What Are The Common General Signs And Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
It is important to note that many skin cancer signs and symptoms are also associated with other diseases and conditions and may not necessarily indicate skin cancer.
The signs and symptoms of skin cancer differ slightly depending on the type of skin cancer.
A basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma may initially present as a bump or a rough patch on the skin. However, the basal cell carcinoma will have a smooth, waxy appearance. It may even be translucent enough to see blood vessels in the middle, and it may be indented in the middle. A squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, will either remain as a reddish, scaly patch or will develop into a rough nodule.
Melanomas can also appear as lumps or moles on the skin. Not all moles are cancerous. In fact, most moles are harmless, and some will eventually fade away. However, some moles can become cancerous. Melanomas or cancerous moles are distinguished by irregular borders and an asymmetrical appearance. They may be more than one color and are typically larger than 6mm in diameter.
Changes in appearance of skin, existing moles or the growth of new moles should be discussed with the doctor.
What Might Other Skin Cancer Symptoms Look Or Feel Like
Here are five less common skin cancer symptoms to be watchful for:
Of course, most of these skin cancer symptoms are commonly associated with less serious conditions, such as minor skin wounds that typically heal within a few days. However, a skin lesion that persists for more than a week should be checked out by a physician.
- BROWSE
What Is My Skin Type
Skin types that are more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
All skin types can be damaged by too much UV radiation. Skin types that are more sensitive to UV radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
People with naturally very dark skin still need to take care in the sun even though they may rarely, if ever, get sunburnt. The larger amount of melanin in very dark skin provides natural protection from UV radiation. This means the risk of skin cancer is lower.
Eye damage can occur regardless of skin type. High levels of UV radiation have also been linked to harmful effects on the immune system.
Vitamin D deficiency may be a greater health concern for people with naturally very dark skin, as it is more difficult for people with this skin type to make vitamin D.
Read Also: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
What Causes Cancer To Form On Your Scalp
The main cause of all types of skin cancer is sun exposure. Your scalp is one of your body parts exposed most to the sun, especially if you are bald or have thin hair. That means its one of the more common spots for skin cancer.
Other potential causes of skin cancer on your scalp include using a tanning bed and having had radiation treatment on your head or neck area.
The best way to prevent skin cancer on your scalp is to protect your scalp when you go into the sun:
- Wear a hat or other head covering whenever possible.
- Spray sunscreen on your scalp.
Other ways to help prevent skin cancer on your scalp are:
- Avoid using tanning beds.
- Limit your time in the sun.
- Check your scalp regularly to spot any potential cancerous spots early. This can help stop precancerous lesions from turning into cancer or stop skin cancer from spreading. You can use a mirror to look at the back and top of your scalp more thoroughly.
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
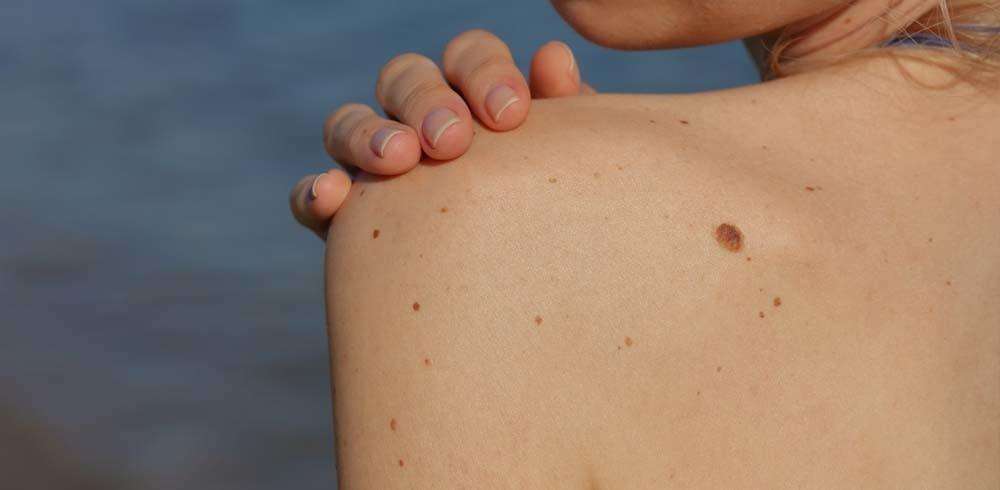
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
Read Also: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, ulcer, mole or sore. It may or may not bleed and can be painful. If you have a preexisting mole, any change in the characteristics of this spot – such as a raised or an irregular border, irregular shape, change in color, increase in size, itching or bleeding – are warning signs of melanoma. Sometimes the first sign of melanoma or squamous cell cancer is an enlarged lymph node.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Specialists
Our head and neck surgeons and speech language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Read Also: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
Exam By A Health Care Professional
Some doctors and other health care professionals do skin exams as part of routine health check-ups.
