How To Detect Skin Cancer
When it comes to skin cancer, we have some good news and some bad news.
First, the bad news: skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States. Each year, nearly 5 million people are treated for skin cancer, and in the last three decades, more Americans have had skin cancer than all other cancers combined.
But heres the good news: You can often see the early warning signs of skin cancerwithout an x-ray or blood test or special diagnostic procedure. If you know what to look for and take action when you see it, most skin cancers can be detected and treated at early stages, when they are most curable.
Even for melanoma, a more dangerous skin cancer type that is more likely to spread to other body areas, the five-year survival rate is 99% for people whose melanoma is detected and treated before it spreads to the lymph nodes.
See A Suspicious Spot See A Dermatologist
If you find a spot on your skin that could be skin cancer, its time to see a dermatologist. Found early, skin cancer is highly treatable. Often a dermatologist can treat an early skin cancer by removing the cancer and a bit of normal-looking skin.
Given time to grow, treatment for skin cancer becomes more difficult.
What If I Have Had A Lot Of Sun Exposure In My Life
Before the dangers of sun exposure were fully understood, many New Zealanders spent a lot of time outdoors without sun protection or used tanning beds. If you are worried you may have increased your risk of skin cancer in this way, the key is to prevent further skin damage and to have regular skin checks with your doctor. If you notice any darker, growing or changing moles, get them checked straight away.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
How Often Should I Get A Skin Cancer Screening
Dr. Perris interest in dermatology began when an early diagnosis of Melanoma saved his fathers life. Since then, Dr. Perri has helped thousands of patients perform skin cancer screenings, and treat skin cancers including Melanoma, Basal Cell, and Squamous Cell. Whether you have risk factors for skin cancer such as a family history of skin cancer or not, Dr. Perri recommends all residents perform regular skin checks and come in annually for a skin cancer screening.
Treatment For Skin Cancer
If you are diagnosed with skin cancer, you may have multiple options for treatment. Based on the specifics of your case, your doctor will recommend your best course of action. The suggested methods for fighting the cancer may include:
- Cryotherapy. In cryotherapy, a doctor freezes and kills precancerous or cancerous skin cells using liquid nitrogen. This technique is most often used to treat minor basal or squamous carcinomas or precancerous skin conditions.
- Surgery. Different types of skin cancer may be removed by surgery. Surgery can be excisional â simply cutting out a cancerous area and the skin surrounding it â or may involve meticulous removal of layers of skin.
- Radiation therapy. In radiation therapy, energy beams are used to kill cancerous cells. Radiation therapy may help finish off a cancer that was not fully removed by surgery, and can also be instrumental in cases that dont allow for surgery.
- Chemotherapy. This type of therapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. To treat some cases of skin cancer, chemotherapy may be applied locally through topical creams or lotions. It may also be administered by IV to target multiple body parts at once.
- Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy, also called biological therapy, involves boosting the immune system to fight cancer cells. With the help of strengthening medicines, the immune system may be better prepared to kill cancerous cells.
You May Like: Web Md Skin Cancers
Who Is At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest in people who have fair or freckled skin that burns easily, light eyes and blond or red hair. Darker-skinned individuals are also susceptible to all types of skin cancer, although their risk is lower.
In addition to complexion, other risk factors include having a family history or personal history of skin cancer, having an outdoor job, and living in a sunny climate. A history of severe sunburns and an abundance of large and irregularly shaped moles are risk factors unique to melanoma.
To Help Identify Potential Risk Factors
If you already have one of the following risks factors for skin cancer, then you might want to start checking yourself annually even sooner than recommended above:
- Being fair-skinned.
- Having red hair or freckles.
- Living near open fields where pesticides could accumulate.
- Working outdoors where UV rays might expose you to harmful chemicals.
You May Like: Is Stage 3 Melanoma Curable
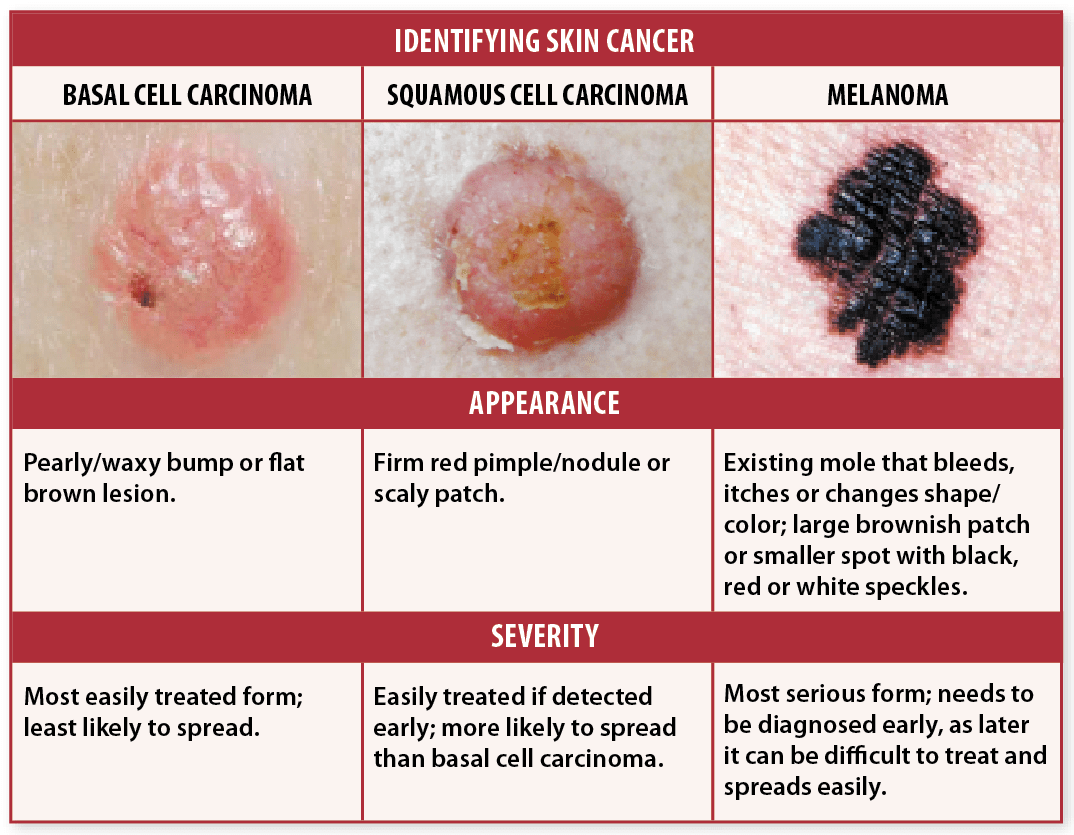
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. Itâs more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Also Check: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer
Screening For Skin Cancer
Again, the best way to screen for skin cancer is knowing your own skin. If you are familiar with the freckles, moles, and other blemishes on your body, you are more likely to notice quickly if something seems unusual.
To help spot potentially dangerous abnormalities, doctors recommend doing regular self-exams of your skin at home. Ideally, these self-exams should happen once a month, and should involve an examination of all parts of your body. Use a hand-held mirror and ask friends or family for help so as to check your back, scalp, and other hard-to-see areas of skin. If you or someone else notices a change on your skin, set up a doctors appointment to get a professional opinion.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
How Can People With Dark Skin Get Skin Cancer
Although dark skin does not burn in the sun as easily as fair skin, everyone is at risk for skin cancer. Even people who don’t burn are at risk for skin cancer. It doesn’t matter whether you consider your skin light, dark, or somewhere in between. You are at risk for skin cancer. Being in the sun can damage your skin. Sunlight causes damage through ultraviolet, or UV rays, . Two parts of UV, UVA and UVB, can both cause damage to skin. Also, the sun isn’t the only cause of skin cancer. There are other causes. That’s why skin cancer may be found in places on the body never exposed to the sun.
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
Does Skin Cancer Affect People With Skin Of Color
People of all skin tones can develop skin cancer. If you are a person of color, you may be less likely to get skin cancer because you have more of the brown pigment, melanin, in your skin.
Although less prevalent than in nonwhite people, when skin cancer does develop in people of color, its often found late and has a worse prognosis. If youre Hispanic, the incidence of melanoma has risen by 20% in the past two decades. If youre Black and develop melanoma, your five-year survival rate is 25% lower than it is for white people . Part of the reason may be that it develops in less typical, less sun-exposed areas and its often in late-stage when diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
Things I Learned From Getting Skin Cancer
by Bex Weller
Well, heres something I never thought Id say: I was diagnosed with skin cancer.
This weird and woeful tale all started about a year ago in April 2021, when I noticed a dry spot of skin on my scalp right along my hairline part. Sometimes Id accidentally scratch the spot while I was washing or styling my hair, and it would start to bleed.
I figured it was a little odd probably nothing to worry about but since I hadnt been for a skin check in a couple of years, I decided to book myself in.
At my appointment, along with a couple of other freckles I was mildly concerned about, I showed the spot to my Doctor. She advised it looked fine and maybe was just a rash or an irritation from a shampoo or something.
About eight months later, I noticed the spot turn into a weird little bobble thing, kind of like a very light coloured mole. It didnt hurt or bother me in any way, but I remembered what they say about watching for any spot changes.
I decided to make another skin check appointment, just in case.
I saw a different Doctor this time, who recognised it immediately as a basal cell carcinoma , the most common form of skin cancer. She performed a biopsy immediately and within a few days, the diagnosis was confirmed. It would have to be removed.
Four weeks later, I attended a day surgery hospital to receive Mohs surgery, widely considered the most effective technique for treating BCCs.
Can Other People Of Color Get Skin Cancer
Its possible for other People of Color to develop skin cancer as well. Its associated with the same types of risks as in Black people.
Compared with white people, the rate of skin cancer in other People of Color is lower. However, its higher than in Black people. For example, according to data from the CDC, in 2018 there were:
- 5 melanoma cases per 100,000 Native American or Alaska Native people
- 4 melanoma cases per 100,000 Latino people
- 1 melanoma cases per 100,000 Asian and Pacific Islander people
There are several types of skin cancer. Its possible that some types may be more common in certain People of Color than in others.
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Cancers
Skin Cancer On The Face: Types And Prevention
Casey Gallagher, MD, is board-certified in dermatology. He is a clinical professor at the University of Colorado in Denver, and co-founder and practicing dermatologist at the Boulder Valley Center for Dermatology in Colorado.
Because it is exposed to the sun more than other parts of the body, the skin on your face is especially vulnerable to skin cancer. And skin cancer on the face can be mistaken for other conditionssuch as age spots, pimples, scarring, acne, styes, and cysts.
Skin cancers that tend to occur more often on the face include actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The face is also a common site of melanoma and there are several other lesser-common skin cancers that can affect the face. The risk of getting skin cancers on the face increases with high amounts of sun exposure and other ultraviolet light exposure.
About 75% of non-melanoma skin cancers occur on the head or neck.
Skin cancer occurs when cells in the skin’s layers become damaged in ways that cause them to look and act differently than the normal healthy cells around them and start to grow out of control. UV rays play a major role in damaging cells by causing gene mutations.
You can watch for signs of skin cancer on your face by paying attention to new or odd-looking spots or feeling growths, splotches, or moles.
Skin Lesion Management Guidelines
If a patient presents with a suspicious lesion:
- Assess the likelihood of melanoma being present then provisionally identify the type of lesion.
- Surgical excision with histology is the first-line treatment for all skin cancer. It has the highest cure rate among available treatments.
- Referral, according to local guidelines, to a General Practitioner with a Special Interest in skin lesions, a Dermatologist, a Plastic Surgeon or an ENT Surgeon may be appropriate for patients with large lesions or lesions with an aggressive growth pattern.
- Patients with superficial basal cell carcinoma or intraepidermal carcinoma may be safely managed with cryotherapy or topical treatments, i.e. fluorouracil or imiquimod creams, when excision is not appropriate because of the location of the lesion or due to cosmetic considerations.
- Topical treatments should not be considered if the diagnosis is uncertain.
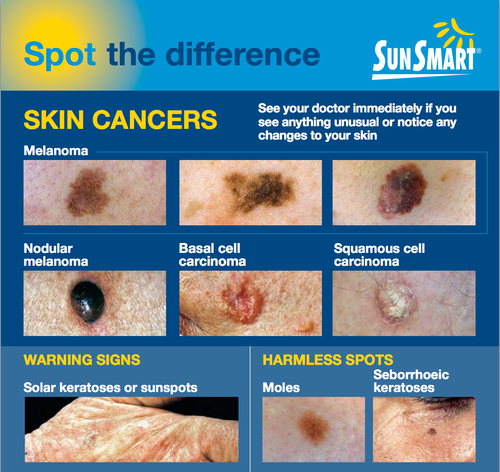
Red-flags: Is this melanoma?
Look for features of a melanoma using the ABCDE rule or the seven-point checklist.
Melanoma risk calculator Best Practice, NZ
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
Skin Cancer Diagnosis Always Requires A Skin Biopsy
When you see a dermatologist because youve found a spot that might be skin cancer, your dermatologist will examine the spot.
If the spot looks like it could be a skin cancer, your dermatologist will remove it all or part of it. This can easily be done during your appointment. The procedure that your dermatologist uses to remove the spot is called a skin biopsy.
Having a skin biopsy is essential. Its the only way to know whether you have skin cancer. Theres no other way to know for sure.
What your dermatologist removes will be looked at under a microscope. The doctor who examines the removed skin will look for cancer cells. If cancer cells are found, your biopsy report will tell you what type of skin cancer cells were found. When cancer cells arent found, your biopsy report will explain what was seen under the microscope.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
The following three sections refer to treatment using x-rays.
Conventional external beam radiation therapy
Historically conventional external beam radiation therapy was delivered via two-dimensional beams using kilovoltage therapy x-ray units, medical linear accelerators that generate high-energy x-rays, or with machines that were similar to a linear accelerator in appearance, but used a sealed radioactive source like the one shown above. 2DXRT mainly consists of a single beam of radiation delivered to the patient from several directions: often front or back, and both sides.
Conventional refers to the way the treatment is planned or simulated on a specially calibrated diagnostic x-ray machine known as a simulator because it recreates the linear accelerator actions , and to the usually well-established arrangements of the radiation beams to achieve a desired plan. The aim of simulation is to accurately target or localize the volume which is to be treated. This technique is well established and is generally quick and reliable. The worry is that some high-dose treatments may be limited by the radiation toxicity capacity of healthy tissues which lie close to the target tumor volume.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy
Recommended Reading: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
How Do You Get Skin Cancer
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.