In Situ And Early Stage Cancer
The sections below will look at early stage cancer in more detail.
Stage 0
This means that cancers or tumors are in situ, or where they originally developed. It means that they have not spread.
This stage is usually highly curable, often through the surgical removal of the tumor or cancerous cells.
Stage 1
Often called early stage cancer, stage 1 cancers or tumors are small and not deeply embedded in surrounding tissues. They have also not spread to other parts of the body or the lymph system.
People with stage 0 or 1 cancers may not notice any symptoms. Others may experience symptoms or notice changes to their body, such as:
- abnormal lumps, bumps, firmness, or swelling
- skin changes, such as new or changing moles, itchiness, scaliness, or becoming dimpled, discolored, darkened, puckered, or inflamed
- a cough or hoarseness that does not improve
- abnormal nipple or genital discharge or changes
- difficulty or pain when urinating
- blood in the urine or stool
- unexplained bruising
- heartburn or indigestion that does not improve
- unexplained, severe exhaustion that does not improve
- unexplained fever or night sweats
- bleeding, pain, or numbness in the mouth or lips
- headaches and seizures
- white or red patches on the tongue or in the mouth
- sores that do not heal
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
- unexplained weight loss or gain
Learning About Clinical Trials
The radiation oncology treatment team is constantly exploring new ways to treat cancer through studies called clinical trials. Todayâs standard radiation therapy treatments are the result of clinical trials completed years ago. For more information on clinical trials, ask your doctor or visit:
National Cancer Institutecancer.gov/clinicaltrials
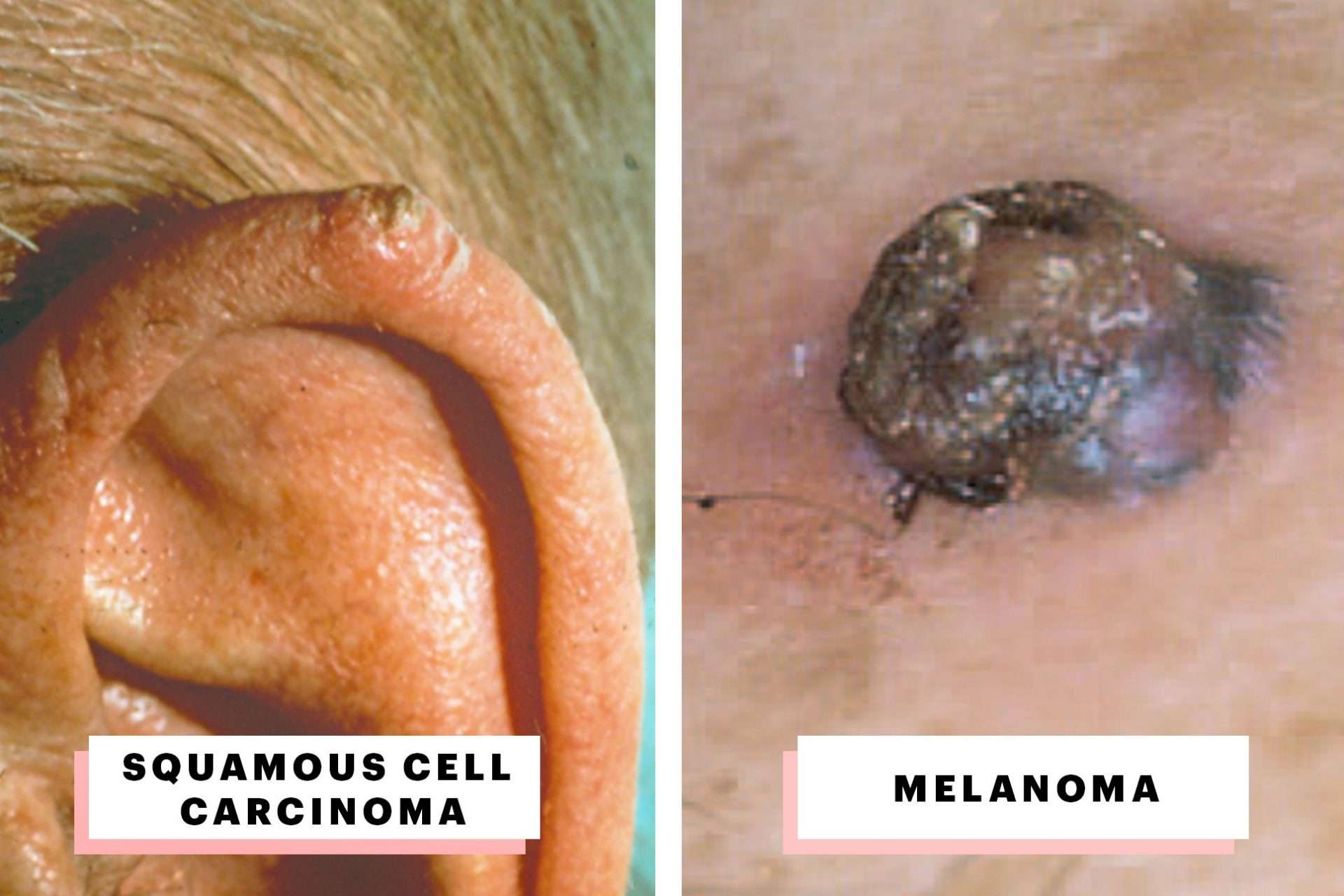
What Are The Different Types Of Melanoma
Melanomas fall into four basic categories.
Also Check: Why Do You Get Skin Cancer
For More Information About Skin Cancer
National Cancer Institute, Cancer Information Service Toll-free: 4-CANCER 422-6237TTY : 332-8615
Skin Cancer Foundation
Media file 1: Skin cancer. Malignant melanoma.
Media file 2: Skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma.
Media file 3: Skin cancer. Superficial spreading melanoma, left breast. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 4: Skin cancer. Melanoma on the sole of the foot. Diagnostic punch biopsy site located at the top. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Media file 5: Skin cancer. Melanoma, right lower cheek. Photo courtesy of Susan M. Swetter, MD, Director of Pigmented Lesion and Cutaneous Melanoma Clinic, Assistant Professor, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System.
Continued
Media file 6: Skin cancer. Large sun-induced squamous cell carcinoma on the forehead and temple. Image courtesy of Dr. Glenn Goldman.
Treating Stage 3 Melanoma
If the melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes , further surgery may be needed to remove them.
Stage 3 melanoma may be diagnosed by a sentinel node biopsy, or you or a member of your treatment team may have felt a lump in your lymph nodes.
The diagnosis of melanoma is usually confirmed using a needle biopsy .
Removing the affected lymph nodes is done under general anaesthetic.
The procedure, called a lymph node dissection, can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to a build-up of fluids in your limbs. This is known as lymphoedema.
Cancer Research UK has more information about surgery to remove lymph nodes.
Read Also: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Causes Of Skin Cancer
Different forms of skin cancer develop when there are mutations in the DNA of skin cells. Skin cancer begins with a mutation in the epidermis, which is the top layer of the skin. Cells begin to multiply and grow out of control, eventually forming a cancerous mass.
While various risk factors have been identified, it is not always apparent what factor actually causes skin cell DNA to mutate.
One cause of skin cancer that is clear is exposure to sunlight . The ultraviolet rays in sunlight and tanning beds can cause extensive damage to the DNA in skin cells. In turn, these damaged cells may someday become cancerous. Harmful UV radiation can occur relatively soon before the appearance of skin cancer, but it can also pre-date a cancer diagnosis by many years.
However, UV radiation cant explain skin cancers that occur on body parts that arent exposed to the sun. This suggests that different causes exist for certain cases of skin cancer. Among these causes, for instance, may be a drastic or repeated exposure to toxic substances.
In some cases, a person may inherit genes that lead to melanoma. Certain gene changes received from a parent could cause a failure in the body to control unruly cell growth, eventually resulting in melanoma. These inherited, or familial, melanomas are relatively rare.
When To Seek Medical Care For Skin Cancer
Many people, especially those who have fair coloring or have had extensive sun exposure, periodically check their entire body for suspicious moles and lesions.
Have your primary health care provider or a dermatologist check any moles or spots that concern you.
See your health care provider to check your skin if you notice any changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of pigmented areas .
If you have skin cancer, your skin specialist or cancer specialist will talk to you about symptoms of metastatic disease that might require care in a hospital.
Also Check: What Does Advanced Melanoma Look Like
How Can I Help My Child Live With Skin Cancer
If your child has skin cancer, you can help him or her during treatment in these ways:
-
Your child may have trouble eating. A dietitian or nutritionist may be able to help.
-
Your child may be very tired. He or she will need to learn to balance rest and activity.
-
Get emotional support for your child. Counselors and support groups can help.
-
Keep all follow-up appointments.
-
Keep your child out of the sun.
After treatment, check your childs skin every month or as often as advised.
How Serious Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell skin cancer, also called basal cell carcinoma, is usually very curable, but it can cause disfigurement and complications if it’s not treated. In the majority of cases, basal cell carcinoma is very treatable.
It is unusual for basal cell carcinoma to cause death. Approximately 2,000 people in the U.S. die each year from basal and squamous skin cancers. In most cases, people who die from these types of skin cancer tend to be older, immunosuppressed, or have been diagnosed at a very late stage.
Also Check: How Dangerous Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Tests That Might Be Done
Biopsy: In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is. There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
Lab tests of biopsy samples: If melanoma is found, lab tests might be done on the cancer cells to see if they have certain gene changes. This might affect your treatment options.
Chest x-ray: This test may be done to see if the melanoma has spread to your lungs.
Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves and their echoes to make pictures of the inside of your body. Ultrasound might be used to look at lymph nodes near the tumor to see if the cancer has spread there.
CT or CAT scan: This test uses x-rays to make detailed pictures of your insides. A CT scan may be used to see if nearby lymph nodes are swollen or if organs like the lungs or liver have spots that might be from the spread of melanoma. If any spots are found, a CT scan might be used to guide a needle into the spots to do a biopsy.
MRI scan: This test uses radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays to make detailed pictures of your insides. It’s very good for looking at the brain and spinal cord. This test can help show if the cancer has spread.
New Treatments New Hope
Whats causing this dramatic change? The study authors believe it mostly comes down to several advances in treatments over the past decade. We looked at how the dates of approval of the new therapies aligned with the drops in mortality, Polsky says.
Historically, the outlook for someone diagnosed with invasive melanoma was not very promising. Once the disease has spread to other areas of the body, it can be difficult to treat, and traditional chemotherapy isnt an effective weapon against it. Melanoma cancer cells are very resistant to dying, Polsky says. In order to deliver enough chemotherapy to kill them, you have to give an amount thats poisonous for the patient.
But there have been some hopeful advances. Starting in 2011, the Food and Drug Administration had approved 10 new treatments for advanced melanoma.
These newer approaches fall into two categories, Polsky says. One type is called immune checkpoint inhibitors. These drugs block the ability of cancer cells to switch off your immune system, Polsky says. So instead of your immune system ignoring the cancer cells, it attacks and kills them.
The other type of treatment includes drugs that target the BRAF gene. The BRAF gene is mutated in about half of melanomas, Polsky says. By targeting the mutated protein in the gene, these drugs shrink cancerous tumors or slow their growth.
Also Check: How To Determine Skin Cancer
How Long Do You Live If You Have Skin Cancer
Among all people with melanoma of the skin, from the time of initial diagnosis, the 5-year survival is 92%. Overall survival at 5 years depends on the thickness of the primary melanoma, whether the lymph nodes are involved, and whether there is spread of melanoma to distant sites.
Tests That May Be Done
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers don’t often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
You May Like: Is Skin Cancer Always Raised
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs its called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancers growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if its unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
Its entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
Read Also: How Long Before Melanoma Is Deadly
Medical Treatment For Skin Cancer
Surgical removal is the mainstay of skin cancer treatment for both basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For more information, see Surgery.People who cannot undergo surgery may be treated by external radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the use of a small beam of radiation targeted at the skin lesion. The radiation kills the abnormal cells and destroys the lesion. Radiation therapy can cause irritation or burning of the surrounding normal skin. It can also cause fatigue. These side effects are temporary. In addition, topical chemotherapy creams have been FDA approved for the treatment of certain low-risk nonmelanoma skin cancers. Patients with advanced or many basal cell carcinomas are sometimes prescribed oral pills to block the growth of these cancers. Side effects include muscle spasms, hair loss, taste changes, weight loss and fatigue.
