a mucous membrane rather than on the skin, a mole may not be present.
Benign Tumors That Start In Melanocytes
A mole is a benign skin tumor that develops from melanocytes. Almost everyone has some moles. Nearly all moles are harmless, but having some types can raise your risk of melanoma. See Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer for more information about moles.
A Spitz nevus is a kind of mole that sometimes looks like melanoma. Its more common in children and teens, but it can also be seen in adults. These tumors are typically benign and dont spread. But sometimes doctors have trouble telling Spitz nevi from true melanomas, even when looking at them under a microscope. Therefore, they are often removed, just to be safe.
You May Like: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
Don’t Miss: Stage 3 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Signs Melanoma Has Spread
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of because it spreads so quickly and so easily. That’s why it’s important to catch melanoma early. After it starts to spread, melanoma is harder to treat.
Melanoma can spread in three ways: directly through your skin, by getting into your bloodstream, and by getting into your lymphatic systempart of your immune system.
Melanoma can spread to almost any part of the body. It usually spreads on your skin, under your skin, or into your lymph nodes. If melanoma gets into your lymphatic system or your bloodstream, it can also spread to distant parts of your body. This is metastatic . Metastatic melanoma spreads most often to the lungs, brain, liver and bones.
If melanoma spreads, it usually happens within two years of getting a diagnosis. The chance that it will spread is higher if your melanoma was thick or ulcerated , if it was already in your lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis, or if you are older than 50.
What Else Should I Know About Treatment For Advanced Melanoma
Thanks to research breakthroughs, more patients diagnosed with advanced melanoma are living longer some for years.
Because these breakthrough are relatively recent, its important to:
-
Work with a team of melanoma specialists.
-
Ask your melanoma specialists if any of the newer treatments are appropriate for you.
-
Realize that no one treatment works for everyone, so you may need to try different treatments or combine treatments.
Researchers continue to study advanced melanoma, and next-generation treatments are now being studied in clinical trials. If you want to know whether you are a match for a trial, you can find out if there are any relevant trials at, Clinical Trial Finder.
Related AAD resources
ReferencesChukwueke U, Batchelor T, et al. Management of brain metastases in patients with melanoma. J Oncol Pract. 2016 12:536-42.
Emory Medical Center. A year in the life: Jimmy Carter shares his cancer experience. Posted July 11, 2016. Last accessed March 26, 2018.
Podlipnik S, Carrera C, et al. Performance of diagnostic tests in an intensive follow-up protocol for patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer stage IIB, IIC, and III localized primary melanoma: A prospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 75:516-24.
Nordmann N, Hubbard M, et al. Effect of gamma knife radiosurgery and programmed cell death 1 receptor antagonists on metastatic melanoma. Cureus. 2017 9: e1943.
You May Like: Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
If melanoma spreads, it will usually begin spreading through channels in the skin to the nearest group of glands . Lymph nodes are part of the bodys immune system, helping to remove unwanted bacteria and particles from the body.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy is a test to determine whether microscopic amounts of melanoma might have spread to the lymph nodes. It is usually carried out by a specialist plastic surgeon, while you are under general anaesthetic.
A combination of blue dye and a weak radioactive chemical is injected around your scar. This is usually done just before the wider area of skin is removed. The solution follows the same channels in the skin as any melanoma.
The first lymph node this reaches is known as the sentinel lymph node. The surgeon can locate and remove the sentinel node, leaving the others intact. The node is then examined for microscopic specks of melanoma .
If the sentinel lymph node is clear of melanoma, it’s extremely unlikely that any other lymph nodes are affected. This can be reassuring because if melanoma spreads to the lymph nodes, it’s more likely to spread elsewhere.
If the sentinel lymph node contains melanoma, there is a risk that other lymph nodes in the same group will contain melanoma.
Your surgeon should discuss the pros and cons of having a sentinel lymph node biopsy before you agree to the procedure. Sentinel lymph node biopsy does not cure melanoma, but is used to investigate the outlook of your condition.
Common Places For Melanoma To Spread
Melanoma can spread from the original site on your skin and form a tumor in any organ or body tissue, but its most likely to metastasize to the lymph nodes, liver, brain, lungs, and less commonly, the bones. Melanoma really likes the brain and the liver, says Lisa Zaba, M.D., dermatologic oncologist at Stanford Medical Center in San Jose, CA. If you notice any of the following red flags, it might mean your melanoma has spread and warrants a call to your doctor right away.
You May Like: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
What Is Metastatic Cancer
Cancer that spreads from where it started to a distant part of the body is called metastatic cancer. For many types of cancer, it is also called stage IV cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
When observed under a microscope and tested in other ways, metastatic cancer cells have features like that of the primary cancer and not like the cells in the place where the metastatic cancer is found. This is how doctors can tell that it is cancer that has spread from another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that spreads to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated as stage IV breast cancer, not as lung cancer.
Sometimes when people are diagnosed with metastatic cancer, doctors cannot tell where it started. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown primary origin, or CUP. See the Carcinoma of Unknown Primary page for more information.
The Distant Spread Of Melanoma
When melanoma spreads to distant areas of the body, it can cause general symptoms. You might feel really tired or not feel like eating anything and you could lose weight.
Your other symptoms will depend on where else the spreads:
-
Lungs. About 30% of metastatic melanomas go to the lungs. When that’s the case, symptoms may include , a that won’t go away, or .
-
Brain. Up to 20% of metastatic spread is to the brain. Symptoms may include and , especially in the morning. , , and also may occur when melanoma spreads to the brain.
-
Liver. Up to 20% of melanomas spread to the liver. A common symptom is swelling and in the upper right part of the belly. Other symptoms include nausea and . Fluid may build up in the belly, and skin or eyes could become yellowish.
-
Bones. About 17% of the time, melanoma metastasizes to the bones. Often, the first sign of this is a broken bone from a minor injury. Bone pain is the main symptom.
Catching melanoma early is the key to preventing it from spreading. After having treatment for melanoma, make sure to follow up with your doctor for several years to make sure melanoma has not spread or come back. You will most likely have periodic imaging tests, like a PET scan, to look for signs of cancer.
Read Also: Cell Cancer Symptoms
What Happens If Melanoma Gets Into Lymph Nodes
If the melanoma has spread into the lymph nodes, it means cancer has spread beyond its original site . It will need a more aggressive line of management.
Melanoma is a rapidly progressive type of skin cancer. The treatment of melanoma depends on the stage of the disease. Lymph nodes are small glands that are part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is involved in the formations of the white blood cells or WBCs. It is also the site where lymph, a clear fluid containing the white blood cells, is filtered. When melanoma begins to spread, it often first goes to the lymph node near the melanoma. The first lymph nodes that drain lymph fluid from the primary tumor are called sentinel lymph nodes. If the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes, it means that the person has stage III melanoma. Knowing the stage of melanoma helps the doctor plan the appropriate treatment. If the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes, the person may need a major surgery that involves the removal of the affected lymph nodes besides the primary tumor.
How Fast Can Melanoma Spread
A second factor that plays an important role in how fast melanoma can spread is the genetic factor. Certain gene abnormalities encourage melanoma to invade the surrounding tissue. This means that certain ways of how cells are composed can affect the speed of the melanoma spreading. This process, though, can vary significantly from one person to another.
If you have been diagnosed with melanoma skin cancer, talk with your doctor about your personal situation and treatment options.
Read Also: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
In a PET scan you are injected with a radioactive substance that is taken up by cancer cells. After about an hour you will lie down on a table while the PET scanner takes pictures of areas of radioactivity in your body. This will show up areas where cancer might have spread to around your whole body.
With machines that can do both a PET and CT scan at the same time, the PET scan can highlight areas where the cancer may have spread to and then the CT scan can provide more detailed information about the spread.
Finding Skin Cancer Early
- Do a skin self-exam regularly. Your partner or a close friend can help you check places that are hard to see, such as your scalp and back.
- Have your doctor check any suspicious skin changes. You may need to see your doctor for regular checkups if you have:
- Familial atypical mole and melanoma syndrome, which is an inherited tendency to develop melanoma. Your doctor may need to check you every 4 to 6 months.
- Increased exposure to ultraviolet radiation because of your job, hobbies, or outdoor activities.
- Abnormal moles called atypical moles. These moles aren’t cancerous. But their presence is a warning of an inherited tendency to develop melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Cancers
Keeping Health Insurance And Copies Of Your Medical Records
Even after treatment, its very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and even though no one wants to think of their cancer coming back, this could happen.
At some point after your cancer treatment, you might find yourself seeing a new doctor who doesnt know about your medical history. Its important to keep copies of your medical records to give your new doctor the details of your diagnosis and treatment. Learn more in Keeping Copies of Important Medical Records.
How Common Is Melanoma
Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but causes the great majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Its one of the most common cancers in young people under 30, especially in young women.
Melanoma incidence has dramatically increased over the past 30 years. Its widely accepted that increasing levels of ultraviolet exposure are one of the main reasons for this rapid rise in the number of melanoma cases.
You May Like: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
Biopsy And Pathological Examination Of A Skin Lesion
Other tests can suggest that cancer is present, but only a biopsy can make a definite diagnosis. Before a biopsy, a health care provider will usually numb the area with a local anesthetic. Anesthetic is medication that blocks the awareness of pain. Then they will remove a part or all of the suspicious skin growth, typically making sure to preserve the entire lesion so the thickness of the potential cancer and its margin can be carefully examined.
A pathologist or dermatopathologist then analyzes the sample removed during the biopsy to figure out if the lesion is a melanoma. A pathologist is a doctor who specializes in interpreting laboratory tests and evaluating cells, tissues, and organs to diagnose disease. A dermatopathologist is a pathologist with specialty training in diagnosing skin cancer and other disorders of the skin using a microscope and other laboratory tests.
The pathologist or dermatopathologist will write a report, called a pathology report, that should include the following information:
-
Thickness of the melanoma
-
Presence or absence of ulceration
-
If the cells are dividing, which is called the mitotic rate, the report will include the type/subtype of melanoma
-
Presence of immune cells called tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
-
Presence or absence of certain markers associated with prognosis and/or response to different therapies
Additional information is described in detail below.