Having regular skin exams is especially important for people who are at high risk of skin cancer, such as people with a weakened immune system or people with conditions such as basal cell nevus syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum . Talk to your doctor about how often you should have your skin examined.
Treatments For Advanced Melanoma
In most cases, treatment can’t cure advanced melanoma. But some can help you live longer and feel better. The goal of any therapy you get will be to shrink or remove your tumor, keep the cancer from spreading further, and ease your symptoms.
Surgery. This is the main way to remove melanoma from the skin and lymph nodes. You might also have an operation on organs where the cancer has spread. Thereâs no guarantee your surgeon will get all of it. Some melanoma is too small to see, even with high-tech scans.
Radiation. Your doctor might recommend radiation to kill any cancer cells that have been left behind after surgery or if melanoma spreads to your brain or bones. It can also relieve pain from the disease or treat melanoma that comes back over and over.
Immunotherapy or biologic therapy. These drugs help your immune system find and attack cancer cells. Depending on the ones you take, you might have to go in for treatment every 2, 3, or 4 weeks.
Your doctor might want you to take more than one drug. Some studies show that people who do have fewer side effects.
The flip side of immunotherapy is that sometimes these drugs cause your immune system to attack healthy organs. Then youâd need to stop melanoma treatment and take drugs to stop the attack.
Chemo can shrink the cancer, but chances are it will start growing again after a few months and youâll need more treatment. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy usually work better.
Other side effects include:
You May Like: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
How Common Is It
Overall, skin cancers are the most common cancers in the United States. But melanoma is less common than the other two major types, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
Each year about 91,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with melanoma of the skin, according to the American Cancer Society. By comparison, about 3.3 million are diagnosed with one or more basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas.
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have skin cancer, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers don’t spread as often as some other types of cancer, so the exact stage might not be too important. Still, your doctor might want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the cancer through the skin. It also tells if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body that are close by or farther away.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Other things can also help you and your doctor decide how to treat your cancer, such as:
- Where the cancer is on your body
- How fast the cancer has been growing
- If the cancer is causing symptoms, such as being painful or itchy
- If the cancer is in a place that was already treated with radiation
- If you have a weakened immune system
Read Also: Stage Iii Melanoma
How Is Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. Basal cell cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes, but they can grow quite large and invade local structures. Squamous cell cancers have a much higher incidence of lymph node involvement in the neck and parotid gland and can spread along nerves.
Melanoma is staged, based not on size but on how deeply it invades the skin layers. Therefore, a superficial or shave biopsy will not provide accurate staging information used to guide treatment. Melanomas can have a very unpredictable course and may spread to distant organs. Melanomas with intermediate thickness often require sentinel node biopsy, a surgical procedure performed by a head and neck surgeon, to determine if microscopic spreading to lymph nodes has occurred.
A Sore That Doesn’t Heal
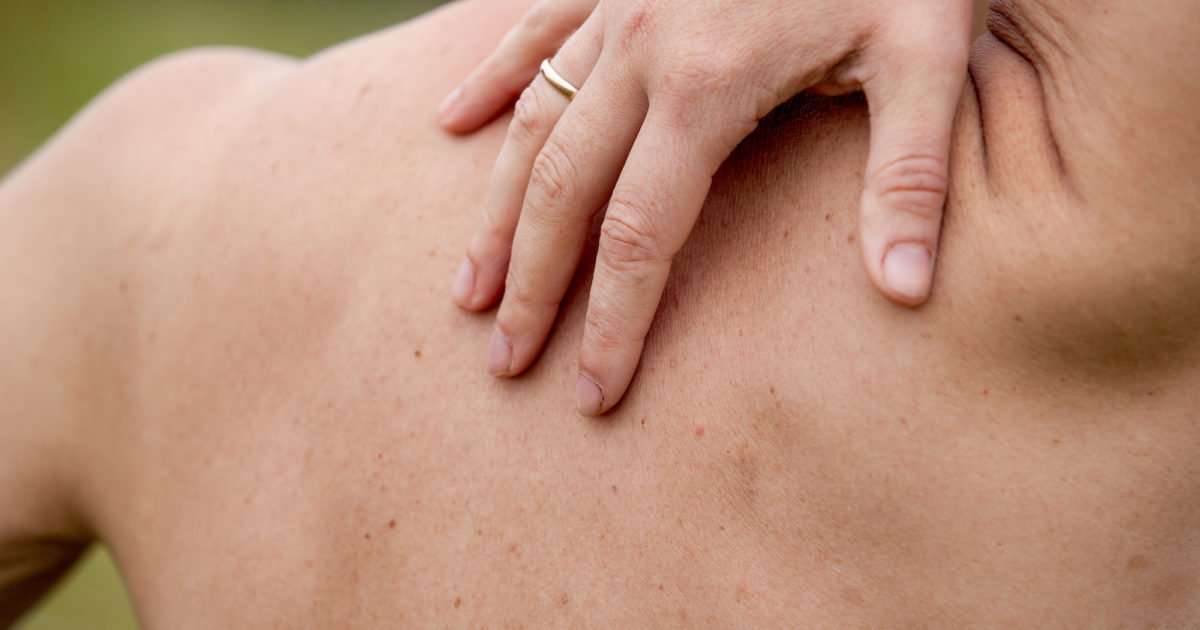
