How Can You Prevent Skin Cancer In Kids
Taking measures to prevent skin cancer in childhood can also lower the risk later on.
Here are some habits to implement:
- Have kids wear sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 every day .
- Avoid being in the sun when its the strongest .
- Encourage kids to wear hats and protective clothing.
- Educate teens about the dangers of tanning salons.
- Model good sun protection behaviors yourself.
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer In A Child
Symptoms of basal cell carcinoma appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, face, neck, arms, and hands. The symptoms can include:
-
A small, raised bump that is shiny or pearly, and may have small blood vessels
-
A small, flat spot that is scaly, irregularly shaped, and pale, pink, or red
-
A spot that bleeds easily, then heals and appears to go away, then bleeds again in a few weeks
-
A growth with raised edges, a lower area in the center, and brown, blue, or black areas
Symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, face, neck, arms, and hands. They can also appear on other parts of the body, such as skin in the genital area. The symptoms can include:
-
A rough or scaly bump that grows quickly
-
A wart-like growth that may bleed or crust over.
-
Flat, red patches on the skin that are irregularly shaped, and may or may not bleed
Symptoms of melanoma include a change in a mole, or a new mole that has ABCDE traits such as:
-
Asymmetry. One half of the mole does not match the other half.
-
Border irregularity. The edges of the mole are ragged or irregular.
-
Color. The mole has different colors in it. It may be tan, brown, black, red, or other colors. Or it may have areas that appear to have lost color.
-
Diameter. The mole is bigger than 6 millimeters across, about the size of a pencil eraser. But some melanomas can be smaller.
-
Evolving. A mole changes in size, shape, or color.
Other symptoms of melanoma can include a mole that:
How We Care For Melanoma
Children with melanoma are treated at Dana-Farber/Boston Childrens Cancer and Blood Disorders Center through our Rare Tumors Program. Our treatment teams have expertise in treating many rare forms of cancer, and many of our specialists are also active researchers, providing your child access to the most advanced treatments available.
You May Like: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
What Should Survivors Of Childhood And Adolescent Cancer Consider After They Complete Treatment
People who have had cancer during childhood or adolescence need follow-up care and enhanced medical surveillance for the rest of their lives because of the risk of complications related to the disease or its treatment that can last for, or arise, many years after they complete treatment for their cancer . Health problems that develop months or years after treatment has ended are known as late effects.
The specific late effects that a person who was treated for childhood cancer might experience depend on the type and location of their cancer, the type of treatment they received, and patient-related factors, such as age at diagnosis. Some people with a history of childhood cancer may need additional follow-up if an inheritedgeneticalteration is found to be the cause of the cancer.
Children and adolescents who were treated for bone cancer, brain tumors, or Hodgkin lymphoma, or who received radiation to their chest, abdomen, or pelvis, have the highest risk of serious late effects from their cancer treatment, including second cancers, joint replacement, hearing loss, and congestive heart failure .
Its important for people who had cancer during childhood or adolescence to have regular medical follow-up examinations so any health problems can be identified and treated as soon as possible. The Childrens Oncology Group has developed long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers.
Skin Cancer In Children: What To Look For
In adults, melanomas tend to appear as darker spots, but in children, melanomas are frequently whitish, yellowish, or red. As with adults, any changes on the skin, especially changes to moles, should be brought to the attention of a doctor. The general recommendations of the ABCDES of what to look for in skin checks apply to children and adults:
- A Asymmetrical shape, like moles that are irregular or not symmetrical
- B Border, moles that have an unclear or unusual border
- C Color, especially the presence of more than one color in a mole
- D Diameter, moles that are larger than 6 mm
- E Evolution, which involves any changes to a mole over time3
Don’t Miss: 2nd Stage Cancer
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
There are many different types of skin cancer . Each type looks different. Also, skin cancer in people with dark skin often looks different from skin cancer in people with fair skin. A change on the skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This may be any new growth on the skin, a sore that doesn’t heal, or a change in an old growth.
If you notice a change on your skin, see your doctor. Don’t wait until the change looks like the more advanced skin cancers in these photos.
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will examine your child’s skin. Tell the healthcare provider:
-
When you first noticed the skin problem
-
If it oozes fluid or bleeds, or gets crusty
-
If its changed in size, color, or shape
-
If your child has pain or itching
Tell the healthcare provider if your child has had skin cancer in the past, and if other your family members have had skin cancer.
Your child’s healthcare provider will likely take a small piece of tissue from a mole or other skin mark that may look like cancer. The tissue is sent to a lab. A doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope. He or she may do other tests to see if cancer cells are in the sample. The biopsy results will likely be ready in a few days or a week. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you the results. He or she will talk with you about other tests that may be needed if cancer is found.
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
How Can I Help My Child Live With Skin Cancer
If your child has skin cancer, you can help him or her during treatment in these ways:
-
Your child may have trouble eating. A dietitian or nutritionist may be able to help.
-
Your child may be very tired. He or she will need to learn to balance rest and activity.
-
Get emotional support for your child. Counselors and support groups can help.
-
Keep all follow-up appointments.
-
Keep your child out of the sun.
After treatment, check your child’s skin every month or as often as advised.
Brain And Spinal Cord Tumors
Brain and spinal cord tumors are the second most common cancers in children, making up about 26% of childhood cancers. There are many types of brain and spinal cord tumors, and the treatment and outlook for each is different.
Most brain tumors in children start in the lower parts of the brain, such as the cerebellum or brain stem. They can cause headaches, nausea, vomiting, blurred or double vision, dizziness, seizures, trouble walking or handling objects, and other symptoms. Spinal cord tumors are less common than brain tumors in both children and adults.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
What Are The Different Types Of Skin Cancer
There are three main types of skin cancer, including:
|
Name |
Description |
|
Basal cell carcinoma |
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for the majority of all diagnosed skin cancers. This is a highly treatable cancer and grows very slowly. Basal cell carcinoma usually appears as a small, shiny bump or nodule on the skin, mainly those areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, neck, arms, hands, and face. It more commonly occurs among people with light-colored eyes, hair, and complexion. |
|
Squamous cell carcinoma |
Squamous cell carcinoma, although more aggressive than basal cell carcinoma, still is highly treatable. It accounts for a much smaller percentage of all skin cancers. Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as nodules or red, scaly patches of skin, and may be found on the face, ears, lips, and mouth. Squamous cell carcinoma can spread to other parts of the body, although this is rare. This type of skin cancer is usually found in fair-skinned people. |
|
Malignant melanoma |
Malignant melanoma accounts for the smallest percentage of all skin cancers but represents the most deaths from skin cancer. Malignant melanoma starts in the melanocyte cells that produce pigment in the skin. Malignant melanoma sometimes begins as a mole that then turns cancerous. This cancer may spread quickly to other parts of the body. Malignant melanoma most often appears on fair-skinned men and women, but people with all skin types may be affected. |
Distinguishing benign moles from melanoma
Sun Exposure & Vitamin D
Some sunlight is good for you and is needed for bone health. It has been suggested by some vitamin D researchers that approximately 5 to 30 minutes of sun exposure at least twice a week to the face, arms, legs, or back without sunscreen usually lead to sufficient vitamin D. Individuals with limited sun exposure need to include good sources of vitamin D in their diet or take a supplement to achieve recommended levels of intake.
UCSF Benioff Childrenâs Hospitals medical specialists have reviewed this information. It is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace the advice of your childâs doctor or other health care provider. We encourage you to discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your childâs provider.
Also Check: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
Treatment Of Recurrent Childhood Melanoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentmelanoma in children may include the following:
- A clinical trial that checks a sample of the patient’s tumor for certain gene changes. The type of targeted therapy that will be given to the patient depends on the type of gene change.
- A clinical trial of immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors in children and adolescents.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
There Are Different Types Of Cancer That Start In The Skin
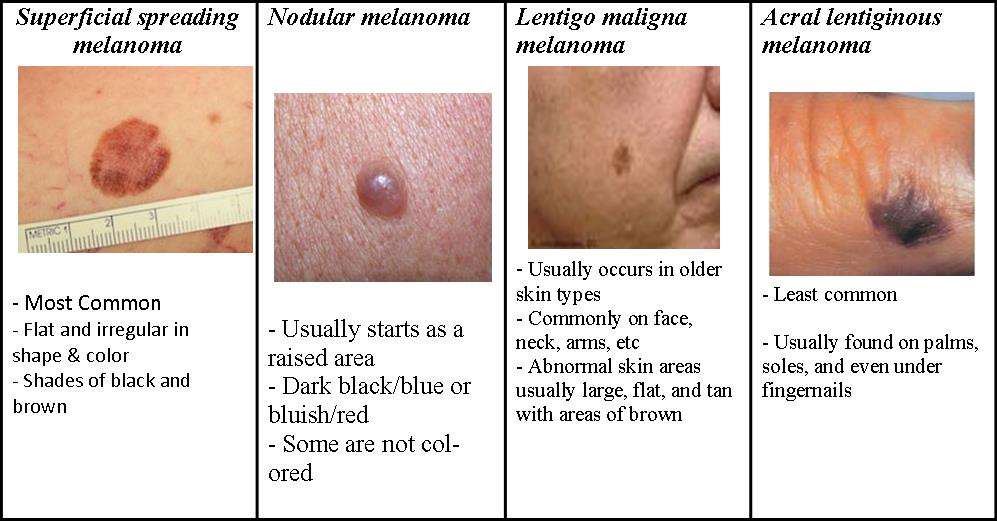
There are two main forms of skin cancer: melanoma and nonmelanoma .
Melanoma is a rare form of skin cancer. Even though melanoma is rare, it is the most common skin cancer in children. It occurs more often in adolescents aged 15 to 19 years. Melanoma is more likely to invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body than other types of skin cancer. When melanoma starts in the skin, it is called cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma may also occur in mucous membranes and the eye . This PDQ summary is about cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma Treatment for more information about intraocular melanoma).
Two other types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. They rarely spread to other parts of the body.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Sun Safety For Children And Babies
Melanoma is among the most common forms of cancer for young adults 15-29. Some experts blame the inappropriate use of sunscreen, saying that people do not apply enough lotion or do not reapply it as frequently as required. Products can no longer claim to be waterproof, only water-resistant, and labels must note a time limit of either 40 or 80 minutes before the sunscreen is ineffective.
Sunscreen is just one of the defenses against the harmful effect of UV radiation. Strategies such as seeking shade and dressing children in sun-protective clothing are just as important. A bad sunburn in childhood or adolescence doubles the risk of melanoma later in life, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Rates of skin cancerincluding melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancercontinue to rise, even in young people. Parents need to be extra vigilant about sun protection all the time. Just one blistering sunburn in childhood more than doubles a persons chances of developing melanoma later in life. Young skin is delicate, thinner, and produces less melanin, a skin protecting pigment. Ultra violet rays reach the skins pigment producing melanin cells, called melanocytes, and cause DNA damage to the skin.
What Is The Outlook For Skin Cancer In Children
Skin cancer in children is on the rise. Theres been an increase in awareness of the dangers of too much UV exposure and the importance of skin cancer screenings. Teach your child how to check for suspicious moles, sores, and growths, and schedule annual visits with your pediatrician.
If your child is at higher risk for melanoma or you or your pediatrician notice any suspicious lesions, have your child see a dermatologist. This will help you catch pediatric melanoma or any other type of skin cancer in children at its earliest, most treatable stage.
Treating early-stage melanoma is usually successful. Surgery may leave little or no scar if the melanoma is diagnosed when its still small.
Read Also: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
How Common Is Childhood Skin Cancer
About 60,000 cases of melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, are diagnosed in the United States each year. Only around 450 of those affected are under the age of 20, according to CureSearch for Childrens Cancer, a foundation dedicated to driving research and innovation for childrens cancers.
But researchers say that cases of pediatric melanoma are going up the incidence has increased an average of 2 percent every year since 1973. The biggest surge is in girls between ages 15 and 19, which is likely related to sun exposure and the use of tanning beds, according to Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Boston Childrens Cancer and Blood Disorders Center.
Melanoma is now the second most common cancer in people ages 15 to 29, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation, and accounts for up to 3 percent of all childhood cancers.
Nonmelanoma skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, are extremely rare in children and teens. A report published in 2019 by the Siteman Cancer Center in Missouri that looked at 7,814 cases of skin cancer in patients younger than 30 found that these types of cancers accounted for only 0.008 percent of all cases.
What Factors Make Children More At Risk For Developing Melanoma
Fair-skinned, light-haired children are at a higher risk for pediatric melanoma. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and a history of sunburns makes you more susceptible to melanoma formation.
A family history of melanoma also increases a childs likelihood of developing skin cancer. In children who have already been treated for melanoma, the chances of additional skin cancers forming is higher than in kids with no skin cancer history.
The use of tanning beds may also explain the growing risk of pediatric melanoma, especially among adolescents.
In general, the risk factors for skin cancer in children over the age of 10 are the same as those for adults, though for younger children the risk factors are less clear.
Read Also: Web Md Skin Cancers
Where Do Children And Adolescents With Cancer Get Treated
Children and adolescents who have cancer are often treated at a childrens cancer center, which is a hospital or a unit within a hospital that specializes in diagnosing and treating patients through 20 years of age. The health professionals at these centers have specific training and expertise to provide comprehensive care for children and adolescents with cancer, and their families.
Childrens cancer centers also participate in clinical trials. The improvements in survival for children with cancer that have occurred over the past half century have been achieved because of treatment advances that were studied and proven to be effective in clinical trials.
More than 90% of children and adolescents who are diagnosed with cancer each year in the United States are cared for at a childrens cancer center that is affiliated with the NCI-supported Childrens Oncology Group . COG is the worlds largest organization that performs clinical research to improve the care and treatment of children and adolescents with cancer. Each year, approximately 4,000 children who are diagnosed with cancer enroll in a COG-sponsored clinical trial. COG trials are sometimes open to older individuals when the type of cancer being studied is one that occurs in children, adolescents, and young adults.
Slop On Spf30 Or Higher Broad
Some tips when using sunscreen with children include:
- Apply sunscreen to any parts of skin not covered by hats or clothing about 20 minutes before going outside.
- From around 3 years of age, encourage your child to start to apply their own sunscreen to help develop independent skills ready for preschool and school. Try applying a dot of sunscreen to each cheek, nose and chin and squiggles of sunscreen to parts of the arms and legs not covered with clothing and teach children how to apply this carefully to cover the skin.
- Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours or more frequently if swimming and sweating even if it is labelled 4-hours water-resistant.
- Never use sunscreen as the only form of sun protection or to prolong the amount of time you or your child spends out in the sun, as it does not offer complete protection.
- Store sunscreen under 30ºC and only use sunscreen within the expiry date.
When considering sunscreen for babies, remember:
Read Also: Stage Iiia Melanoma Prognosis