How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
First, your dermatologist may ask you if you have noticed any changes in any existing moles, freckles or other skin spots or if youve noticed any new skin growths. Next, your dermatologist will examine all of your skin, including your scalp, ears, palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, around your genitals and between your buttocks.
If a skin lesion is suspicious, a biopsy may be performed. In a biopsy, a sample of tissue is removed and sent to a laboratory to be examined under a microscope by a pathologist. Your dermatologist will tell you if your skin lesion is skin cancer, what type you have and discuss treatment options.
What Causes Squamous Cell Cancer
Skin cancer is caused by mutations that occur in skin cell DNA. These changes cause abnormal cells to multiply out of control. When this occurs in the squamous cells, the condition is known as SCC.
UV radiation is the most common cause of the DNA mutations that lead to skin cancer. UV radiation is found in sunlight as well as in tanning lamps and beds.
While frequent exposure to UV radiation greatly increases your risk of skin cancer, the condition can also develop in people who dont spend much time in the sun or in tanning beds.
These people may be genetically predisposed to skin cancer, or they may have weakened immune systems that increase their likelihood of getting skin cancer.
Those who have received radiation treatment may also be at greater risk of skin cancer.
Risk factors for SCC include:
- having fair skin
- having light-colored hair and blue, green, or gray eyes
- having long-term exposure to UV radiation
- living in sunny regions or at a high altitude
- having a history of multiple severe sunburns, especially if they occurred early in life
- having a history of being exposed to chemicals, such as arsenic
Skin Cancer Can Look Like Many Things Therefore People Can Go Long Periods Of Time Without Recognizing That They Have A Skin Cancer Says Dr Steven Musick Md A Board Certified Dermatologist Who Runs Musick Dermatology Llc In Swansea Il Which Provides State
Not only can skin cancer mimic many benign conditions such as pimples and skin barnacles, but a tumor can develop in areas that are difficult to inspect or that are not considered during a persons self-skin exam.
For example, it would be difficult for one to examine their scalp unless theyre bald. Inside the ears is another hard-to-visualize location.
And then there are areas that people wouldnt think to check, such as between their butt cheeks, inside their belly button, between their toes, the soles of their feet and even the pupils of their eyes.
Yes, melanoma can grow in the pupils and go unnoticed for long periods of time.
Melanoma, along with squamous cell carcinoma, can also pop up internally, including within the genitals, mouth, nose and lungs.
Another factor that influences how long a person can have skin cancer and not know it is where they live.
If they live in a Third, and especially Fourth, World nation, they can have a basal cell carcinoma that goes undiagnosed for many years due to lack of skin cancer awareness campaigns and adequate skin cancer screenings.
However, this type of tumor will continue progressing, though very slowly it wont stop growing just because its untreated.
Recommended Reading: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Are All Moles Cancerous
Most moles are not cancerous. Some moles are present at birth, others develop up to about age 40. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles.
In rare cases, a mole can turn into melanoma. If you have more than 50 moles, you have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your skin is the largest organ in your body. It needs as much attention as any other health concern. What may seem like an innocent cosmetic imperfection, may not be. Performing regular skin self-checks is important for everyone and is especially important if you are a person at increased risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is also color-blind. If you are a person of color, skin cancer can happen to you. Check your skin every month for any changes in skin spots or any new skin growths. Consider taking skin selfies so you can easily see if spots change over time. If youre a person of color, be sure to check areas more prone to cancer development, such as the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, your genital area and under your nails. Takes steps to protect your skin. Always wear sunscreen with SPF of at least 30 every day of the year. Wear UV-A/UV-B protective sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeve shirts and pants. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin check.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/19/2021.
References
What Are Some Of The Lesser

Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Don’t Miss: Melanoma 3b
What Are The Chances Of Skin Cancer Recurrence Where Can It Reoccur
Having one skin cancer puts you at higher risk of having another skin cancer. Between 30% and 50% of people with a non-melanoma skin cancer develop a second non-melanoma skin cancer within 5 years. Between 2% and 10% of melanoma survivors develop a second primary melanoma.
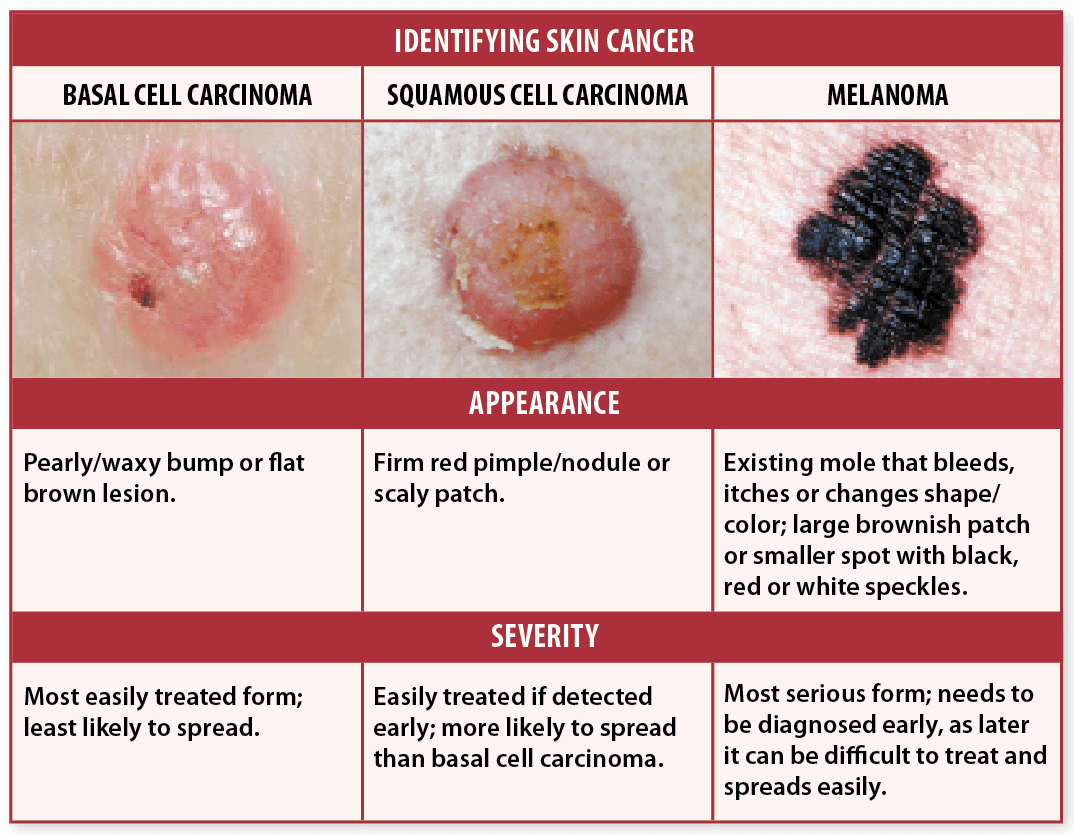
What Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Look Like
Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in appearance, but here, weve provided some examples of how it might appear on your skin.
Squamous cell carcinoma initially appears as a skin-colored or light red nodule, usually with a rough surface. They often resemble warts and sometimes resemble open bruises with raised, crusty edges. The lesions tend to develop slowly and can grow into a large tumor, sometimes with central ulceration.
SCCs can occur on any part of the body, but they are more common on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp, ear or face, so pay attention to these areas.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops slowly but can spread to the lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated. If caught early though, it is highly treatable. Early detection strategies are crucial for a successful outcome.
You will notice that all these skin cancer pictures are quite different from one another. Note that not all squamous cell cancers have the same appearance so these photos should serve as a general reference for what they can look like.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prevention:
Disadvantages of the treatment theres a chance of scarring. There is it. There wasnt any mortality connected with second primary tumors. Its important that populations at probability particularly those who have fair skin residing in regions with high UV radiation exposure know of means to reduce the danger of the status. The growth of cancer cells within this area is comparatively slow. A couple of months before, a little growth appeared on the top side of my left forearm. There is typically an obvious growth on the epidermis or an ulcerated location.
Unfortunately, there is absolutely no control regarding how deep the tissue was destroyed. Modern-day treatment approaches are now increasingly complex, as sophisticated methods are developed to attempt to preserve vocal function. These cells are located in the top layer of the epidermis.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a disease that can easily be brought about by an individuals working atmosphere or living atmosphere. It may be a serious medical condition but it is very easy to avoid and prevent. This is a disease that can be easily caused by a persons living environment or working environment.
The sooner a skin cancer is identified, the simpler its to deal with. Cutting out the tumor, together with a little margin of normal skin, is frequently used to deal with squamous cell cancers.
Recommended Reading: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
Laser Surgery Is Not Fda
Laser surgery is not currently used as a standard treatment for basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It can, however, be an effective secondary treatment. Laser treatment is sometimes used after Mohs surgery to complete the removal of cancer cells. Lasers are effective at removing precancerous lesions, but have not been proven effective at treating cancer yet.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
What Is Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Invasive squamous cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that occurs in the flat cells that make up the outer layer of skin and the linings of some organs, known as squamous cells. In this case, the word invasive means that the cancerous tumor has penetrated deeply into the skin or organ, as opposed to remaining a surface lesion. For example, in cases of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, the tumor may have penetrated into the dermis through the epidermis. Depending on the location, size, and severity of the tumor, there are several different courses of treatment that may be pursued.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer after basal cell carcinoma. Most often it is caused by exposure to UV rays, either through natural sunlight or by indoor tanning. People with fair skin are particularly susceptible. It can also occur in organs as diverse as the prostate, bladder, and larynx, although these are nowhere near as common as squamous cell skin cancer. Exposure to radiation or chemical carcinogens, as well as some inflammatory or scarring disorders, can also increase the risk of squamous cell cancer.
You May Like: How Do Carcinomas Spread
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cells are a normal skin cell near the epidermis . With SCCs, your body grows too many of the cells. Usually its because the cells DNA has been damaged. That damage comes mainly from sunlight but other things can damage it including:
- Other UV light exposure .
- Ionizing radiation .
- Viral infections .
- Chemicals .
Also, certain genetic conditions, illnesses that cause skin inflammation or scarring , and medical treatments that suppress the immune system , can increase your risk of SCCs. These illnesses and treatments cause chronic damage to the skin and/or the inability of DNA to repair itself.
Dr. Rx
The virus that causes warts can cause some SCCs. Sometimes patients with numerous SCCs who are immunosuppressed may be able to decrease their risk of getting an SCC by getting the HPV vaccination. Dr. Levy
Also Check: If You Have Skin Cancer How Do You Feel
What Increases My Risk For Scc
- Age 60 years or older
- Fair skin or light hair
- A history of long-term exposure to the sun or ultraviolet rays from tanning beds
- Exposure to chemicals such as coal tars, arsenic, or radium
- A history of other skin disorders, such as actinic keratosis, radiation dermatitis, or burn scars
- Cigarette or alcohol use
- A human papillomavirus infection
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Warning Signs
At the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic we use the adage The faster a Squamous Cell Carcinoma grows the faster it needs to go.
Faster growing Squamous Cell Carcinoma are more likely to be
- aggressive,
- Invade and potentially penetrate the skin
- spread .
If they do spread this high growth rate is often maintained leading to a rapidly progressive clinical course which is associated with higher fatality rates.
Any rapidly growing lump or change in a pre-existing or new skin growth, should prompt an immediate visit to a Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic.
Read Also: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
What Do Cancer Survival Rates Mean
When learning about cancer survival rates, its important to keep in mind that these statistics are based on a very large and diverse group of people. Because no two people with squamous cell carcinoma are alike, the general survival rate cannot be used to predict a specific patients outcome. Additionally, survival rates are broad benchmarks. While useful as a baseline point of reference for physicians, this information is not detailed enough to reflect the different treatments people have had, nor is it recent enough to include the results of the latest breakthrough treatments now available to patients through clinical trials .
The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma usually first appears as a red, scaly plaque of skin or as a hard domed bump. Both varieties typically feel rough and crusty and can bleed when scraped. Growths may also be pink and dry and may itch or burn.
As mentioned above, the cancer usually forms on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, lips, arms, legs, and tops of the hands, but it can also more rarely appear on areas not exposed to the sun including the lower lip, genitals, in the lining of organs and the passages of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops slowly but can spread to the lymph nodes and other organs if left untreated. If caught early though, it is highly treatable.
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Read Also: Skin Cancer Mayo
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cells are found throughout the body. They make up the outer part of your skin. They also line the inside of many organs, including your lungs, bladder, and kidneys.
When cancer starts in squamous cells, it may be referred to as squamous cell carcinoma. It may also be named for the part of the body where the cancerous cells are located. If the squamous cells in your skin are cancerous, you have squamous cell carcinoma of the skin .
If these cancerous cells multiply instead of dying off, they may grow into a solid tumor on your skin. Not all squamous cell skin cancers look the same. Signs may include:
- A firm, red bump. It may have raised edges with a lower center
- A flat patch of scaly skin
- Growths that resemble warts
- A sore on your lip or inside your mouth
- A sore that wont heal. It may repeatedly ooze, bleed or crust over
Squamous cell skin cancer usually occurs on skin with lots of sun exposure, like the face, lips, ears and neck. But it can occur anywhere on the body. This includes hidden places like the inside of your mouth or genitals.
You can find squamous cell carcinoma and other skin cancers early with regular skin exams. Your primary care doctor or a dermatologist can check your skin during routine medical visits. They can check areas that are hard for you to see, like your scalp and back.
Between medical exams, you should regularly check your own skin. When youre familiar with the look and feel of your skin, you can identify new or suspicious changes.
Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hi a family member has just been diagnosed with this can someone tell me how serious this is? Caused by over exposure to sun lump on the scalp.
Welcome to Cancer Chat, Hawk.
Im sorry youve not received a reply from anyone here yet.
Ive had a little look on the forum and found a similar conversation between another member and one of our cancer nurses, Jean. It might be of some help and reassurance: Skin cancer. It explains a little bit about the difference between basal cell skin cancer , and squamous cell skin cancer, the type of skin cancer that your family member has.
You May Like: How Is Skin Cancer Detected And Diagnosed
Also Check: Merkel Cancer Prognosis