Many skin cancers are first dismissed as being due to a bug bite, minor injury, or irritation, but become more obvious when they don’t go away over time. If you notice a sore on your skin that refuses to heal, even if it seems to be healing but then reappears, talk to your healthcare provider. In general, any skin change that hasn’t resolved on its own over a period of two weeks should be evaluated.
You May Like: Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Red Flag #: Swollen Lymph Nodes
If melanoma spreads, it often goes to the lymph nodes first, says Melinda L. Yushak, M.D., assistant professor of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta. The cancer cells will first travel to the nodes closest to the original tumor, she says. Lymph nodes are located throughout your entire body, but large clusters are found in the neck, underarms, chest, abdomen, and groin. If the cancer has made its way to the lymph nodes, it usually wont be painful, but theyll feel swollen or even hard to the touch, Dr. Zaba says.
Where Does Bcc Develop
As the above pictures show, this skin cancer tends to develop on skin that has had lots of sun exposure, such as the face or ears. Its also common on the bald scalp and hands. Other common areas for BCC include, the shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
While rare, BCC can also form on parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure, such as the genitals.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented
Skin cancer is almost entirely preventable. Making a part of your life, avoiding sunburn, and checking your skin regularly will help prevent further damage to your skin.
Protect your skin from UV radiation and help prevent skin cancer by:
- slipping on sun-protective clothing: cover your shoulders, neck, arms, legs and body.
- slopping on sunscreen thats rated SPF 30+ or higher, broad-spectrum and water resistant.
- slapping on a hat that shades your face, neck and ears.
- seeking shade under trees, umbrellas and buildings from direct sunlight and reflective surfaces.
- sliding on sunglasses that wrap around your face to protect your eyes and surrounding skin.
- staying away from sun lamps, solariums or sunbeds, which emit dangerous levels of UV radiation.
UV radiation from the sun varies depending on time of day, season, where you live and cloud coverage. Protect your skin whenever UV Index levels are above 3. Use Cancer Council Australias free SunSmart app to check the UV Index for your area any time.
Most Australians will get enough vitamin D even with sun protection at UV level 3 or above. Babies and children should be protected from the sun, since they are particularly vulnerable to UV radiation harm.
While using fake tanning cream isnt harmful to your skin, it offers no protection from UV radiation. You still need to protect yourself from the sun.
You May Like: Is Melanoma Bad
When To See A Doctor
It is always vital to seek medical advice early for a skin change, no matter how small it may appear. Make an appointment with your doctor for a skin exam if you notice:
- Any new changes, lesions, or persistent marks on your skin
- A mole that is asymmetrical, has an irregular border, is multicolored, is large in diameter, is evolving, or has begun to crust or bleed
- An âugly ducklingâ mole on the skin
- Any changes to your skin that you are concerned about
Looking For Signs Of Skin Cancer
Non melanoma skin cancers tend to develop most often on skin that’s exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancers early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, you’ll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you cant see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a friend to look. This is very important if you’re regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.
You can take a photo of anything that doesn’t look quite right. If you can it’s a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area when you take the photo. This gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if it’s changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.
-
Northern Ireland Cancer Network, December 2012
-
Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology VT De Vita, TS Lawrence and SA RosenbergWolters Kluwer, 2018
-
Cancer and its managementJ Tobias and D HochhauserBlackwell, 2015
Also Check: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading