How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
The Importance Of Annual Skin Cancer Checks
Annual skin cancer screenings are an essential tool that we use at Cochise Oncology to identify potential skin cancer lesions early. These assessments can give you peace of mind and identify potential cancer candidates.
A skin cancer screening is a physical examination performed by oncologists to determine the health of your skin. Doctors will look for large, asymmetric moles or skin imperfections that indicate possible cancer. If they discover a skin imperfection requiring closer inspection, they may take a small sample of tissue and send it to the lab for further investigation.
You May Like: Body Cancer Symptoms
What Is Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. When it spreads to other places in your body, it’s called metastatic, or advanced. You may also hear your doctor refer to it as stage IV melanoma.
Melanoma often spreads to:
Although in many cases metastatic melanoma canât be cured, treatments and support can help you live longer and better. Doctors have therapies that have greatly increased survival rates. And researchers are working to find new medications that can do even more.
Remember: You still have control over the decisions you make about your treatment and your life. It’s important to have people you can talk to about your plans, your fears, and your feelings. So find support and learn about your treatment options. That will help you make the most of your life.
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Carcinoma Lung Cancer
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
Its common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful.
It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.
All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
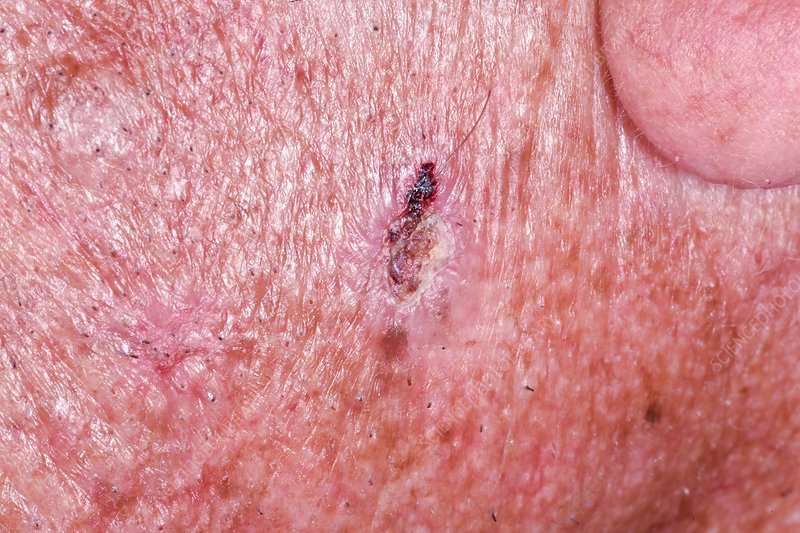
Warning sign: A sore that doesnt heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesnt heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if its red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
Donât Miss: Melanoma Stage 3 Life Expectancy
Read Also: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Nose
The nose is a relatively common spot for skin cancer to develop. Skin cancer often starts on the face because it’s usually the body part that’s exposed to the sun. The two most common types of skin cancer that develop on the nose are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . While both types of skin cancer should be addressed right away, BCC is usually slow-growing and SCC grows more quickly. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer ,with about 80% of cases occurring on the face and 25 to 30% on the nose.
The third type of skin cancer, melanoma, is rare and much more serious. It almost always requires excisional surgery to remove it. Fortunately, most forms of skin cancer are very treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, topical treatments, and more.
What If I Have Metastatic Melanoma Symptoms
Whether you have a suspicious mole or are experiencing some symptoms of advanced-stage melanoma, it is important to consult with a physician to receive an accurate diagnosis, as many other conditions can cause similar symptoms. At Moffitt Cancer Center, we provide a comprehensive range of screening, diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services for patients with melanoma and other types of cancer. Within our Cutaneous Oncology Program, our multispecialty team includes surgeons, dermatologists, medical oncologists and other experts who work together as a tumor board to ensure our patients receive the best possible treatment and care.
If you would like to schedule an appointment at Moffitt to discuss your metastatic melanoma symptoms, call or fill out a new patient registration form online. We do not require a referral to schedule an appointment.
- BROWSE
Read Also: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
What Is Skin Cancer And Melanoma
Skin cancer is a disease that occurs when your skin cells grow abnormally, usually from too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
This uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells forms a tumour in the skin. Tumours are either benign , or malignant .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer: each year, more than 13,000 Australians are diagnosed with a melanoma and almost 980,000 new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers are treated. Skin cancer is mostly preventable, and there are effective treatment options available.
Skin cancers are named according to the cells in which they form. There are 3 main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma begins in the lower segment of cells of the epidermis your outer layer of skin. These tend to grow slowly, and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma grows from the flat cells found in the top layer of your epidermis. SCC can grow quickly on the skin over several weeks or months. Bowens disease is an early form of SCC that hasnt grown beyond the top layer of skin.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes cells that give your skin its colour. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer but is considered the most serious because it can spread quickly throughout the body.
BCC and SCC are also called non-melanoma skin cancers. BCC represents more than 2 in 3 non-melanoma skin cancers, and around 1 in 3 are SCC. There are other types of non-melanoma skin cancers, but they are rare.
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Laser Surgery Is Not Fda
Laser surgery is not currently used as a standard treatment for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It can, however, be an effective secondary treatment. Laser treatment is sometimes used after Mohs surgery to complete the removal of cancer cells. Lasers are effective at removing precancerous lesions, but have not been proven effective at treating cancer yet.
Does Skin Cancer Affect People With Skin Of Color
People of all skin tones can develop skin cancer. If you are a person of color, you may be less likely to get skin cancer because you have more of the brown pigment, melanin, in your skin.
Although less prevalent than in nonwhite people, when skin cancer does develop in people of color, its often found late and has a worse prognosis. If youre Hispanic, the incidence of melanoma has risen by 20% in the past two decades. If youre Black and develop melanoma, your five-year survival rate is 25% lower than it is for white people . Part of the reason may be that it develops in less typical, less sun-exposed areas and its often in late-stage when diagnosed.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Can Skin Cancer Spread To Other Parts Of The Body
Yes, it can. However, it depends on the type of skin cancer and its stage.
Non-melanoma skin cancers are less likely to spread. Basal cell carcinoma usually does not migrate to other parts of the body, but there is a small chance that squamous cell cancer will do so.
Melanoma skin cancer spreads more readily than non-melanoma, making it more dangerous. It can spread to the lymph nodes and, from there, to other organs in the body.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
Read Also: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women.
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
Theyre more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole thats getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
Metastatic And Recurrent Melanoma
Melanoma can spread to other parts of the body, where it can cause tumours. When melanoma has spread and appears as a tumour in another part of the body, it sometimes can be successfully treated with surgery. But metastatic melanoma usually needs other treatments, too, such as chemotherapy, interferon, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Metastatic melanoma and melanoma that can’t be removed with surgery may be treated with inhibitors.
Melanoma can come back after treatment. This is called recurrent melanoma. All of the treatments mentioned above may be used for recurrent melanoma as well as:
- Hyperthermic isolated limb perfusion. If the melanoma is on your arm or leg, chemotherapy medicine may be added to a warm solution and injected into the bloodstream of that arm or leg. The flow of blood to and from that limb is stopped for a short time so the medicine can go right to the tumour.
- Medicines injected directly into the tumour.
- Lasers to destroy the tumour.
If your melanoma can’t be cured, your doctors will try to control symptoms, reduce complications, and keep you comfortable.
Your doctor may recommend that you join a clinical trial if one is available in your area. Clinical trials may offer the best treatment option for people who have metastatic cancer. Clinical trials study other treatments, such as combinations of chemotherapy, vaccines, and immunotherapies. They are also studying targeted therapy.
You can find more information about skin cancer online:
Read Also: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
See A Suspicious Spot See A Dermatologist
If you find a spot on your skin that could be skin cancer, its time to see a dermatologist. Found early, skin cancer is highly treatable. Often a dermatologist can treat an early skin cancer by removing the cancer and a bit of normal-looking skin.
Given time to grow, treatment for skin cancer becomes more difficult.
Skin Exam And Physical
You may have had a complete skin exam during your last dermatology appointment. Dermatologists often perform this exam when a patient has a suspicious spot on their skin that could be skin cancer.
During a complete skin exam, your dermatologist examines you head to toe. This exam includes a look at all of your skin, including the skin on your scalp, face, genitals, and the bottoms of your feet. Your dermatologist will also examine your nails and look inside your mouth.
If you did not have a complete skin exam before being diagnosed with melanoma, youll have one at your next appointment.
During a complete skin exam, your dermatologist may use a device called a dermatoscope
This device provides a closer look at the spots on your skin.
At your next appointment, youll receive a physical. During your physical, your dermatologist will ask how youre feeling and about your health, illnesses, and injuries. Your dermatologist will also want to know what diseases run in your family and the medications you take.
During your physical, your dermatologist will check your lymph nodes to find out if any feel swollen. There are many reasons for swollen lymph nodes. For example, if you have an infection or recently received a vaccination, lymph nodes can feel swollen. When you have melanoma, the swelling might be a sign that the cancer has spread.
If youre unsure what diseases your close blood relatives have had, try to find out
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
What Does Skin Cancer In Dogs Look Like
Most types of skin cancer will start out looking like some sort of growth or wart. Most often, they will be quite small and may appear suddenly. They can be tough to spot under fur, and you may not notice them initially. You are more likely to feel them as lumps or bumps.
Cancer may also appear as a sore, though that is more likely as the cancer grows.
You May Like: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Also Check: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
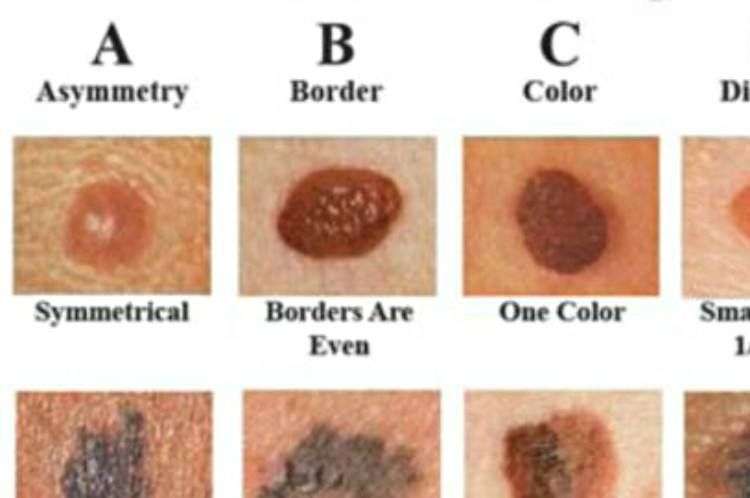
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.