When To Visit A Podiatrist
Podiatrists are uniquely trained as lower extremity specialists to recognize and treat abnormal conditions on the skin of the lower legs and feet. Skin cancers affecting the feet may have a very different appearance from those arising on the rest of the body. For this reason, a podiatrist’s knowledge and clinical training is of extreme importance for patients for the early detection of both benign and malignant skin tumors.
Learn the ABCDs of melanoma. If you notice a mole, bump, or patch on the skin that meets any of the following criteria, see a podiatrist immediately:
- Asymmetry – If the lesion is divided in half, the sides don’t match.
- Borders – Borders look scalloped, uneven, or ragged.
- Color – There may be more than one color. These colors may have an uneven distribution.
- Diameter The lesion is wider than a pencil eraser .
To detect other types of skin cancer, look for spontaneous ulcers and non-healing sores, bumps that crack or bleed, nodules with rolled or donut-shaped edges, or scaly areas.
Does An Actinic Keratosis Hurt
While most people see only a change to their skin, an AK can:
-
Itch
-
Feel tender or painful when touched
-
Stick to your clothing, causing discomfort
-
Bleed
If you find a change on your skin that could be an actinic keratosis, protect your health by seeing a board-certified dermatologist. Should that change be an AK, you have a greater risk of developing skin cancer. Being under the care of a board-certified dermatologist helps to find skin cancer early when its highly treatable.
While having skin thats been badly damaged by the sun or indoor tanning greatly increases your risk of developing AKs, other things can increase your risk. Youll find out what else may increase your risk of developing AKs at, Actinic keratosis: Causes.
Related AAD resources
ImagesImages 1,2, and 9: Used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
Images 3,4,5,6,7,8,10: Used with permission of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology:
-
Image 3: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 76:349-50.
-
Image 4: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007 56:125-43.
-
Image 5: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 69:e5-e6.
-
Image 6: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 62:85-95.
-
Images 7, 8: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012 66:173-84.
-
Image 10: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 42 part 2:S8-S10.
Rigel DS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia JL, et al. Dermatology. . Mosby Elsevier, Spain, 2008:1645-58.
How Are Moles Evaluated
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDE’s of melanoma — or one that’s tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesn’t heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole — see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
Read Also: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
Generally found on the ears, face and mouth, squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive than basal cell. Untreated, it may push through the skin layers to the lymphatic system, bloodstream and nerve routes, where it can cause pain and symptoms of serious illness.
Appearance
Squamous cell cancer often starts as a precancerous lesion known as actinic keratosis . When it becomes cancerous, the lesion appears raised above the normal skin surface and is firmer to the touch. Sometimes the spot shows only a slight change from normal skin.
Other signs include:
- Any change, such as crusting or bleeding, in an existing wart, mole, scar or other skin lesion
- A wart-like growth that crusts and sometimes bleeds
- A scaly, persistent reddish patch with irregular borders, which may crust or bleed
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes
- A raised growth with a depression in the center that occasionally bleeds and may rapidly increase in size
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
A Sore That Doesn’t Heal
Many skin cancers are first dismissed as being due to a bug bite, minor injury, or irritation, but become more obvious when they don’t go away over time. If you notice a sore on your skin that refuses to heal, even if it seems to be healing but then reappears, talk to your healthcare provider. In general, any skin change that hasn’t resolved on its own over a period of two weeks should be evaluated.
Skin Cancer Pictures: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer images by skin cancer type. Skin cancer can look different than the photos below.
Basal Cell Carcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Bowens Disease | Keratoacanthoma | Actinic Keratosis | Melanoma
Skin cancer often presents itself as a change in the skins appearance. This could be the appearance of a new mole or other mark on the skin or a change in an existing mole.
Please remember that you should always seek advice from your doctor if you have any concern about your skin. Skin cancers often look different from skin cancer images found online.
Read Also: Melanoma 3c
What Causes Skin Cancer In A Child
Exposure to sunlight is the main factor for skin cancer. Skin cancer is more common in people with light skin, light-colored eyes, and blond or red hair. Other risk factors include:
-
Age. Your risk goes up as you get older.
-
Family history of skin cancer
-
Having skin cancer in the past
-
Time spent in the sun
-
Using tanning beds or lamps
-
History of sunburns
-
Having atypical moles . These large, oddly shaped moles run in families.
-
Radiation therapy in the past
-
Taking a medicine that suppresses the immune system
-
Certain rare, inherited conditions such as basal cell nevus syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum
-
HPV infection
-
Actinic keratoses or Bowen disease. These are rough or scaly red or brown patches on the skin.
How Can I Help My Child Live With Skin Cancer
If your child has skin cancer, you can help him or her during treatment in these ways:
-
Your child may have trouble eating. A dietitian or nutritionist may be able to help.
-
Your child may be very tired. He or she will need to learn to balance rest and activity.
-
Get emotional support for your child. Counselors and support groups can help.
-
Keep all follow-up appointments.
-
Keep your child out of the sun.
After treatment, check your child’s skin every month or as often as advised.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
What Causes Skin Cancer
Most cases of skin cancer are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet light from sunlight and tanning beds.
Risk factors for developing skin cancer include:
- Ultraviolet exposure from the sun or tanning beds
- Having certain types of moles
- Having fair skin that freckles or burns easily, light hair, and blue or green eyes
- Family history of skin cancer
- Personal history of skin cancers
- Having a compromised immune system, such as people who have HIV/AIDS, are organ transplant recipients, or are receiving certain medical treatments such as chemotherapy
- Older age: the risk increases as people age
- Being male
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
The second most common form of cancer in the skin is squamous cell carcinoma. At first, cancer cells appear as flat patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, reddish, or brown surface. These abnormal cells slowly grow in sun-exposed areas. Without proper treatment, squamous cell carcinoma can become life-threatening once it has spread and damaged healthy tissue and organs.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iii Melanoma Prognosis
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Scalp
The methods for treating skin cancer on the scalp vary depending on the type of cancer. The earlier it is, the better.
The most common form of treatment for basal cell and squamous cell cancers, as well as some types of melanoma, is minor surgery to cut out the cancerous portion of skin. NextGen OMS offers comprehensive head and neck surgery options, which are ideal for removing many types of early-stage skin cancer on the head.
This is why the five-year survival rate for many types of skin cancer is so high when theyre treated early. When it reoccurs, its usually because it went through metastasis before removal, in which case youll need further treatment.
If surgery is not available as an option, your doctor may suggest radiation therapy instead. This isnt used very often on the scalp because surgery is almost always possible for skin cancer on head and scalp areas, but doctors occasionally use it for skin cancer on nearby regions like the nose and ears.
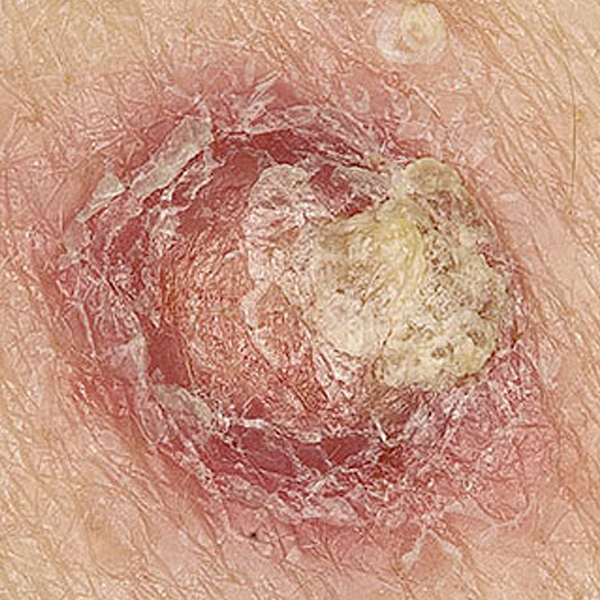
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is one of the most common forms of skin cancer. It can develop on parts of the body that get a lot of sun, such as the head, neck, face, hands and arms. Squamous cell carcinoma is not as dangerous as melanoma, but it can spread to other parts of the body if not treated. Every year, some people in Australia die from aggressive SCCs.
Recommended Reading: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Many early-stage small basal cell cancers or squamous cell cancers can be removed by Mohs surgery, a technique that spares normal tissue through repeated intraoperative margin testing, removing only the cancer and leaving adjacent normal tissue. Tumors with nerve involvement, lymph node involvement or of a large size are not suitable for Mohs surgery. They require a multimodality approach to treatment, with formal surgical resection and adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy.