In advanced cases of melanoma, immune therapies, vaccines, or chemotherapy may be used. These treatments are typically offered as clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies of new therapies to see if they can be tolerated and work better than existing therapies.
Also Check: Can Red Spots Be Skin Cancer
What Exams And Tests Diagnose Skin Cancer
If you have a worrisome mole or other lesion, your primary-care provider will probably refer you to a dermatologist. The dermatologist will examine any moles in question and, in many cases, the entire skin surface.
- Any lesions that are difficult to identify, or are thought to be skin cancer, may then be checked.
- A sample of skin will be taken so that the suspicious area of skin can be examined under a microscope.
- A biopsy can almost always be done in the dermatologist’s office.
If a biopsy shows that you have malignant melanoma, you will probably undergo further testing to determine the extent of spread of the disease, if any. This may involve blood tests, a chest X-ray, and other tests as needed.
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
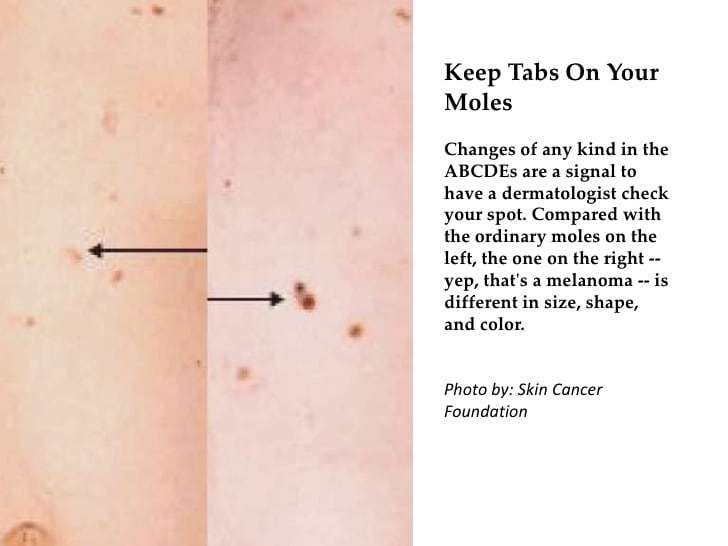
Moles, also called nevi, are groups of normal-appearing cells of melanocytic origin in the dermis. They are harmless brown spots on the skin. Melanoma usually looks different from the ordinary moles. The best way to find any suspicious moles on your body is to do a skin examination to look for the ABCDEs of melanoma. The first sign of melanoma is often a change in the size, shape, or color of a mole.
Melanoma also may appear as a new, black, abnormal or “ugly-looking” mole. Rarely, melanoma is not pigmented and is more difficult to diagnose. It may also appear as a non-healing ulcer or a new scar-like lump in the skin.
Melanoma checklist:Examine yourself from head to toe and check for the following changes in your mole
| Melanoma has a diameter of 6mm or more. | ||
| E | EVOLUTION | There is a history of change in the lesion size, shape, color, elevation or any symptoms such as bleeding, ulceration, itching or crusting. |
If you see one or more, make an appointment with a dermatologist immediately.
Don’t Miss: Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Hereditary
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Surgical Treatment Options For Skin Cancer
Surgical Removal. Surgical removal of skin cancer can be done in the office while you remain awake. A topical anesthetic is used to numb the area. There are three types of surgical removal that are used to treat skin cancer.
- Excision. The skin cancer and the surrounding area of normal skin are removed. Removing some normal skin is necessary to ensure that all stray cancer cells are removed. Dr. Warmuth will then look at this tissue under a high-powered microscope to ensure that the area of margin removed is free from cancer cells. If any normal-looking skin is found to have cancer cells, you will be referred to have more treatment, MOHs surgery.
- MOHs Micrographic Surgery. MOHs surgery allows for the selective removal of tumors with the preservation of as much of the surrounding normal tissue as possible. It offers the highest chance for complete removal of cancer while sparing normal tissue because it precisely maps the location of cancer. The cure rate for new cancers with the MOHs procedure can exceed 97 percent.
- Curettage and Electrodessication. Skin cancer is removed from your skin using a technique called curetting. Then electrodesiccation is used to destroy any remaining cancer cells with heat. This procedure is not performed in areas of heavy hair growth, such as the scalp, a mans beard area, or an armpit.
Read Also: What Are The Chances Of Skin Cancer