See A Suspicious Spot See A Dermatologist
If you find a spot on your skin that could be skin cancer, its time to see a dermatologist. Found early, skin cancer is highly treatable. Often a dermatologist can treat an early skin cancer by removing the cancer and a bit of normal-looking skin.
Given time to grow, treatment for skin cancer becomes more difficult.
Red Pinpricks With Flu
A red pinprick rash under the skin can signal meningitis, a sometimes fatal condition.
The symptoms of meningitis mimic the flu , and the rash may not always occur early on.
It starts as small, red pinpricks before spreading quickly and turning into red or purple blotches, the NHS says.
You can check if you or your child has it by pressing a glass against the rash – if it does not fade on pressure, then it is caused by meningitis.
It can be a sign of sepsis caused by meningitis and you should call 999 straight away.
All parents are told to vaccinate their babies against meningitis very early on.
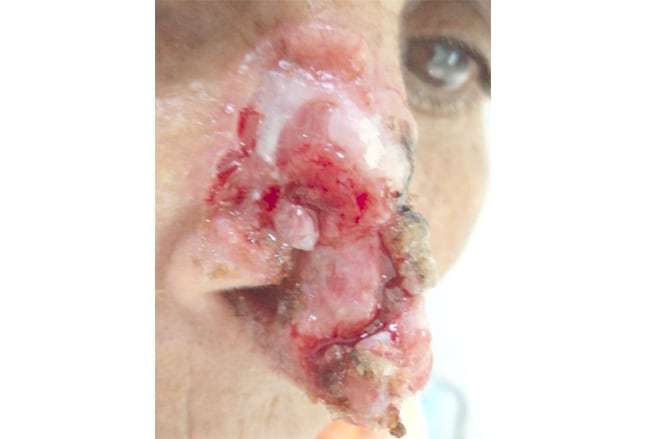
What Happens If Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive and potentially fatal form of skin cancer. It typically affects people above the age of 50 and those who have weakened immune systems. In most cases, Merkel cell carcinoma begins as a skin-toned growth that may bleed easily. The bumps or nodules may also have blue, purple, or red coloring. Because the Merkle cells are near nerve endings, this form of cancer has numerous health risks, and if left untreated, Merkle cell cancer may spread to the brain, lungs, or bones, becoming fatal.
Don’t Miss: What Does Melanoma Under The Toenail Look Like
A Dangerous Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
Melanoma Fact
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Deadly Skin Cancer Rates Soar For Generation Of Baby Boomers
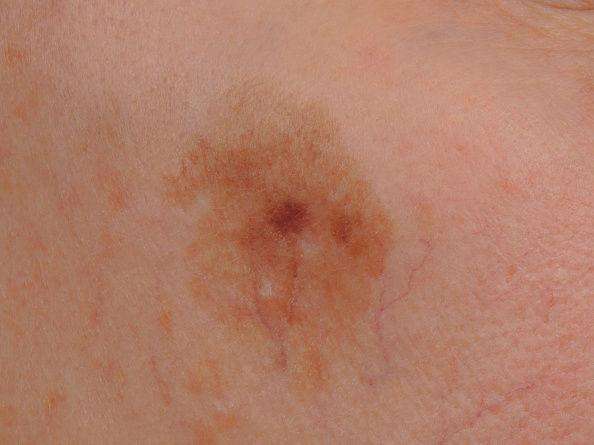
- 3 minute read
People in their 60s and 70s are now over five times more likely to be diagnosed with malignant melanoma the deadliest type of skin cancer than their parents would have been 30 years ago, reveal new Cancer Research UK statistics to launch the 2010 SunSmart campaign today .
Of all ages, this generation has seen the biggest increase in incidence rates of melanoma, rising from seven cases per 100,000 people in the mid 1970s to 36 cases per 100,000 today.
The stark rise shows the impact that a shift in tanning behaviour has had on a whole generation of men and women who would have been in their 20s and 30s during the dawn of cheap package holidays in the 1970s when sunburn before suntan was a common ritual and sunbeds arrived in the UK.
For men in their 60s and 70s the rates of melanoma have risen most dramatically they are now over seven times more likely to be diagnosed with the disease than in the 1970s.
Sue Deans, a 64 year old grandmother from Dorset, was diagnosed with malignant melanoma after discovering a lump in her lymph nodes. She had a mole removed a few years earlier but was shocked to be diagnosed with skin cancer. She had an operation to remove the tumour.
Theres nothing clever about having a tan. I am now always careful not to burn by wearing sun screen and sitting in the shade. And my young grandson has very fair skin so I worry about him and make sure he is protected.
ENDS
Read Also: How To Tell If Melanoma Has Spread
How Dangerous Is Each Type Of Skin Cancer
Although there are several types of skin cancers, the three most common forms are squamous cell carcinoma , basal cell carcinoma and melanoma. SCC and BCC are commonly referred to as nonmelanoma skin cancers and make up the vast majority of skin cancer diagnoses.
According to a 2015 study published in JAMA Dermatology, its believed that over three million people in the United States are diagnosed annually with nonmelanoma skin cancers
Below, well break down the three main types of skin cancers and discuss how deadly each type is:
Historic Progress New Options More Hope
While melanoma is one of the most dangerous forms of skin cancer, promising new treatment options are improving quality of life and increasing survival rates for patients with advanced melanoma.
If youve been diagnosed, your treatment choices depend on the stage of the disease, the location of the tumor and your overall health. Options include:
Also Check: How Many People Die From Skin Cancer Every Year
Look Out For An Ugly Duckling
The Ugly Duckling is another warning sign of melanoma. This recognition strategy is based on the concept that most normal moles on your body resemble one another, while melanomas stand out like ugly ducklings in comparison. This highlights the importance of not just checking for irregularities, but also comparing any suspicious spot to surrounding moles to determine whether it looks different from its neighbors. These ugly duckling lesions or outlier lesions can be larger, smaller, lighter or darker, compared to surrounding moles. Also, isolated lesions without any surrounding moles for comparison are considered ugly ducklings.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
The following three sections refer to treatment using x-rays.
Conventional external beam radiation therapy
Historically conventional external beam radiation therapy was delivered via two-dimensional beams using kilovoltage therapy x-ray units, medical linear accelerators that generate high-energy x-rays, or with machines that were similar to a linear accelerator in appearance, but used a sealed radioactive source like the one shown above. 2DXRT mainly consists of a single beam of radiation delivered to the patient from several directions: often front or back, and both sides.
Conventional refers to the way the treatment is planned or simulated on a specially calibrated diagnostic x-ray machine known as a simulator because it recreates the linear accelerator actions , and to the usually well-established arrangements of the radiation beams to achieve a desired plan. The aim of simulation is to accurately target or localize the volume which is to be treated. This technique is well established and is generally quick and reliable. The worry is that some high-dose treatments may be limited by the radiation toxicity capacity of healthy tissues which lie close to the target tumor volume.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy
Read Also: How To Tell If Something Is Skin Cancer
What Happens If Melanoma Is Left Untreated
Even though this form of skin cancer impacts a relatively low percentage of patients, melanoma skin cancers make up the majority of skin cancer deaths. Melanoma lesions often look like moles, freckles, or sunspots, and they may even develop within an existing mark on your body. Unlike other forms of skin cancer that are slow to progress and unlikely to spread to other areas, melanoma advances quickly and can form or spread anywhere on the body. In order to diagnose melanoma in the earliest stages, patients need to remember the ABCDEFs of melanoma, as discussed above.
Stop Tumors In Their Tracks
Every melanoma has the potential to become deadly, but the difference between an in situ melanoma and one that has begun to metastasize cannot be overstated. There is a drastic change in the survival rate for the various stages of tumors, highlighting the importance of detecting and treating melanomas before they have a chance to progress. Its impossible to predict exactly how fast a melanoma will move from stage to stage, so you should be taking action as soon as possible.
To be sure youre spotting any potential skin cancers early, The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends monthly skin checks, and scheduling an annual total-body skin-exam with a dermatologist. These skin exams can help you take note of any new or changing lesions that have the potential to be cancerous, and have them biopsied and taken care of before they can escalate.
Trust your instincts and dont take no for an answer, Leland says. Insist that a doctor biopsy anything you believe is suspicious.
Read Also: What Does Skin Cancer Of The Lip Look Like
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Basal cell carcinoma
-
BCC frequently develops in people who have fair skin. People who have skin of color also get this skin cancer.
-
BCCs often look like a flesh-colored round growth, pearl-like bump, or a pinkish patch of skin.
-
BCCs usually develop after years of frequent sun exposure or indoor tanning.
-
BCCs are common on the head, neck, and arms however, they can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment for BCC are important. BCC can grow deep. Allowed to grow, it can penetrate the nerves and bones, causing damage and disfigurement.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
-
People who have light skin are most likely to develop SCC. This skin cancer also develops in people who have darker skin.
-
SCC often looks like a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens.
-
SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
-
SCC can grow deep into the skin, causing damage and disfigurement.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent SCC from growing deep and spreading to other areas of the body.
SCC can develop from a precancerous skin growth
-
People who get AKs usually have fair skin.
-
AKs usually form on the skin that gets lots of sun exposure, such as the head, neck, hands, and forearms.
-
Because an AK can turn into a type of skin cancer, treatment is important.
Melanoma
How Can I Tell If I Have Skin Cancer
¿Cómo se ve el cáncer de la piel? ¿Cómo puedo prevenir el cáncer de piel?¿Estoy en riesgo de desarrollar melanoma?Cáncer de piel en personas de colorCómo examinar sus manchasNoe Rozas comparte su
Skin cancer is actually one of the easiest cancers to find. Thats because skin cancer usually begins where you can see it.
You can get skin cancer anywhere on your skin from your scalp to the bottoms of your feet. Even if the area gets little sun, its possible for skin cancer to develop there.
You can also get skin cancer in places that may surprise you. Skin cancer can begin under a toenail or fingernail, on your genitals, inside your mouth, or on a lip.
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Syndromes Associated With A Predisposition To Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell nevus syndrome
BCNS, also known as Gorlin Syndrome, Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, and nevoid BCC syndrome, is an autosomal dominant disorder with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 57,000 individuals. The syndrome is notable for complete penetrance and high levels of variable expressivity, as evidenced by evaluation of individuals with identical genotypes but widely varying phenotypes. The clinical features of BCNS differ more among families than within families. BCNS is primarily associated with germline pathogenic variants in PTCH1, but families with this phenotype have also been associated with alterations in PTCH2 and SUFU.
Other associated benign neoplasms include gastric hamartomatous polyps, congenital pulmonary cysts, cardiac fibromas, meningiomas, craniopharyngiomas, fetal rhabdomyomas, leiomyomas, mesenchymomas, basaloid follicular hamartomas, and nasal dermoid tumors. Development of meningiomas and ependymomas occurring postradiation therapy has been documented in the general pediatric population radiation therapy for syndrome-associated intracranial processes may be partially responsible for a subset of these benign tumors in individuals with BCNS. In addition, radiation therapy of malignant medulloblastomas in the BCNS population may result in many cutaneous BCCs in the radiation ports. Similarly, treatment of BCC of the skin with radiation therapy may result in induction of large numbers of additional BCCs.
DNA repair genes
Rare syndromes
Rombo syndrome
Economic Burden Of Skin Cancer
In addition to causing illness and death, skin cancer is costly to the nation. Skin cancer treatment is estimated to cost about $8.1 billion in the United States each year, $4.8 billion of which is for NMSC and $3.3 billion of which is for melanoma. Several new medications are available for skin cancer, which increases treatment options but could also lead to higher costs.-
Skin cancer also results in significant costs beyond those related to treatment. Annual costs associated with lost workdays and restricted-activity days are estimated at $76.8 million for NMSC and $29.4 million for melanoma., An individual in the United States dying from melanoma loses an average of 20.4 years of potential life, compared with an average of 16.6 years for all malignant cancers. Annual productivity losses associated with these lost years is estimated to cost an additional $4.5 billion .,
You May Like: What Is The Most Serious Type Of Skin Cancer
Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Sun exposure and other risk factors
Sun exposure is the major known environmental factor associated with the development of skin cancer of all types however, different patterns of sun exposure are associated with each major type of skin cancer. Unlike basal cell carcinoma , SCC is associated with chronic exposure, rather than intermittent intense exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Occupational exposure is the characteristic pattern of sun exposure linked with SCC. Other agents and factors associated with SCC risk include tanning beds, arsenic, therapeutic radiation , chronic skin ulceration, and immunosuppression.
Characteristics of the skin
Like melanoma and BCC, SCC occurs more frequently in individuals with lighter skin than in those with darker skin. A case-control study of 415 cases and 415 controls showed similar findings relative to Fitzpatrick type I skin, individuals with increasingly darker skin had decreased risks of skin cancer . The same study found that blue eyes and blond/red hair were also associated with increased risks of SCC, with crude ORs of 1.7 for blue eyes, 1.5 for blond hair, and 2.2 for red hair.
Immunosuppression
Personal history of BCC, SCC, and melanoma skin cancers
Family history of squamous cell carcinoma or associated premalignant lesions
Recurrent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas are the most common type of skin cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. These cancers develop within the basal cell layer of the skin, in the lowest part of the epidermis.
Patients who have had basal cell carcinoma once have an increased risk of developing a recurrent basal cell cancer. Basal cell cancers may recur in the same location that the original cancer was found or elsewhere in the body. As many as 50 percent of cancer patients are estimated to experience basal cell carcinoma recurrence within five years of the first diagnosis.
Basal cell carcinomas typically grow slowly, and it is rare for them to metastasize or spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. But early detection and treatment are important.
After completing treatment for basal cell carcinoma, it is important to perform regular self-examinations of the skin to look for new symptoms, such as unusual growths or changes in the size, shape or color of an existing spot. Skin cancers typically develop in areas of the body that are exposed to the sun, but they may also develop in areas with no sun exposure. Tell your oncologist or dermatologist about any new symptoms or suspicious changes you may have noticed.
- Have a history of eczema or dry skin
- Have been exposed to high doses of UV light
- Had original carcinomas several layers deep in the skin
- Had original carcinomas larger than 2 centimeters
You May Like: What Kind Of Cancer Is Skin Cancer
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
You May Like: How Fast Can Skin Cancer Kill You