Melanoma is more likely to spread, and aggressive surgical resection with wide margins is required, in addition to radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery provides comprehensive surgical care and treatment for head and neck cancers. Our surgeons are at the leading edge of head and neck cancer treatment. You will benefit from the skilled care of head and neck surgeons, guiding clinical advancements in the field of head and neck cancer care.
What Happens When Skin Cancer Goes Untreated
If you notice an abnormality on your skin you may be tempted to ignore it. However, if it is skin cancer you could be putting your health at risk by waiting to get a skin and mole check. There are three main types of skin cancer in Australia with melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and they each have their own set of unique characteristics. The most important thing to remember is that if you delay treatment of skin cancer it could have life threatening consequences:
You May Like: How Fast Does Cancer Spread Without Treatment
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
It is usually possible to completely remove an SCC. The best type oftreatment for you will depend on the size of the SCC and where it is.
Usually, the doctor will remove an SCC using simple skin surgery. Theywill then look at the area under a microscope to check all the cancer has beenremoved. If it has spread, you might need radiotherapy afterwards.
Other ways of removing the SCC are:
- scraping it off then sealing the base of the wound with an electric needle or liquid nitrogen
- using a laser to burn the SCC away
- freezing it off
- Applying creams, liquids or lotions directly onto the SCC. Sometimes the doctor will shine a light on the area to make the medicine work
After treatment, you will need follow-up appointments with your doctor. You will be at greater risk of developing another skin cancer, so its more important than ever to protect your skin from the sun.
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. Theres also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but its extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although its often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if its not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
Also Check: Can You Get Cancer In The Back Of Your Neck
Melanoma Signs And Symptoms
Melanoma skin cancer is much more serious than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It can spread quickly to other organs and causes the vast majority of skin cancer deaths in the United States. Usually melanomas develop in or around an existing mole.
Appearance
Signs and symptoms of melanoma vary depending on the exact type and may include:
- A flat or slightly raised, discolored patch with irregular borders and possible areas of tan, brown, black, red, blue or white
- A firm bump, often black but occasionally blue, gray, white, brown, tan, red or your usual skin tone
- A flat or slightly raised mottled tan, brown or dark brown discoloration
- A black or brown discoloration, usually under the nails, on the palms or on the soles of the feet
See more pictures and get details about different types of melanoma in our dedicated melanoma section.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Get To Know Your Skin
The sooner a skin cancer is identified and treated, the better your chance of avoiding surgery or, in the case of a serious melanoma or other skin cancer, potential disfigurement or even death.
It is also a good idea to talk to your doctor about your level of risk and for advice on early detection.
It’s important to get to know your skin and what is normal for you, so that you notice any changes. Skin cancers rarely hurt and are much more frequently seen than felt.
Develop a regular habit of checking your skin for new spots and changes to existing freckles or moles.
Read Also: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
How To Check Your Skin
- Make sure you check your entire body, as skin cancers can sometimes occur on parts of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet, between fingers and toes and under nails.
- Undress completely and make sure you have good light.
- Use a mirror to check hard to see spots, like your back and scalp, or get a family member, partner or friend to check for you.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Actinic Keratosis
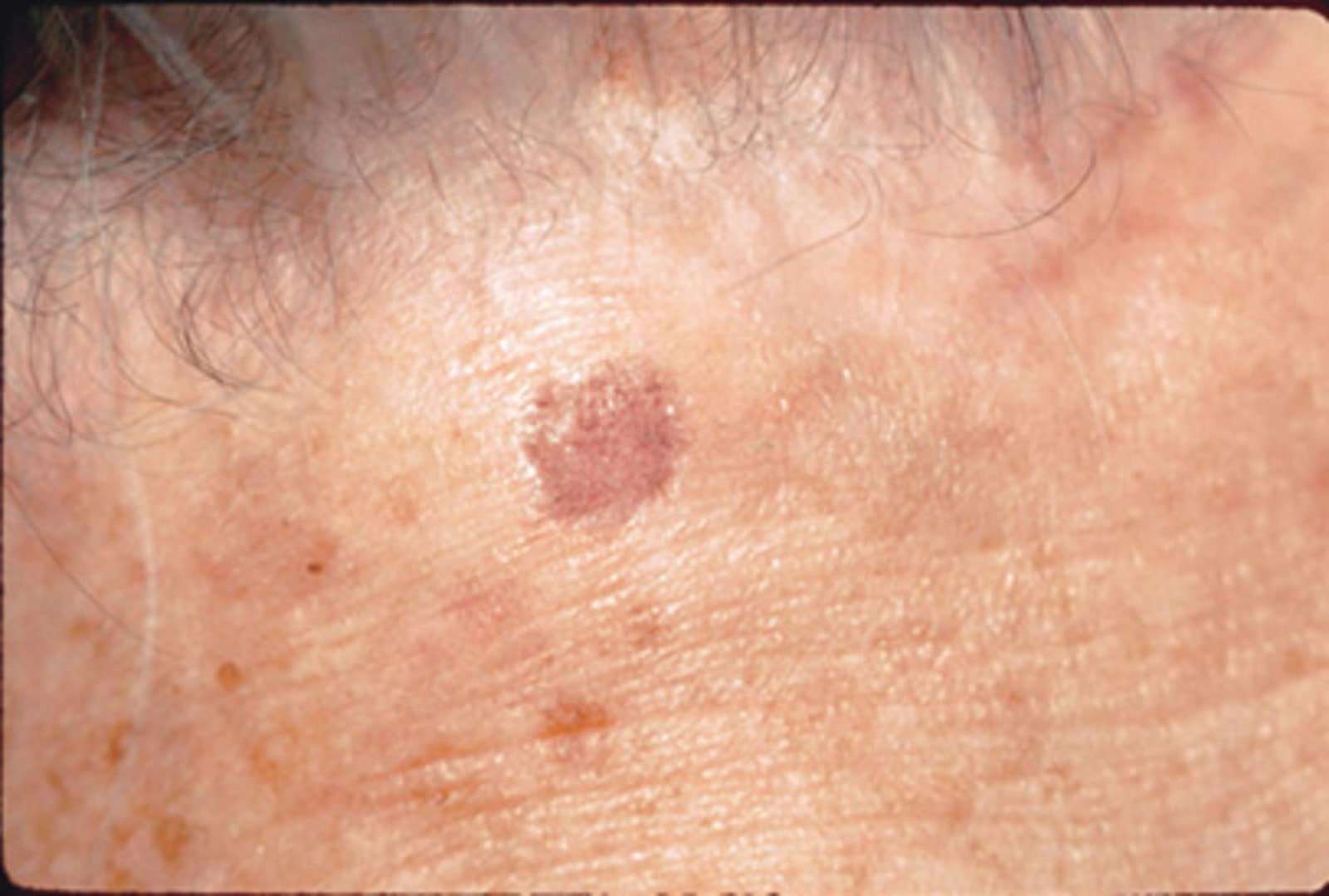
An actinic keratosis develops when skin has been badly damaged by ultraviolet light from the sun or indoor tanning.
Signs of actinic keratosis
The brown spots on this mans face may look like age spots, but theyre actually actinic keratoses.
Left untreated, some actinic keratoses turn into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Thats why its important to know if you have any of these precancerous growths on your skin.
The following pictures show some diverse ways that it can appear.
Don’t Miss: Scc Cancer Stages
What Do Actinic Keratoses Look Like
AKs often appear as small dry, scaly or crusty patches of skin. They may be red, light or dark tan, white, pink, flesh-toned or a combination of colors and are sometimes raised. Because of their rough texture, actinic keratoses are often easier to feel than see. For photos, go to our warning signs page.
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment for skin cancer depends on the size and severity of the skin cancer. Typical treatments include the following:
- Surgery. The best way to prevent the skin cancer from spreading or growing is to surgically remove it.
- Radiation therapy.Radiation involves beams of high-powered energy that can destroy cancer cells. Its often used if your doctor cant remove all of the skin cancer during surgery.
- Chemotherapy. This intravenous drug treatment kills cancer cells. Some lotions and creams with cancer-killing medications may be used if you have skin cancer thats confined to the top layers of your skin.
- PDT is a combination of medication and laser light thats used to destroy cancer cells.
- Biologic therapy. Biologic therapy involves medication that boosts your bodys natural ability to fight cancer.
Treatments for skin cancer are most successful when the cancer is found early, particularly before it spreads to other organs in a process known as metastasis.
The cancer is more likely to grow and spread to nearby tissues and organs if its not detected and treated early.
Anyone can develop psoriasis. Certain risk factors increase the chances that youll develop the skin condition.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy