How Can I Tell If My Mole Is Cancerous
While you cannot self-diagnose skin cancer, there are certain qualities to look for in a mole to be able to tell if its one specific type known as melanoma. These are often called the ABCDEs of melanoma, or Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolution.
Benign moles are typically perfect circles or ovals. If they are asymmetrical, it may be a sign of melanoma skin cancer. Melanoma typically has an uneven border around it that can sometimes appear rigid, while regular moles are smooth.
Benign moles tend to be one color, while melanomas can be multiple different browns and can even appear white, red, or blue.
Do I Have Skin Cancer
Youre scrolling through your Facebook feed on a Saturday morning when you stumble across a post from one of your friends:
As you reach forward to type your get well message to John, a mole on your forearm comes into view. While youve had the mole since you were a teenager, you instantly question whether it could be skin cancer. After all, you and John grew up together you spent your summers on the beach, often competing to see who had the best color. If he has skin cancer, you are at risk too, right?
Before you panic, ask yourself the following questions about the mole you just became reacquainted with:
- If you draw a line down the center of your worrisome spot, are the two halves different? Are they asymmetrical?
- Are the borders of your spot uneven or jagged?
- Does the mole have multiple colors in it?
- Is your mole larger than a pencil eraser?
- Has the mole changed over time? You might find that it has gotten larger or feels a bit more raised, or its just itchy in a way you never noticed before.
- Does the mole look different from the others on your body?
- Have you gone more than a year without a visit to your dermatologist?
If you answered yes to any of the above questions, make an appointment with your dermatologist and be sure to share your concerns. And even if you answered, I dont know to one, go ahead and make the call. While a yes or an Im not so sure response in no way guarantees that you have skin cancer, it means there may be cause for concern.
Work With Us Dermatology Partners
Dr. Peckham is one of the many skilled dermatologists who are part of the U.S. Dermatology Partners network of specialists. If you want to work with one of our dedicated professionals, complete our simple online appointment request form. A U.S. Dermatology Partners team in your community will be in touch soon to schedule your appointment time and discuss your treatment options.
Find a location near me
Sign Up for Our Newsletter!
Get the latest updates on news, specials and skin care information.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
Generally found on the ears, face and mouth, squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive than basal cell. Untreated, it may push through the skin layers to the lymphatic system, bloodstream and nerve routes, where it can cause pain and symptoms of serious illness.
Appearance
Squamous cell cancer often starts as a precancerous lesion known as actinic keratosis . When it becomes cancerous, the lesion appears raised above the normal skin surface and is firmer to the touch. Sometimes the spot shows only a slight change from normal skin.
Other signs include:
- Any change, such as crusting or bleeding, in an existing wart, mole, scar or other skin lesion
- A wart-like growth that crusts and sometimes bleeds
- A scaly, persistent reddish patch with irregular borders, which may crust or bleed
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes
- A raised growth with a depression in the center that occasionally bleeds and may rapidly increase in size
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
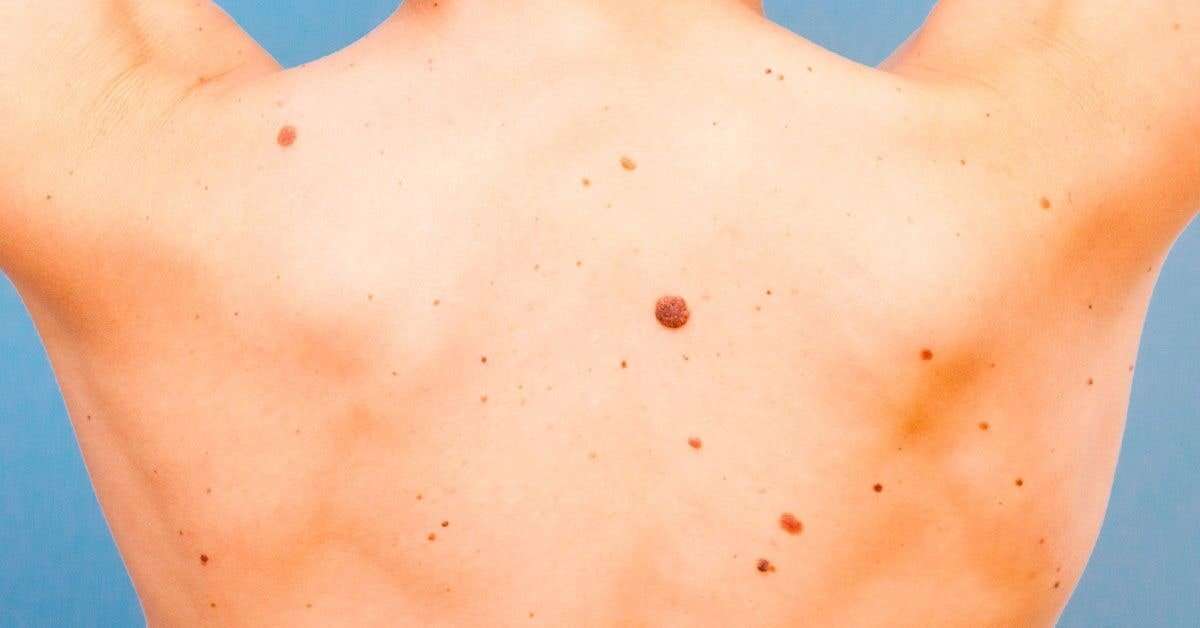
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
Staging For Basal Cell Carcinoma And Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin Depends On Where The Cancer Formed
Staging for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the eyelid is different from staging for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma found on other areas of the head or neck. There is no staging system for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma that is not found on the head or neck.
Surgery to remove the primary tumor and abnormal lymph nodes is done so that tissue samples can be studied under a microscope. This is called pathologic staging and the findings are used for staging as described below. If staging is done before surgery to remove the tumor, it is called clinical staging. The clinical stage may be different from the pathologic stage.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups.
Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems.
After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. A combination of sun protection measures should be used during sun protection times .
As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times.
It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Who Should Have A Skin Cancer Check
If you think you have a high risk of skin cancer, speak to your doctor. It is also important you become familiar with your skin so that you can pick up any changes. Most melanomas are found by individuals themselves or by their partners or other family members.
Look out for:
- any crusty sores that dont heal
- changes to the colour, size, shape or thickness of moles and freckles over a period of weeks or months
- new spots
- small lumps that are red, pale or pearly in colour
If you notice any of the above, its important to see your doctor.
Don’t Miss: What Does Well Differentiated Mean
Symptoms And Warning Signs
Skin cancer warning signs can vary so greatly that healthcare professionals have devised a simplified system for determining skin cancer apart from typical skin birthmarks, moles, and age or sunspots. This method, known as the ABCDE rule, enables you to quickly detect visual differences in your skin.
Can Skin Cancer Spread To Other Parts Of The Body
Yes, it can. However, it depends on the type of skin cancer and its stage.
Non-melanoma skin cancers are less likely to spread. Basal cell carcinoma usually does not migrate to other parts of the body, but there is a small chance that squamous cell cancer will do so.
Melanoma skin cancer spreads more readily than non-melanoma, making it more dangerous. It can spread to the lymph nodes and, from there, to other organs in the body.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Complementary And Alternative Treatments For Stage 4 Melanoma
Complementary and alternative approaches, also called CAM, are types of therapies not clinically proven however still typically accepted as possible methods to assist treat a specific condition. The following treatments include complementary techniques or treatments that can be used in combination with traditional medication for patients with sophisticated cancer malignancy.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if skin cancer spreads to the lung, the cancer cells in the lung are actually skin cancer cells. The disease is metastatic skin cancer, not lung cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Do Carcinomas Spread
Make An Appointment With A Dermatologist
After you have performed regular skin checks and once you discover a suspicious lesion, you have done your job. Now its time to see a dermatologist, a skin care specialist who can determine the definitive diagnosis. This may require a minor outpatient surgical procedure known as a biopsy. Occasionally, a more significant surgery will be required.
The biopsy specimen will be sent to the pathology lab who can determine whether or not the lesion was a skin cancer and, if it was, what type. Found early, skin cancer, even melanoma, is very treatable.
As for Peggy and Tina, happy to announce, neither were diagnosed with skin cancer.
Can Melanoma Be Prevented
You can’t control how fair your skin is or whether you have a relative with cancerous moles. But there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing melanoma. The most important is limiting your exposure to the sun.
Take these precautions:
- Avoid the strongest sun of the day between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen whenever you’re in the sun.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and cover up with long, loose cotton clothing if you burn easily.
- Stay out of the tanning salon. Even one indoor tanning session increases your risk of getting melanoma.
Also, be sure to check your moles often . Keep dated records of each mole’s location, size, shape, and color, and get anything suspicious checked out right away.
Not all skin cancer is melanoma, but every case of melanoma is serious. So now that you know more about it, take responsibility for protecting yourself and do what you can to lower your risk.
You can find more information online at:
Also Check: Well Differentiated Meaning
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
Biological Therapies And Melanoma
Biological therapies are treatments using substances made naturally by the body. Some of these treatments are called immunotherapy because they help the immune system fight the cancer, or they occur naturally as part of the immune system.
There are many biological therapies being researched and trialled, which in the future may help treat people with melanoma. They include monoclonal antibodies and vaccine therapy.
You May Like: Body Cancer Symptoms
Amount Of Exposure To Sunlight
The damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation accumulate over the years. In general, the risk of developing skin cancer increases with the amount of time spent under the sun and the intensity of radiation. The intensity of radiation varies according to the season of the year, time of day, geographic location , elevation above sea level, reflection from surfaces , stratospheric ozone, clouds, and air pollution.
Recent studies have focused on the effects of intermittent sun exposure in comparison to chronic exposure. It appears that the type of exposure may influence the type of cancer that develops. For example, intermittent solar exposure may be an important factor leading to the onset of basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Childhood sun exposure may also play an important part in the development of these cancers later in adult life. The pattern for cutaneous melanoma is similar to that for basal cell carcinoma.
In contrast, the relationship between squamous cell carcinoma and solar UVR appears to be quite different. For squamous cell tumours, high levels of chronic occupational sunlight exposure, especially in the 10 years prior to diagnosis, results in an elevated risk for this cancer in the highest exposure group.
Abcde Melanoma Detection Guide
A is for Asymmetry
Look for spots that lack symmetry. That is, if a line was drawn through the middle, the two sides would not match up.
B is for Border
A spot with a spreading or irregular edge .
C is for Colour
Blotchy spots with a number of colours such as black, blue, red, white and/or grey.
D is for Diameter
Look for spots that are getting bigger.
E is for Evolving
Spots that are changing and growing.
These are some changes to look out for when checking your skin for signs of any cancer:
- New moles.
- Moles that increases in size.
- An outline of a mole that becomes notched.
- A spot that changes colour from brown to black or is varied.
- A spot that becomes raised or develops a lump within it.
- The surface of a mole becoming rough, scaly or ulcerated.
- Moles that itch or tingle.
- Moles that bleed or weep.
- Spots that look different from the others.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Oral Medications For Advanced Bcc
It is rare for skin cancer to reach advanced stages, but when it does, oral medications may help. In addition to chemotherapy, targeted drugs may be used to treat advanced skin cancer. Targeted therapy means that the medication is able to directly target the cancer cells without destroying healthy cells. This can help to reduce side effects from treatment.
Vismodegib and sonidegib are hedgehog pathway inhibitors that work to prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading. The capsules are taken once per day and may be considered after surgery and other treatments. These medications come with several possible side effects and should never be taken during pregnancy since they can affect fetal growth.
Cetuximab is an EGFR inhibitor that can help to stop the spread of cancerous squamous cells. Its possible side effects include skin infections, diarrhea, mouth sores, and loss of appetite.
First A Little About Skin Cancer

Skin cancer is a broad term, and this type of cancer can be classified as melanoma and non-melanoma.
As the most common form of cancer in the United States, one out of five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime.
When detected early, skin cancer is very treatable and many times curable.
The most common areas for skin cancer are:
- Backs of hands
- Neck
Also Check: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans